Abstract
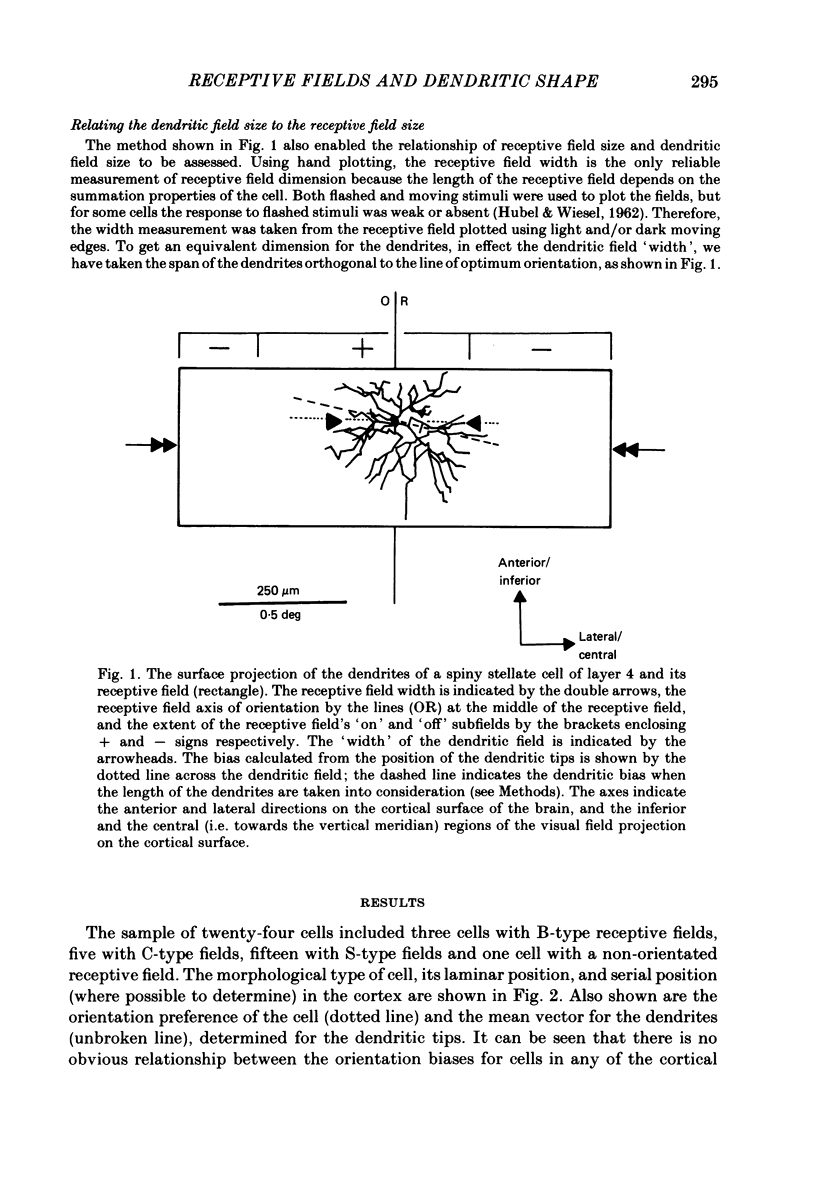
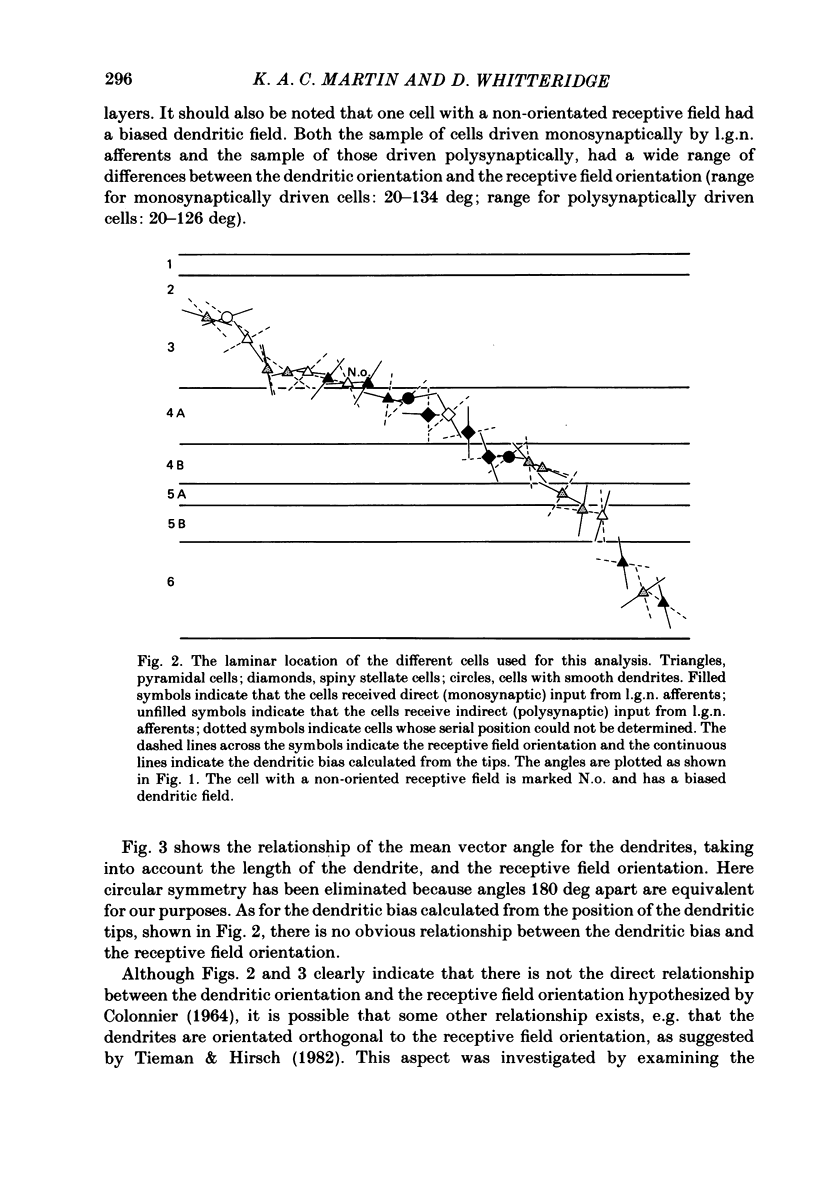
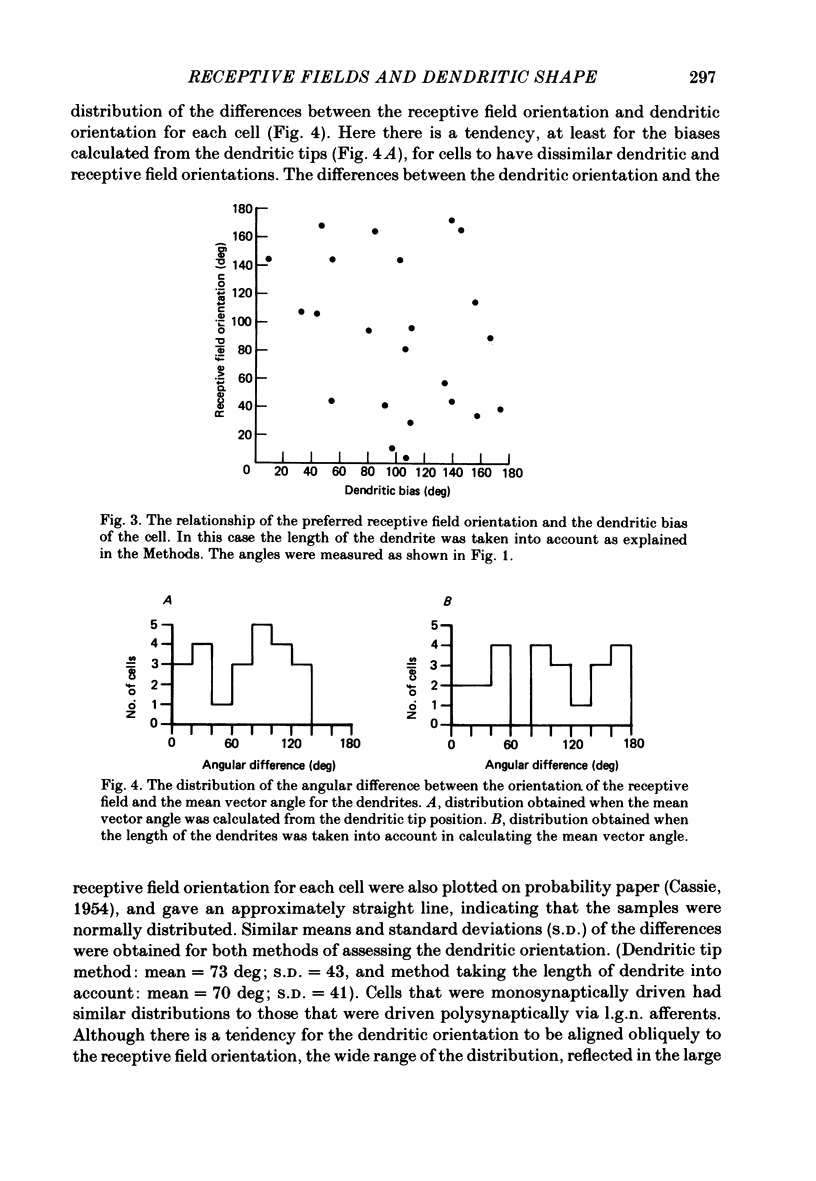
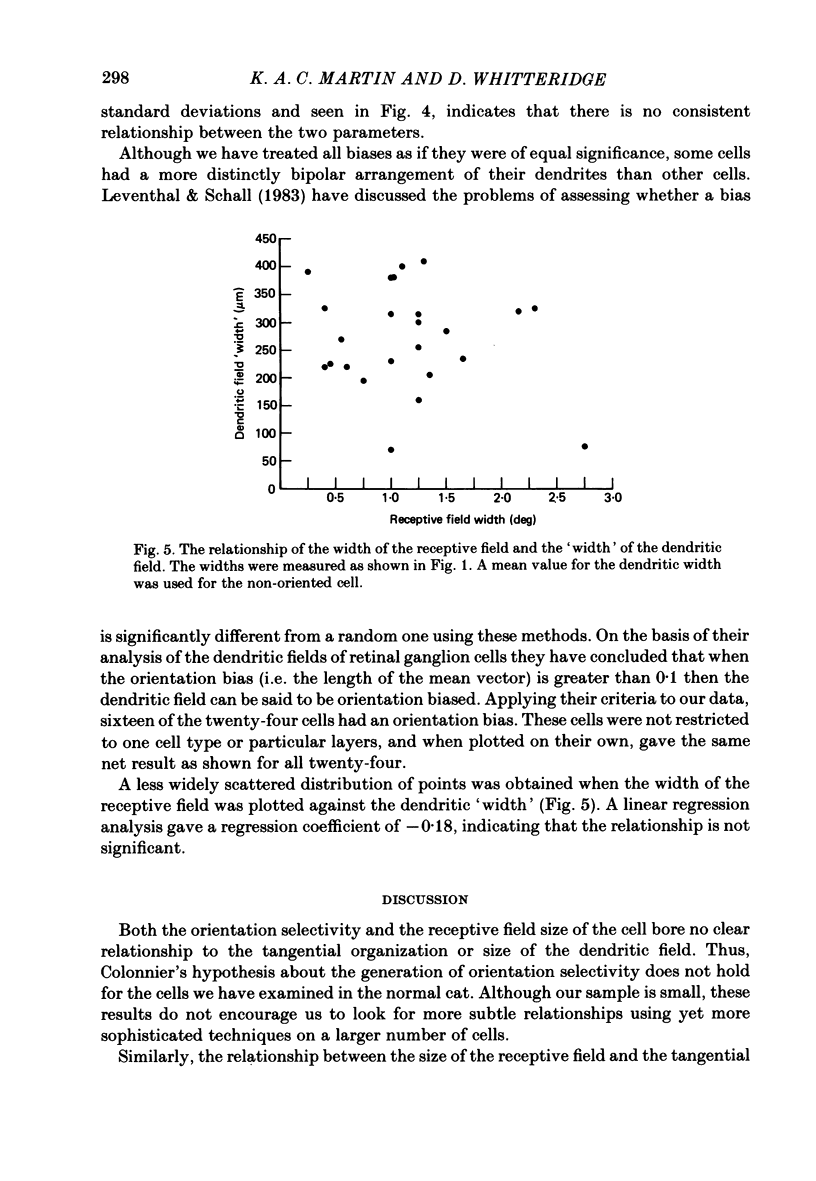
In this study, we examined the hypothesis that some features of the receptive fields of cortical neurones are determined by the extent to which their dendrites can sample from different parts of the visual field representation on the cortex. In particular, the orientation selectivity and size of the receptive fields of cortical neurones were examined for their relationship to the tangential organization of the dendrites of cortical neurones. Single neurones in the visual cortex of anaesthetized and paralysed cats were physiologically characterized and injected intracellularly with horseradish peroxidase (HRP). In some cases it was possible to identify whether the neurones received direct (monosynaptic) or indirect (polysynaptic) input from afferents of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The dendritic arborizations of the HRP-filled cells, sampled from all layers, were reconstructed in three dimensions with computer assistance, and rotated to give the tangential or surface view. The bias in the tangential arrangement of the dendrites was determined by calculating the mean vector angle for the distribution of the dendrites of each cell. This bias was related to the orientation selectivity of the neurones. There was no consistent relationship between orientation selectivity and the tangential bias of the dendritic tree. The width of the receptive fields was compared to the equivalent 'width' of the tangential extent of the dendrites. There was no significant relationship between the two widths. The tangential arrangement of the dendritic field does not appear to be important in determining the orientation selectivity or the size of the receptive fields of neurones in the cat visual cortex. The former feature of the receptive fields may be determined by inhibitory processes, while the extent and number of the afferents providing input to a single neurone may determine the latter property.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C. Heavy metal intensification of DAB-based HRP reaction product. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Jun;29(6):775–775. doi: 10.1177/29.6.7252134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilge M., Bingle A., Seneviratne K. N., Whitteridge D. A map of the visual cortex in the cat. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(2):116P–118P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore C., Cooper G. F. Development of the brain depends on the visual environment. Nature. 1970 Oct 31;228(5270):477–478. doi: 10.1038/228477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasdel G. G., Mitchell D. E., Muir D. W., Pettigrew J. D. A physiological and behavioural study in cats of the effect of early visual experience with contours of a single orientation. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;265(3):615–636. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullier J., Henry G. H. Ordinal position of neurons in cat striate cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Sep;42(5):1251–1263. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.5.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLONNIER M. THE TANGENTIAL ORGANIZATION OF THE VISUAL CORTEX. J Anat. 1964 Jul;98:327–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman P. D., Flood D. G., Whitehead M. C., Emerson R. C. Spatial sampling by dendritic trees in visual cortex. Brain Res. 1981 Jun 9;214(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90435-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson I. M., Whitteridge D. The nature of the boundary between cortical visual areas II and III in the cat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Dec 13;199(1136):445–462. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferster D., LeVay S. The axonal arborizations of lateral geniculate neurons in the striate cortex of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Dec 15;182(4 Pt 2):923–944. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert C. D. Laminar differences in receptive field properties of cells in cat primary visual cortex. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):391–421. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert C. D., Wiesel T. N. Clustered intrinsic connections in cat visual cortex. J Neurosci. 1983 May;3(5):1116–1133. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-05-01116.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert C. D., Wiesel T. N. Morphology and intracortical projections of functionally characterised neurones in the cat visual cortex. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):120–125. doi: 10.1038/280120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert C. D., Wiesel T. N. Morphology and intracortical projections of functionally characterised neurones in the cat visual cortex. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):120–125. doi: 10.1038/280120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. Receptive fields of single neurones in the cat's striate cortex. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:574–591. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex. J Physiol. 1962 Jan;160:106–154. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond P., Andrews D. P. Orientation tuning of cells in areas 17 and 18 of the cat's visual cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1978 Mar 15;31(3):341–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00237294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond P. Cat retinal ganglion cells: size and shape of receptive field centres. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(1):99–118. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanker J. S., Yates P. E., Metz C. B., Rustioni A. A new specific, sensitive and non-carcinogenic reagent for the demonstration of horseradish peroxidase. Histochem J. 1977 Nov;9(6):789–792. doi: 10.1007/BF01003075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry G. H., Bishop P. O., Dreher B. Orientation, axis and direction as stimulus parameters for striate cells. Vision Res. 1974 Sep;14(9):767–777. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(74)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry G. H., Bishop P. O., Tupper R. M., Dreher B. Orientation specificity and response variability of cells in the striate cortex. Vision Res. 1973 Sep;13(9):1771–1779. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(73)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry G. H., Dreher B., Bishop P. O. Orientation specificity of cells in cat striate cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1974 Nov;37(6):1394–1409. doi: 10.1152/jn.1974.37.6.1394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch H. V., Spinelli D. N. Visual experience modifies distribution of horizontally and vertically oriented receptive fields in cats. Science. 1970 May 15;168(3933):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3933.869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leventhal A. G., Schall J. D. Structural basis of orientation sensitivity of cat retinal ganglion cells. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Nov 10;220(4):465–475. doi: 10.1002/cne.902200408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levick W. R., Thibos L. N. Analysis of orientation bias in cat retina. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:243–261. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. A., Somogyi P., Whitteridge D. Physiological and morphological properties of identified basket cells in the cat's visual cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1983;50(2-3):193–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00239183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. A., Whitteridge D. Form, function and intracortical projections of spiny neurones in the striate visual cortex of the cat. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:463–504. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orban G. A., Kennedy H. The influence of eccentricity on receptive field types and orientation selectivity in areas 17 and 18 of the cat. Brain Res. 1981 Mar 9;208(1):203–208. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90633-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peichl L., Wässle H. The structural correlate of the receptive field centre of alpha ganglion cells in the cat retina. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:309–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry V. H., Linden R. Evidence for dendritic competition in the developing retina. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):683–685. doi: 10.1038/297683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherk H., Stryker M. P. Quantitative study of cortical orientation selectivity in visually inexperienced kitten. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Jan;39(1):63–70. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillito A. M. Inhibitory mechanisms influencing complex cell orientation selectivity and their modification at high resting discharge levels. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:33–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillito A. M., Kemp J. A., Milson J. A., Berardi N. A re-evaluation of the mechanisms underlying simple cell orientation selectivity. Brain Res. 1980 Aug 4;194(2):517–520. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91234-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillito A. M. The contribution of inhibitory mechanisms to the receptive field properties of neurones in the striate cortex of the cat. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;250(2):305–329. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinelli D. N., Barrett T. W. Visual receptive field organization of single units in the cat's visual cortex. Exp Neurol. 1969 May;24(1):76–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tieman S. B., Hirsch H. V. Exposure to lines of only one orientation modifies dendritic morphology of cells in the visual cortex of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Nov 10;211(4):353–362. doi: 10.1002/cne.902110403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsumoto T., Eckart W., Creutzfeldt O. D. Modification of orientation sensitivity of cat visual cortex neurons by removal of GABA-mediated inhibition. Exp Brain Res. 1979 Jan 15;34(2):351–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00235678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. R., Sherman S. M. Receptive-field characteristics of neurons in cat striate cortex: Changes with visual field eccentricity. J Neurophysiol. 1976 May;39(3):512–533. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.3.512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


