Abstract
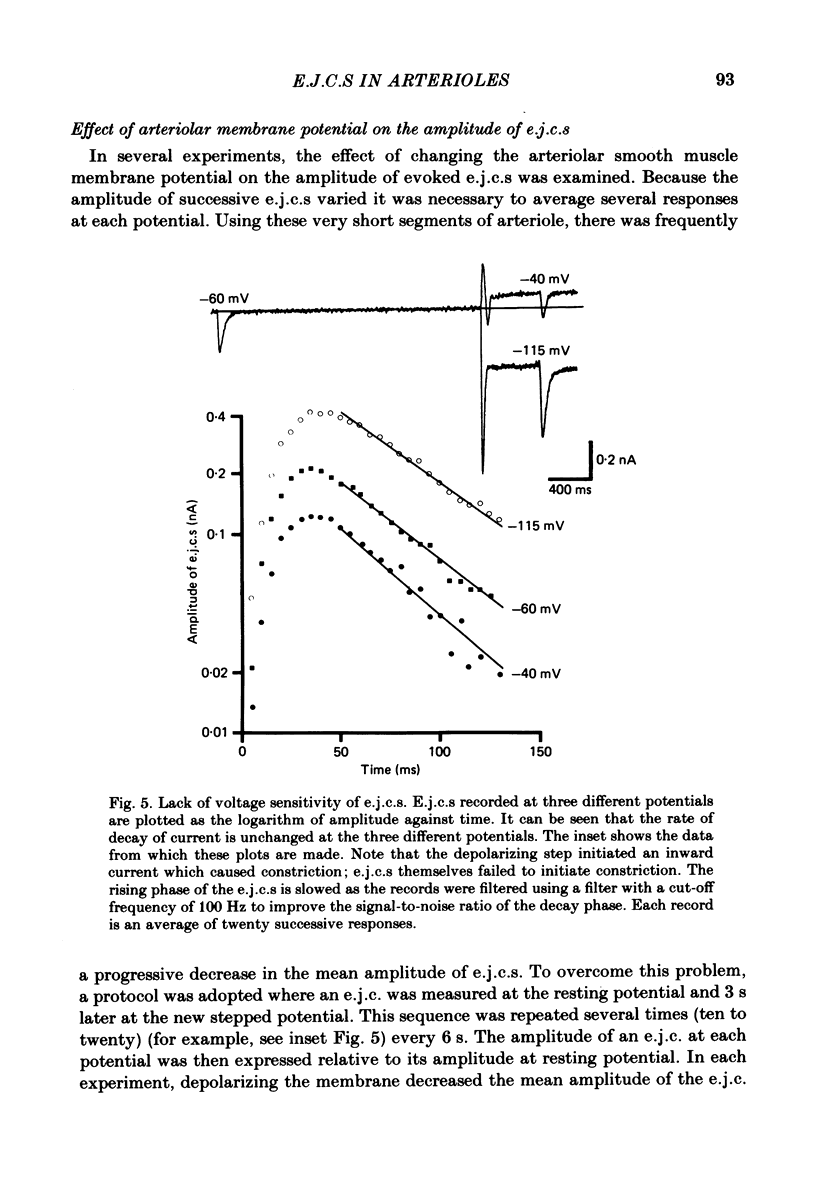
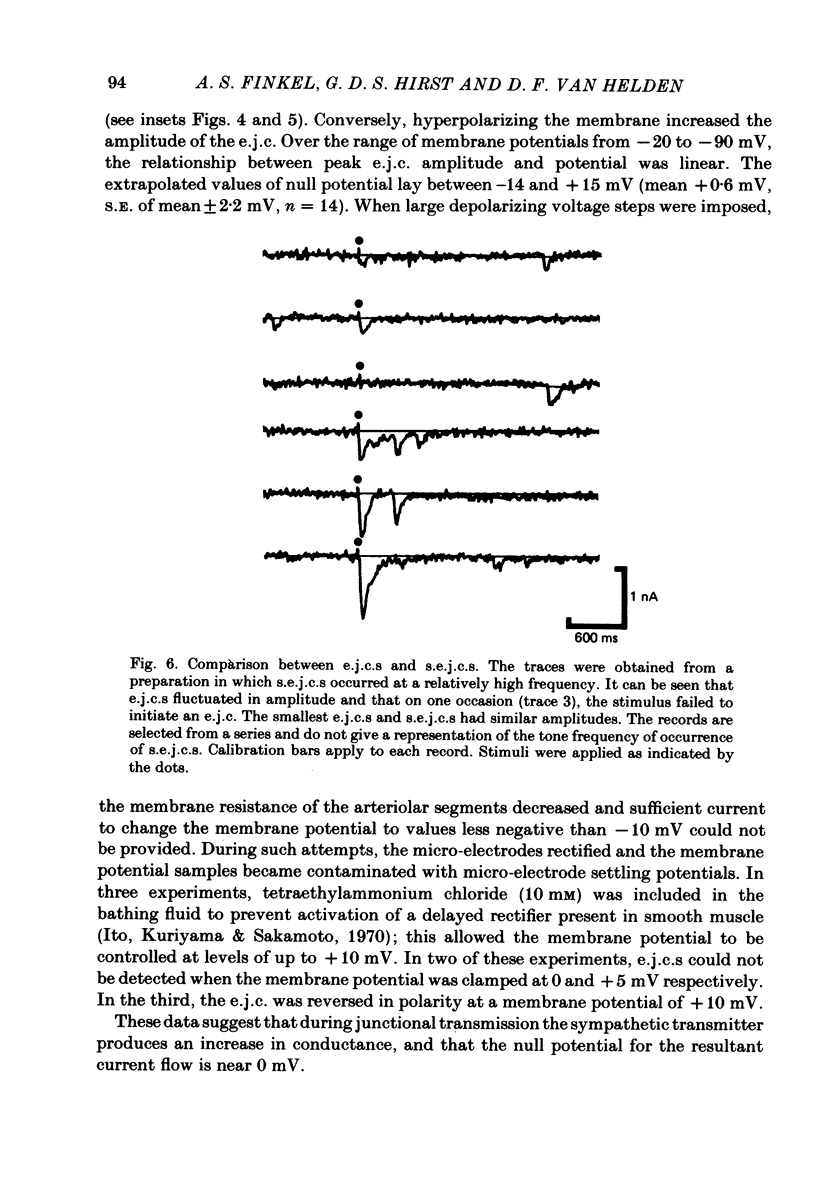
Excitatory junction potentials and excitatory junction currents have been recorded from short segments of arterioles taken from the submucosa of guinea-pig small intestine. Excitatory junction currents reached their peak amplitudes by 20 ms and then decayed, with a time course that could be described by a single exponential (mean time constant of decay approximately 50 ms). The null potential for excitatory junction currents obtained by extrapolation was near 0 mV. The time course of excitatory junction currents failed to show voltage sensitivity. Spontaneous excitatory junction currents had the same time course as evoked currents; the amplitudes of spontaneous currents were less than an order of magnitude different from that of evoked currents.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. Transmission from vasoconstrictor and vasodilator nerves to single smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig uterine artery. J Physiol. 1969 Dec;205(3):695–708. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeley A. G., Cunnane T. C. The packeted release of transmitter from the sympathetic nerves of the guinea-pig vas deferens: an electrophysiological study. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:85–96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bywater R. A., Taylor G. S. The passive membrane properties and excitatory junction potentials of the guinea pig deferens. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:303–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derkach V. A., Selyanko A. A., Skok V. I. Acetylcholine-induced current fluctuations and fast excitatory post-synaptic currents in rabbit sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:511–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J. Nonlinear voltage dependence of excitatory synaptic current in crayfish muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1974;352(3):227–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00590488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel A. S. A cholinergic chloride conductance in neurones of Helix aspersa. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:119–135. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel A. S., Redman S. J. The synaptic current evoked in cat spinal motoneurones by impulses in single group 1a axons. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:615–632. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W. Generation of end-plate potentials. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jan;56(1):177–247. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.1.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsborg B. L. Ion movements in junctional transmission. Pharmacol Rev. 1967 Sep;19(3):289–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
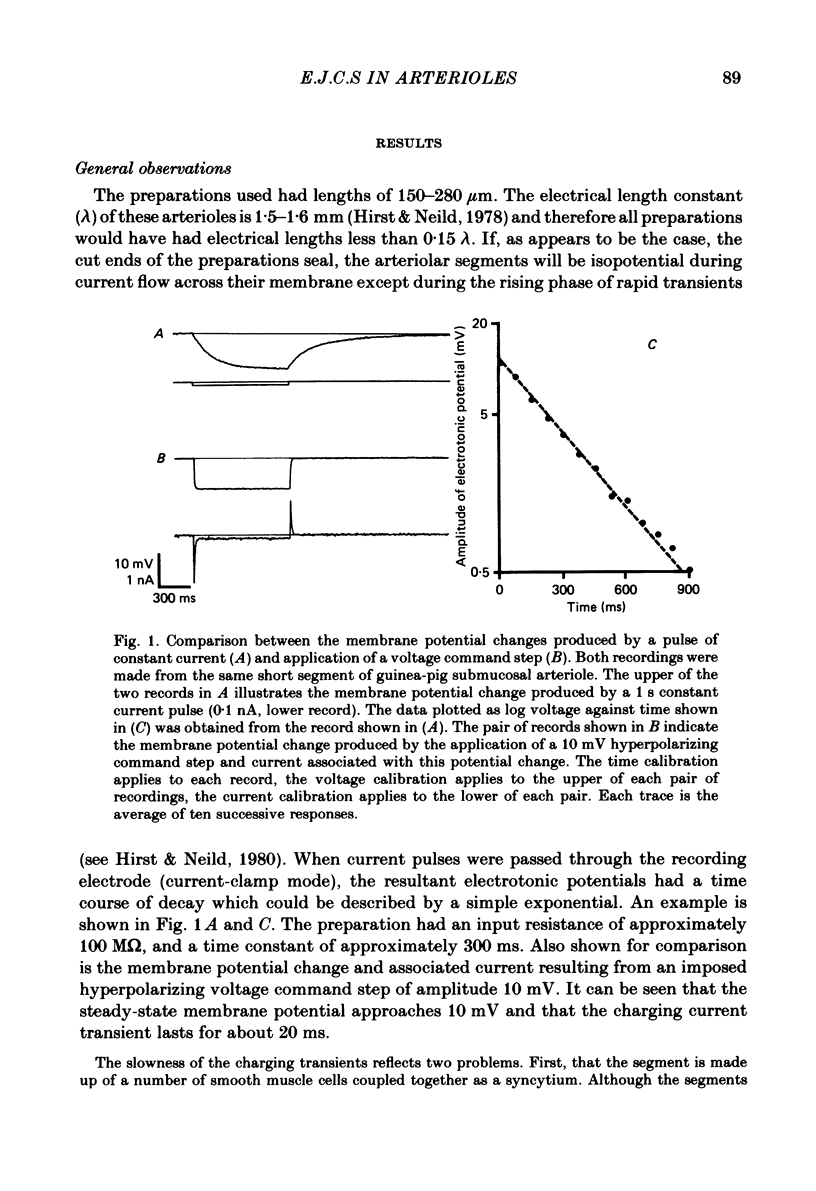
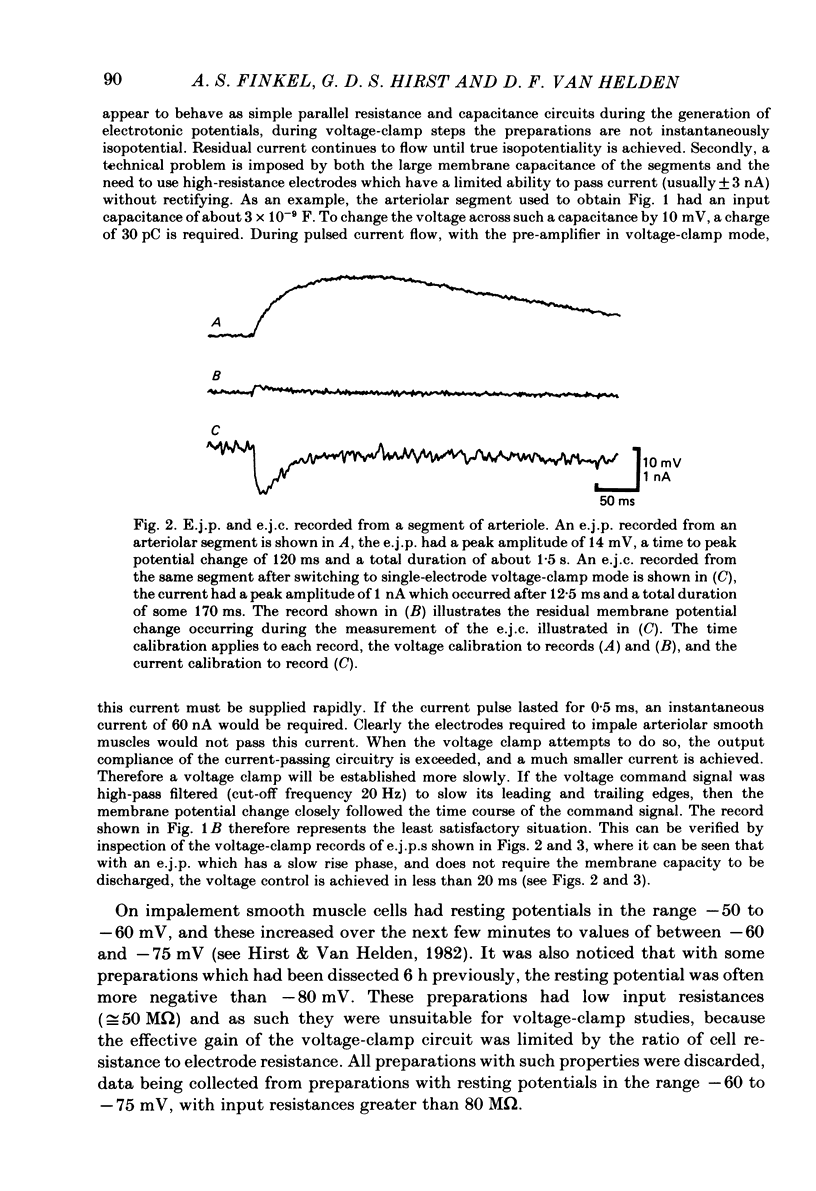
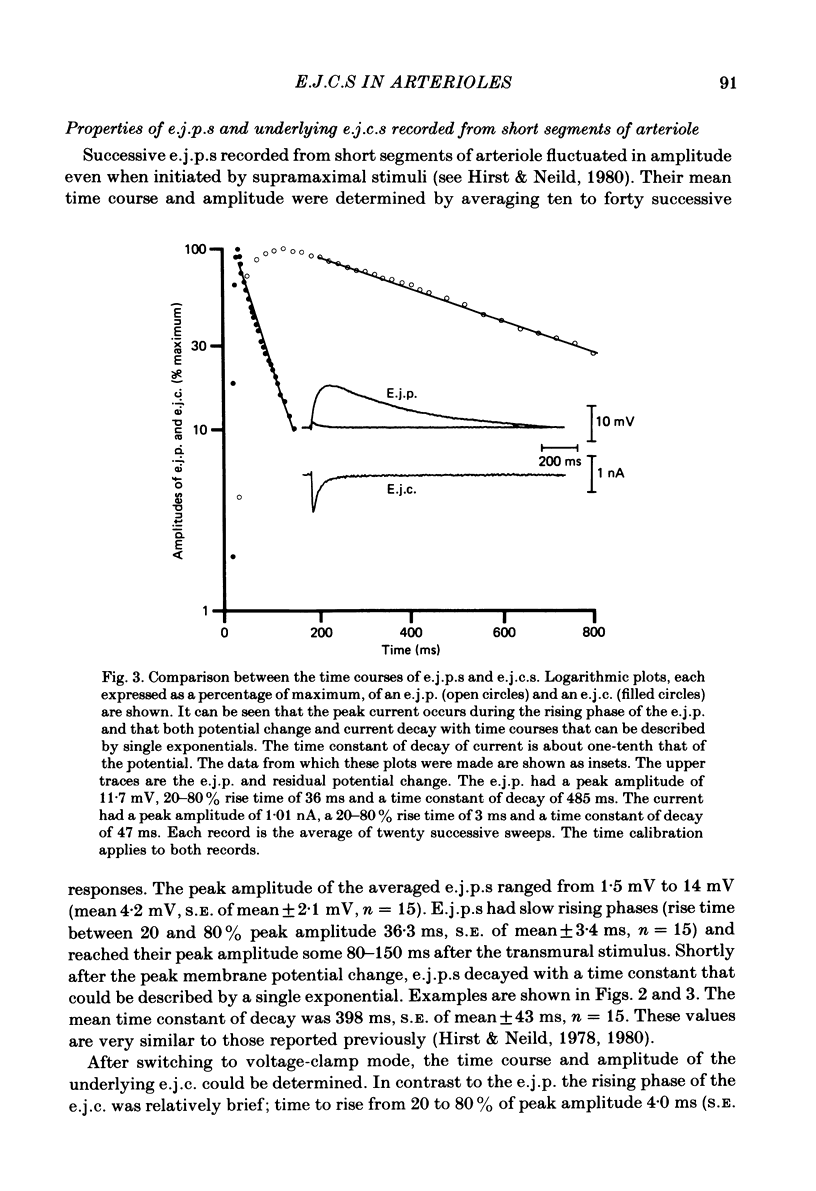
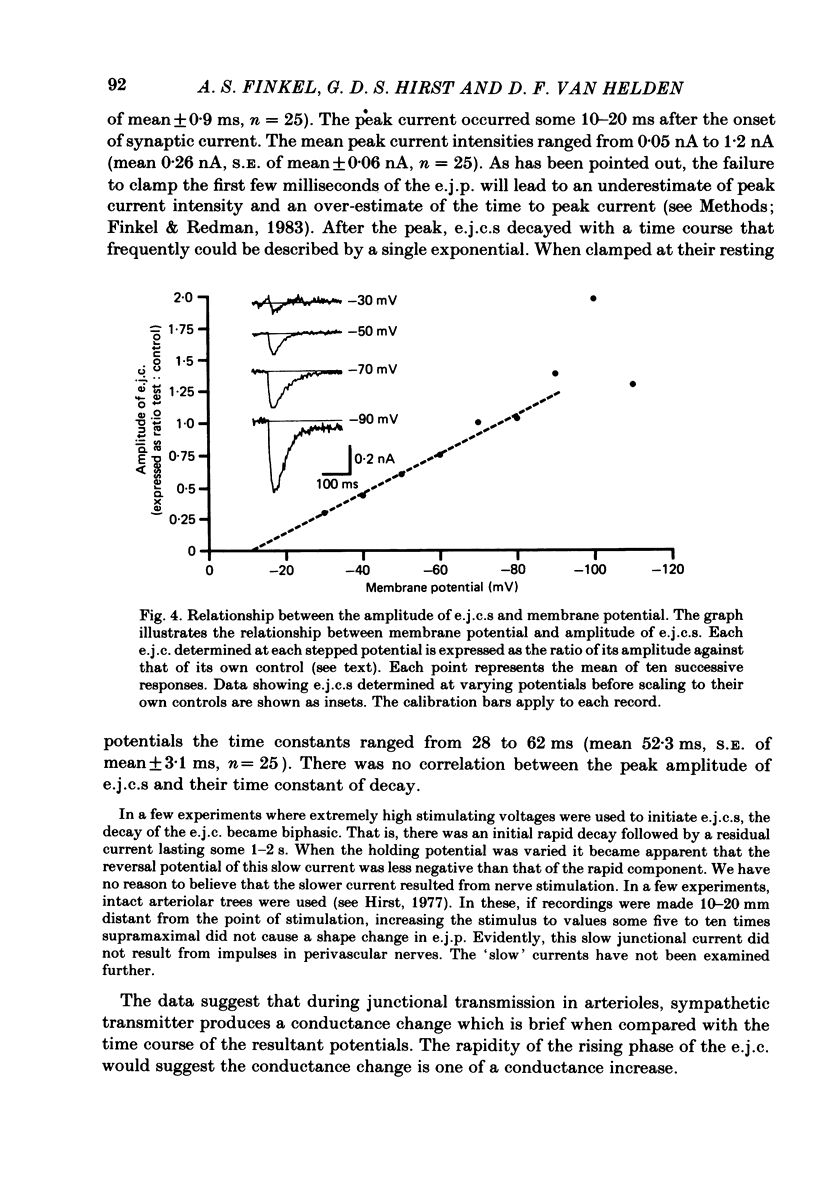
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. An analysis of excitatory junctional potentials recorded from arterioles. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:87–104. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. Localization of specialized noradrenaline receptors at neuromuscular junctions on arterioles of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1981;313:343–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. Some properties of spontaneous excitatory junction potentials recorded from arterioles of guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:43–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D. Neuromuscular transmission in arterioles of guinea-pig submucosa. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):263–275. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., van Helden D. F. Ionic basis of the resting potential of submucosal arterioles in the ileum of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:53–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman M. E., Surprenant A. M. Some properties of the excitatory junction potentials recorded from saphenous arteries of rabbits. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:337–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua C., Cragg B. Measurements of smooth muscle cells in arterioles of guinea pig ileum. Acta Anat (Basel) 1980;107(2):224–230. doi: 10.1159/000145246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Kuriyama H., Sakamoto Y. Effects of tetraethylammonium chloride on the membrane activity of guinea-pig stomach smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(2):445–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. Adrenergic transmissions in the guinea-pig mesenteric artery and their cholinergic modulations. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:383–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. The effect of voltage on the time course of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):151–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera K., Takeuchi A. Effects of membrane potential and temperature on the excitatory post-synaptic current in the crayfish muscle. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:183–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. The characteristics of synaptic currents and responses to acetylcholine of rat submandibular ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:23–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H. An electrophysiological study of excitatory neuromuscular transmission in the guinea-pig main pulmonary artery. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:47–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Active phase of frog's end-plate potential. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Jul;22(4):395–411. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.4.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


