Abstract
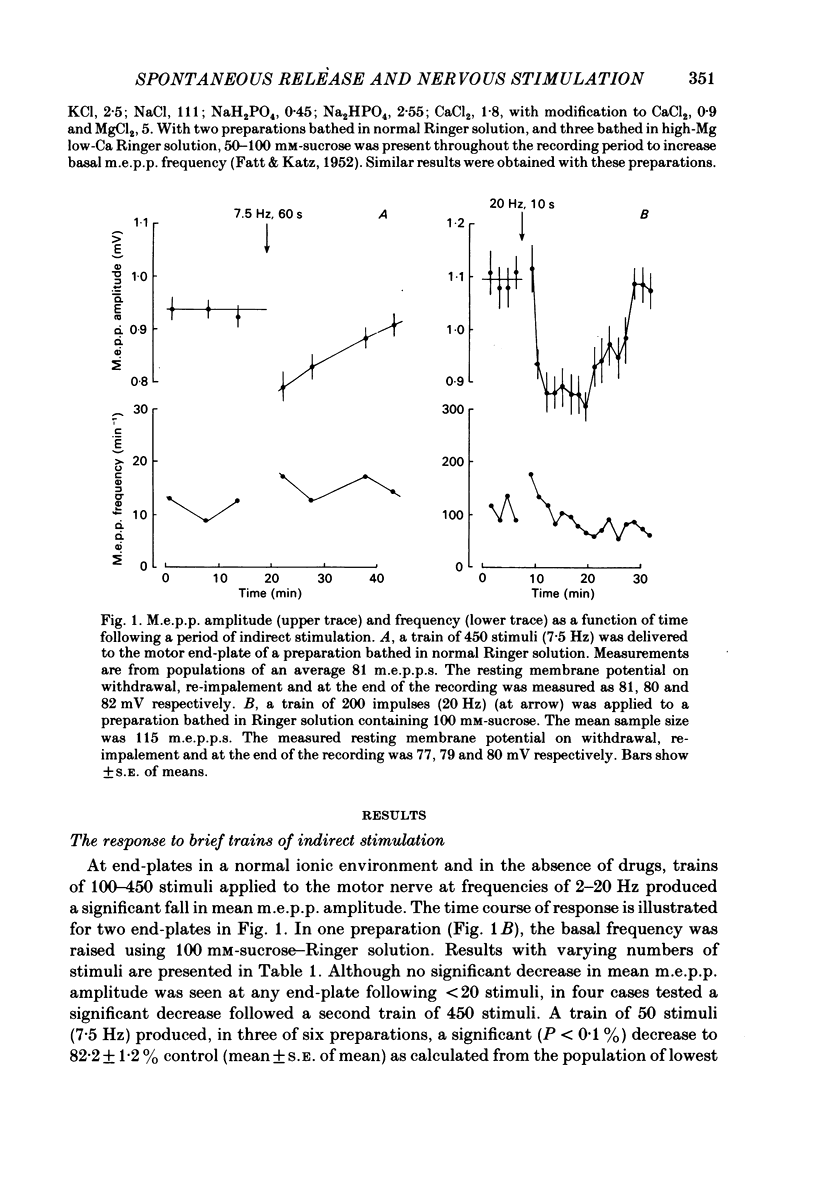
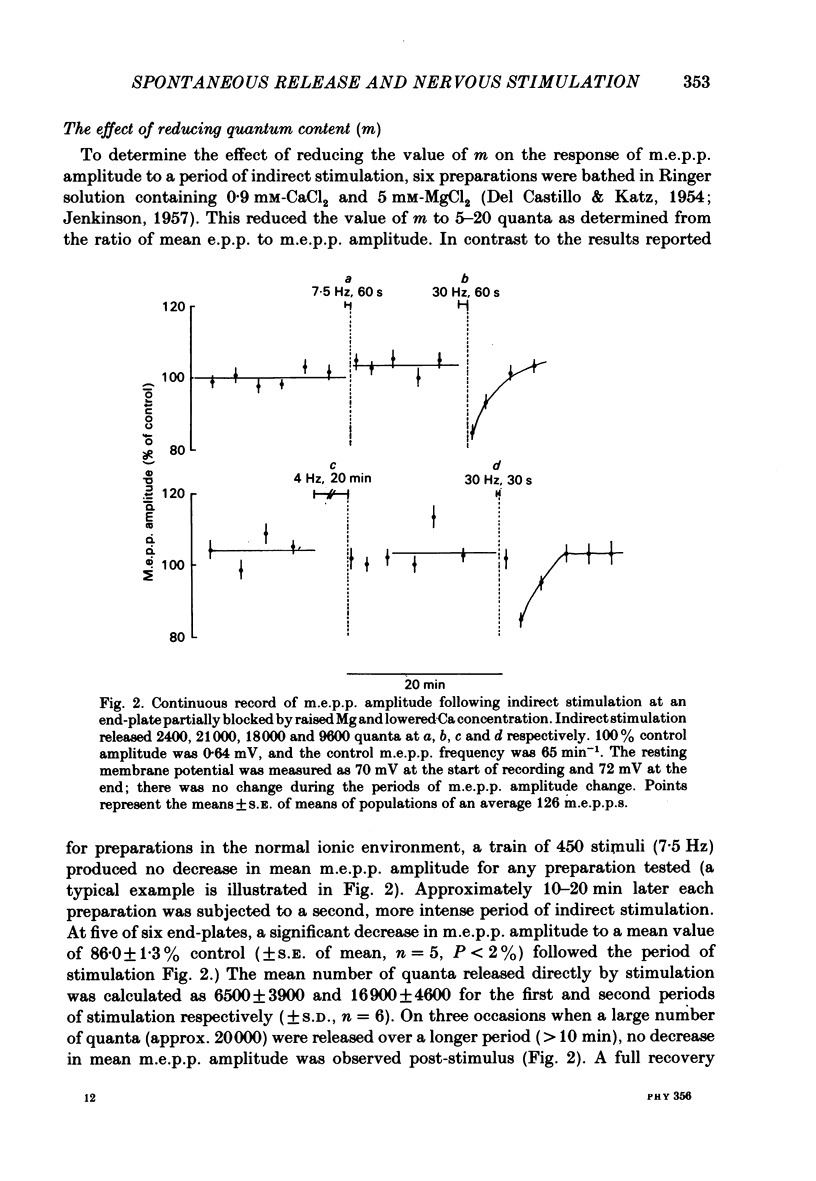
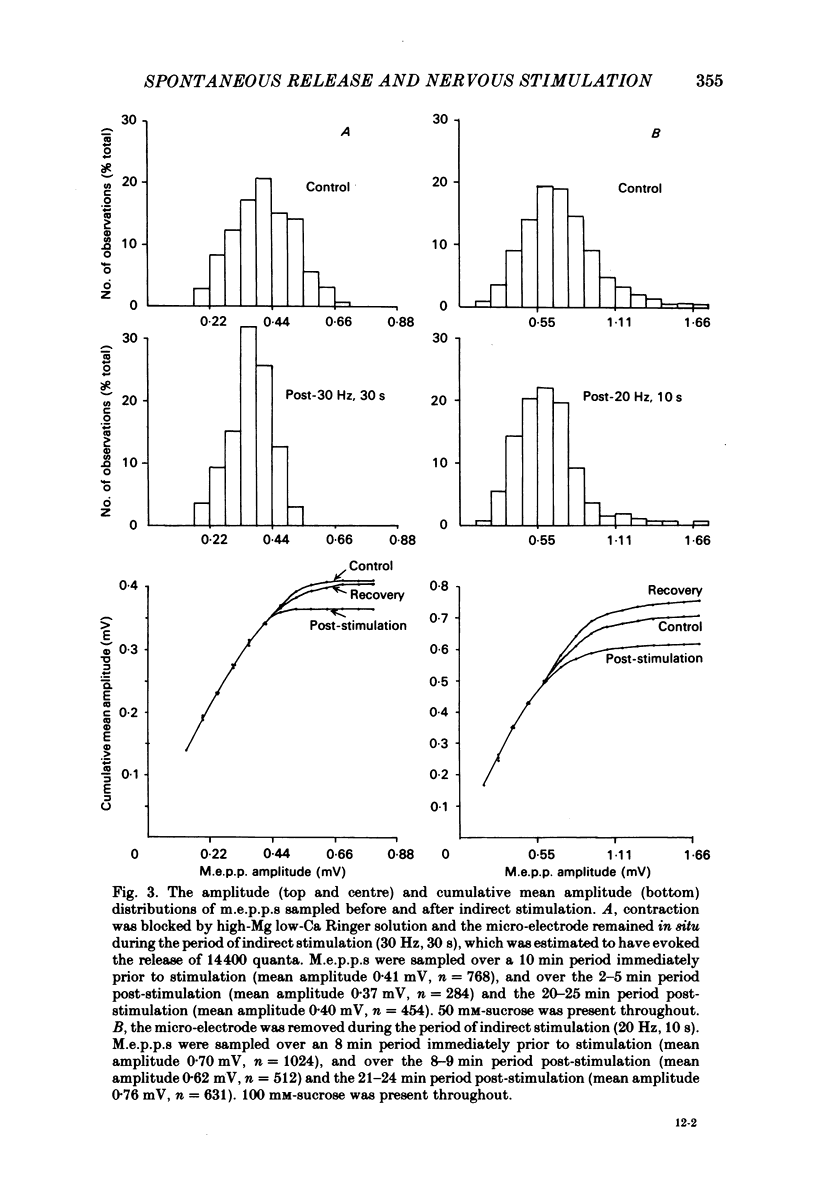
The amplitude of miniature end-plate potentials (m.e.p.p.s), recorded at the frog neuromuscular junction in a normal ionic environment and in absence of drugs, was examined following 10-450 nerve impulses using conventional electrophysiological techniques and on-line computational analysis. In both contracting preparations and non-contracting preparations pre-treated with glycerol, 100 or more nerve impulses resulted in a maximal fall in mean amplitude of about 20% with recovery apparent over the next 10-20 min. In an altered ionic environment with a lowered Ca and raised Mg concentration, 450 nerve impulses did not produce a decrease in mean amplitude but a similar reduction was seen following a larger number of impulses. The reduction in amplitude was estimated to follow the release of the order of 5000-10000 quanta at end-plates in a normal ionic environment and on average 17000 quanta in the presence of a lowered Ca and raised Mg concentration. Changes in the mean size of the spontaneous quantal response is considered to be a presynaptic event and to reflect the loss and slow recovery of larger packets of transmitter from a vesicular store that is readily released by nerve impulses.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Couteaux R., Pécot-Dechavassine M. Les zones spécialisées des membranes présynaptiques. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1974 Jan 7;278(2):291–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELMQVIST D., QUASTEL D. M. PRESYNAPTIC ACTION OF HEMICHOLINIUM AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. J Physiol. 1965 Apr;177:463–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S., Dennis M. J., Jan Y., Jan L., Evans L. Synaptic vesicle exocytosis captured by quick freezing and correlated with quantal transmitter release. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):275–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The nature of the antagonism between calcium and magnesium ions at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1957 Oct 30;138(3):434–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. F., Kwanbunbumpen S. Some effects of nerve stimulation andhemicholinium on quantal transmitter release at the mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):51–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. On the factors which determine the amplitude of the miniature end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):267–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly S. S., Robbins N. Bimodal miniature and evoked end-plate potentials in adult mouse neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1984 Jan;346:353–363. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel M. E., Gross C. E. Multimodal distribution of frog miniature endplate potentials in adult denervated and tadpole leg muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jul;64(1):85–103. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel M. E., Llados F., Matteson D. R. Histograms of the unitary evoked potential of the mouse diaphragm show multiple peaks. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:211–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Turkanis S. A., Weakly J. N. Correlation between nerve terminal size and transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):545–556. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. A study of desensitization of acetylcholine receptors using nerve-released transmitter in the frog. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:225–250. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan E. M. Changes in statistical release parameters during prolonged stimulation of preganglionic nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(2):477–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan E. M., Martin A. R. Non-linear summation of end-plate potentials in the frog and mouse. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:307–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M. D. Binomial analysis of quantal transmitter release at glycerol treated frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;250(1):121–142. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernig A. Estimates of statistical release parameters from crayfish and frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(1):207–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernig A. Localization of active sites in the neuromuscular junction of the frog. Brain Res. 1976 Dec 10;118(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90841-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann H. Vesicle recycling and transmitter release. Neuroscience. 1979;4(12):1773–1804. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann H., Whittaker V. P. Morphological and biochemical heterogeneity of cholinergic synaptic vesicles. Nature. 1977 Jun 16;267(5612):633–635. doi: 10.1038/267633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


