Abstract
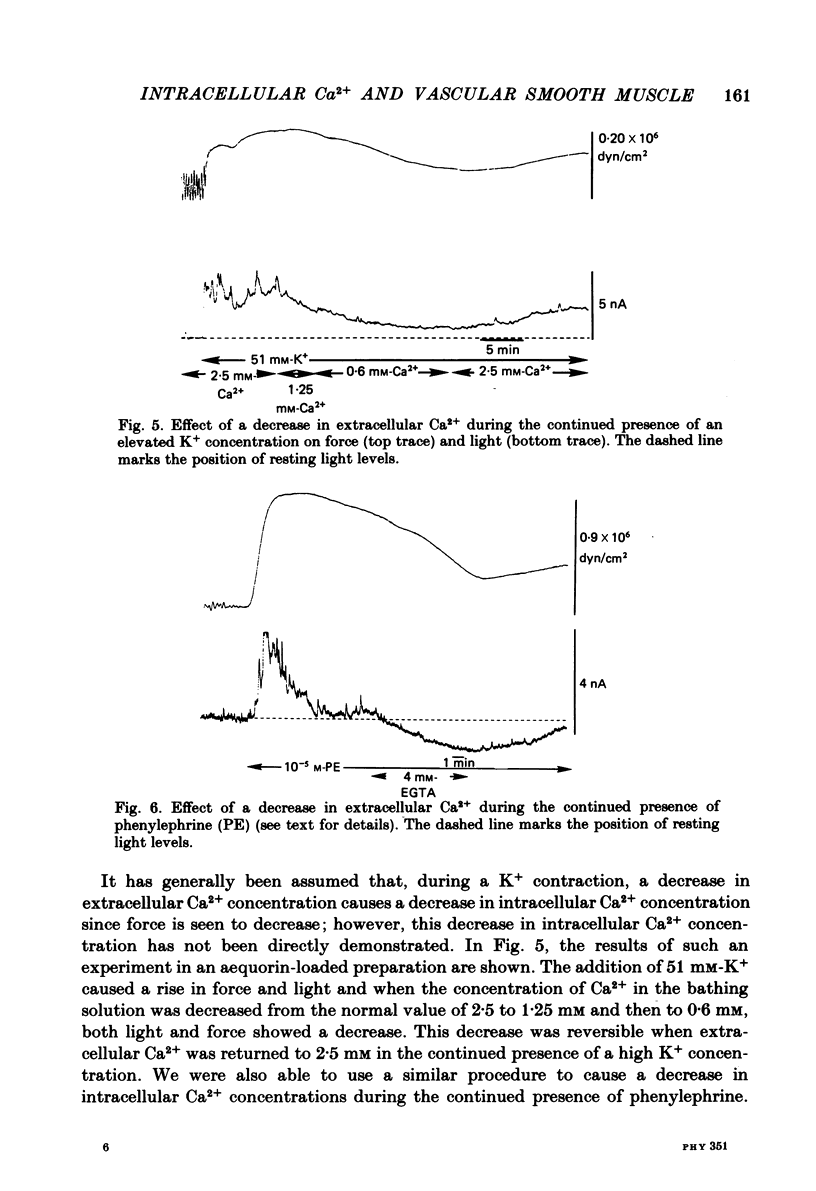
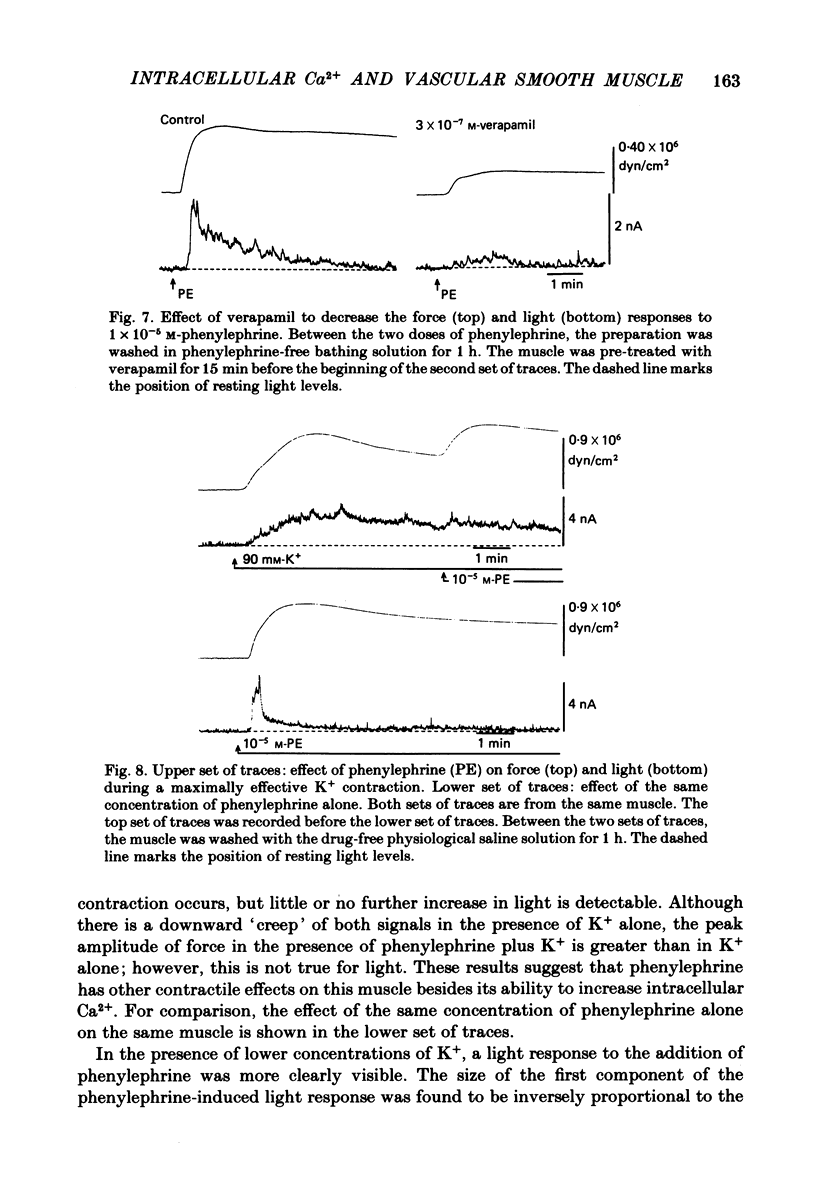
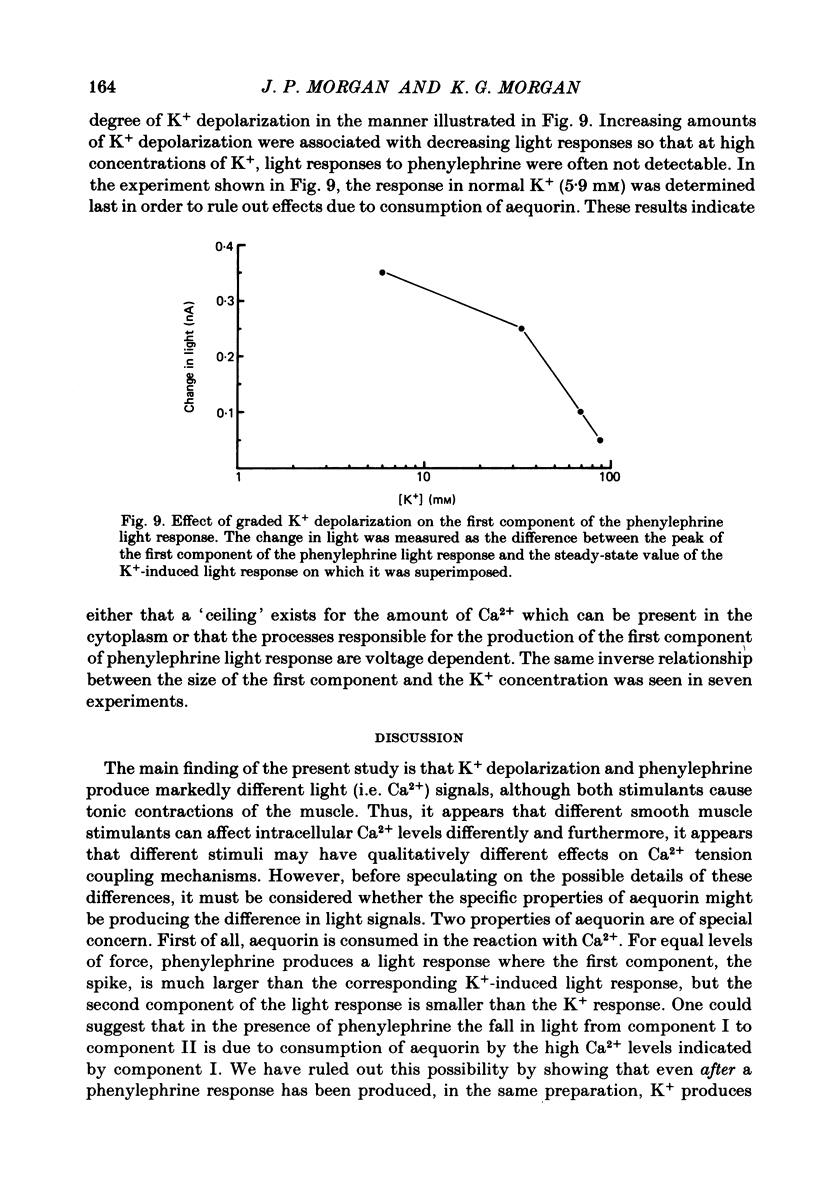
Aequorin was loaded into cells of the ferret portal vein in order to follow intracellular Ca2+ levels during smooth muscle contraction. In response to a single d.c. pulse, the aequorin signal reaches a peak during the rising phase of the evoked force transient and begins to rapidly fall while force is still rising. In response to the addition of phenylephrine to the bathing solution, the aequorin signal rises rapidly to a peak while force is still rising but then falls rapidly to a lower level from which it declines more slowly, staying above base-line levels as long as force is maintained. In response to the elevation of K+ concentration in the bathing solution, light and force rise together and the elevated light level is maintained as long as is force. With increasing concentrations of K+, force increases up to a concentration of 50-60 mM but light increases up to 90 mM, suggesting that at a concentration of 50-60 mM-K+, the Ca2+ concentration may be saturating with respect to a site of action on the contractile apparatus. During the period of force maintenance, phenylephrine produces a larger ratio of force to light than does K+ depolarization. The maintenance of force in the presence of either phenylephrine or elevated K+ requires an elevation of intracellular Ca2+ levels above base-line values. These results suggest that phenylephrine can increase the effectiveness of Ca2+ on the contractile apparatus.
Full text
PDF

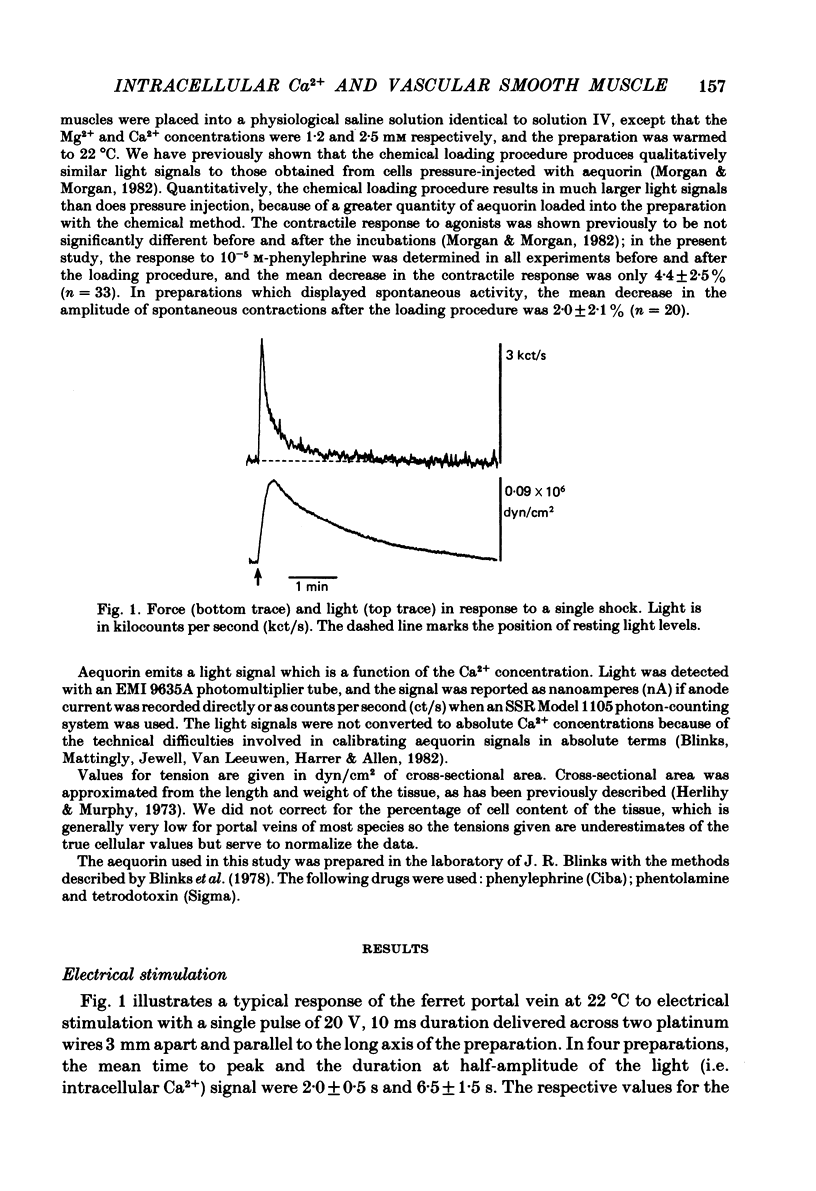
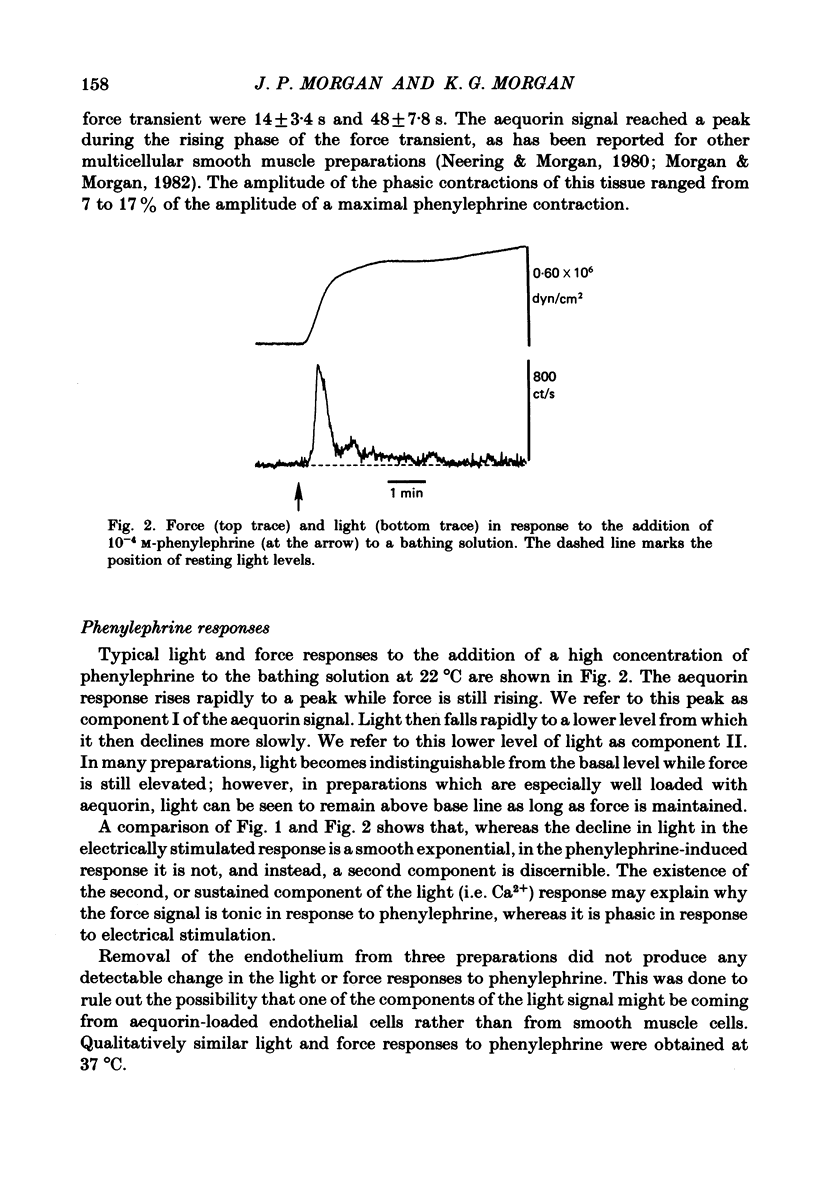
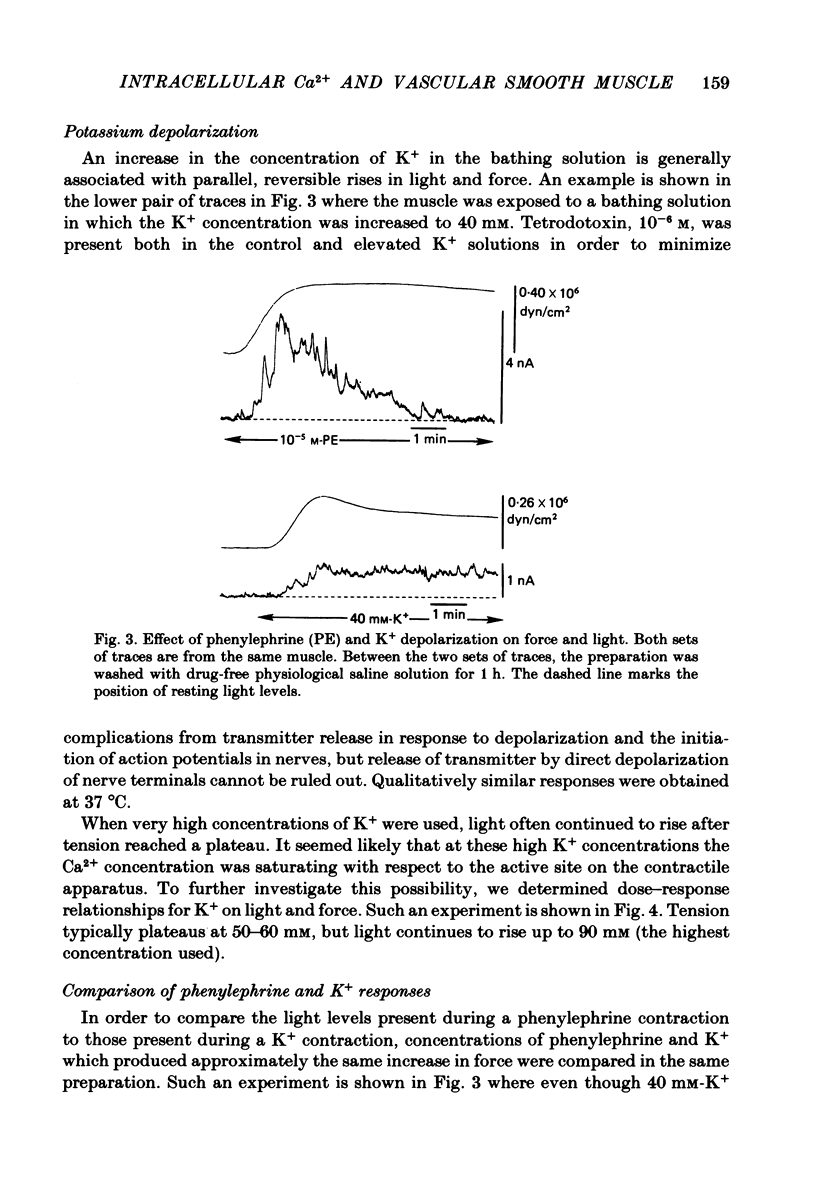
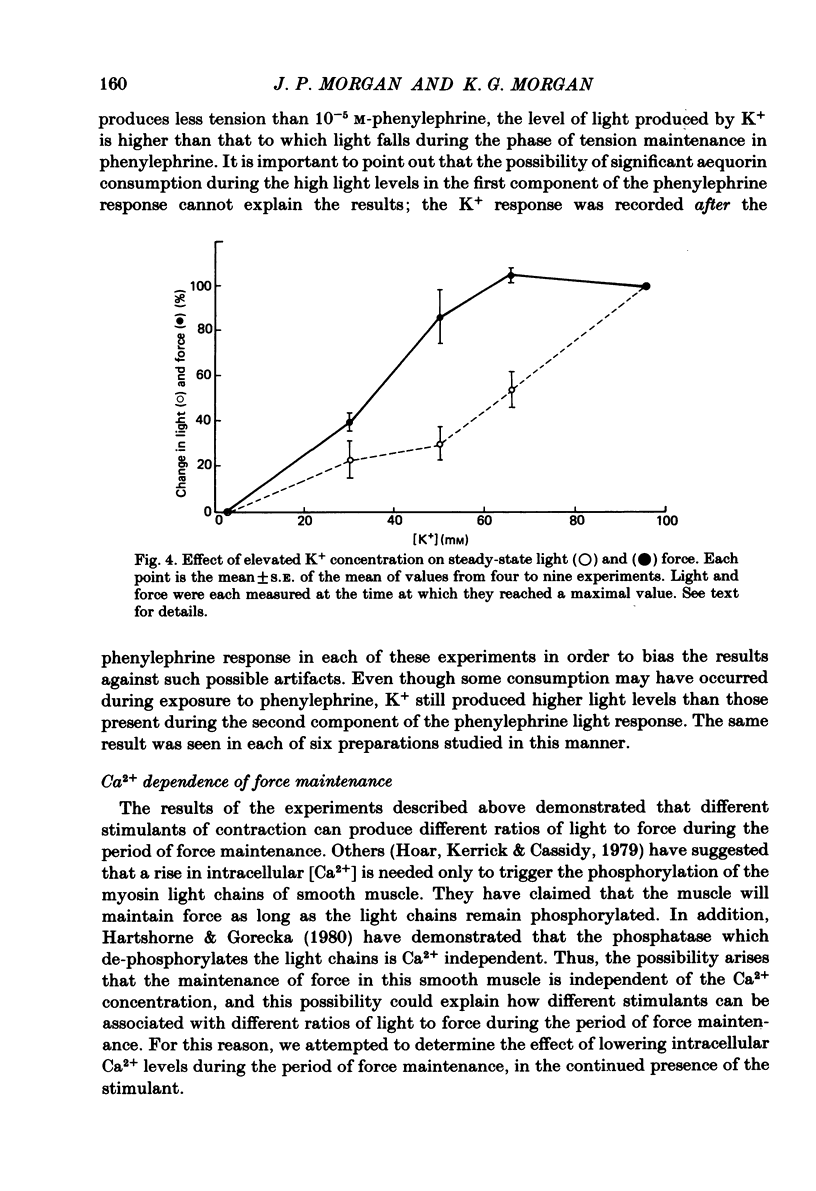




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aksoy M. O., Murphy R. A., Kamm K. E. Role of Ca2+ and myosin light chain phosphorylation in regulation of smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jan;242(1):C109–C116. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.1.C109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Wier W. G., Hess P., Prendergast F. G. Measurement of Ca2+ concentrations in living cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;40(1-2):1–114. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(82)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mey J. G., Vanhoutte P. M. Role of the intima in cholinergic and purinergic relaxation of isolated canine femoral arteries. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:347–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droogmans G., Raeymaekers L., Casteels R. Electro- and pharmacomechanical coupling in the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit ear artery. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Aug;70(2):129–148. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay F. S., Shlevin H. H., Granger W. C., Jr, Taylor S. R. Aequorin luminescence during activation of single isolated smooth muscle cells. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):506–508. doi: 10.1038/280506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golenhofen K., Hermstein N., Lammel E. Membrane potential and contraction of vascular smooth muscle (portal vein) during application of noradrenaline and high potassium, and selective inhibitory effects of iproveratril (verapamil). Microvasc Res. 1973 Jan;5(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/s0026-2862(73)80007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlihy J. T., Murphy R. A. Length-tension relationship of smooth muscle of the hog carotid artery. Circ Res. 1973 Sep;33(3):275–283. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.3.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoar P. E., Kerrick W. G., Cassidy P. S. Chicken gizzard: relation between calcium-activated phosphorylation and contraction. Science. 1979 May 4;204(4392):503–506. doi: 10.1126/science.432654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman M. E., Kasby C. B., Suthers M. B., Wilson J. A. Some properties of the smooth muscle of rabbit portal vein. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):111–132. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. Excitation--contraction coupling in smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:513–535. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp014000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClellan G. B., Winegrad S. The regulation of the calcium sensitivity of the contractile system in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Dec;72(6):737–764. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.6.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Vascular smooth muscle: the first recorded Ca2+ transients. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):75–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00584972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neering I. R., Morgan K. G. Use of aequorin to study excitation--contraction coupling in mammalian smooth muscle. Nature. 1980 Dec 11;288(5791):585–587. doi: 10.1038/288585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W. Effect of histamine on the energy metabolism of K+-depolarized hog carotid artery. Circ Res. 1982 Jun;50(6):848–855. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.6.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEPHENSON R. P. A modification of receptor theory. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1956 Dec;11(4):379–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1956.tb00006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saida K. Intracellular Ca release in skinned smooth muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Aug;80(2):191–202. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Breemen C., Farinas B. R., Casteels R., Gerba P., Wuytack F., Deth R. Factors controlling cytoplasmic Ca 2+ concentration. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Mar 15;265(867):57–71. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1973.0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


