Abstract
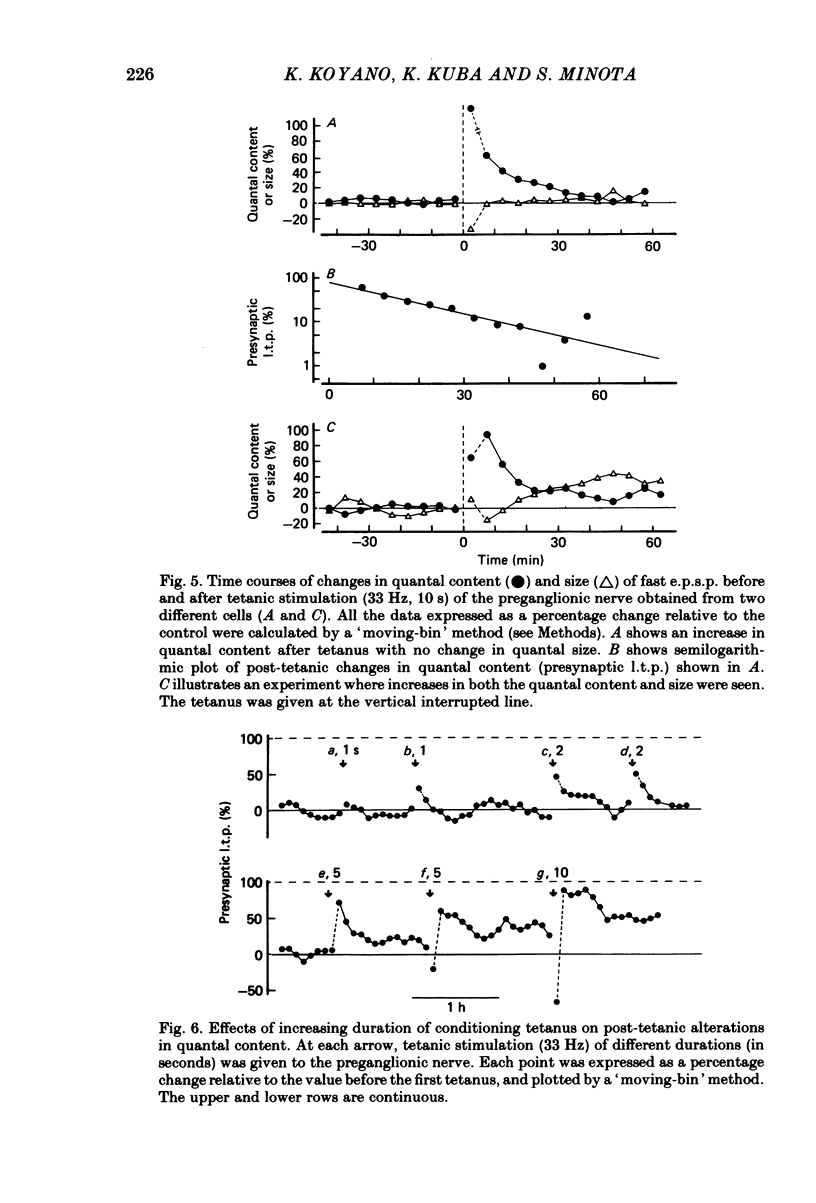
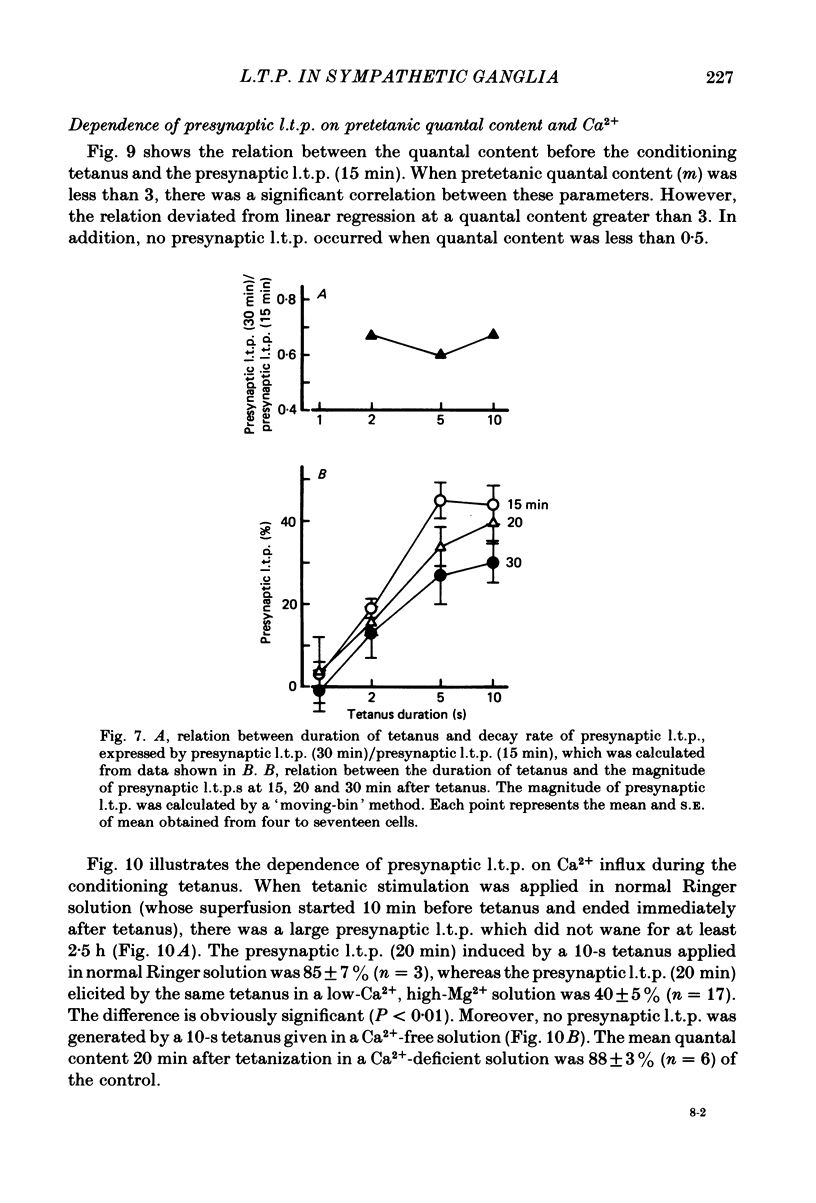
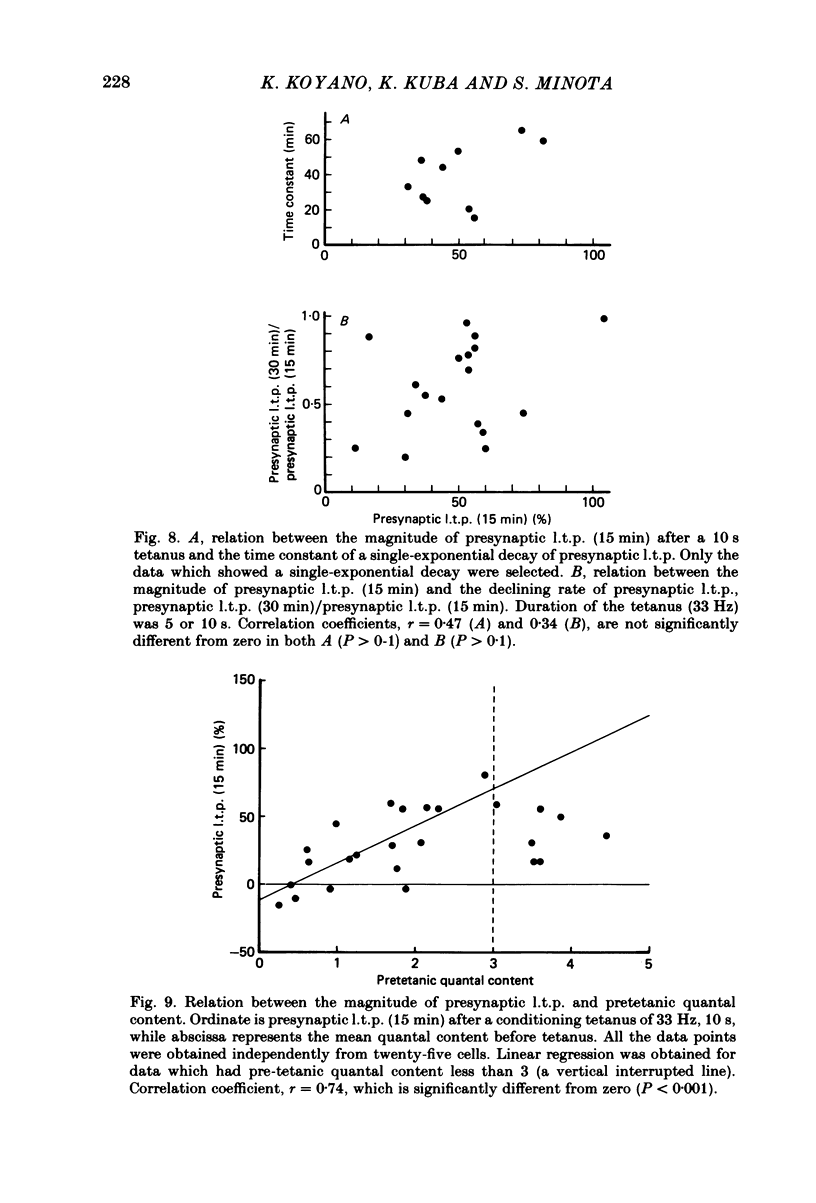
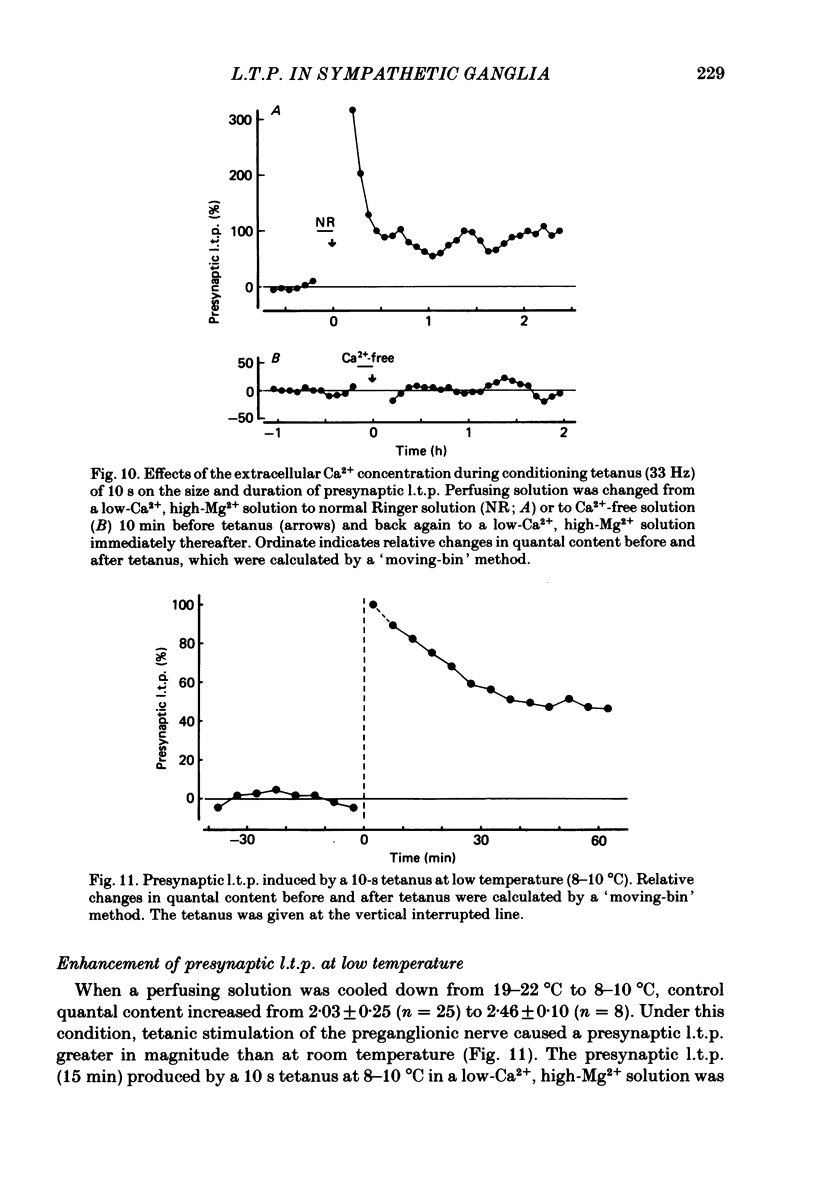
Long-lasting potentiation of transmitter release induced by repetitive presynaptic activities in bull-frog sympathetic ganglia was studied by recording intracellularly fast excitatory post-synaptic potentials (fast e.p.s.p.s.). Following a brief period of post-tetanic potentiation or depression (less than 10 min), the amplitude of the fast e.p.s.p. was potentiated for a period between several tens of minutes and more than 2 h in response to tetanic stimulation of the preganglionic nerve in twenty-one out of twenty-eight cells. Quantal analysis revealed that this long-term potentiation of the fast e.p.s.p. (l.t.p.) was accompanied by an increase in quantal content m (in nine out of twenty-one cells), quantal size (four cells) or both (eight cells). The increased quantal content (presynaptic l.t.p.) declined exponentially (ten cells) or decayed gradually to a certain enhanced level which lasted several hours. In contrast, the increased quantal size grew with a relatively long latency (10-25 min) and remained relatively constant for at least 2 h. The magnitude of presynaptic l.t.p. increased with increased duration of the presynaptic tetanus (33 Hz) from 2 to 5 s. No l.t.p. was elicited by a 1-s tetanus, whereas the time course appears to be independent of the tetanus duration and the magnitude of l.t.p. There was a positive correlation between the magnitude of presynaptic l.t.p. and the pre-tetanic quantal content up to m = 3, but the former deviated from linear regression when the value of the latter exceeded 3. No l.t.p. occurred when quantal content was less than 0.5. A tetanus (33 Hz, 10 s) applied in Ca2+-free solution elicited no presynaptic l.t.p., while the same tetanus in normal Ringer solution produced a large presynaptic l.t.p. Presynaptic l.t.p. was enhanced in magnitude at low temperature (8-10 degrees C). These results demonstrate the existence of a use-dependent, long-term potentiation of transmitter release in bull-frog sympathetic ganglia. Several possible mechanisms are discussed in terms of Ca2+-buffering mechanisms of the presynaptic nerve terminals.
Full text
PDF

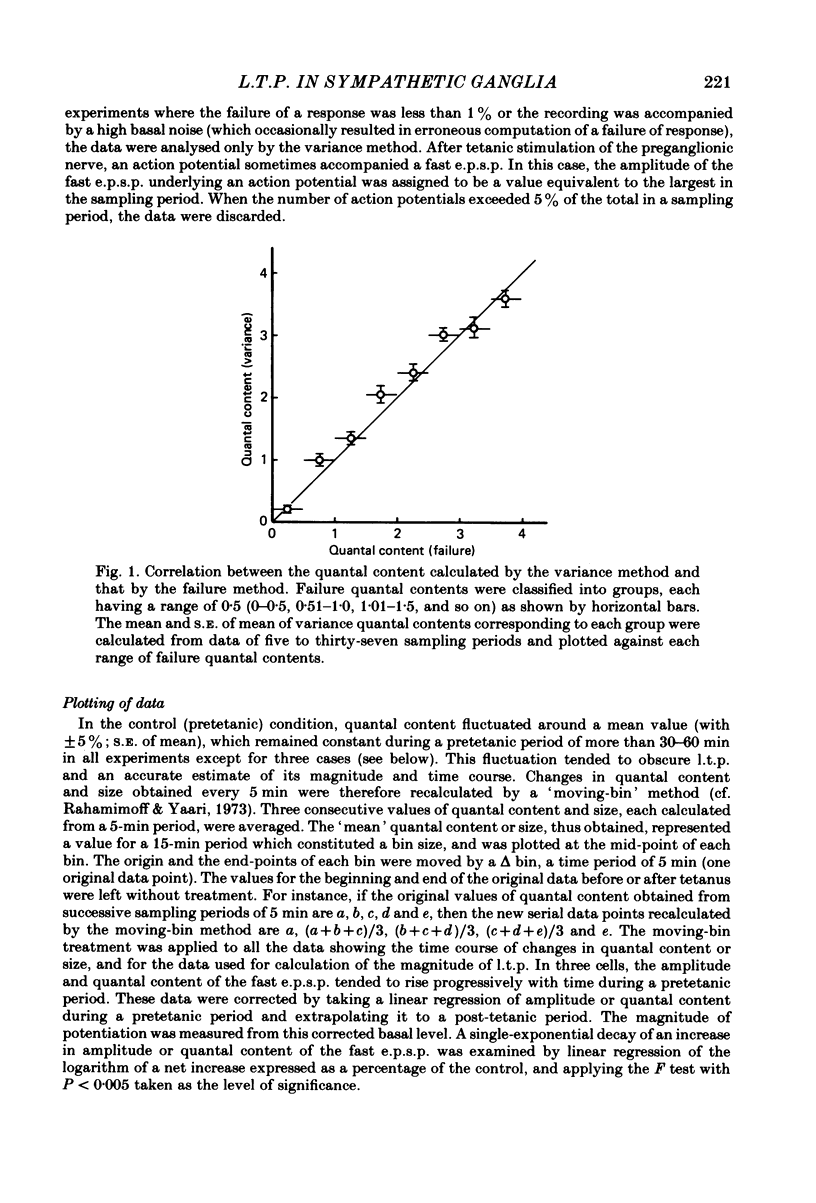

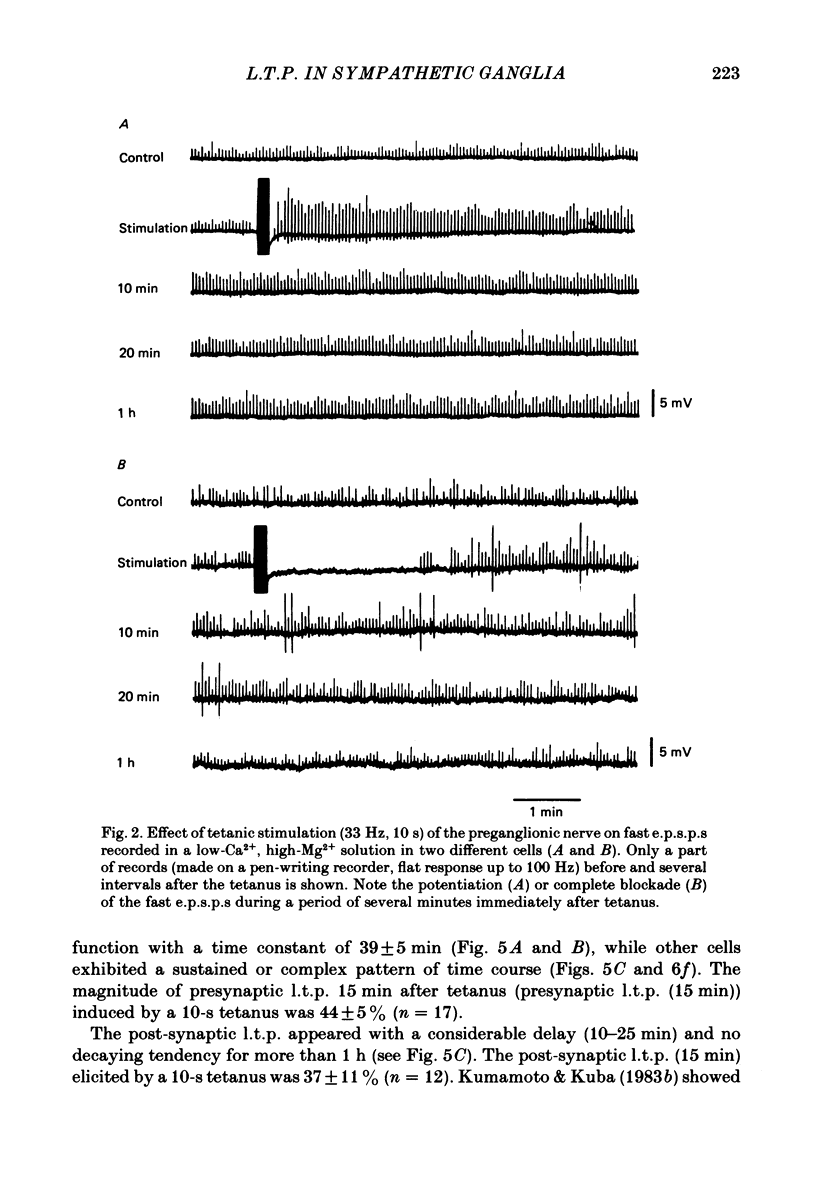
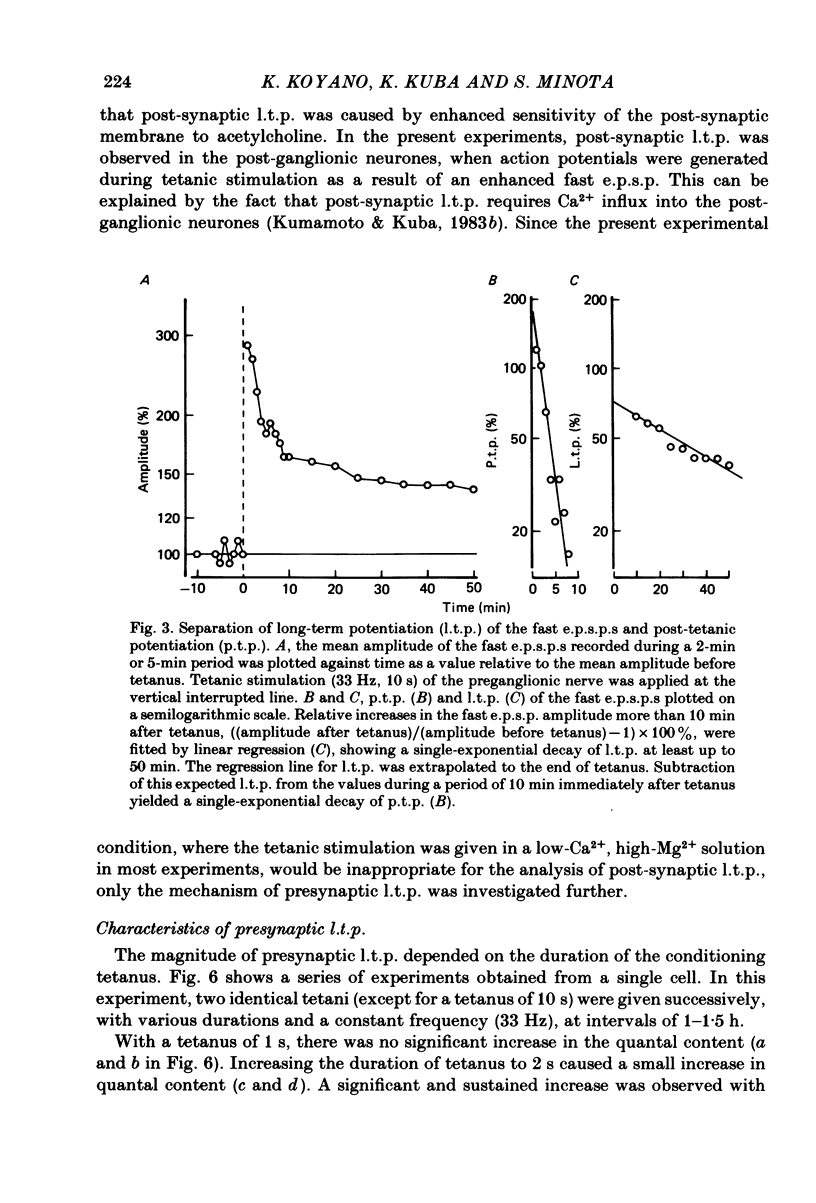
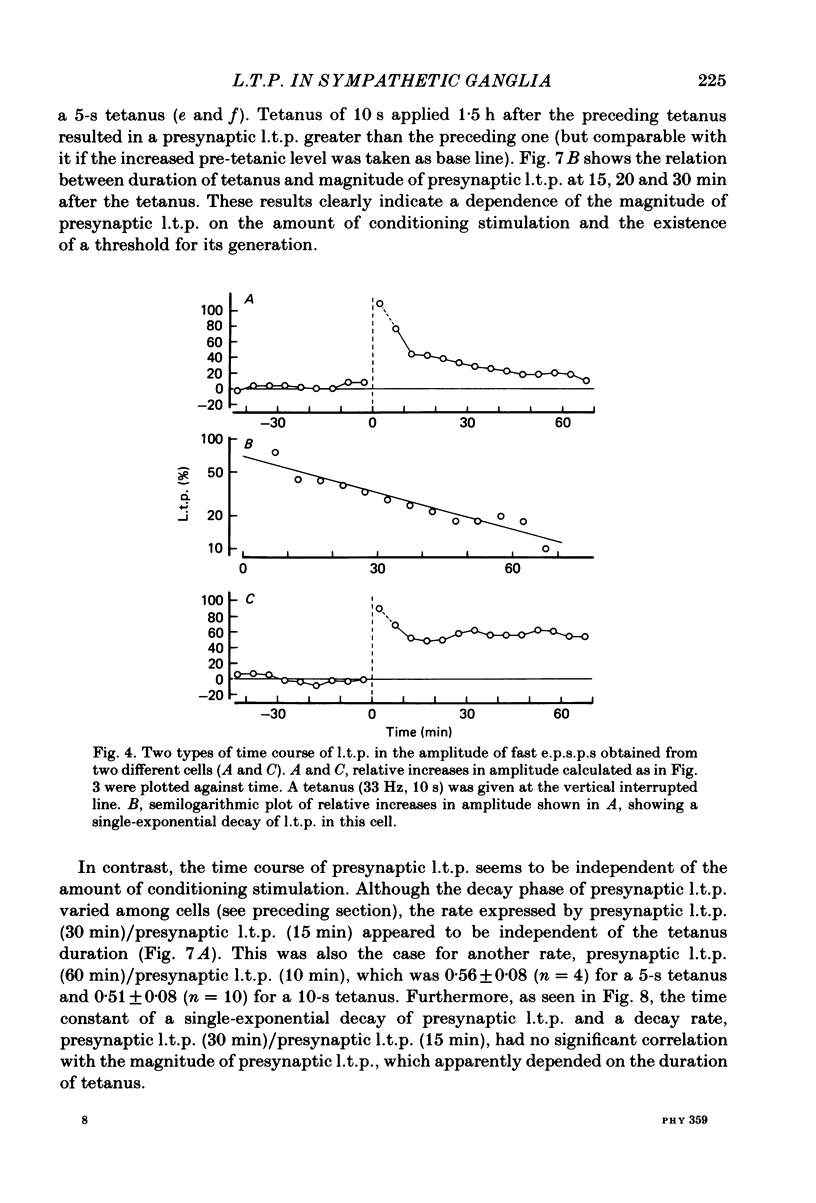




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P., Sundberg S. H., Sveen O., Swann J. W., Wigström H. Possible mechanisms for long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in hippocampal slices from guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1980 May;302:463–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baranyi A., Feher O. Long-term facilitation of excitatory synaptic transmission in single motor cortical neurones of the cat produced by repetitive pairing of synaptic potentials and action potentials following intracellular stimulation. Neurosci Lett. 1981 May 29;23(3):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birks R. I. A long-lasting potentiation of transmitter release related to an increase in transmitter stores in a sympathetic ganglion. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(3):847–862. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birks R. I. Activation of feline acetylcholine synthesis in the absence of release: dependence on sodium, calcium and the sodium pump. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:347–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Ratzlaff R. W., Kendrick N. C., Schweitzer E. S. Calcium buffering in presynaptic nerve terminals. I. Evidence for involvement of a nonmitochondrial ATP-dependent sequestration mechanism. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Jul;72(1):15–41. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Lomo T. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the anaesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(2):331–356. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brattin W. J., Waller R. L. Calcium inhibition of rat liver microsomal calcium-dependent ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6724–6729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., McAfee D. A. Long-term synaptic potentiation in the superior cervical ganglion. Science. 1982 Mar 12;215(4538):1411–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.6278593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellucci V., Kandel E. R. Presynaptic facilitation as a mechanism for behavioral sensitization in Aplysia. Science. 1976 Dec 10;194(4270):1176–1178. doi: 10.1126/science.11560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton M. P., Smith S. J., Zucker R. S. Role of presynaptic calcium ions and channels in synaptic facilitation and depression at the squid giant synapse. J Physiol. 1982 Feb;323:173–193. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Tillotson D. L. Calcium-mediated inactivation of the calcium conductance in caesium-loaded giant neurones of Aplysia californica. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:265–280. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erulkar S. D., Rahamimoff R. The role of calcium ions in tetanic and post-tetanic increase of miniature end-plate potential frequency. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:501–511. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel E. R., Schwartz J. H. Molecular biology of learning: modulation of transmitter release. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):433–443. doi: 10.1126/science.6289442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):481–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Kato E., Kumamoto E., Koketsu K., Hirai K. Sustained potentiation of transmitter release by adrenaline and dibutyryl cyclic AMP in sympathetic ganglia. Nature. 1981 Jun 25;291(5817):654–656. doi: 10.1038/291654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Koketsu K. Synaptic events in sympathetic ganglia. Prog Neurobiol. 1978;11(2):77–169. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(78)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K. Release of calcium ions linked to the activation of potassium conductance in a caffeine-treated sympathetic neurone. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:251–269. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto E., Kuba K. Independence of presynaptic bimodal actions of adrenaline in sympathetic ganglia. Brain Res. 1983 Apr 18;265(2):344–347. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90354-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto E., Kuba K. Sustained rise in ACh sensitivity of a sympathetic ganglion cell induced by postsynaptic electrical activities. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):145–146. doi: 10.1038/305145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K., Landau E. M. Depression and recovery of transmission at the squid giant synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(1):13–32. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Zengel J. E. A quantitative description of tetanic and post-tetanic potentiation of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(1):183–208. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallart A., Martin A. R. An analysis of facilitation of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):679–694. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyagawa M., Minota S., Koketsu K. Antidromic inhibition of acetylcholine release from presynaptic nerve terminals in bullfrog's sympathetic ganglia. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 16;224(2):305–313. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90861-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISHI S., KOKETSU K. Electrical properties and activities of single sympathetic neurons in frogs. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1960 Feb;55:15–30. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030550104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff R., Yaari Y. Delayed release of transmitter at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(1):241–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J. Post-tetanic potentiation at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):121–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukahara N. Synaptic plasticity in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:351–379. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D. Ionic mechanism of post-tetanic potentiation at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(2):431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zengel J. E., Magleby K. L., Horn J. P., McAfee D. A., Yarowsky P. J. Facilitation, augmentation, and potentiation of synaptic transmission at the superior cervical ganglion of the rabbit. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Aug;76(2):213–231. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Characteristics of crayfish neuromuscular facilitation and their calcium dependence. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;241(1):91–110. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


