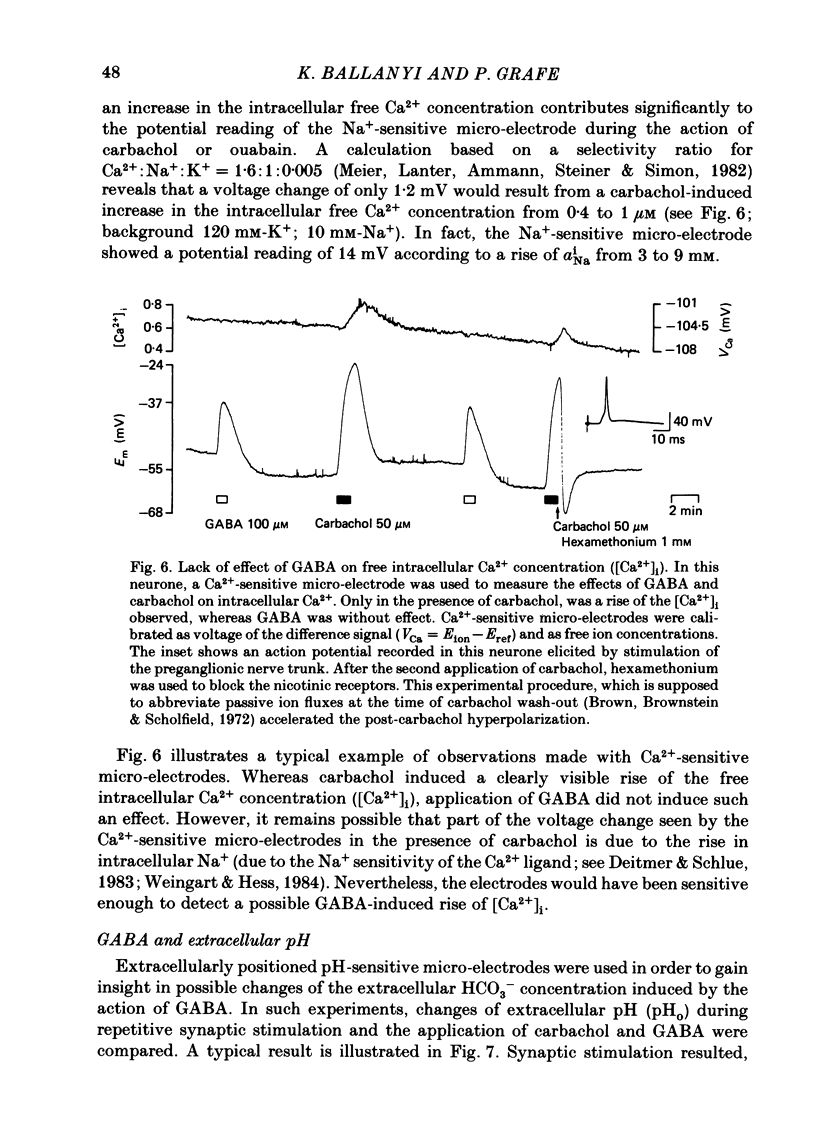
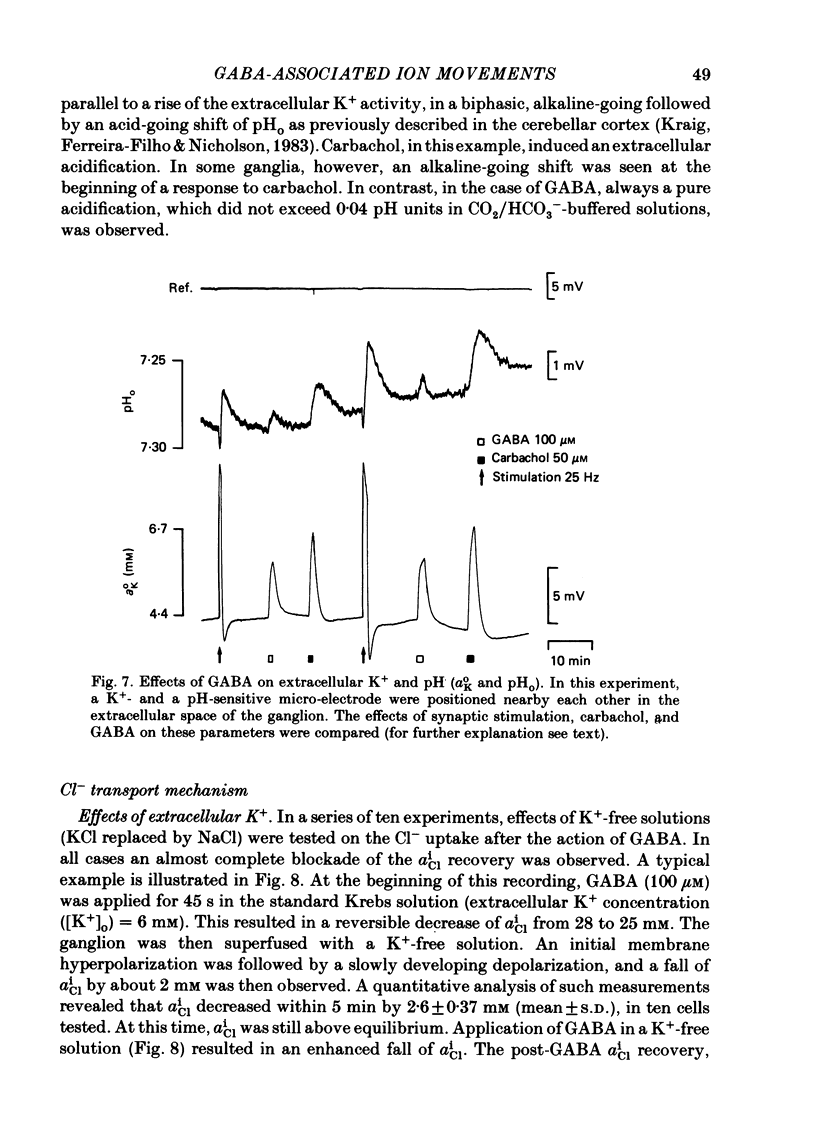
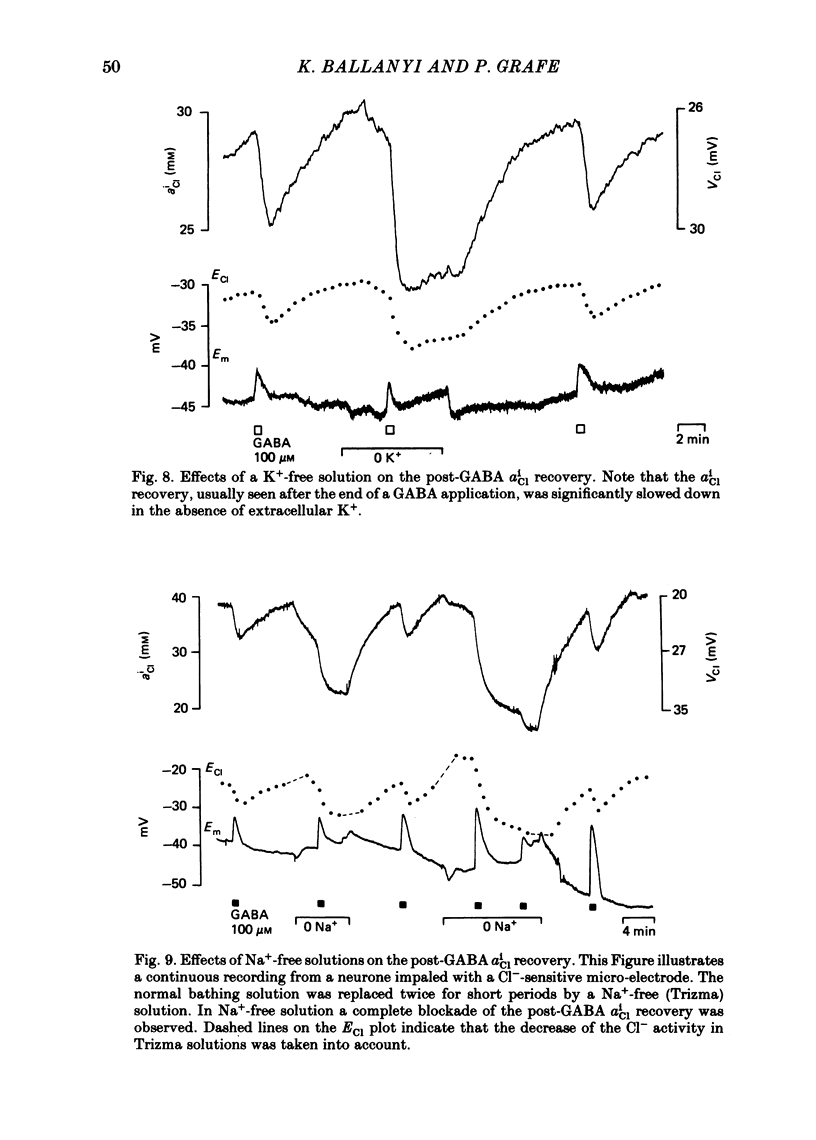
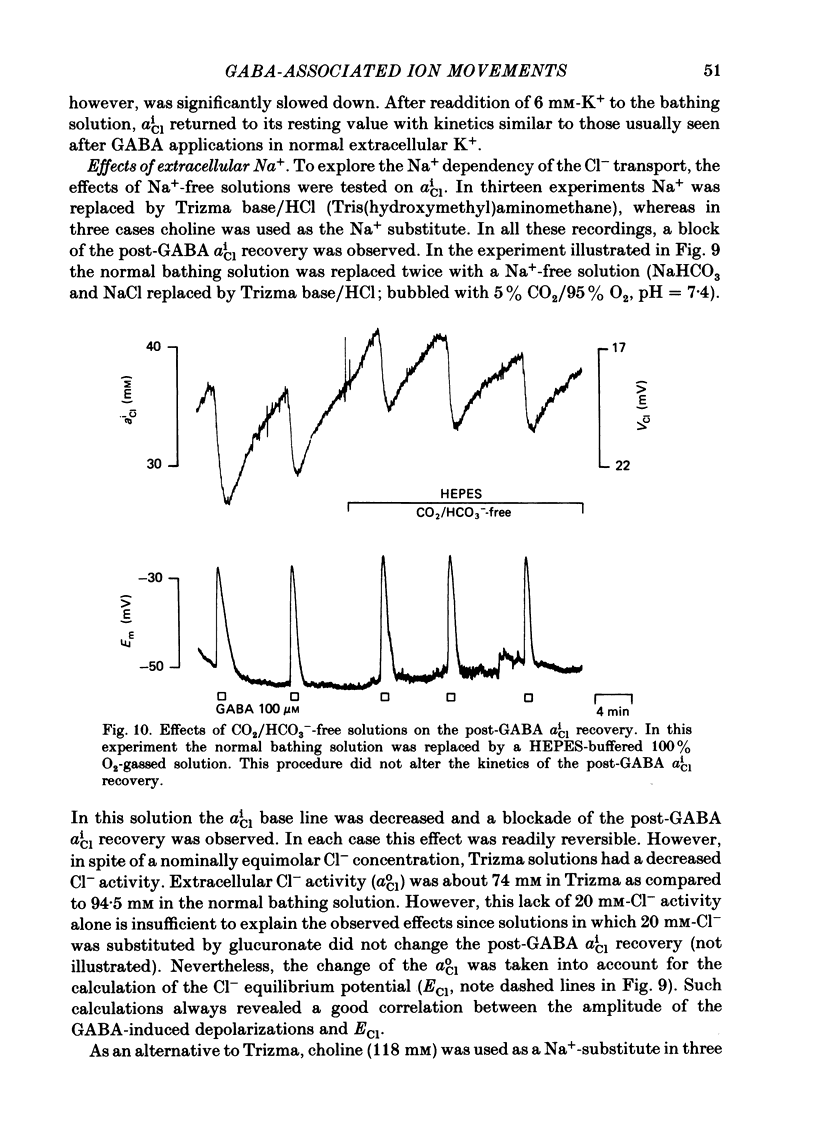
Abstract
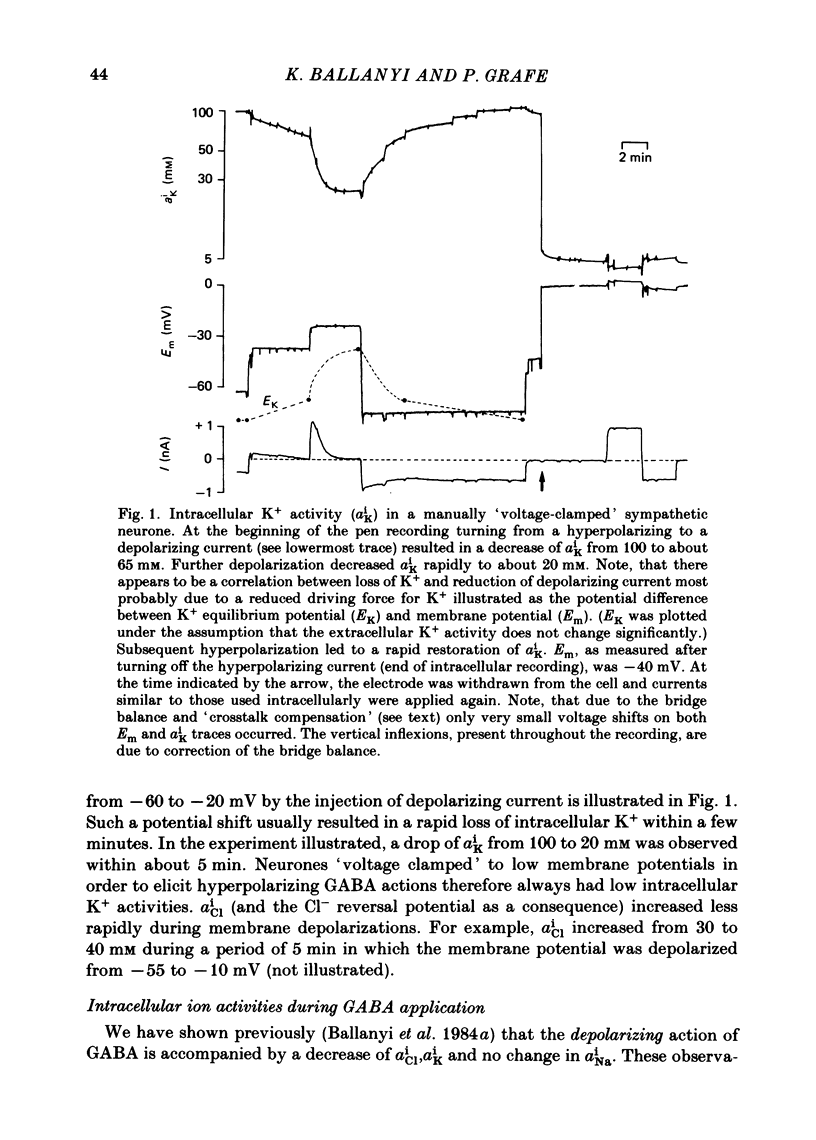
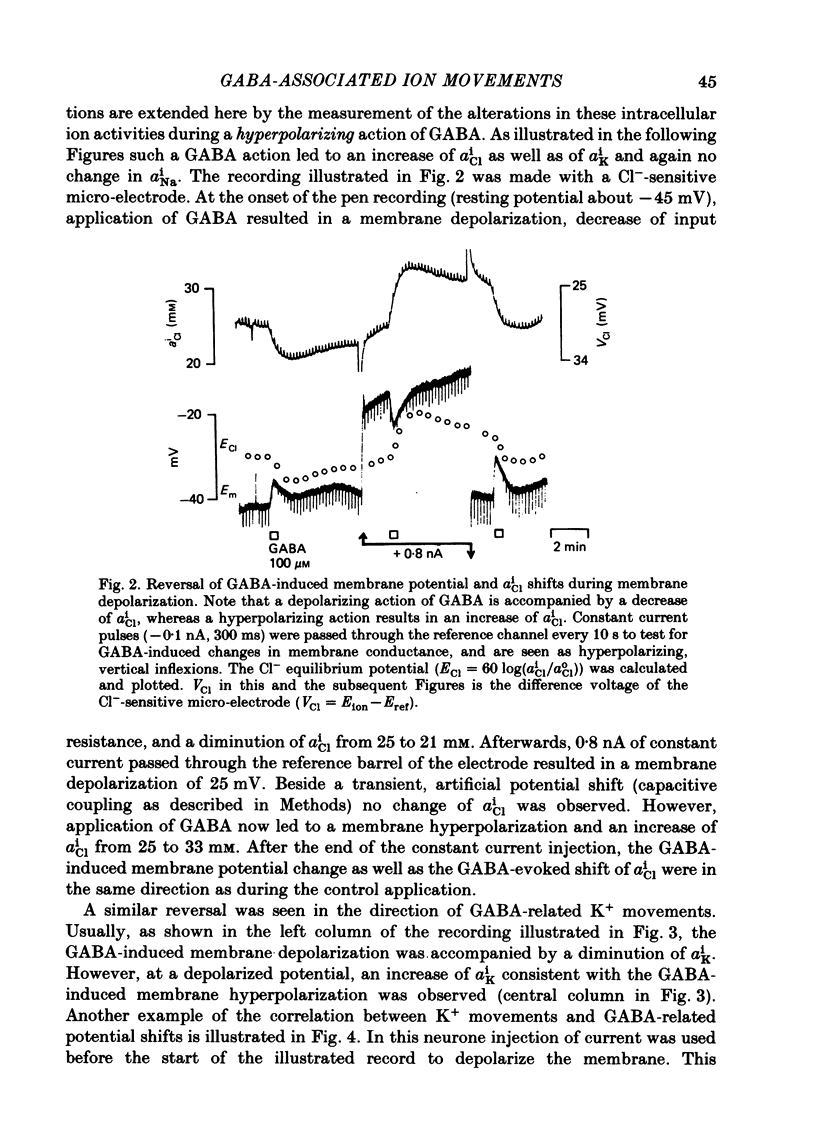
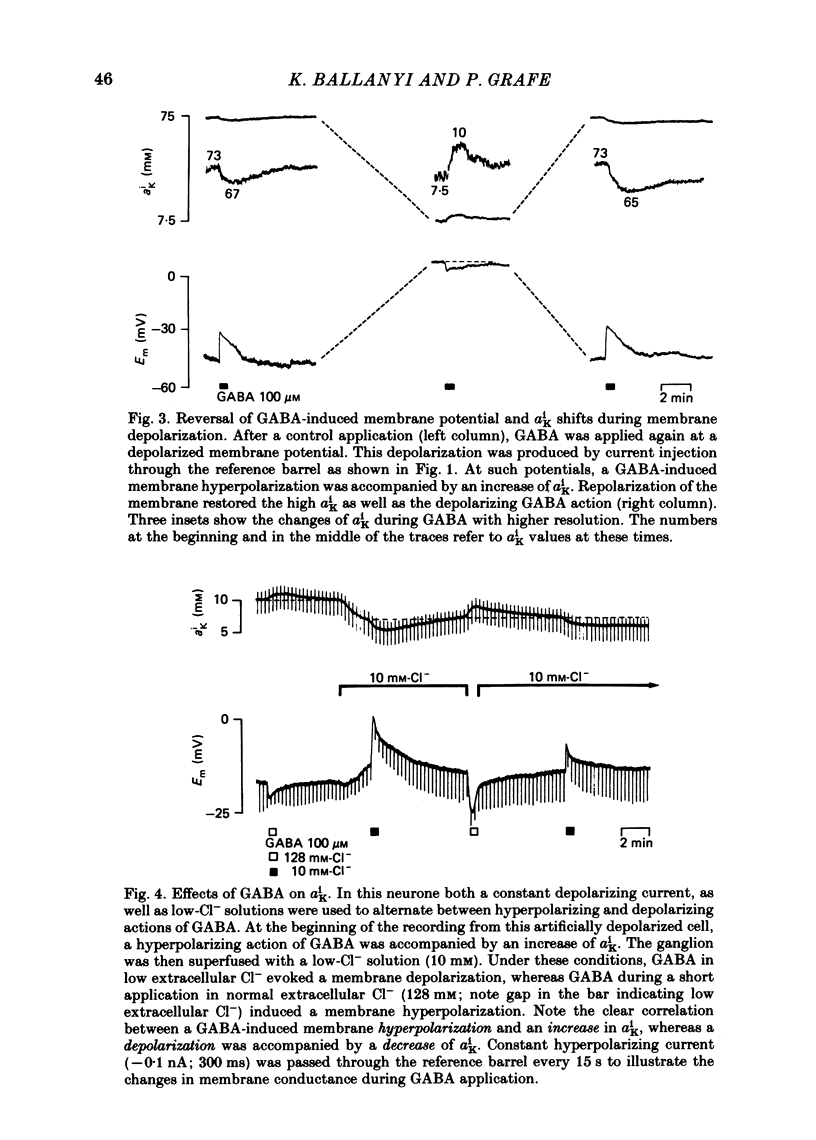
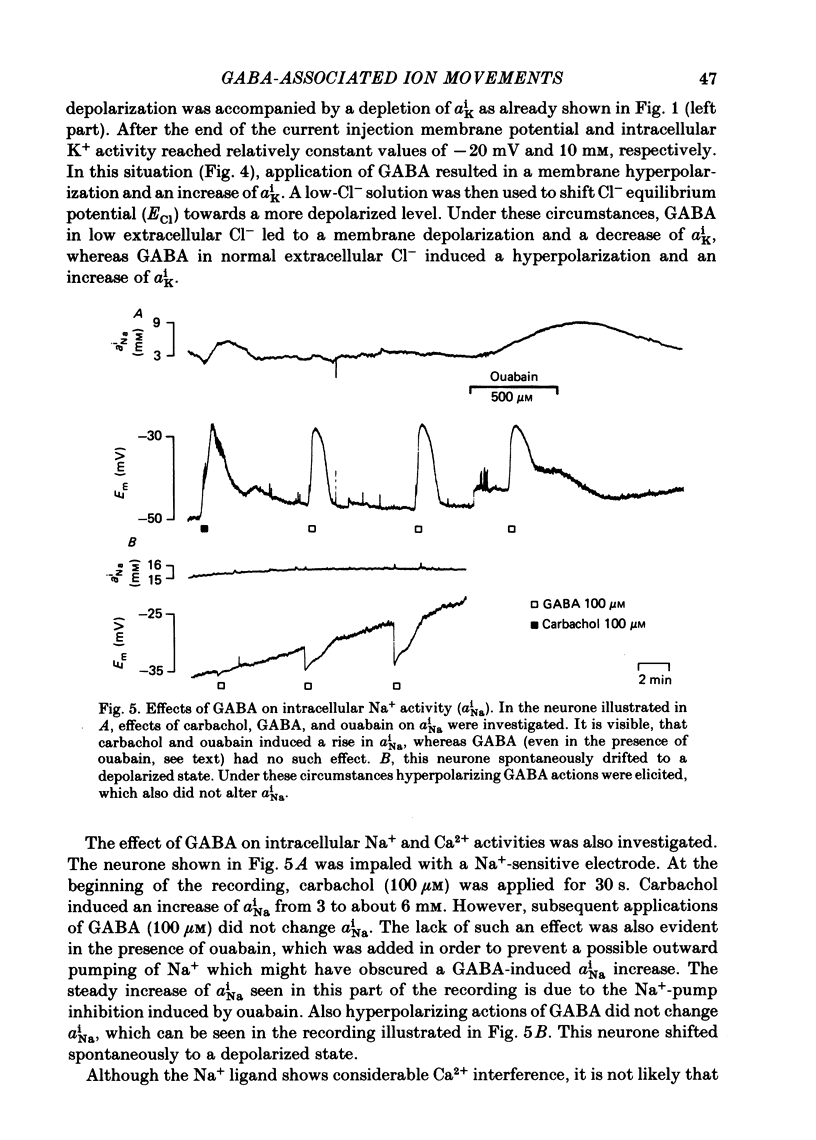
Double-barrelled ion-sensitive micro-electrodes were used to measure the changes of the intracellular activities of Cl-, K+, and Na+ (aiCl, aiK, aiNa) in neurones of isolated rat sympathetic ganglia during the action of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). The membrane potential of some of the neurones was manually 'voltage clamped' by passing current through the reference barrel of the ion-sensitive micro-electrode. This enabled us to convert the normal depolarizing action of GABA into a hyperpolarization. A GABA-induced membrane depolarization was accompanied by a decrease of aiCl, aiK and no change in aiNa, whereas a GABA-induced membrane hyperpolarization resulted in an increase of aiCl, aiK and also no change in aiNa. GABA did not change the free intracellular Ca2+ concentration, as measured with a Ca2+-sensitive micro-electrode, whereas such an effect was seen during the action of carbachol. pH-sensitive electrodes, on the other hand, revealed a small GABA-induced extracellular acidification. The inward pumping of Cl- following the normal, depolarizing action of GABA required the presence of extracellular K+ as well as Na+, whereas CO2/HCO3--free solutions did not influence the uptake process. Furosemide, but not DIDS, blocked the inward pumping of Cl-. In conclusion, our data show that only changes in intracellular activities of K+ and Cl- are associated with the action of GABA. Furthermore, they indicate that a K+/Cl- co-transport, and not a Cl-/HCO3- counter-transport, may be involved in the homoeostatic mechanism which operates to restore the normal transmembrane Cl- distribution after the action of GABA.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A. Actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid on sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;250(1):85–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad H. R., Loeschcke H. H. Fast bicarbonate-chloride exchange between brain cells and brain extracellular fluid in respiratory acidosis. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Dec;395(4):293–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00580792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aickin C. C., Brading A. F. The role of chloride-bicarbonate exchange in the regulation of intracellular chloride in guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:587–606. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aickin C. C., Deisz R. A., Lux H. D. Ammonium action on post-synaptic inhibition in crayfish neurones: implications for the mechanism of chloride extrusion. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:319–339. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aickin C. C., Deisz R. A., Lux H. D. Mechanisms of chloride transport in crayfish stretch receptor neurones and guinea pig vas deferens: implications for inhibition mediated by GABA. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Jun 29;47(3):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90520-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiton J. F., Chipperfield A. R., Lamb J. F., Ogden P., Simmons N. L. Occurrence of passive furosemide-sensitive transmembrane potassium transport in cultured cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 7;646(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballanyi K., Grafe P., Reddy M. M., ten Bruggencate G. Different types of potassium transport linked to carbachol and gamma-aminobutyric acid actions in rat sympathetic neurons. Neuroscience. 1984 Jul;12(3):917–927. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Brownstein M. J., Scholfield C. N. Origin of the after-hyperpolarization that follows removal of depolarizing agents from the isolated superior cervical ganglion of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Apr;44(4):651–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb07305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisz R. A., Lux H. D. The role of intracellular chloride in hyperpolarizing post-synaptic inhibition of crayfish stretch receptor neurones. J Physiol. 1982 May;326:123–138. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W., Schlue W. R. Intracellular Na+ and Ca2+ in leech Retzius neurones during inhibition of the Na+-K+ pump. Pflugers Arch. 1983 May;397(3):195–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00584357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschenes M., Feltz P. GABA-induced rise of extracellular potassium in rat dorsal root ganglia: an electrophysiological study in vivo. Brain Res. 1976 Dec 24;118(3):494–499. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90319-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duhm J., Göbel B. O. Role of the furosemide-sensitive Na+/K+ transport system in determining the steady-state Na+ and K+ content and volume of human erythrocytes in vitro and in vivo. J Membr Biol. 1984;77(3):243–254. doi: 10.1007/BF01870572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstl J., Galvan M., ten Bruggencate G. Extracellular K+ concentration during electrical stimulation of rat isolated sympathetic ganglia, vagus and optic nerves. Neuroscience. 1982;7(12):3221–3229. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90244-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. P., Nakamura J., Shinnick-Gallagher P. The effects of temperature, pH and Cl-pump inhibitors on GABA responses recorded from cat dorsal root ganglia. Brain Res. 1983 May 16;267(2):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90877-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvan M., Dörge A., Beck F., Rick R. Intracellular electrolyte concentrations in rat sympathetic neurones measured with an electron microprobe. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Mar;400(3):274–279. doi: 10.1007/BF00581559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geck P., Pietrzyk C., Burckhardt B. C., Pfeiffer B., Heinz E. Electrically silent cotransport on Na+, K+ and Cl- in Ehrlich cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 4;600(2):432–447. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90446-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafe P., Rimpel J., Reddy M. M., ten Bruggencate G. Lithium distribution across the membrane of motoneurons in the isolated frog spinal cord. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Jun;393(4):297–301. doi: 10.1007/BF00581413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greger R., Schlatter E., Lang F. Evidence for electroneutral sodium chloride cotransport in the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Mar;396(4):308–314. doi: 10.1007/BF01063936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Schmidt W. F., 3rd, McManus T. J. Catecholamine-stimulated ion transport in duck red cells. Gradient effects in electrically neutral [Na + K + 2Cl] Co-transport. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jul;80(1):125–147. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann E. K. Anion exchange and anion-cation co-transport systems in mammalian cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 1;299(1097):519–535. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K. Active accumulation and exchange transport of chloride in astroglial cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 6;646(1):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraig R. P., Ferreira-Filho C. R., Nicholson C. Alkaline and acid transients in cerebellar microenvironment. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Mar;49(3):831–850. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.3.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kregenow F. M. Osmoregulatory salt transporting mechanisms: control of cell volume in anisotonic media. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:493–505. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.002425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo Y., Fukuda H. Alteration of extracellular K+-activity induced by amino acids in the frog spinal cord. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;26(3):385–387. doi: 10.1254/jjp.26.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeffler J. P., Desaulles E., Demeneix B. A., Feltz P. Electrophysiological study with K+- and Ca2+-sensitive micropipettes of GABA receptors in the rat neurointermediate lobe in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Dec 31;34(3):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. C., Lanter F., Ammann D., Steiner R. A., Simon W. Applicability of available ion-selective liquid-membrane microelectrodes to intracellular ion-activity measurements. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Mar;393(1):23–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00582386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody W. J., Jr The ionic mechanism of intracellular pH regulation in crayfish neurones. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:293–308. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A. The blockade of GABA mediated responses in the frog spinal cord by ammonium ions and furosemide. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:121–132. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. M. Cation-coupled chloride influx in squid axon. Role of potassium and stoichiometry of the transport process. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jun;81(6):909–925. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.6.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimazaki H., Oakley B., 2nd Reaccumulation of [K+]o in the toad retina during maintained illumination. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Sep;84(3):475–504. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.3.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syková E. GABA-induced changes of extracellular K+-activity in the frog spinal cord. Physiol Bohemoslov. 1979;28(2):189–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Experimental displacement of intracellular pH and the mechanism of its subsequent recovery. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:3P–22P. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. The role of bicarbonate, chloride and sodium ions in the regulation of intracellular pH in snail neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):317–338. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Rink T. J. Ca2+-selective electrodes: a novel PVC-gelled neutral carrier mixture compared with other currently available sensors. J Neurosci Methods. 1981 Jun;4(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(81)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan-Jones R. D. Regulation of chloride in quiescent sheep-heart Purkinje fibres studied using intracellular chloride and pH-sensitive micro-electrodes. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:111–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingart R., Hess P. Free calcium in sheep cardiac tissue and frog skeletal muscle measured with Ca2+-selective microelectrodes. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Sep;402(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00584824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojtowicz J. M., Nicoll R. A. Selective action of piretanide on primary afferent GABA responses in the frog spinal cord. Brain Res. 1982 Mar 18;236(1):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpaw E. W., Martin D. L. Cl- transport in a glioma cell line: evidence for two transport mechanisms. Brain Res. 1984 Apr 16;297(2):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90573-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


