Abstract
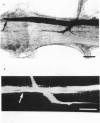
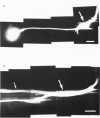
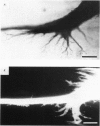
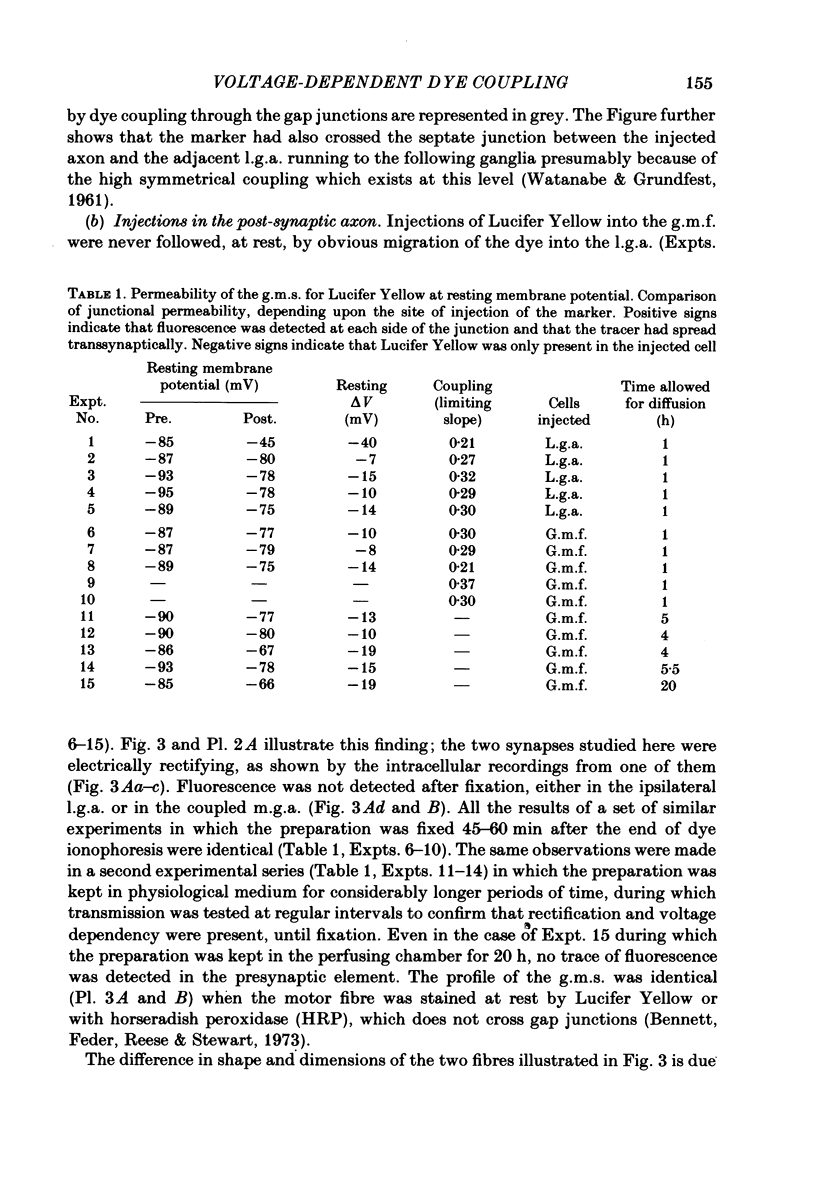
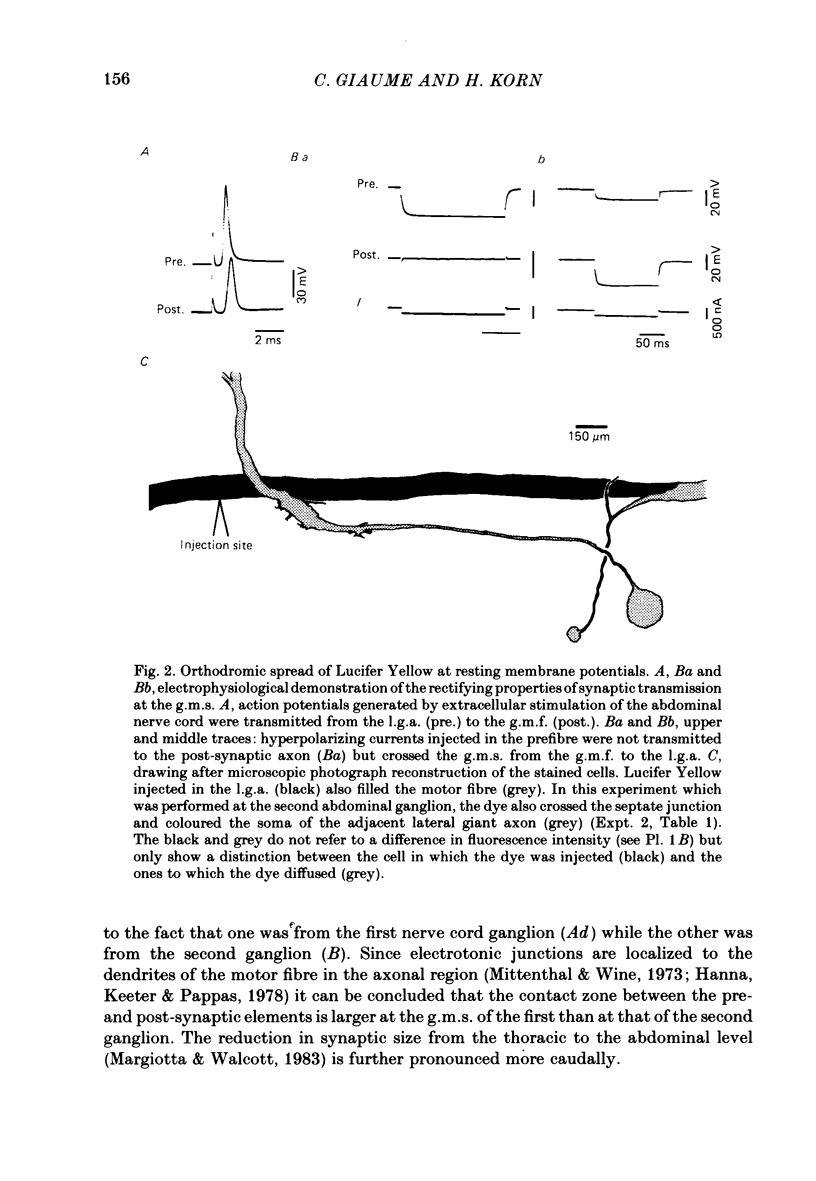
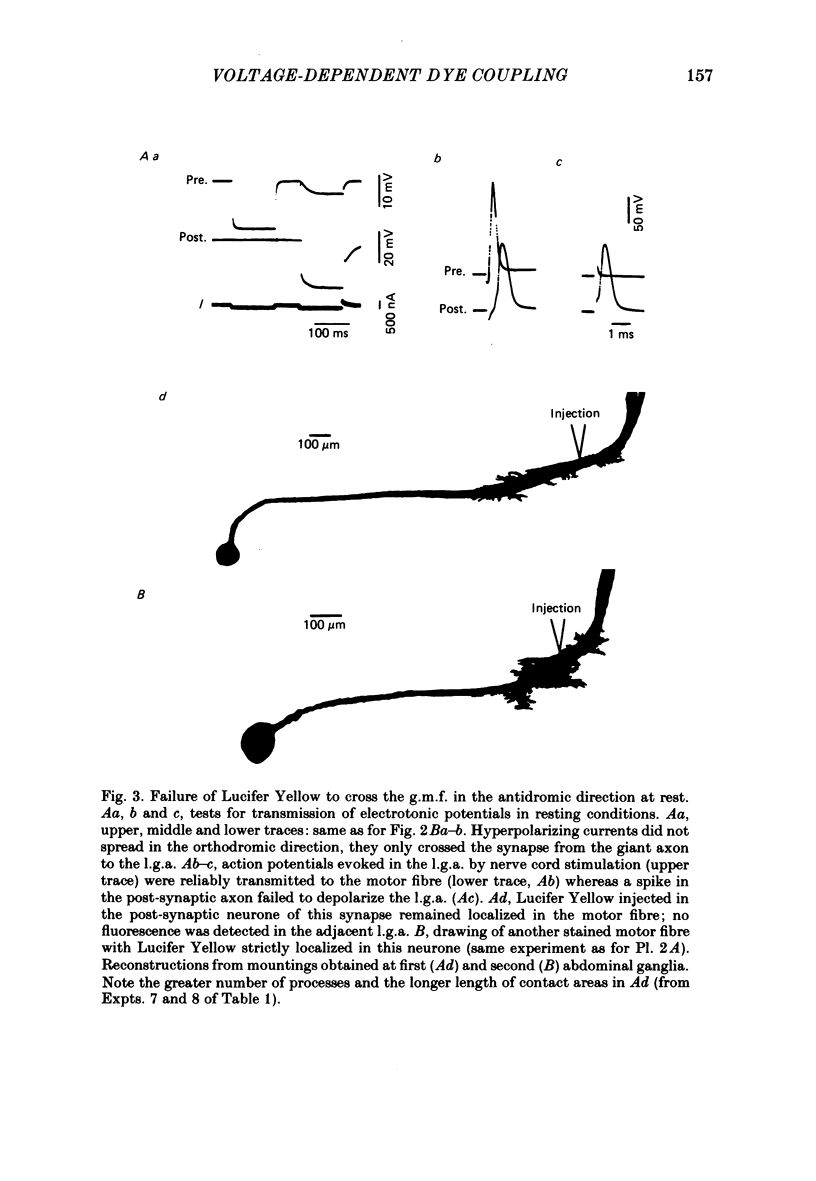
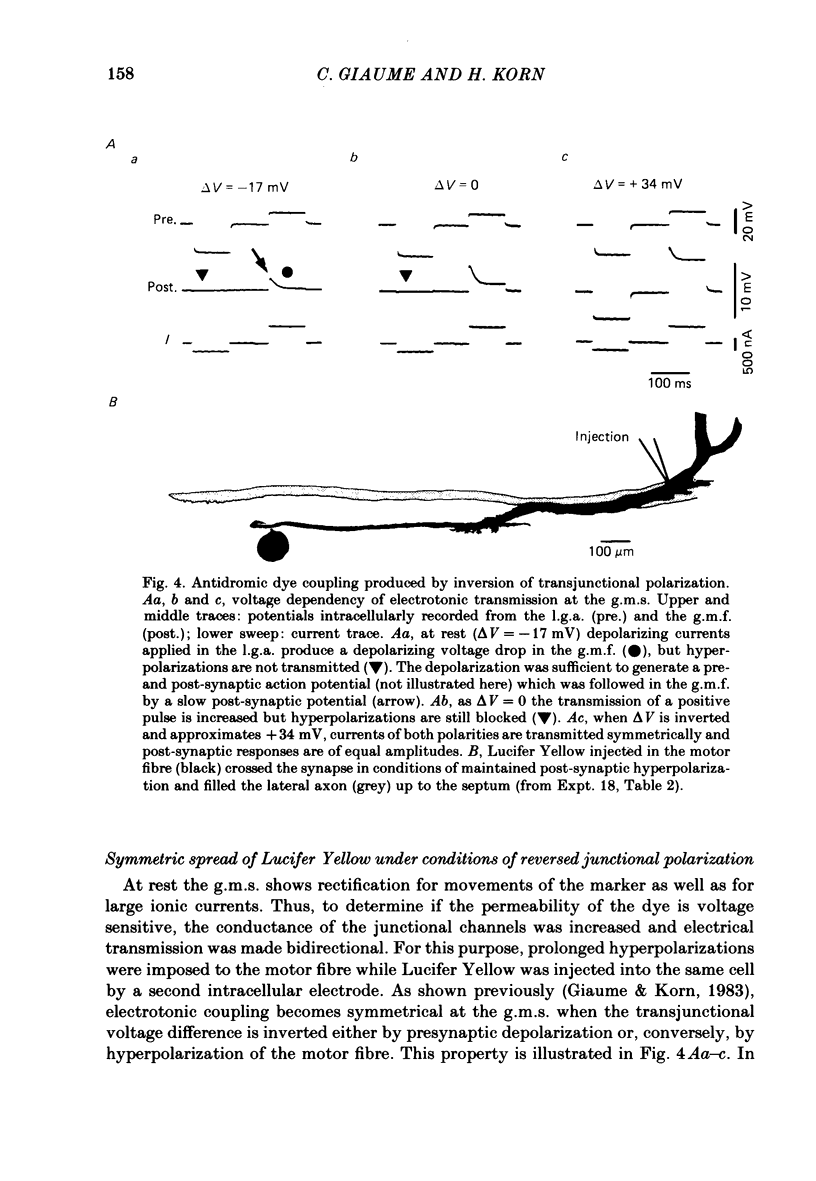
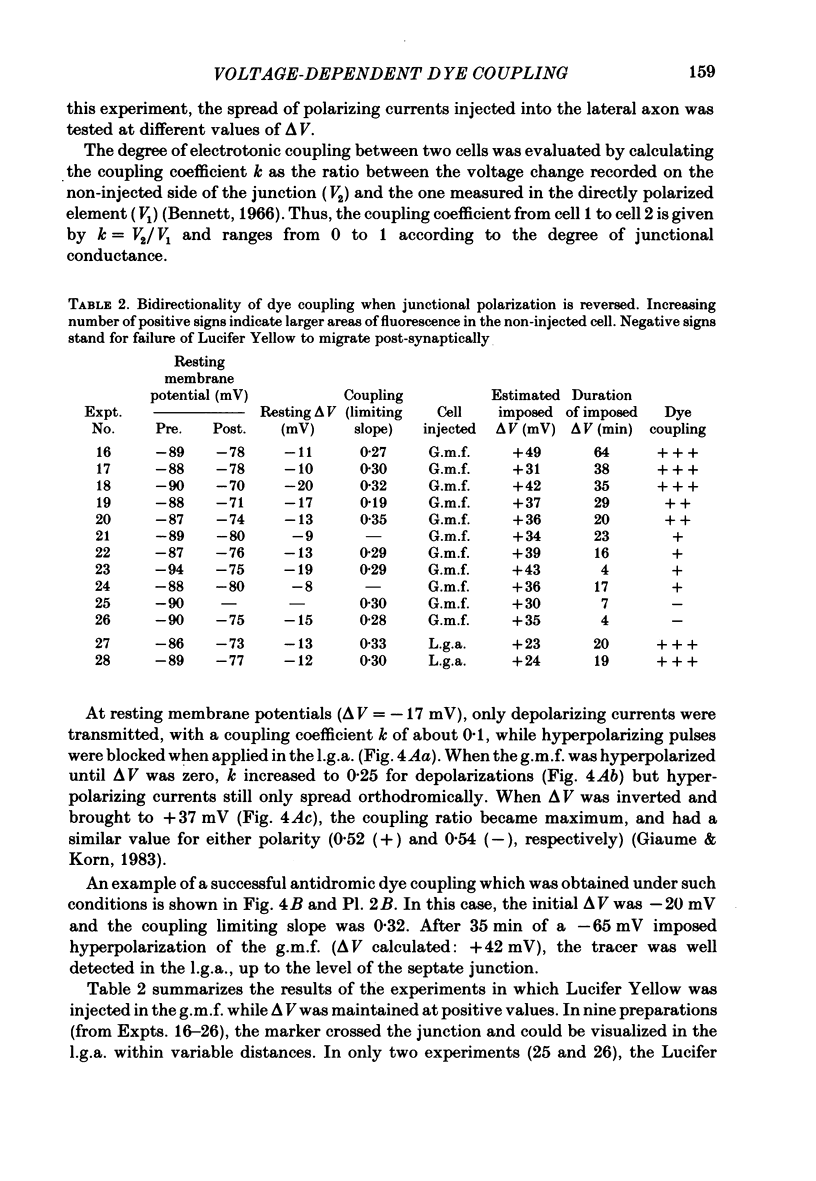
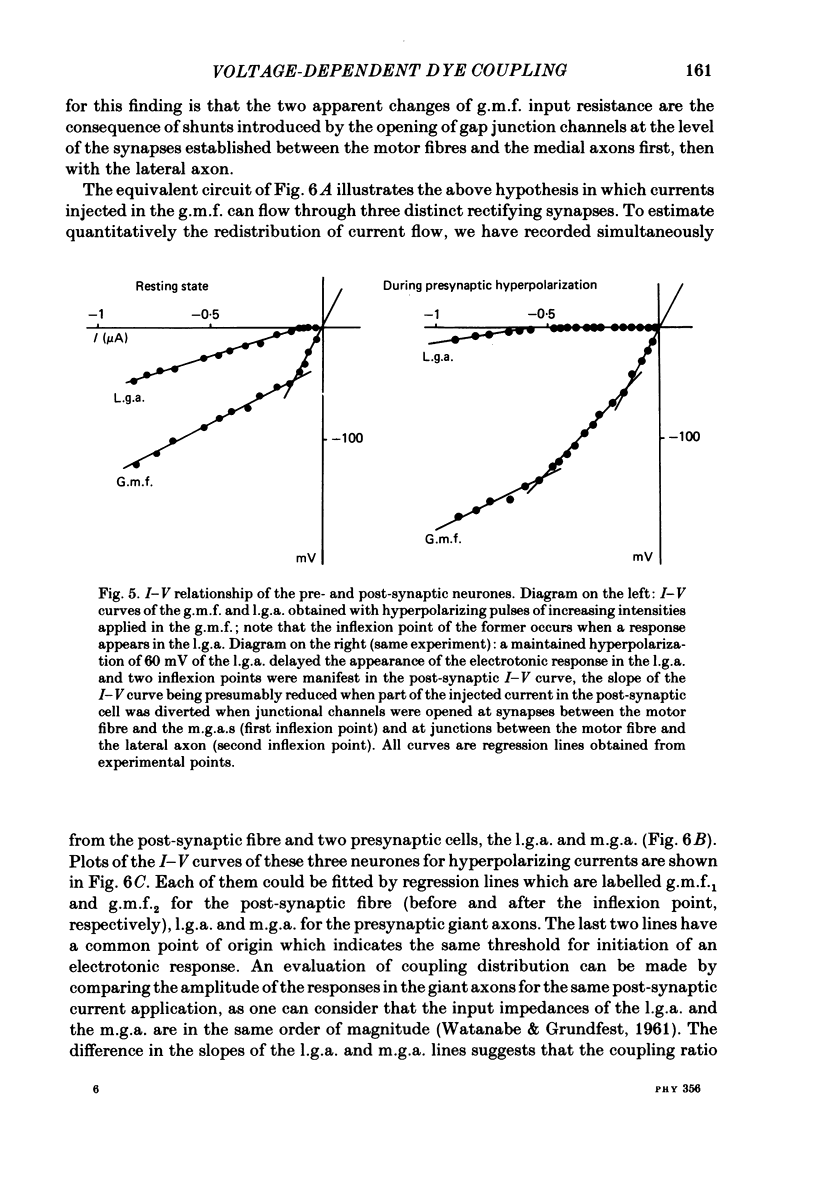
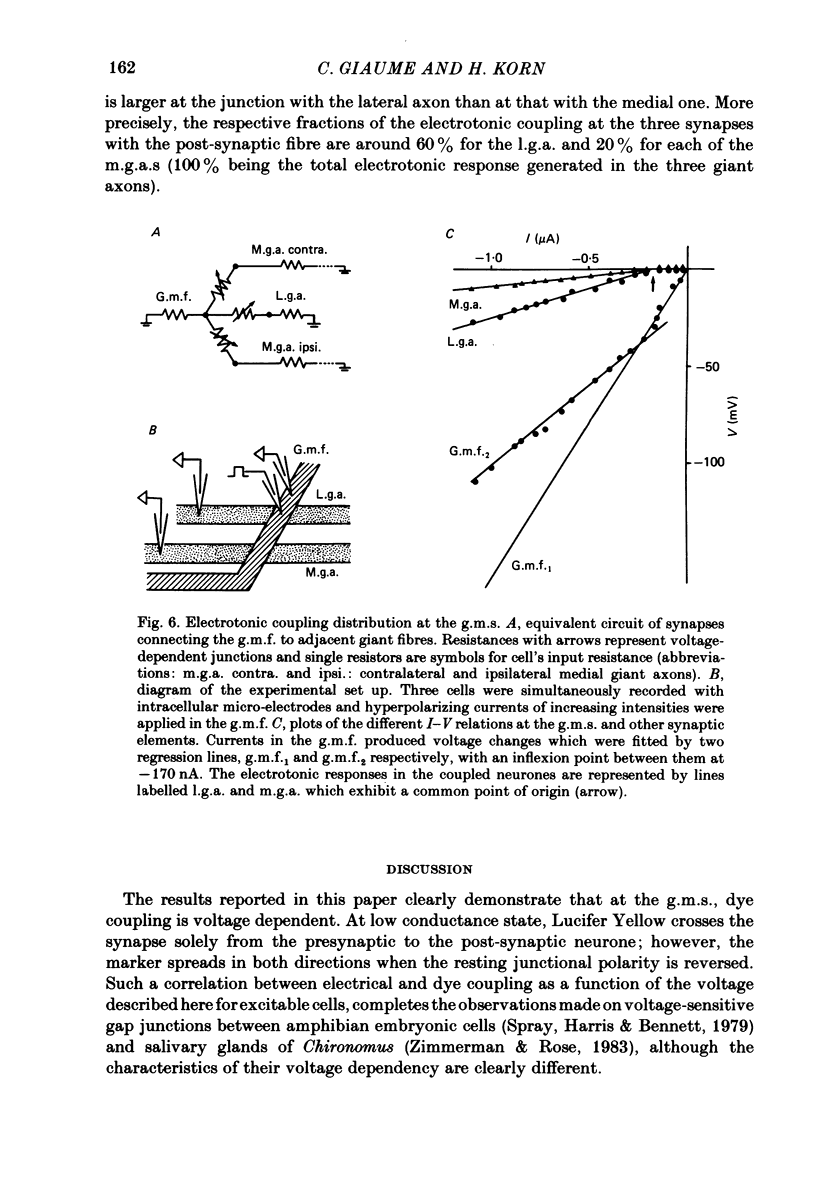
At the crayfish giant motor synapse, the lateral giant axon (l.g.a.) and the giant motor fibre (g.m.f.) form an electrotonic junction which exhibits two states of ionic coupling (Furshpan & Potter, 1959a; Giaume & Korn, 1983). Junctional conductance is low at resting membrane potentials (i.e. with lateral axon more negative than the motor fibre) and high when the polarity of the voltage difference (delta V) across the synapse is reversed. For these two states of conductance, junctional permeability was investigated using the intercellular tracer Lucifer Yellow. The dye was ionophoretically injected into either the presynaptic (l.g.a.) or the post-synaptic (g.m.f.) cell. In the high conductance state (delta V greater than 0), fluorescence was detected in both neurones whether Lucifer Yellow had been injected pre- or post-synaptically. By contrast, at the resting junctional polarization (delta V less than 0) Lucifer Yellow spread from the giant axon to the g.m.f., but not from the g.m.f. to the giant axons. These data demonstrate that dye transfer at the giant motor synapse, like ionic coupling, is sensitive to junctional polarization and is more marked in the high conductance state. Possible explanations for the asymmetry observed in the low conductance state are discussed.
Full text
PDF
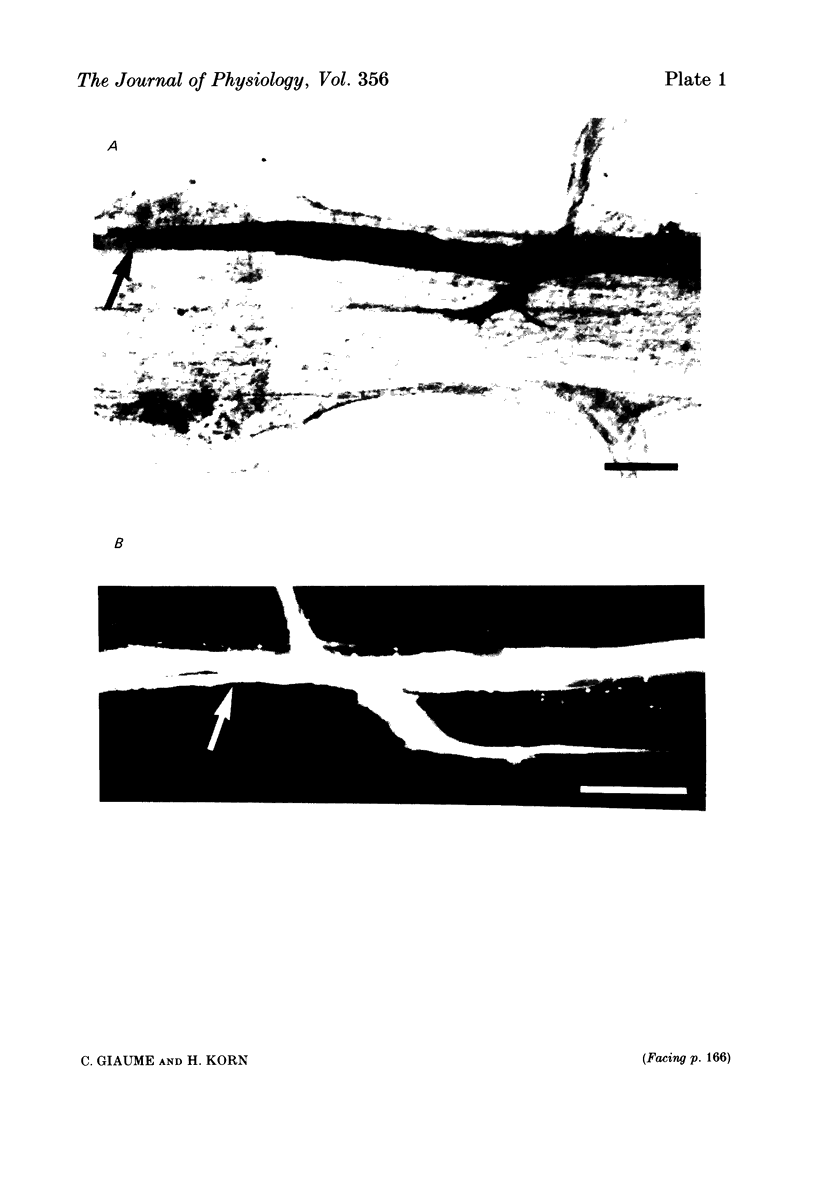











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Audesirk G., Audesirk T., Bowsher P. Variability and frequent failure of lucifer yellow to pass between two electrically coupled neurons in Lymnaea stagnalis. J Neurobiol. 1982 Jul;13(4):369–375. doi: 10.1002/neu.480130407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A. A., Bennett M. V. A rectifying electrotonic synapse in the central nervous system of a vertebrate. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Feb;53(2):211–237. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V. Physiology of electrotonic junctions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):509–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V., Spira M. E., Spray D. C. Permeability of gap junctions between embryonic cells of Fundulus: a reevaluation. Dev Biol. 1978 Jul;65(1):114–125. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink P. R., Dewey M. M. Evidence for fixed charge in the nexus. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):101–102. doi: 10.1038/285101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURSHPAN E. J., POTTER D. D. Slow post-synaptic potentials recorded from the giant motor fibre of the crayfish. J Physiol. 1959 Mar 3;145(2):326–335. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURSHPAN E. J., POTTER D. D. Transmission at the giant motor synapses of the crayfish. J Physiol. 1959 Mar 3;145(2):289–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flagg-Newton J. L., Loewenstein W. R. Asymmetrically permeable membrane channels in cell junction. Science. 1980 Feb 15;207(4432):771–773. doi: 10.1126/science.7352287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flagg-Newton J., Simpson I., Loewenstein W. R. Permeability of the cell-to-cell membrane channels in mammalian cell juncton. Science. 1979 Jul 27;205(4404):404–407. doi: 10.1126/science.377490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaume C., Korn H. Bidirectional transmission at the rectifying electrotonic synapse: a voltage-dependent process. Science. 1983 Apr 1;220(4592):84–87. doi: 10.1126/science.6298940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna R. B., Keeter J. S., Pappas G. D. The fine structure of a rectifying electrotonic synapse. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):764–773. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. L., Spray D. C., Bennett M. V. Control of intercellular communication by voltage dependence of gap junctional conductance. J Neurosci. 1983 Jan;3(1):79–100. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-01-00079.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Junctional intercellular communication: the cell-to-cell membrane channel. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):829–913. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margiotta J. F., Walcott B. Conductance and dye permeability of a rectifying electrical synapse. Nature. 1983 Sep 1;305(5929):52–55. doi: 10.1038/305052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittenthal J. E., Wine J. J. Connectivity patterns of crayfish giant interneurons: visualization of synaptic regions with cobalt dye. Science. 1973 Jan 12;179(4069):182–184. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4069.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls J. G., Purves D. Monosynaptic chemical and electrical connexions between sensory and motor cells in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):647–667. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remler M., Selverston A., Kennedy D. Lateral giant fibers of cray fish: location of somata by dye injection. Science. 1968 Oct 11;162(3850):281–283. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3850.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel J. P., Karnovsky M. J. Hexagonal array of subunits in intercellular junctions of the mouse heart and liver. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jun;33(3):C7–C12. doi: 10.1083/jcb.33.3.c7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringham G. L. Localization and electrical characteristics of a giant synapse in the spinal cord of the lamprey. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):395–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A., Krasne F. B., Hagiwara G., Wine J. J., Kramer A. P. Segmental giant: evidence for a driver neuron interposed between command and motor neurons in the crayfish escape system. J Neurophysiol. 1982 May;47(5):761–781. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.47.5.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I., Rose B., Loewenstein W. R. Size limit of molecules permeating the junctional membrane channels. Science. 1977 Jan 21;195(4275):294–296. doi: 10.1126/science.831276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. G., Baumann F. The functional organization within the ommatidium of the lateral eye of limulus. Prog Brain Res. 1969;31:313–349. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)63248-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Harris A. L., Bennett M. V. Voltage dependence of junctional conductance in early amphibian embryos. Science. 1979 Apr 27;204(4391):432–434. doi: 10.1126/science.312530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. W. Functional connections between cells as revealed by dye-coupling with a highly fluorescent naphthalimide tracer. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):741–759. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. W. Lucifer dyes--highly fluorescent dyes for biological tracing. Nature. 1981 Jul 2;292(5818):17–21. doi: 10.1038/292017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triller A., Korn H. Morphologically distinct classes of inhibitory synapses arise from the same neurons: ultrastructural identification from crossed vestibular interneurons intracellularly stained with HRP. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Nov 20;203(1):131–155. doi: 10.1002/cne.902030111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE A., GRUNDFEST H. Impulse propagation at the septal and commissural junctions of crayfish lateral giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Nov;45:267–308. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]