Abstract
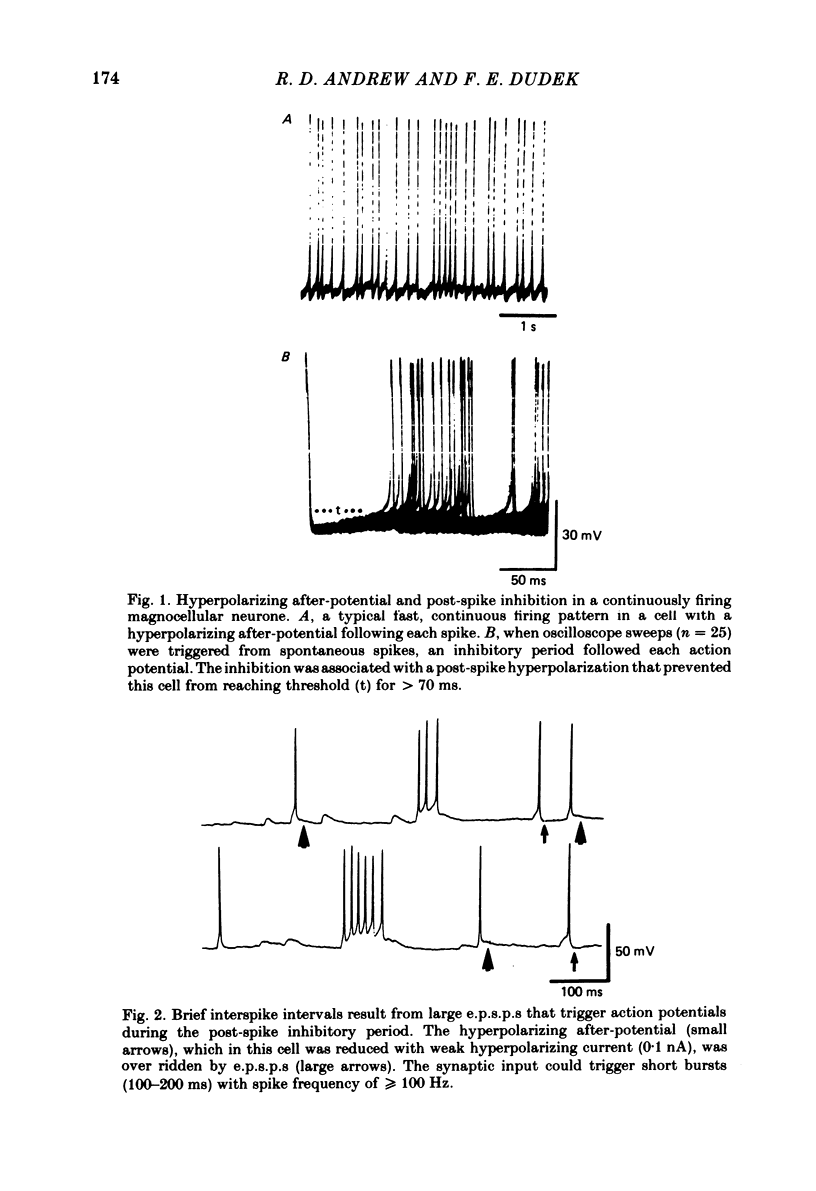
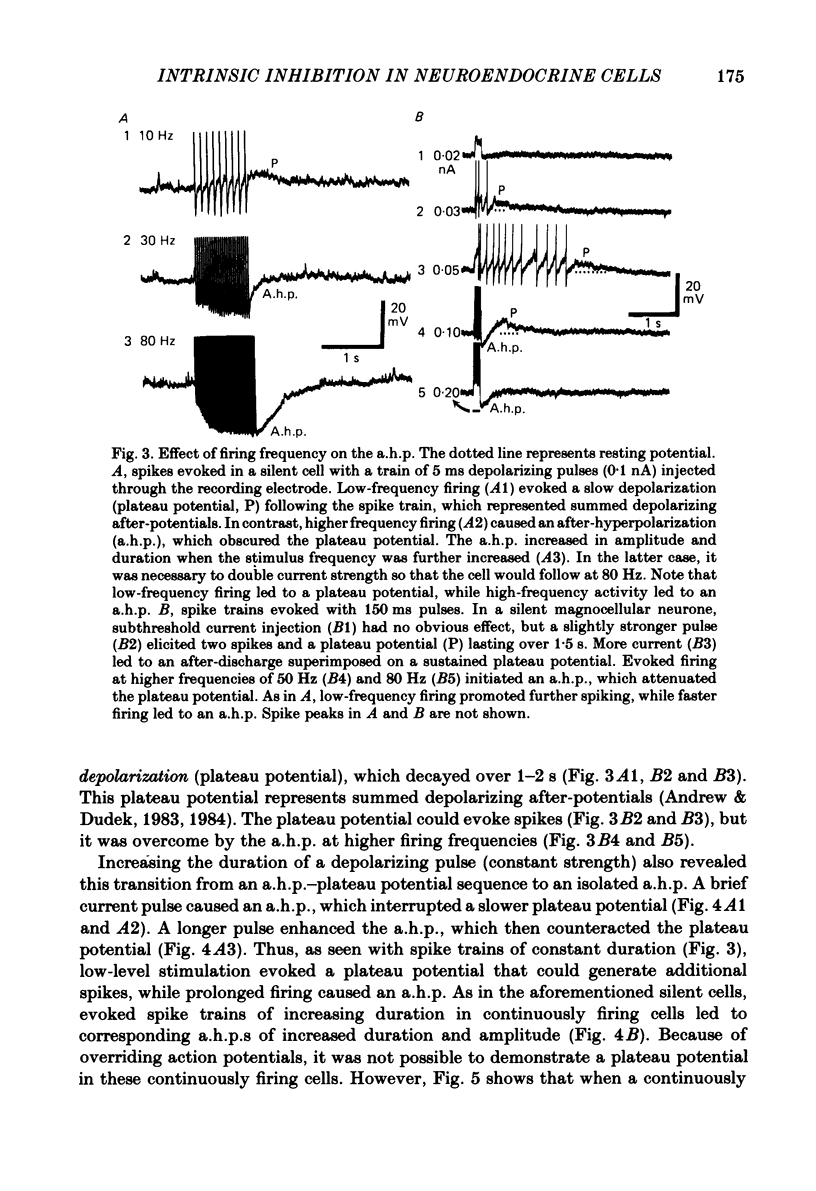
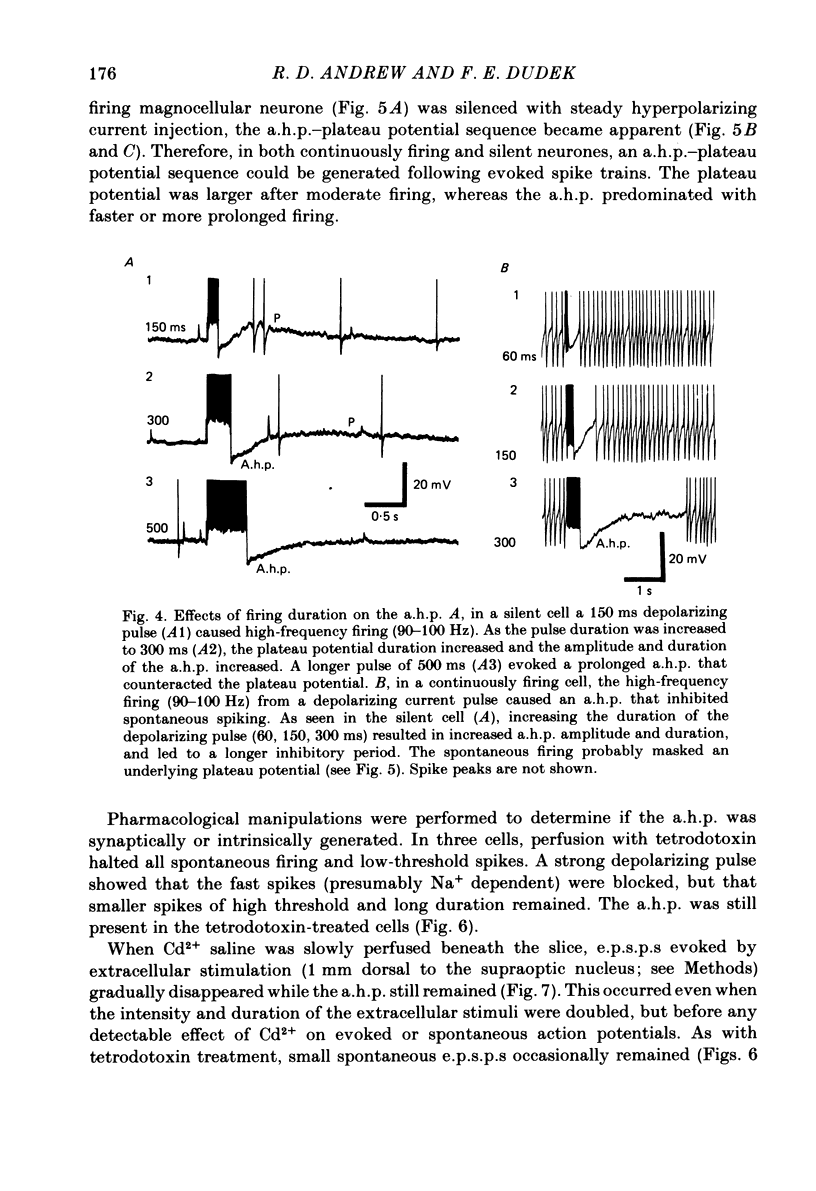
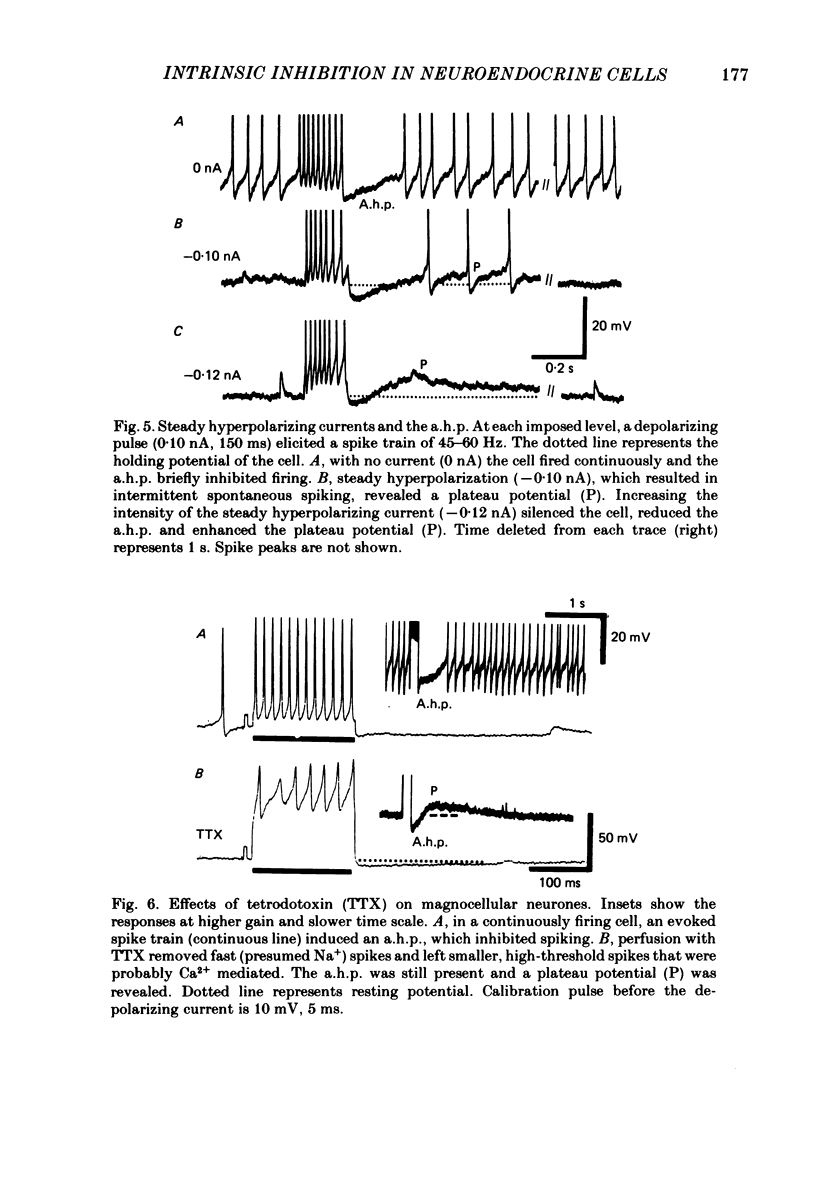
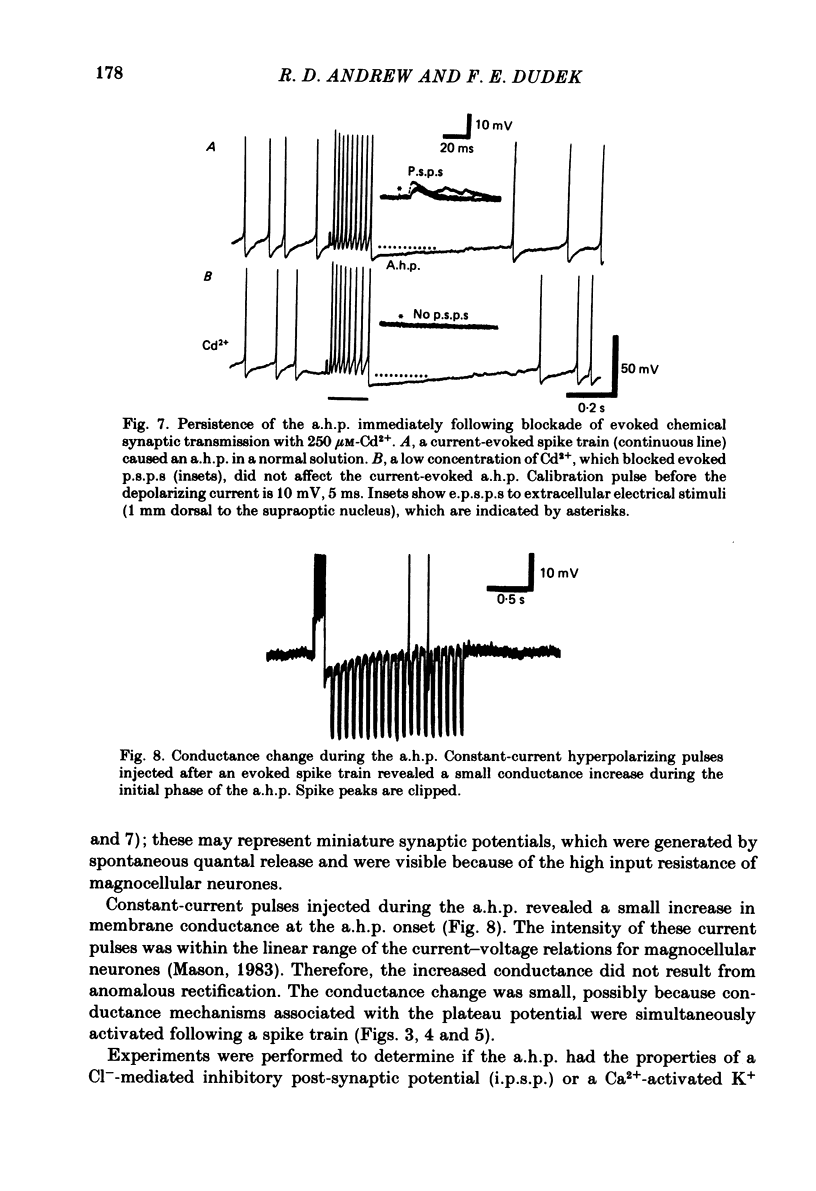
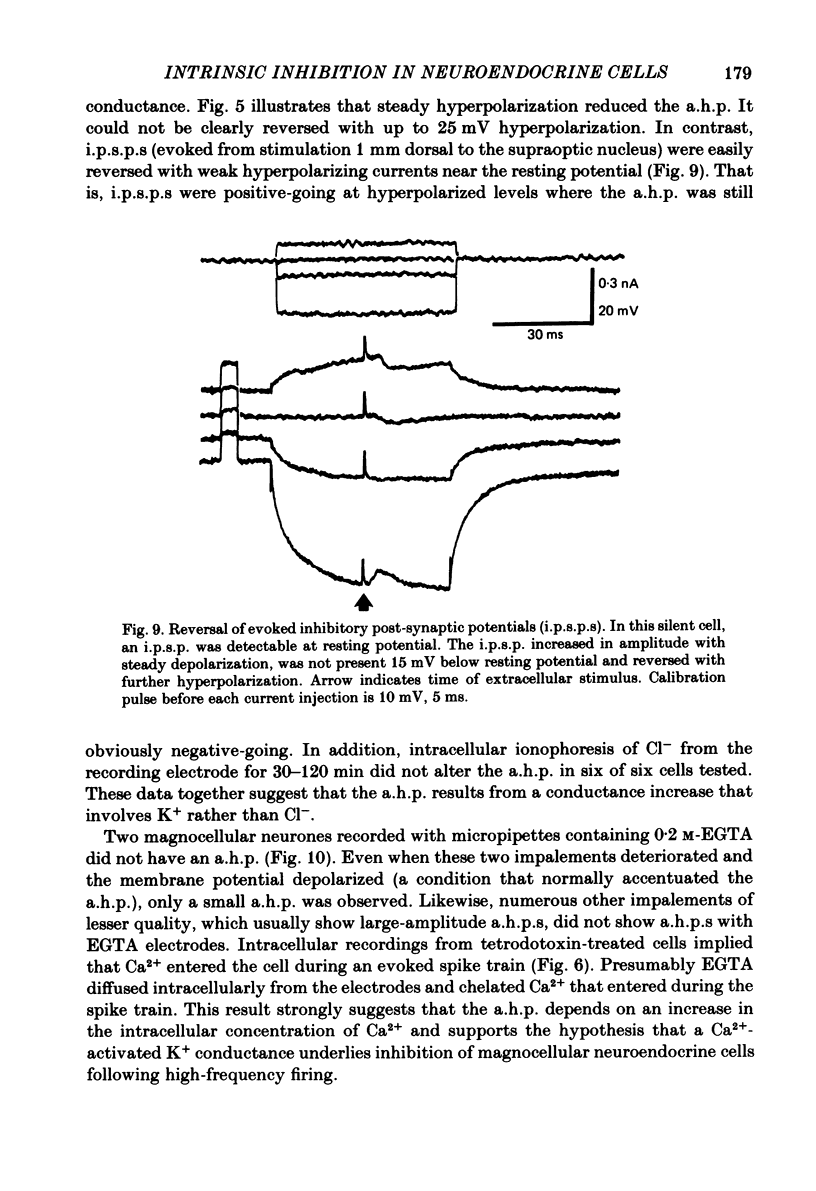
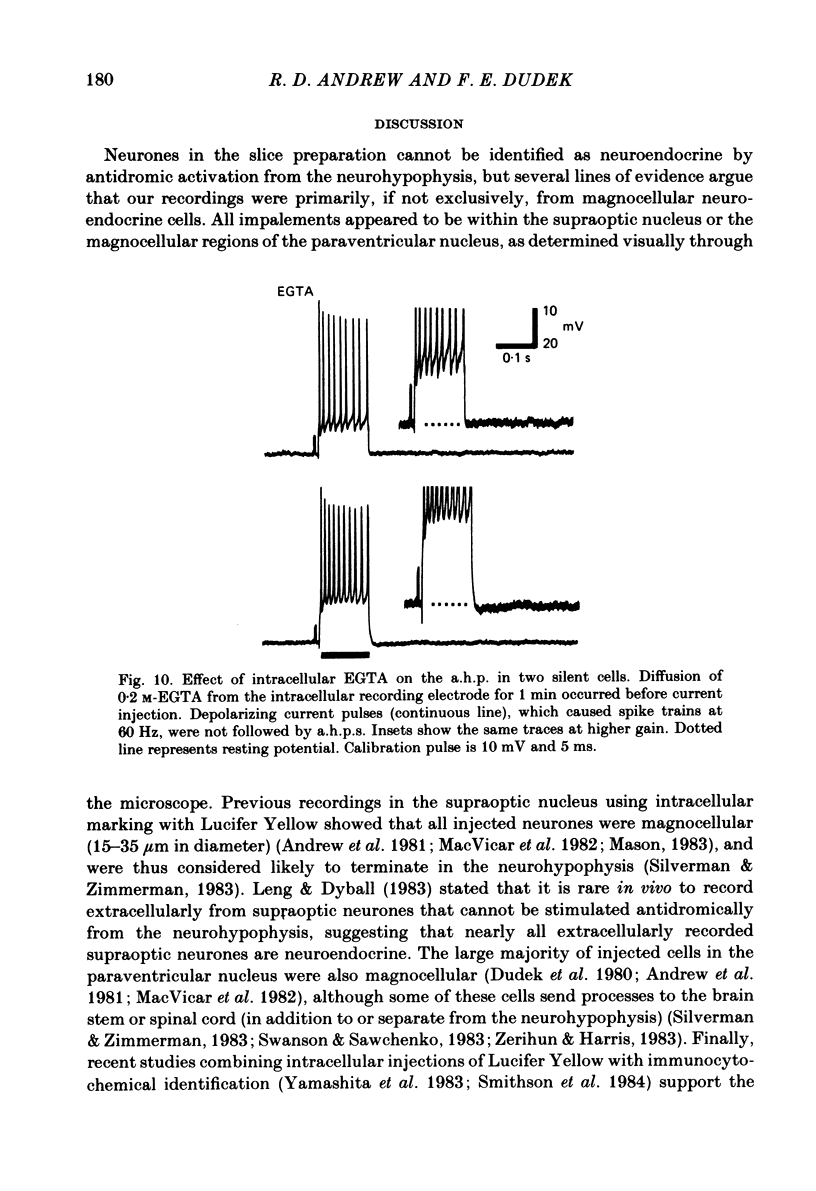
Endogenous mechanisms of inhibition in magnocellular neuroendocrine cells were studied with intracellular recordings in the rat hypothalamic slice preparation. Hyperpolarizing after-potentials (duration up to 125 ms) followed single action potentials and after-hyperpolarizations (a.h.p.s) lasting hundreds of milliseconds followed brief evoked spike trains. The amplitude and duration of the a.h.p. increased after spike trains of longer duration or higher frequency. The a.h.p. appears endogenous, rather than synaptically mediated from recurrent inhibition, because it persisted after pharmacological blockade of axonal conduction or of chemical synaptic transmission. The reversal potential of the a.h.p. was at least 20 mV more negative than that of inhibitory post-synaptic potentials. Cl- ionophoresis did not alter the a.h.p. Chelation of intracellular Ca2+ with EGTA injection eliminated the a.h.p. A Ca2+-activated K+ conductance, rather than recurrent synaptic inhibition, apparently causes the a.h.p. and is at least partly responsible for the inhibition after single spikes in magnocellular neurones. During hormone release, this endogenous mechanism may contribute to the post-burst silent period in putative oxytocinergic cells and to the interburst interval in phasic neurones, which are known to fire repetitive bursts associated with vasopressin release.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akaishi T., Ellendorff F. Electrical properties of paraventricular neurosecretory neurons with and without recurrent inhibition. Brain Res. 1983 Feb 28;262(1):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90479-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alger B. E., Nicoll R. A. Epileptiform burst afterhyperolarization: calcium-dependent potassium potential in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. Science. 1980 Dec 5;210(4474):1122–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.7444438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew R. D., Dudek F. E. Burst discharge in mammalian neuroendocrine cells involves an intrinsic regenerative mechanism. Science. 1983 Sep 9;221(4615):1050–1052. doi: 10.1126/science.6879204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew R. D., MacVicar B. A., Dudek F. E., Hatton G. I. Dye transfer through gap junctions between neuroendocrine cells of rat hypothalamus. Science. 1981 Mar 13;211(4487):1187–1189. doi: 10.1126/science.7466393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Crayton J. W., Nicoll R. A. Antidromic and orthodromic responses of paraventricular and supraoptic neurosecretory cells. Brain Res. 1971 Oct 29;33(2):353–366. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimble M. J., Dyball R. E. Characterization of the responses of oxytocin- and vasopressin-secreting neurones in the supraoptic nucleus to osmotic stimulation. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):253–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Harris M. C., Tribollet E. Excitation of phasically firing hypothalamic supraoptic neurones by carotid occlusion in rats. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(2):337–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Kelly J. S. Recurrent inhibition of antidromically identified rat supraoptic neurones. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(1):87–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Tribollet E., Baertschi A. J. Excitation of supraoptic neurones by vaginal distention in lactating rats; correlation with neurohypophysial hormone release. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 3;113(3):600–605. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudek F. E., Hatton G. I., Macvicar B. A. Intracellular recordings from the paraventricular nucleus in slices of rat hypothalamus. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:101–114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton A., Dyball R. E. Phasic firing enhances vasopressin release from the rat neurohypophysis. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):433–440. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Hermann A., Thomas M. V. Ionic requirements for membrane oscillations and their dependence on the calcium concentration in a molluscan pace-maker neurone. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:185–217. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Linström S., Takata M. Afterhyperpolarization mechanism in the dorsal spinocerebellar tract cells of the cat. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:283–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton G. I., Doran A. D., Salm A. K., Tweedle C. D. Brain slice preparation: hypothalamus. Brain Res Bull. 1980 Jul-Aug;5(4):405–414. doi: 10.1016/s0361-9230(80)80010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward J. N., Jennings D. P. Activity of magnocellular neuroendocrine cells in the hypothalamus of unanaesthetized monkeys. I. Functional cell types and their anatomical distribution in the supraoptic nucleus and the internuclear zone. J Physiol. 1973 Aug;232(3):515–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward J. N., Jennings D. P. Activity of magnocellular neuroendocrine cells in the hypothalamus of unanaesthetized monkeys. II. Osmosensitivity of functional cell types in the supraoptic nucleus and the internuclear zone. J Physiol. 1973 Aug;232(3):545–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotson J. R., Prince D. A. A calcium-activated hyperpolarization follows repetitive firing in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Feb;43(2):409–419. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.43.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDEL E. R. ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF HYPOTHALAMIC NEUROENDOCRINE CELLS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Mar;47:691–717. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.4.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss J. Z., Palkovits M., Záborszky L., Tribollet E., Szabó D., Makara G. B. Quantitative histological studies on the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in rats. II. Number of local and certain afferent nerve terminals. Brain Res. 1983 Apr 11;265(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi K., Yamashita H. Studies of antidromically identified neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus by intracellular and extracellular recordings. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(3):683–705. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Puil E., Werman R. EGTA and motoneuronal after-potentials. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:199–223. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng G., Dyball R. E. Intercommunication in the rat supraoptic nucleus. Q J Exp Physiol. 1983 Jul;68(3):493–504. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1983.sp002742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng G. The effects of neural stalk stimulation upon firing patterns in rat supraoptic neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1981;41(2):135–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00236603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M. Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell somata in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:171–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léránth C., Záborszky L., Marton J., Palkovits M. Quantitative studies on the supraoptic nucleus in the rat. I. Synaptic organization. Exp Brain Res. 1975 May 22;22(5):509–523. doi: 10.1007/BF00237351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacVicar B. A., Andrew R. D., Dudek F. E., Hatton G. I. Synaptic inputs and action potentials of magnocellular neuropeptidergic cells: intracellular recording and staining in slices of rat hypothalamus. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Jan;8(1):87–93. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. T. Electrical properties of neurons recorded from the rat supraoptic nucleus in vitro. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Jan 22;217(1207):141–161. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negoro H., Holland R. C. Inhibition of unit activity in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus following antidromic activation. Brain Res. 1972 Jul 20;42(2):385–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90538-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negoro H., Visessuwan S., Holland R. C. Inhibition and excitation of units in paraventricular nucleus after stimulation of the septum, amygdala and neurohypophysis. Brain Res. 1973 Jul 27;57(2):479–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Barker J. L. The pharmacology of recurrent inhibition in the supraoptic neurosecretory system. Brain Res. 1971 Dec 24;35(2):501–511. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90491-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D. A., Wakerley J. B. Electrophysiology of hypothalamic magnocellular neurones secreting oxytocin and vasopressin. Neuroscience. 1982 Apr;7(4):773–808. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzberg B. M., Obaid A. L., Senseman D. M., Gainer H. Optical recording of action potentials from vertebrate nerve terminals using potentiometric probes provides evidence for sodium and calcium components. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):36–40. doi: 10.1038/306036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Slawsky M. Probable calcium spikes in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 21;135(1):157–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Stafstrom C. E. Effects of EGTA on the calcium-activated afterhyperpolarization in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells. Science. 1980 Dec 5;210(4474):1125–1126. doi: 10.1126/science.6777871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman A. J., Zimmerman E. A. Magnocellular neurosecretory system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1983;6:357–380. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.06.030183.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sofroniew M. V., Glasmann W. Golgi-like immunoperoxidase staining of hypothalamic magnocellular neurons that contain vasopressin, oxytocin or neurophysin in the rat. Neuroscience. 1981;6(4):619–643. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Sawchenko P. E. Hypothalamic integration: organization of the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1983;6:269–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.06.030183.001413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M. Responses of supraoptic neurons to electrical stimulation of the medial amygdaloid nucleus. Neuroscience. 1982;7(9):2197–2205. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90130-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakerley J. B., Lincoln D. W. The milk-ejection reflex of the rat: a 20- to 40-fold acceleration in the firing of paraventricular neurones during oxytocin release. J Endocrinol. 1973 Jun;57(3):477–493. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0570477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A. Afterpotential generation in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jan;45(1):86–97. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita H., Inenaga K., Kawata M., Sano Y. Phasically firing neurons in the supraoptic nucleus of the rat hypothalamus: immunocytochemical and electrophysiological studies. Neurosci Lett. 1983 May 27;37(1):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90509-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerihun L., Harris M. An electrophysiological analysis of caudally-projecting neurones from the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in the rat. Brain Res. 1983 Feb 14;261(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



