Abstract
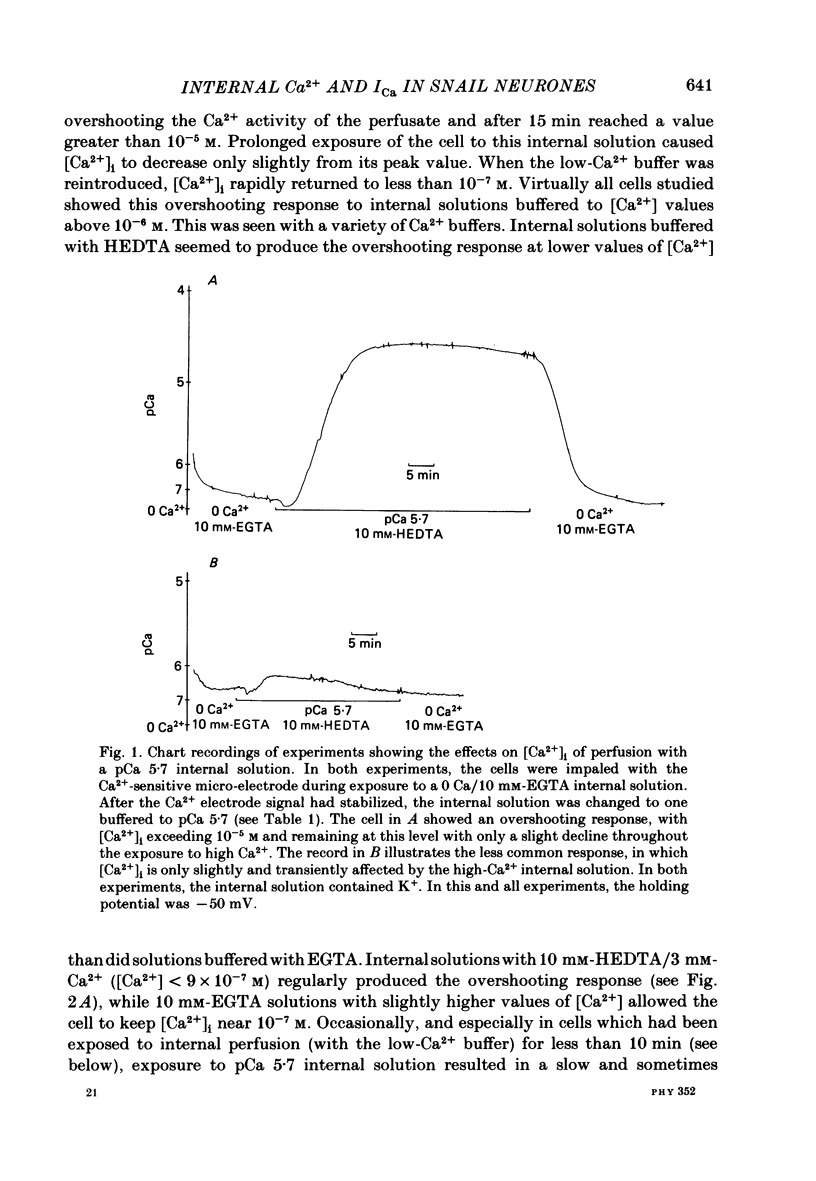
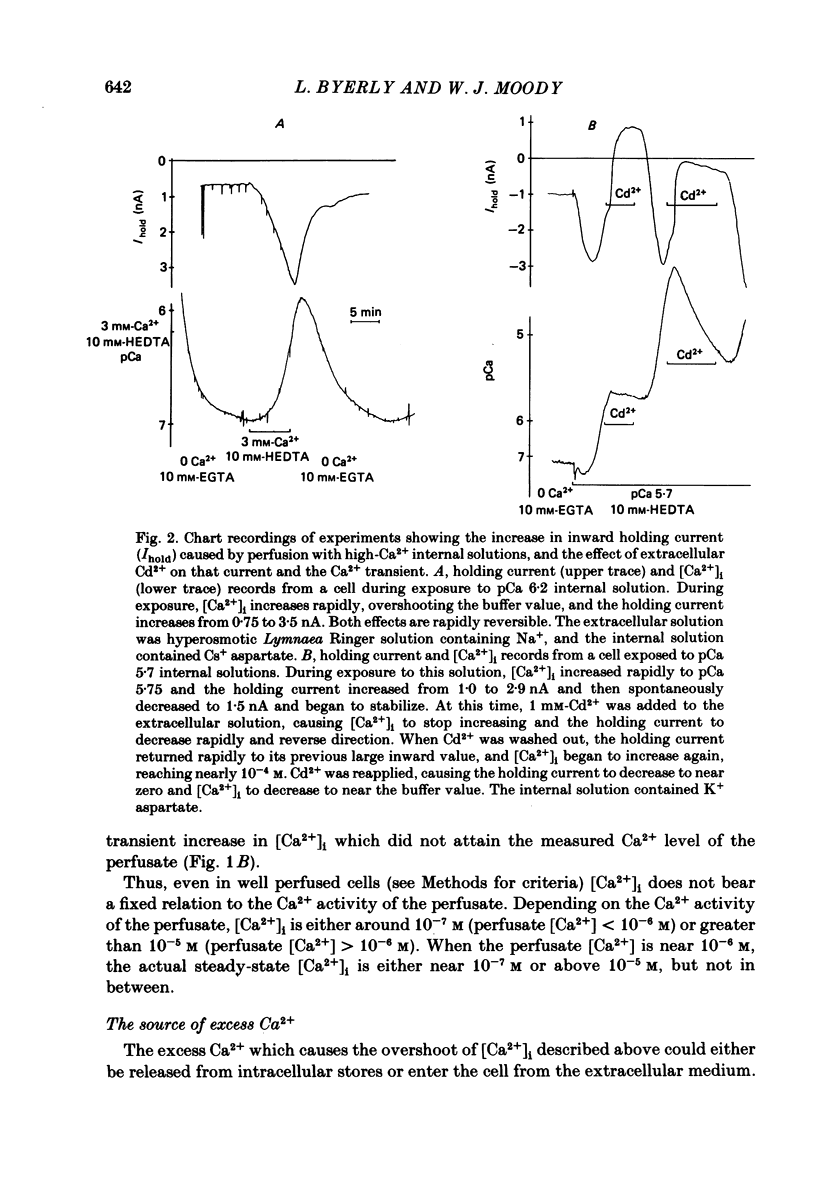
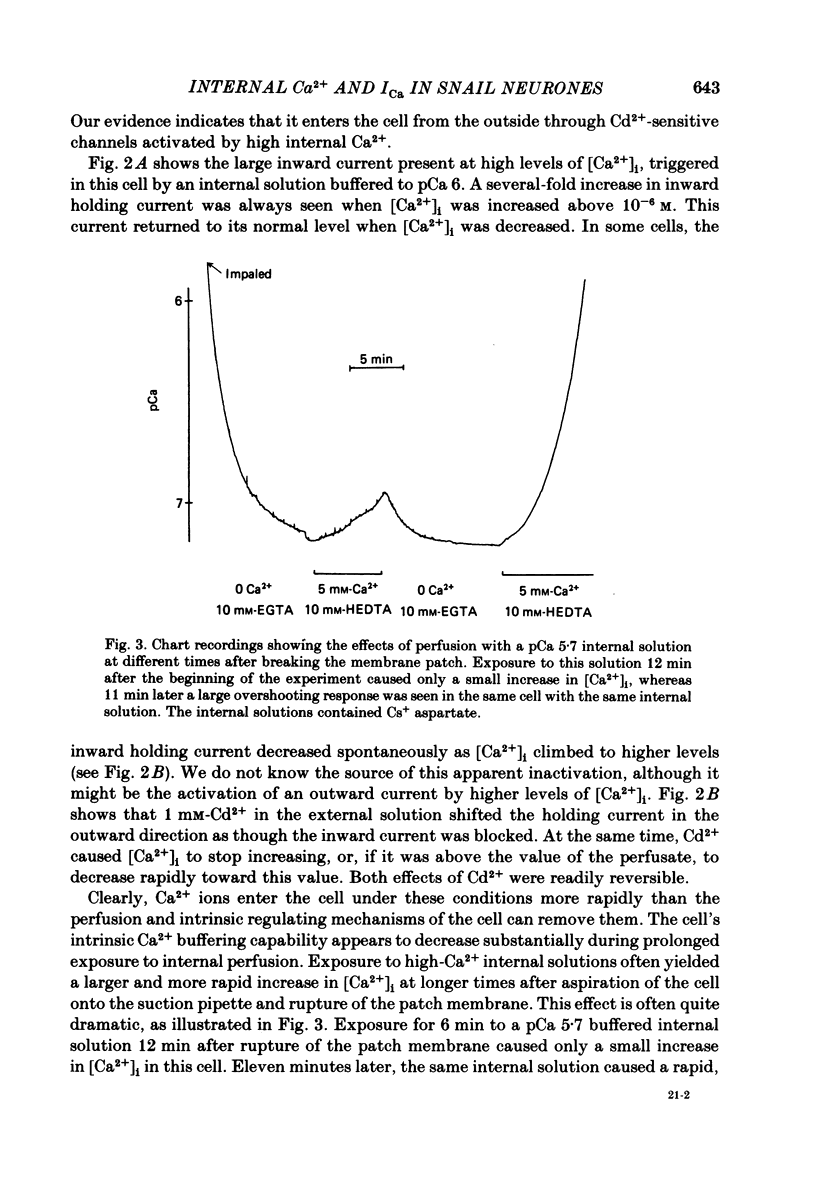
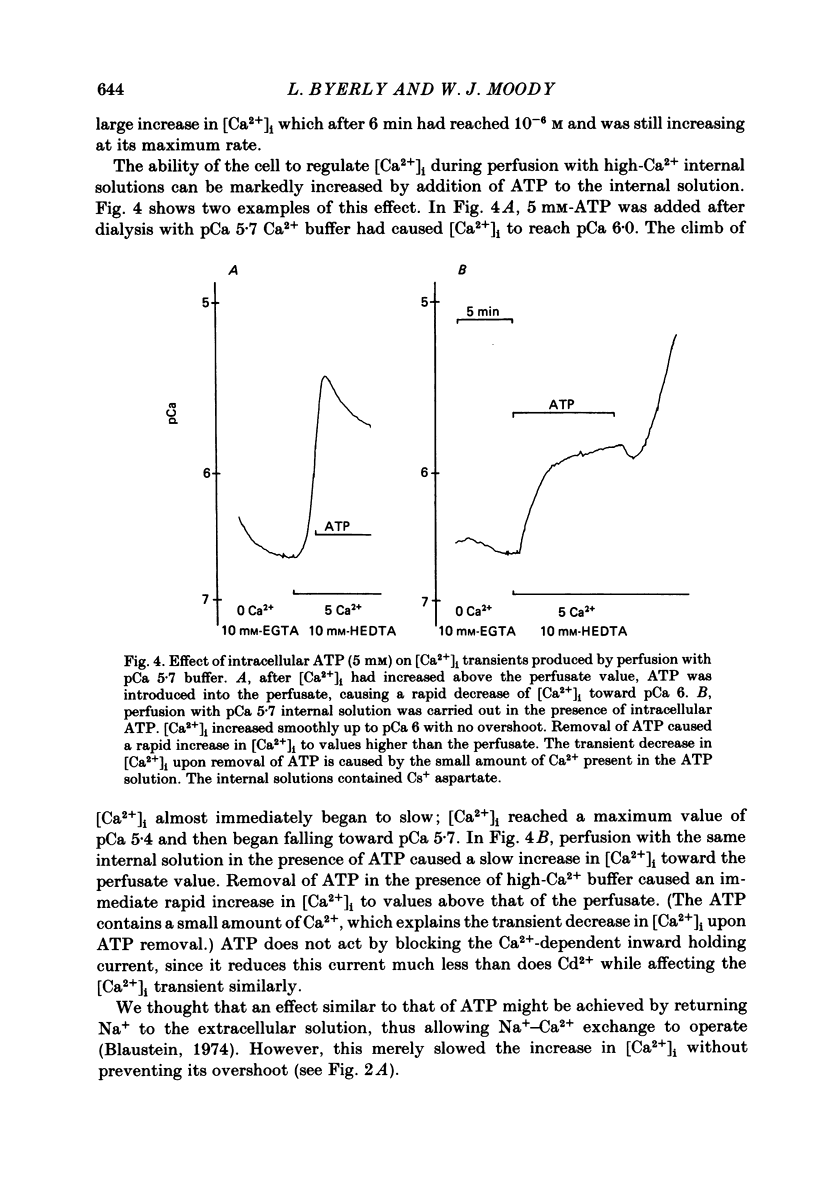
Neuronal somata of Lymnaea stagnalis were internally perfused and voltage clamped using the suction pipette method. The cells were exposed to internal solutions buffered to various concentrations of Ca2+ while the cytoplasmic Ca2+ activity [( Ca2+]i) was monitored with a Ca2+ -sensitive micro-electrode. [Ca2+]i was usually about 10(-7) M when the cell was perfused with a solution buffered to any level of Ca2+ from 9 X 10(-7) to below 10(-8) M. With internal solutions buffered to 10(-6) M-Ca2+ or greater, [Ca2+]i increased rapidly and overshot the perfusate Ca2+ activity by up to two orders of magnitude. It was thus virtually impossible to hold [Ca2+]i steady at any levels other than about 10(-7) M or 10(-4) M using internal perfusion of simple ionic internal solutions. The excess Ca2+ which caused the overshoot of [Ca2+]i entered the cell from the external solution through Cd2+ -sensitive channels. Cd2+ in the external solution prevented or reversed the overshoot of [Ca2+]i and brought [Ca2+]i to near the perfusate level. ATP added to the internal solution also prevented [Ca2+]i from overshooting the perfusate level during perfusion with high-Ca2+ buffers. By monitoring [Ca2+]i with a Ca2+ -sensitive micro-electrode, we were able to estimate the relationship between [Ca2+]i and the Ca2+ current (ICa) measured under voltage clamp. ICa was completely blocked as [Ca2+]i was raised to 10(-6) M. We believe that the discrepancy between our data and other estimates of the ICa vs. [Ca2+]i relationship using internal perfusion of molluscan nerve cells results from the incorrect assumption that [Ca2+]i is controlled adequately during internal perfusion.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akaike N., Lee K. S., Brown A. M. The calcium current of Helix neuron. J Gen Physiol. 1978 May;71(5):509–531. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.5.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Leefmans F. J., Rink T. J., Tsien R. Y. Free calcium ions in neurones of Helix aspersa measured with ion-selective micro-electrodes. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:531–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammann D., Lanter F., Steiner R. A., Schulthess P., Shijo Y., Simon W. Neutral carrier based hydrogen ion selective microelectrode for extra- and intracellular studies. Anal Chem. 1981 Dec;53(14):2267–2269. doi: 10.1021/ac00237a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Stanfield P. R. Calcium dependence of the inactivation of calcium currents in skeletal muscle fibers of an insect. Science. 1981 Jul 10;213(4504):224–226. doi: 10.1126/science.213.4504.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L., DiPolo R., Osses L., Barnola F., Campos M. A (Ca2+, Mg2+)-ATPase activity in plasma membrane fragments isolated from squid nerves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 9;644(1):147–152. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. The interrelationship between sodium and calcium fluxes across cell membranes. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1974;70:33–82. doi: 10.1007/BFb0034293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P., Eckert R. Calcium entry leads to inactivation of calcium channel in Paramecium. Science. 1978 Dec 15;202(4373):1203–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.103199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Hagiwara S. Calcium currents in internally perfused nerve cell bodies of Limnea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:503–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Meech R., Moody W., Jr Rapidly activating hydrogen ion currents in perfused neurones of the snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:199–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christoffersen G. R., Simonsen L. Ca++ sensitive microelectrode: intracellular steady state measurement in nerve cell. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Dec;101(4):492–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb06034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Neher E., Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):752–754. doi: 10.1038/294752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doroshenko P. A., Kostyuk P. G., Martynyuk A. E. Intracellular metabolism of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate and calcium inward current in perfused neurones of Helix pomatia. Neuroscience. 1982;7(9):2125–2134. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doroshenko P. A., Tsyndrenko A. Ia. Deistvie vnutrikletochnogo kal'tsiia na kal'tsievyi vkhodiashchii tok. Neirofiziologiia. 1978;10(2):203–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Nakajima S. Effects of the intracellular Ca ion concentration upon the excitability of the muscle fiber membrane of a barnacle. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):807–818. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harafuji H., Ogawa Y. Re-examination of the apparent binding constant of ethylene glycol bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid with calcium around neutral pH. J Biochem. 1980 May;87(5):1305–1312. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmeier G., Lux H. D. The time courses of intracellular free calcium and related electrical effects after injection of CaCl2 into neurons of the snail, Helix pomatia. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Sep;391(3):242–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00596178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A. Effects of calcium and calcium-chelating agents on the inward and outward current in the membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):569–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Akaike N., Brown A. M. Properties of internally perfused, voltage-clamped, isolated nerve cell bodies. J Gen Physiol. 1978 May;71(5):489–507. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.5.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marban E., Rink T. J., Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Free calcium in heart muscle at rest and during contraction measured with Ca2+ -sensitive microelectrodes. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):845–850. doi: 10.1038/286845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D. Inactivation of Ca conductance dependent on entry of Ca ions in molluscan neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1497–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbach J. A. Changes in intracellular pH affect calcium currents in Paramecium caudatum. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Sep 22;216(1203):209–224. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Single Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channels in neuroblastoma. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):357–359. doi: 10.1038/296357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


