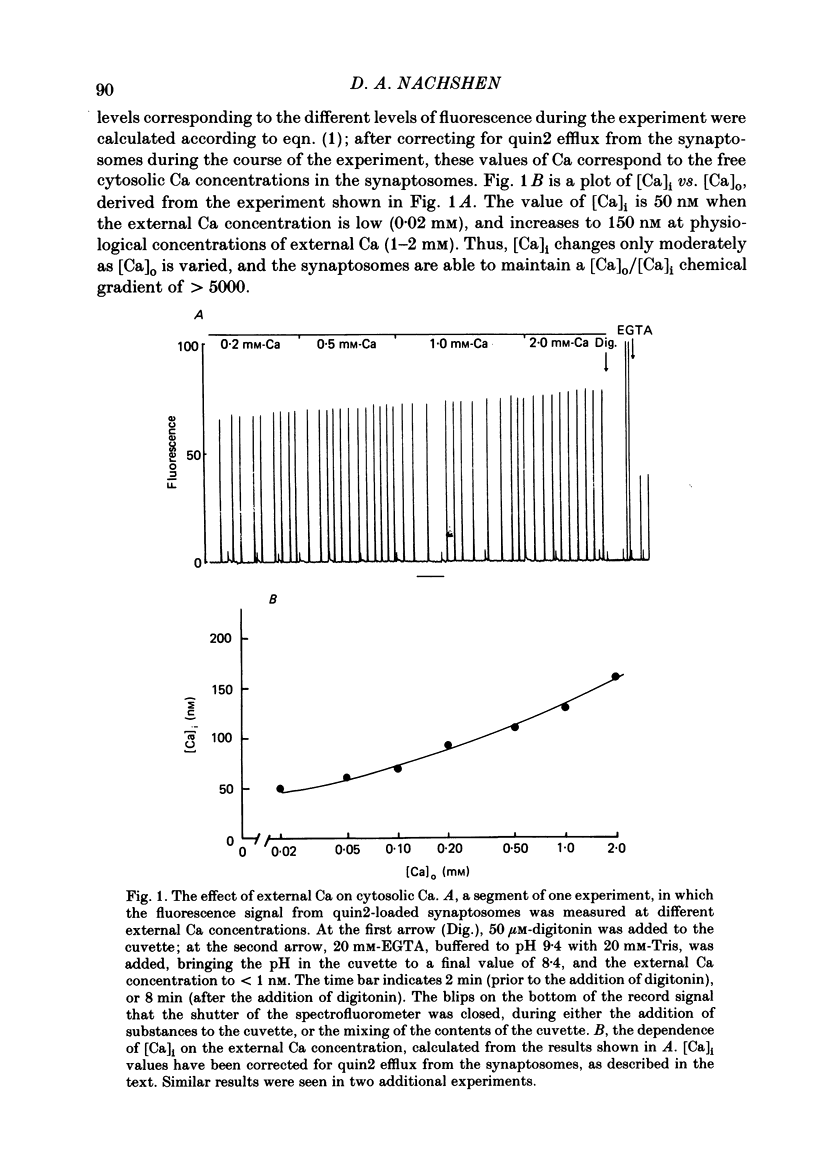
Abstract
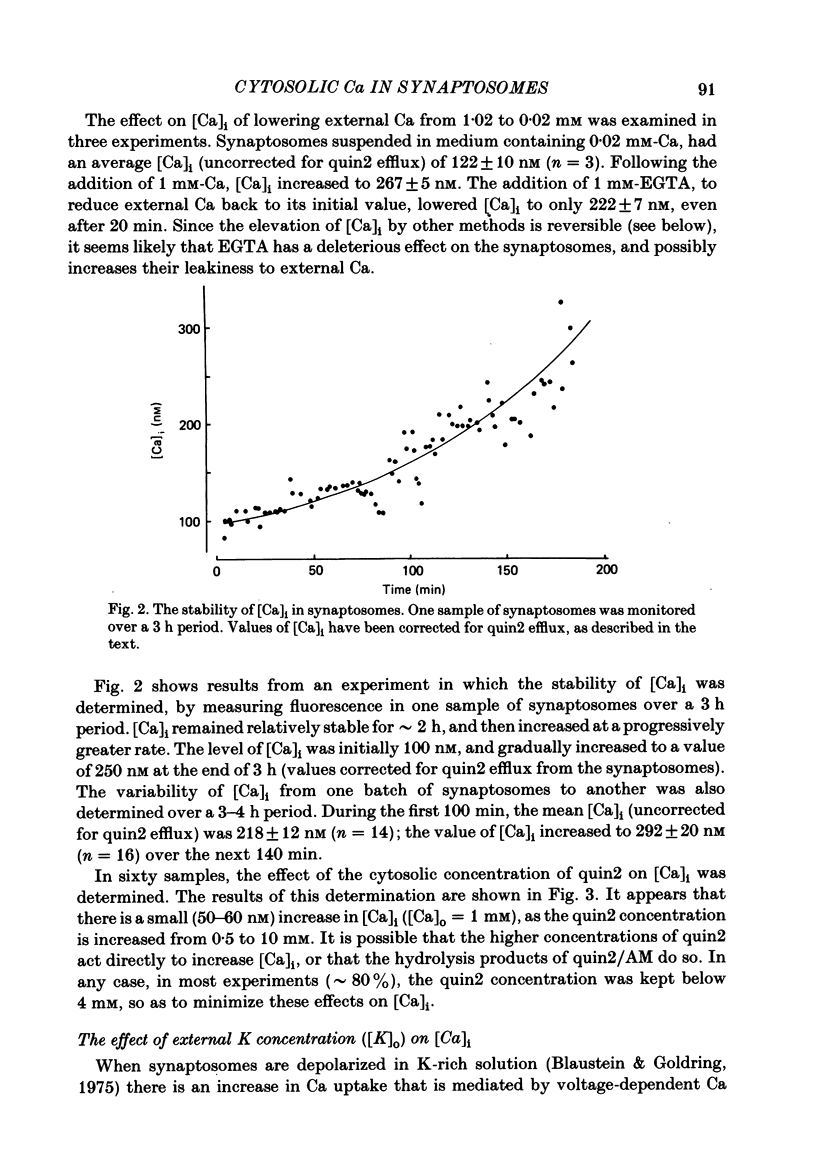
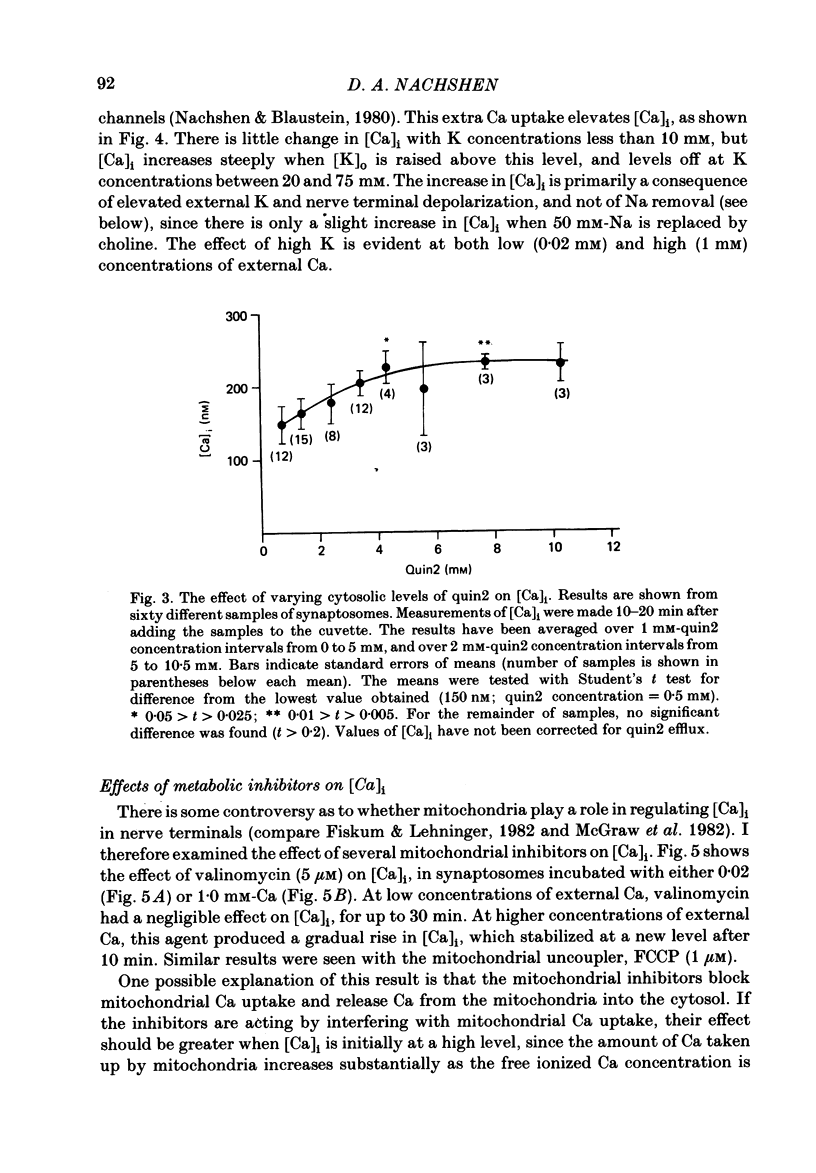
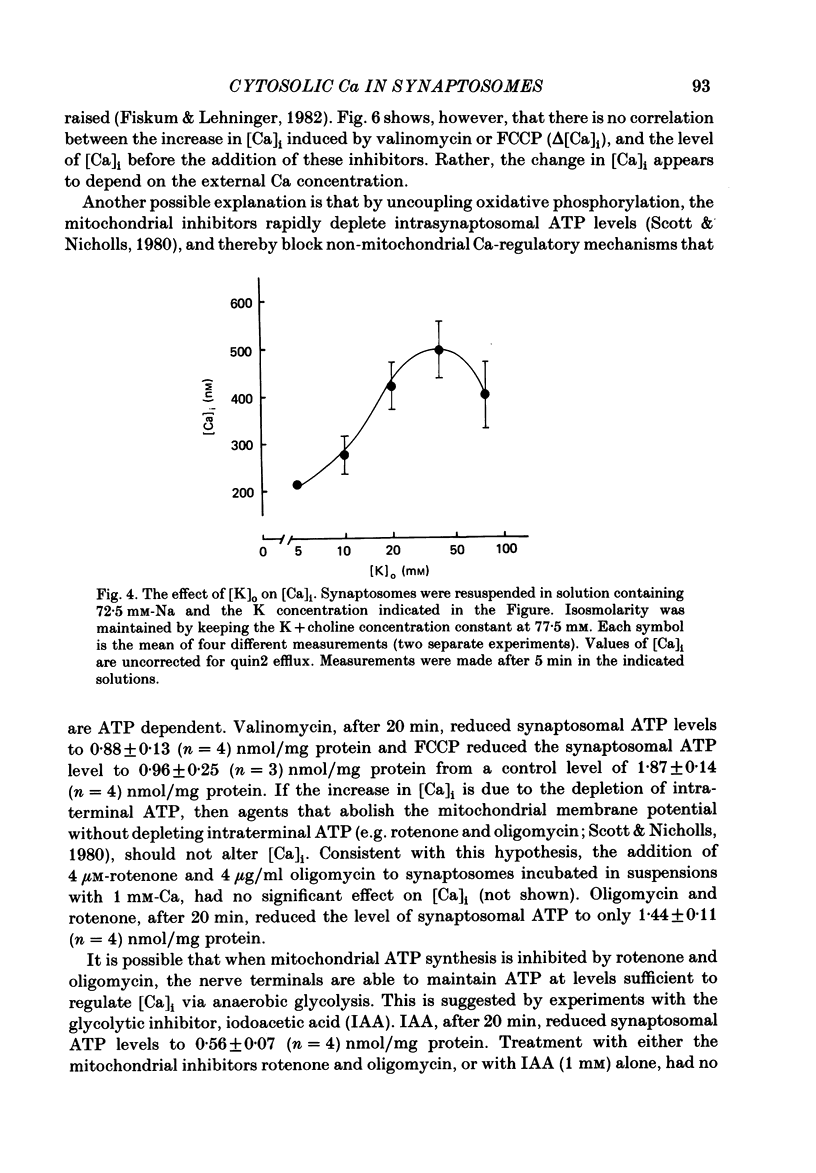
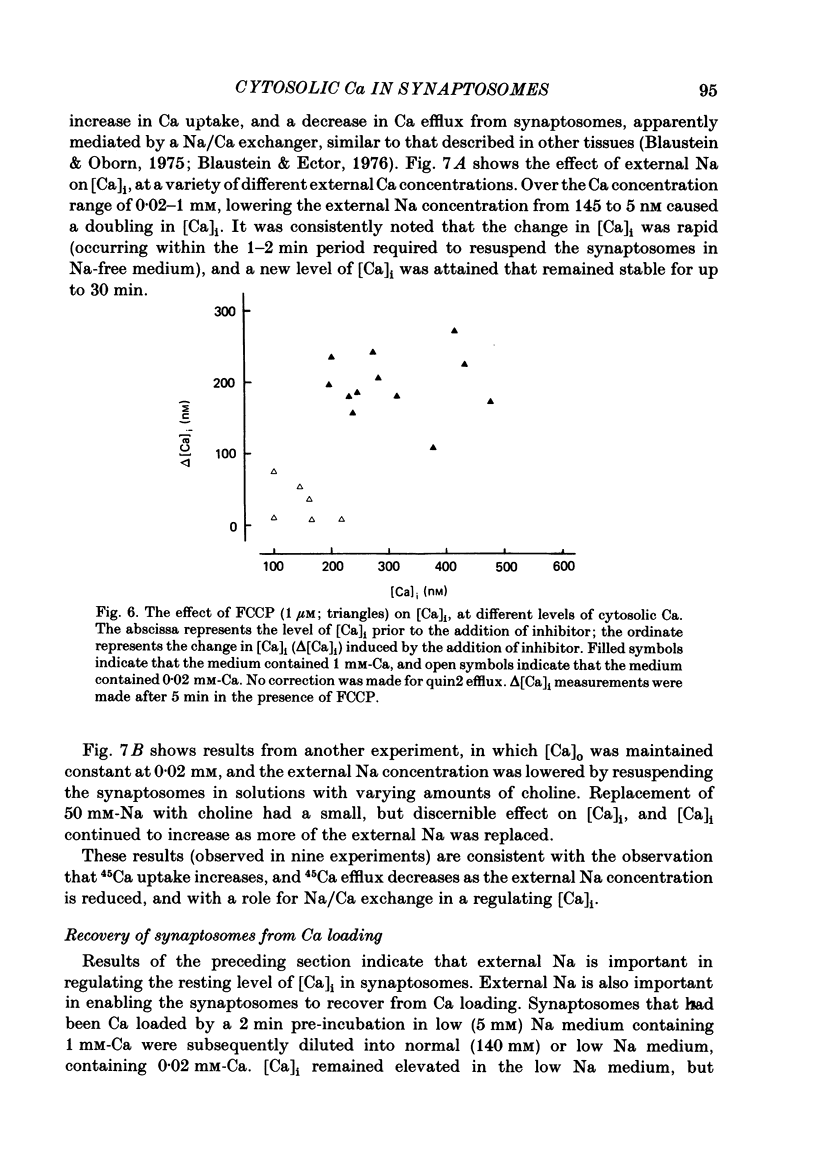
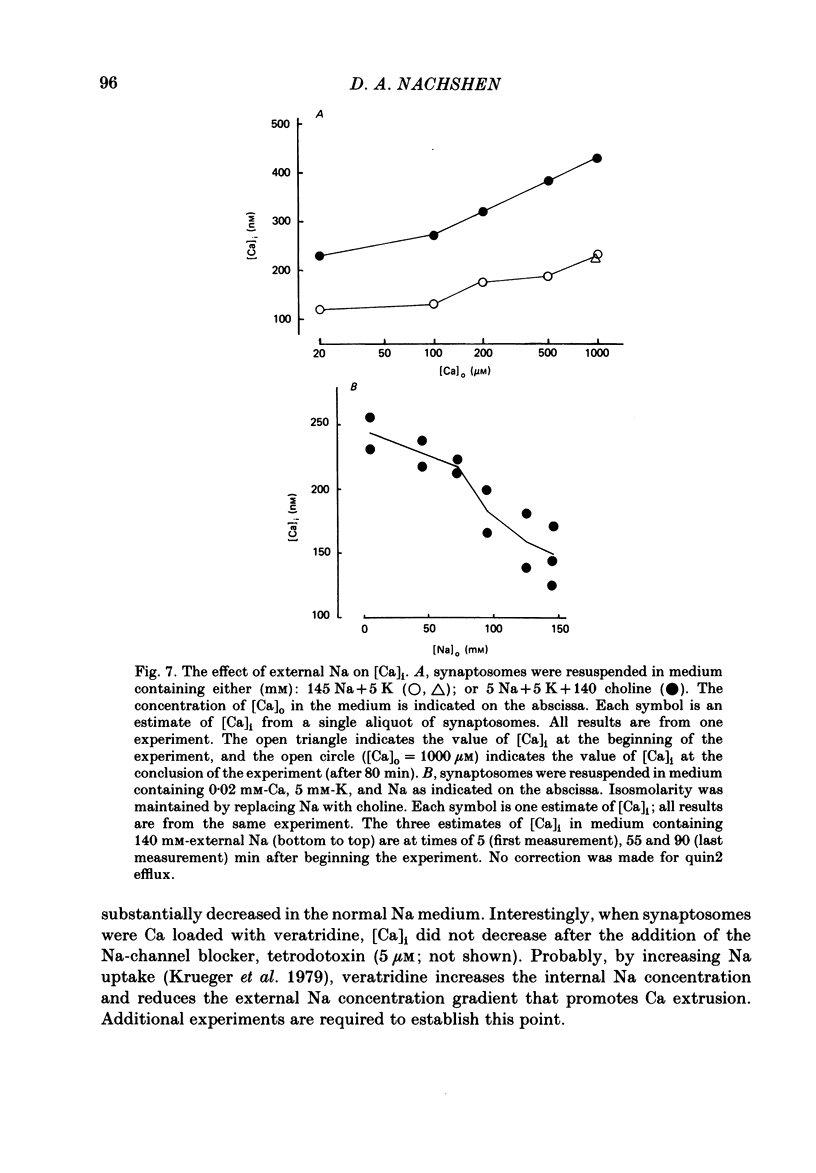
The regulation of cytosolic Ca concentration ([Ca]i) was studied with the fluorescent Ca indicator, quin2, in pinched-off presynaptic nerve endings (synaptosomes) isolated from rat brain. The resting [Ca]i is 0.1-0.2 microM, in solutions containing 1-2 mM-Ca. [Ca]i increases by only 100-150 nM when the external Ca concentration is increased from 0.02 to 2 mM. The mitochondrial inhibitors valinomycin and fluoro-carbonyl cyanide phenylhydrazone (FCCP) increase [Ca]i by 100-200 nM. This increase is not correlated with the resting level of [Ca]i prior to the addition of inhibitors, but it is dependent on the presence of external Ca. It seems likely that the effect of these inhibitors on [Ca]i is a secondary consequence of metabolic inhibition. [Ca]i increases by about 2-fold when the external Na concentration is lowered from 145 to 5 mM, and returns to its initial level when external Na is restored. This recovery occurs also in the presence of FCCP. These results suggest that Na/Ca exchange, but not mitochondrial Ca uptake, plays a role in regulating [Ca]i and in allowing the nerve terminals to recover from Ca loading.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerman K. E., Nicholls D. G. Intrasynaptosomal compartmentation of calcium during depolarization-induced calcium uptake across the plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 6;645(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Leefmans F. J., Rink T. J., Tsien R. Y. Free calcium ions in neurones of Helix aspersa measured with ion-selective micro-electrodes. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:531–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Ector A. C. Carrier-mediated sodium-dependent and calcium-dependent calcium efflux from pinched-off presynaptic nerve terminals (synaptosomes) in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 21;419(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90355-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Effects of potassium, veratridine, and scorpion venom on calcium accumulation and transmitter release by nerve terminals in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;247(3):617–655. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Goldring J. M. Membrane potentials in pinched-off presynaptic nerve ternimals monitored with a fluorescent probe: evidence that synaptosomes have potassium diffusion potentials. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;247(3):589–615. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Oborn C. J. The influence of sodium on calcium fluxes in pinched-off nerve terminals in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;247(3):657–686. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr Regulation of intracellular calcium in squid axons. Fed Proc. 1980 Aug;39(10):2778–2782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denzlinger C., Hertting G., Jackisch R. Synaptosomal calcium uptake systems: prostaglandins are probably not involved in the regulation of calcium fluxes into and within the nerve endings. J Neurochem. 1982 Aug;39(2):499–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb03972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipolo R., Requena J., Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J., Scarpa A., Tiffert T. Ionized calcium concentrations in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Apr;67(4):433–467. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. L. Sodium channel, sodium pump, and sodium-calcium exchange activities in synaptosomal plasma membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10986–10990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajós F. An improved method for the preparation of synaptosomal fractions in high purity. Brain Res. 1975 Aug 15;93(3):485–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90186-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Forn J., Greengard P. Depolarization-induced phosphorylation of specific proteins, mediated by calcium ion influx, in rat brain synaptosomes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2764–2773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Ratzlaff R. W., Strichartz G. R., Blaustein M. P. Saxitoxin binding to synaptosomes, membranes, and solubilized binding sites from rat brain. J Membr Biol. 1979 Nov 30;50(3-4):287–310. doi: 10.1007/BF01868894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi J., Huttner W. B., Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T. Free cytoplasmic Ca2+ and neurotransmitter release: studies on PC12 cells and synaptosomes exposed to alpha-latrotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):620–624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachshen D. A., Blaustein M. P. Some properties of potassium-stimulated calcium influx in presynaptic nerve endings. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Dec;76(6):709–728. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.6.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachshen D. A., Drapeau P. A buffering model for calcium-dependent neurotransmitter release. Biophys J. 1982 May;38(2):205–208. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84548-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachshen D. A. The early time course of potassium-stimulated calcium uptake in presynaptic nerve terminals isolated from rat brain. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:251–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., Metcalfe J. C., Smith G. A., Hesketh T. R. Changes in free-calcium levels and pH in synaptosomes during transmitter release. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 16;803(4):215–220. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90110-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott I. D., Akerman K. E., Nicholls D. G. Calcium-ion transport by intact synaptosomes. Intrasynaptosomal compartmentation and the role of the mitochondrial membrane potential. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 15;192(3):873–880. doi: 10.1042/bj1920873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott I. D., Nicholls D. G. Energy transduction in intact synaptosomes. Influence of plasma-membrane depolarization on the respiration and membrane potential of internal mitochondria determined in situ. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):21–33. doi: 10.1042/bj1860021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. Intracellular measurements of ion activities. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1983;12:91–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.12.060183.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


