Abstract
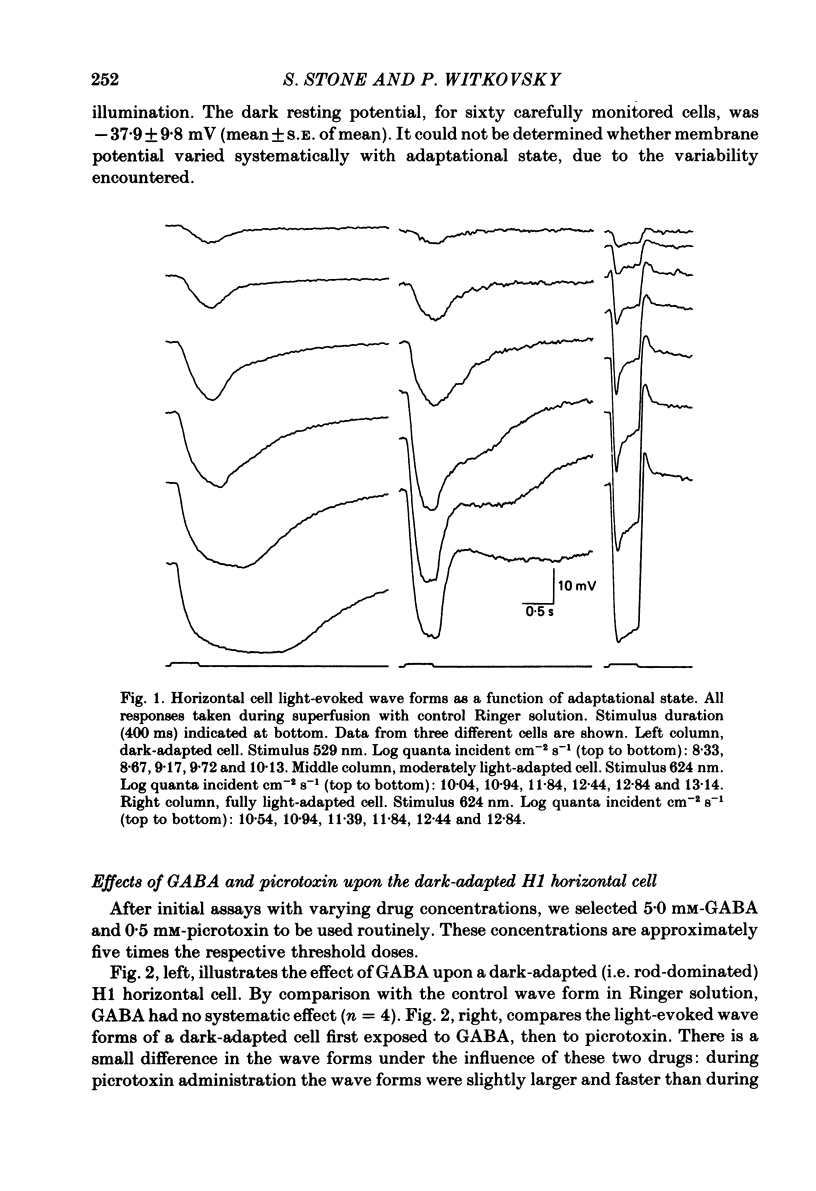
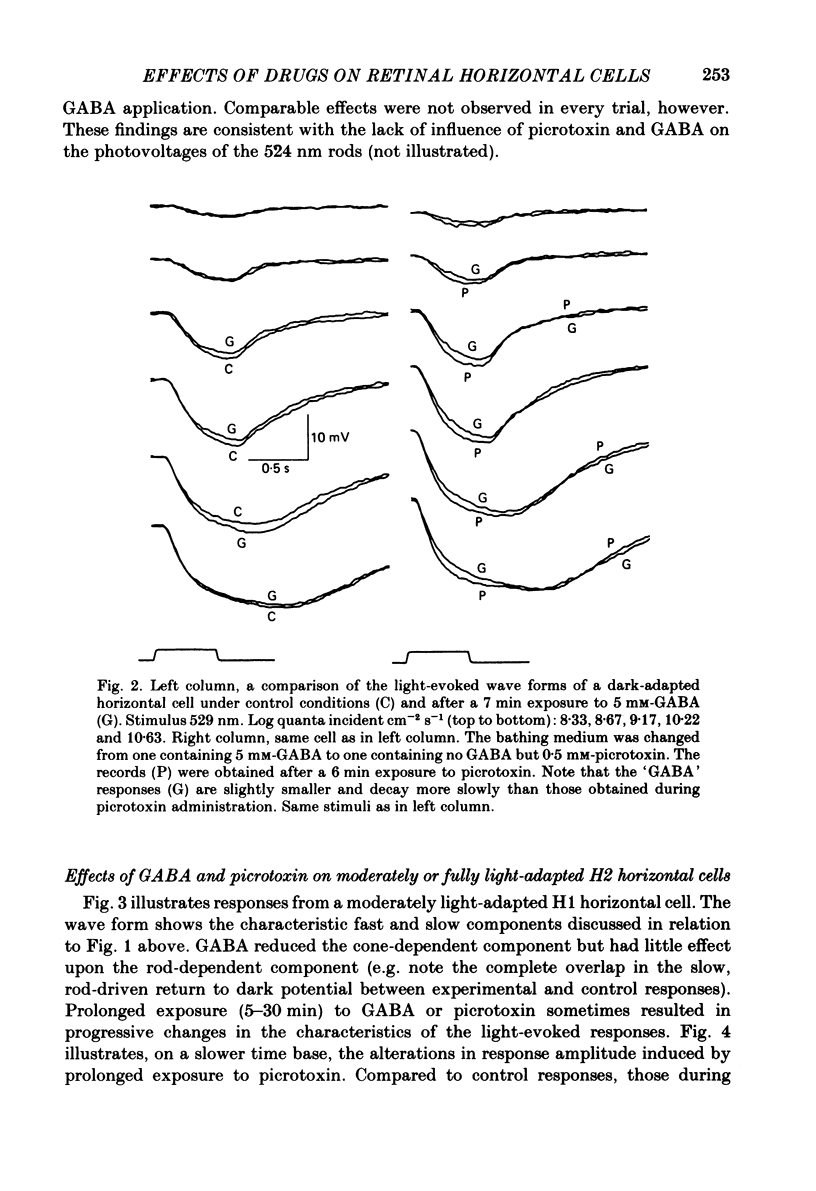
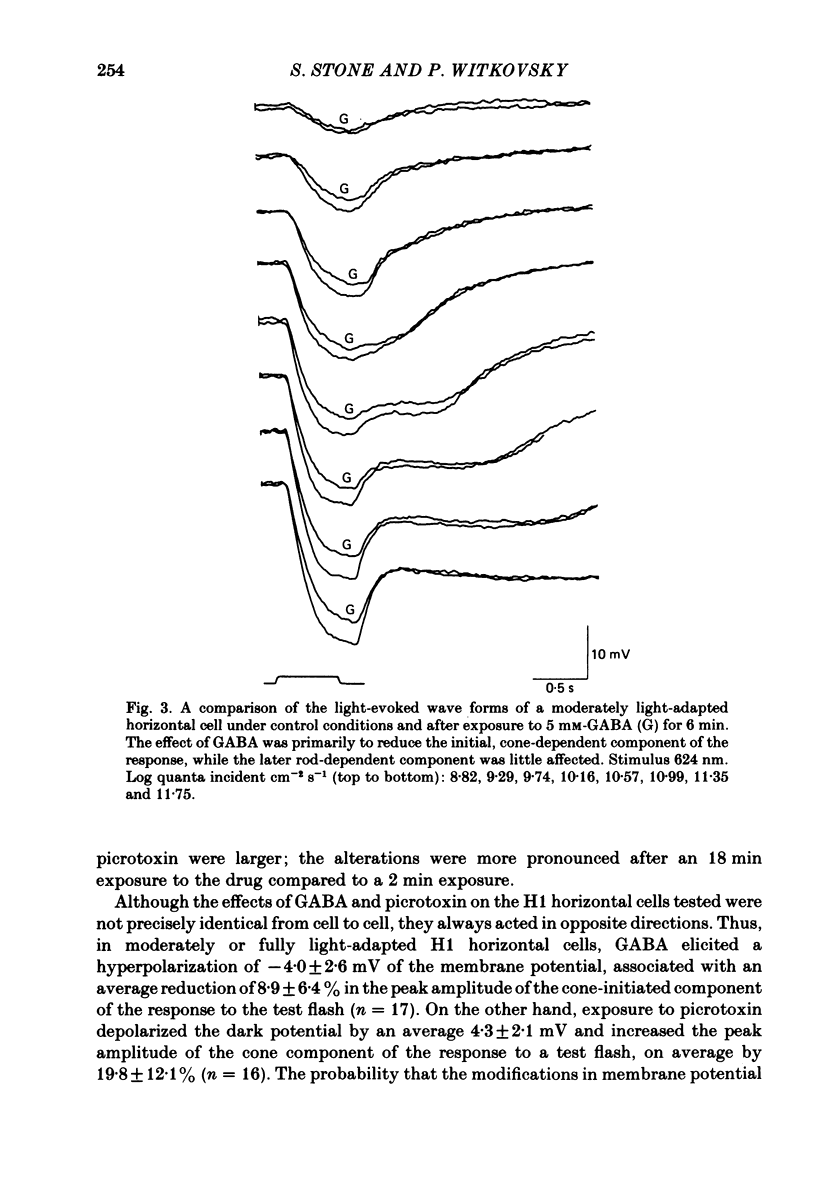
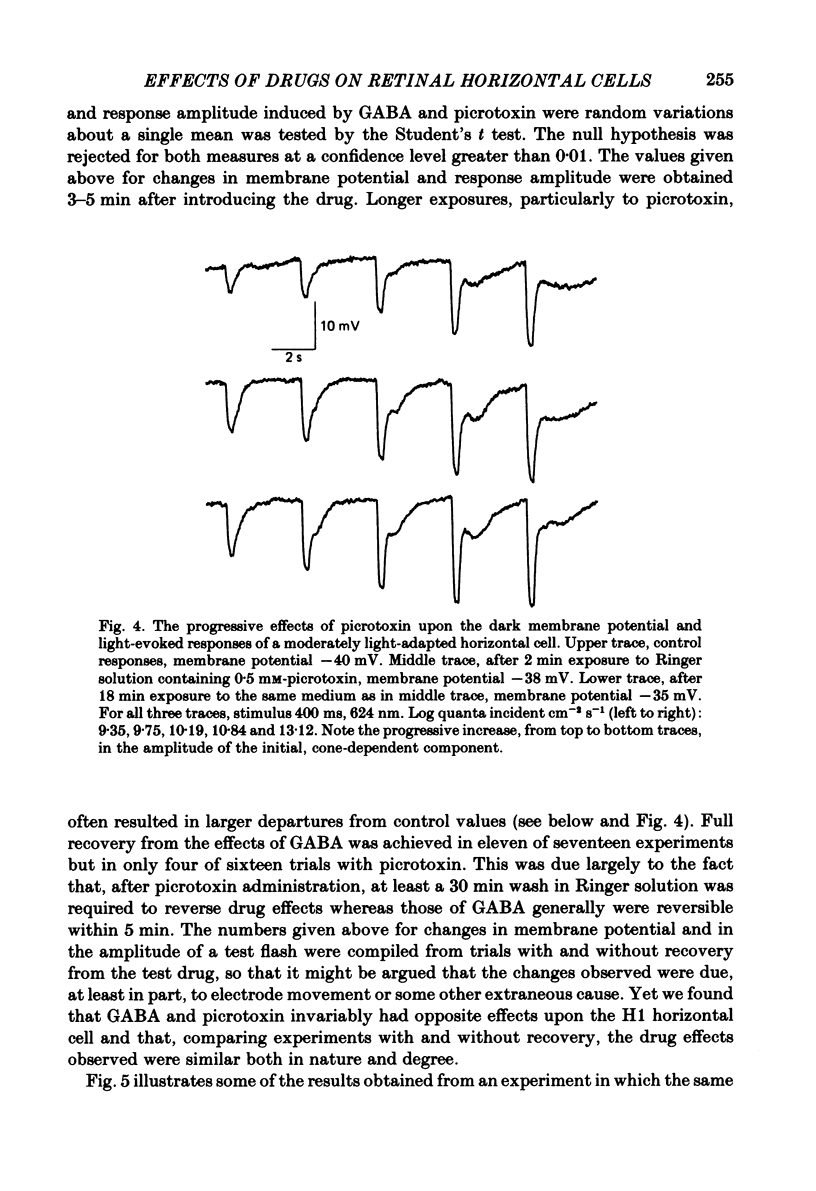
We examined the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glycine and their respective antagonists, picrotoxin and strychnine, upon the membrane potential and light-evoked responses of the type H1 horizontal cell of the Xenopus retina. This horizontal cell receives mixed input from rod and cone receptors. Under control conditions the mean membrane potential was -37.8 +/- 9.7 mV. Addition of 5 mM-GABA to the superfusate hyperpolarized the cell by 4.0 +/- 2.6 mV within 3-5 min; addition of 0.5 mM-picrotoxin depolarized the cell by 4.3 +/- 2.1 mV. Prolonged (greater than 15 min) exposures to the drugs elicited more pronounced changes in membrane potential. GABA and picrotoxin affected primarily the cone-dependent input to the H1 horizontal cell. Under dark-adapted conditions, response wave forms were essentially unaltered by the drugs, but when the horizontal cell was moderately or fully light adapted, GABA reduced and picrotoxin enhanced the cone-dependent component of its response to light. Long-term (greater than 15 min) exposures to GABA and picrotoxin elicited changes in response kinetics usually associated with dark and light adaptation, respectively. Glycine, at bath concentrations of 0.6 mM or greater, depolarized horizontal cells by 21 mV on average and reduced or abolished their light response. This action did not occur in the presence of 0.1 mM-strychnine. When all light-evoked activity was blocked by 20-40 mM-magnesium, the depolarizing action of glycine still occurred. Thus, glycine appears to act directly upon the horizontal cell membrane. Neither GABA nor glycine, nor their respective antagonists, affected the spatial extent of the horizontal cell receptive field.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attwell D., Werblin F. S., Wilson M., Wu S. M. A sign-reversing pathway from rods to double and single cones in the retina of the tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:313–333. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Fuortes M. G., O'Bryan P. M. Receptive fields of cones in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1971 Apr;214(2):265–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt D. A. Responses and receptive-field organization of cones in perch retinas. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Jan;40(1):53–62. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. L., Dowling J. E. The role of the retinal interplexiform cell: effects of 6-hydroxydopamine on the spatial properties of carp horizontal cells. Brain Res. 1983 Apr 4;264(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90830-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. E., Ripps H. Effect of magnesium on horizontal cell activity in the skate retina. Nature. 1973 Mar 9;242(5393):101–103. doi: 10.1038/242101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. E., Ripps H. Visual adaptation in the retina of the skate. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Oct;56(4):491–520. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.4.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. E., Werblin F. S. Organization of retina of the mudpuppy, Necturus maculosus. I. Synaptic structure. J Neurophysiol. 1969 May;32(3):315–338. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.3.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassin G., Witkovsky P. Intracellular recording from identified photoreceptors and horizontal cells of the Xenopus retina. Vision Res. 1983;23(10):921–931. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(83)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollyfield J. G., Rayborn M. E., Sarthy P. V., Lam D. M. The emergence, localization and maturation of neurotransmitter systems during development of the retina in Xenopus laevis. I. Gamma aminobutyric acid. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Dec 15;188(4):587–598. doi: 10.1002/cne.901880406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A. Electrical connexions between horizontal cells in the dogfish retina. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):95–105. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasansky A. Lateral contacts and interactions of horizontal cell dendrites in the retina of the larval tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:59–68. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasansky A. Organization of the outer synaptic layer in the retina of the larval tiger salamander. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973;265(872):471–489. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1973.0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer M. Electrophysiological studies of drug actions on horizontal cells. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;113:257–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc R. E., Lam D. M. Glycinergic pathways in the goldfish retina. J Neurosci. 1981 Feb;1(2):152–165. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-02-00152.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc R. E., Stell W. K., Bok D., Lam D. M. GABA-ergic pathways in the goldfish retina. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Nov 15;182(2):221–244. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. F., Dacheux R. F. Intracellular chloride in retinal neurons: measurement and meaning. Vision Res. 1983;23(4):399–411. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(83)90087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. F., Frumkes T. E., Slaughter M., Dacheux R. F. Physiological and pharmacological basis of GABA and glycine action on neurons of mudpuppy retina. I. Receptors, horizontal cells, bipolars, and G-cells. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Apr;45(4):743–763. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.4.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Otsu K., Otsuka T. Effects of chemicals on receptors and horizontal cells in the retina. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):899–913. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Shimoda Y., Nakatani K. Effects of GABA on neuronal activities in the distal retina of the carp. Sens Processes. 1978 Dec;2(4):334–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Shimoda Y., Nakatani K., Miyachi E., Watanabe S. GABA-mediated negative feedback from horizontal cells to cones in carp retina. Jpn J Physiol. 1982;32(6):911–926. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.32.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccolino M., Neyton J., Witkovsky P., Gerschenfeld H. M. gamma-Aminobutyric acid antagonists decrease junctional communication between L-horizontal cells of the retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3671–3675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayborn M. E., Sarthy P. V., Lam D. M., Hollyfield J. G. The emergence, localization, and maturation of neurotransmitter systems during development of the retina in Xenopus laevis: II. Glycine. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Feb 1;195(4):585–593. doi: 10.1002/cne.901950404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Calcium-independent release of GABA from isolated horizontal cells of the toad retina. J Physiol. 1982 Feb;323:211–227. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stell W. K., Kretz R., Lightfoot D. O. Horizontal cell connectivity in goldfish. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;113:51–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephan P., Weiler R. Morphology of horizontal cells in the frog retina. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;221(2):443–449. doi: 10.1007/BF00216747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana M. Membrane properties of solitary horizontal cells isolated from goldfish retina. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:141–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teranishi T., Negishi K., Kato S. Dopamine modulates S-potential amplitude and dye-coupling between external horizontal cells in carp retina. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):243–246. doi: 10.1038/301243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda J., Kujiraoka T., Fujimoto M. The opponent color process and interaction of horizontal cells. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;113:151–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov I. U. Izuchenie sinapticheskoi peredachi mezhdu fotoretseptorom i gorizontal'noi kletkoi pri pomoshchi élektricheskikh razdrazhenii setchatki. Biofizika. 1968 Sep-Oct;13(5):809–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voaden M. J., Marshall J., Murani N. The uptake of [3H]gamma-amino butyric acid and [3H]glycine by the isolated retina of the frog. Brain Res. 1974 Feb 15;67(1):115–132. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90302-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkovsky P., Levine J. S., Engbretson G. A., Hassin G., MacNichol E. F., Jr A microspectrophotometric study of normal and artificial visual pigments in the photoreceptors of Xenopus laevis. Vision Res. 1981;21(6):867–873. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(81)90187-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkovsky P., Owen W. G., Woodworth M. Gap junctions among the perikarya, dendrites, and axon terminals of the luminosity-type horizontal cell of the turtle retina. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Jun 1;216(4):359–368. doi: 10.1002/cne.902160402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkovsky P., Powell C. C. Synapse formation and modification between distal retinal neurons in larval and juvenile Xenopus. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Mar 11;211(1184):373–389. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkovsky P., Stone S. Rod and cone inputs to bipolar and horizontal cells of the Xenopus retina. Vision Res. 1983;23(11):1251–1258. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(83)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Brandon C., Su Y. Y., Lam D. M. Immunocytochemical and autoradiographic localization of GABA system in the vertebrate retina. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Sep 25;39:229–238. doi: 10.1007/BF00232576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. M., Dowling J. E. Effects of GABA and glycine on the distal cells of the cyprinid retina. Brain Res. 1980 Oct 20;199(2):401–414. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90697-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazulla S., Kleinschmidt J. Carrier-mediated release of GABA from retinal horizontal cells. Brain Res. 1983 Mar 14;263(1):63–75. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91201-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazulla S., Kleinschmidt J. Dopamine blocks carrier-mediated release of GABA from retinal horizontal cells. Brain Res. 1982 Feb 4;233(1):211–215. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90944-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


