Abstract
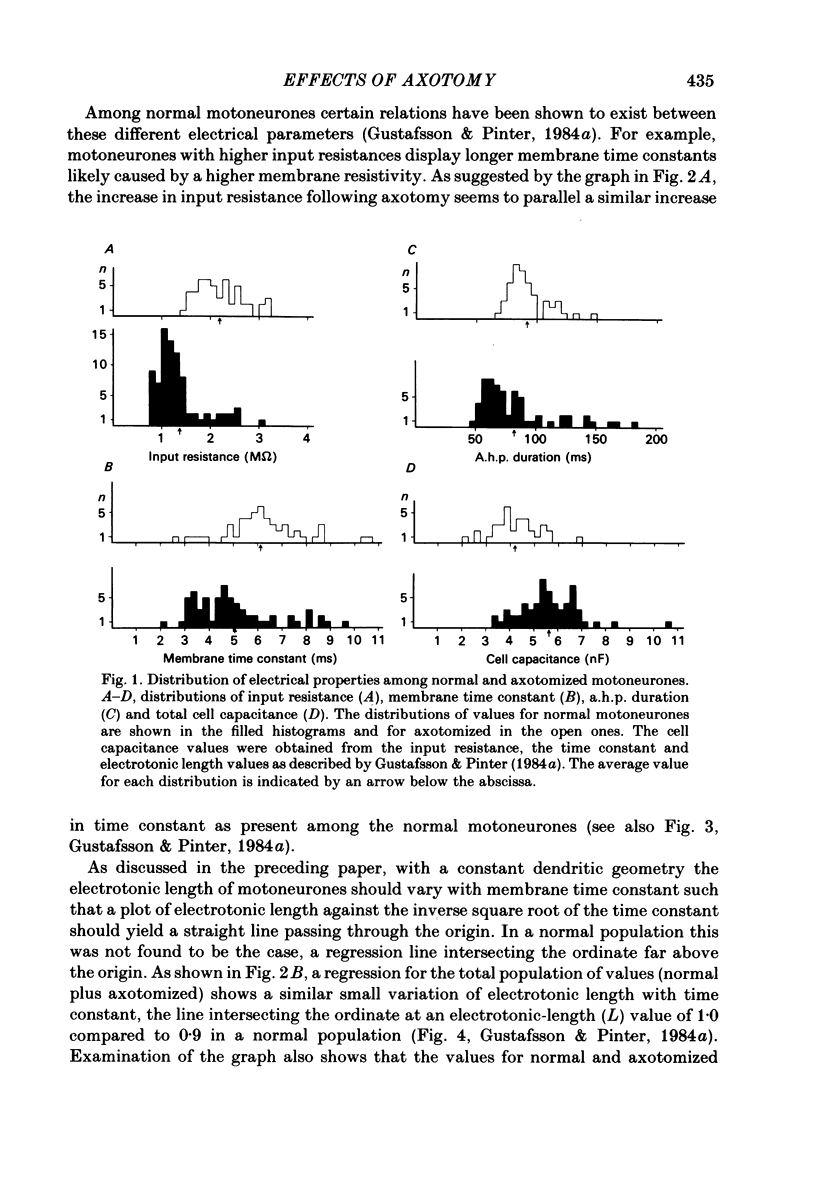
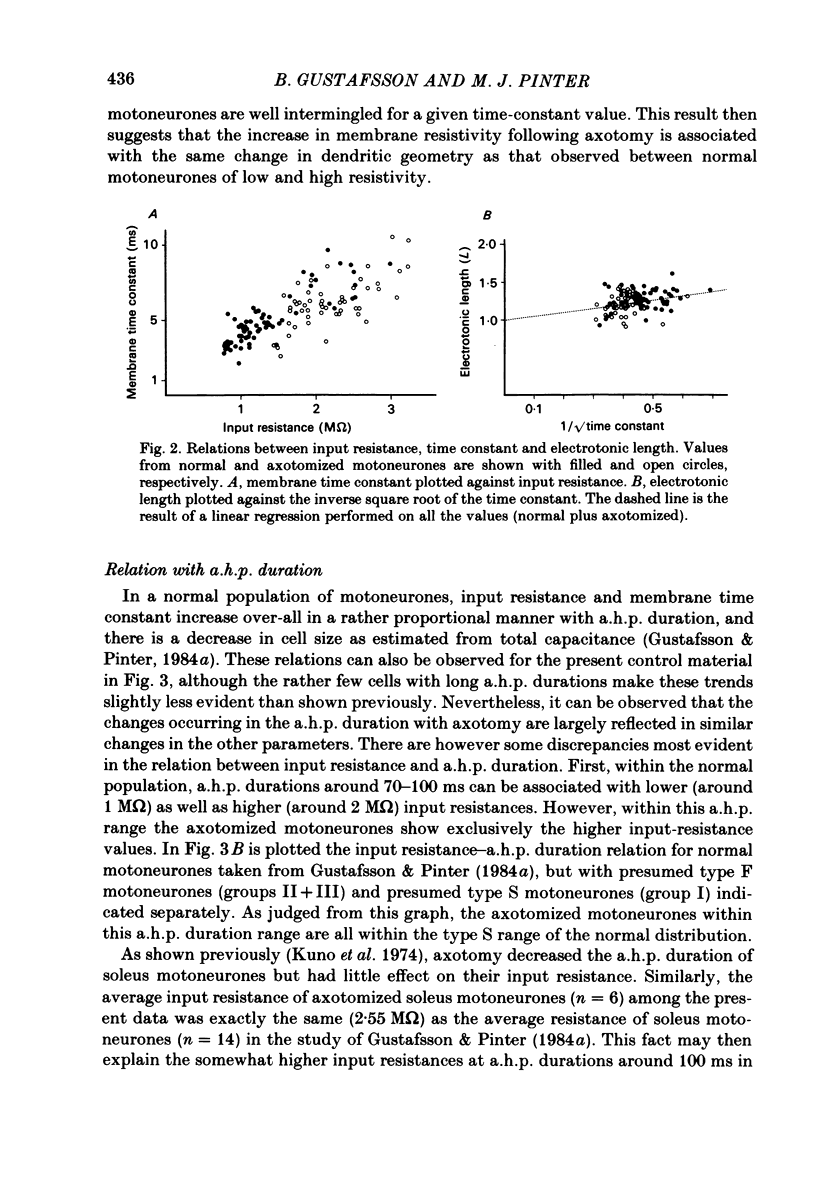
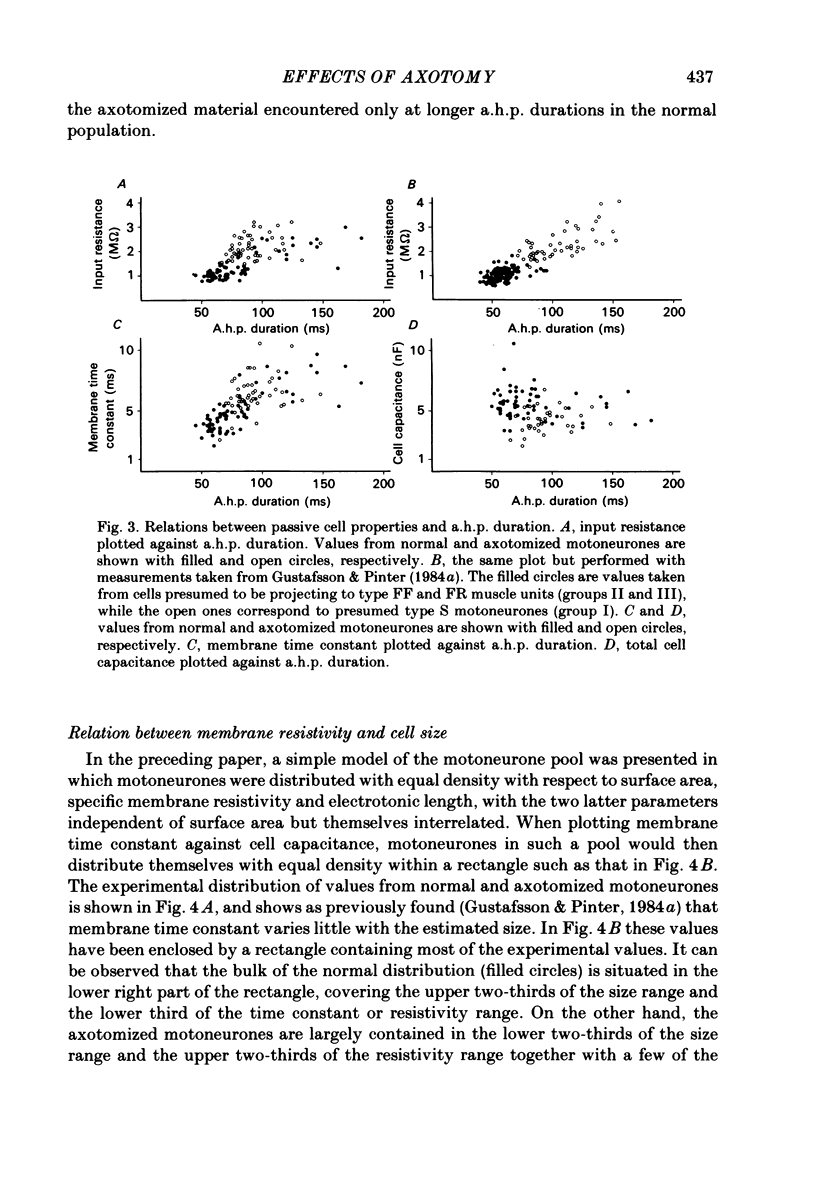
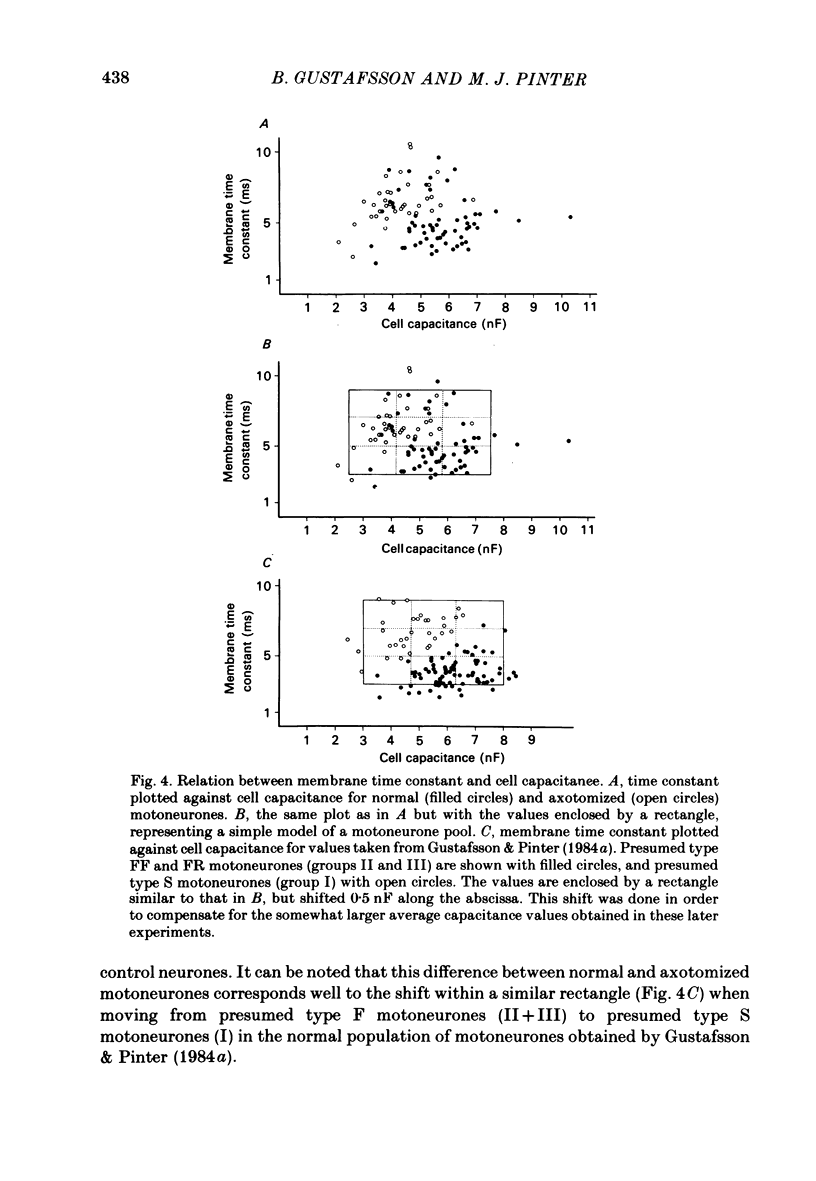
Previously obtained experimental results concerning the effect of axotomy on motoneurone passive electrical properties have been re-analysed. As shown earlier, axotomy causes an average increase of motoneurone input resistance, membrane time constant and after-hyperpolarization duration. The present analysis suggests that the increased input resistance is related to a higher specific membrane resistivity, a decreased cell size and an altered dendritic geometry. The results also suggest that the change takes place only in neurones projecting to fast-twitch muscle units and produces in them passive electrical properties normally exhibited only by motoneurones projecting to slow-twitch units. Based on the notion that axotomy causes a 'dedifferentiation' of motoneurone properties, the present results might be taken to indicate that undifferentiated motoneurones are slow in character. A possible scheme in which a post-natal differentiation of motoneurone properties may lead to muscle differentiation is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke R. E., Dum R. P., Fleshman J. W., Glenn L. L., Lev-Tov A., O'Donovan M. J., Pinter M. J. A HRP study of the relation between cell size and motor unit type in cat ankle extensor motoneurons. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Jul 20;209(1):17–28. doi: 10.1002/cne.902090103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. Motor unit types of cat triceps surae muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(1):141–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Nelson P. G. Accommodation to current ramps in motoneurons of fast and slow twitch motor units. Int J Neurosci. 1971 Jun;1(6):347–356. doi: 10.3109/00207457109146983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. The action potentials of the alpha motoneurones supplying fast and slow muscles. J Physiol. 1958 Jul 14;142(2):275–291. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleshman J. W., Munson J. B., Sypert G. W., Friedman W. A. Rheobase, input resistance, and motor-unit type in medial gastrocnemius motoneurons in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Dec;46(6):1326–1338. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.46.6.1326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallego R., Huizar P., Kudo N., Kuno M. Disparity of motoneurone and muscle differentiation following spinal transection in the kitten. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:253–265. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B. Changes in motoneurone electrical properties following axotomy. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:197–215. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Katz R., Malmsten J. Effects of chronic partial deafferentiation on the electrical properties of lumbar alpha-motoneurones in the cat. Brain Res. 1982 Aug 19;246(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90138-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Pinter M. J. Relations among passive electrical properties of lumbar alpha-motoneurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:401–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Llinás R. Control of rhythmic firing in normal and axotomized cat spinal motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1977 May;40(3):480–488. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.3.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizar P., Kuno M., Miyata Y. Differentiation of motoneurones and skeletal muscles in kittens. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(2):465–479. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Miller S., Porter R., Redman S. J. The time course of minimal excitory post-synaptic potentials evoked in spinal motoneurones by group Ia afferent fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):353–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNO M. Excitability following antidromic activation in spinal motoneurones supplying red muscles. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:374–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellerth J. O., Mellström A., Skoglund S. Postnatal excitability changes of kitten motoneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Sep;83(1):31–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb05048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D., Monster A. W. Threshold current for repetitive impulse firing in motoneurones innervating muscle fibres of different fatigue sensitivity in the cat. Brain Res. 1981 Dec 14;229(1):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90756-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D., Zwaagstra B. Input conductance axonal conduction velocity and cell size among hindlimb motoneurones of the cat. Brain Res. 1981 Jan 12;204(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90591-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Llinás R. Enhancement of synaptic transmission by dendritic potentials in chromatolysed motoneurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;210(4):807–821. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Miyata Y., Muñoz-Martinez E. J. Differential reaction of fast and slow alpha-motoneurones to axotomy. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;240(3):725–739. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner B. E., Watson W. E. Retraction and expansion of the dendritic tree of motor neurones of adult rats induced in vivo. Nature. 1971 Sep 24;233(5317):273–275. doi: 10.1038/233273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfhake B., Kellerth J. O. Does alpha-motoneurone size correlate with motor unit type in cat triceps surae? Brain Res. 1982 Nov 18;251(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90738-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


