Abstract
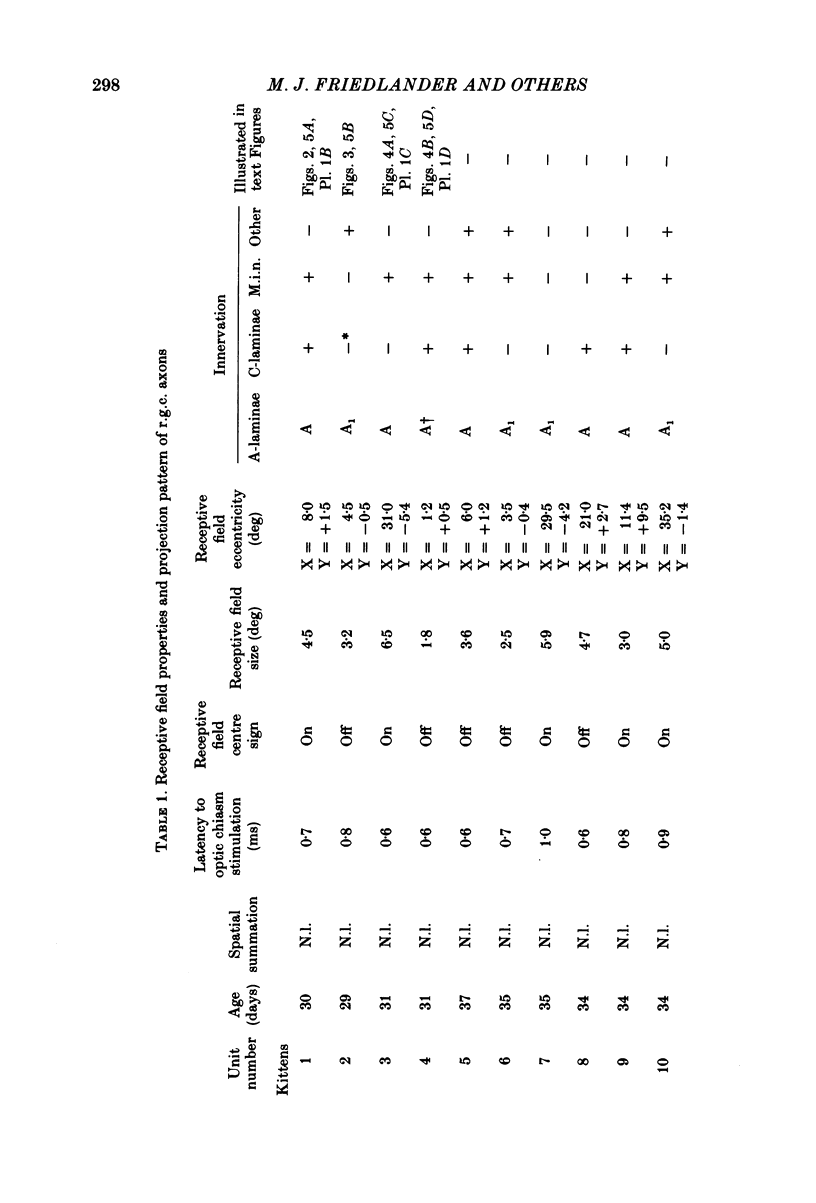
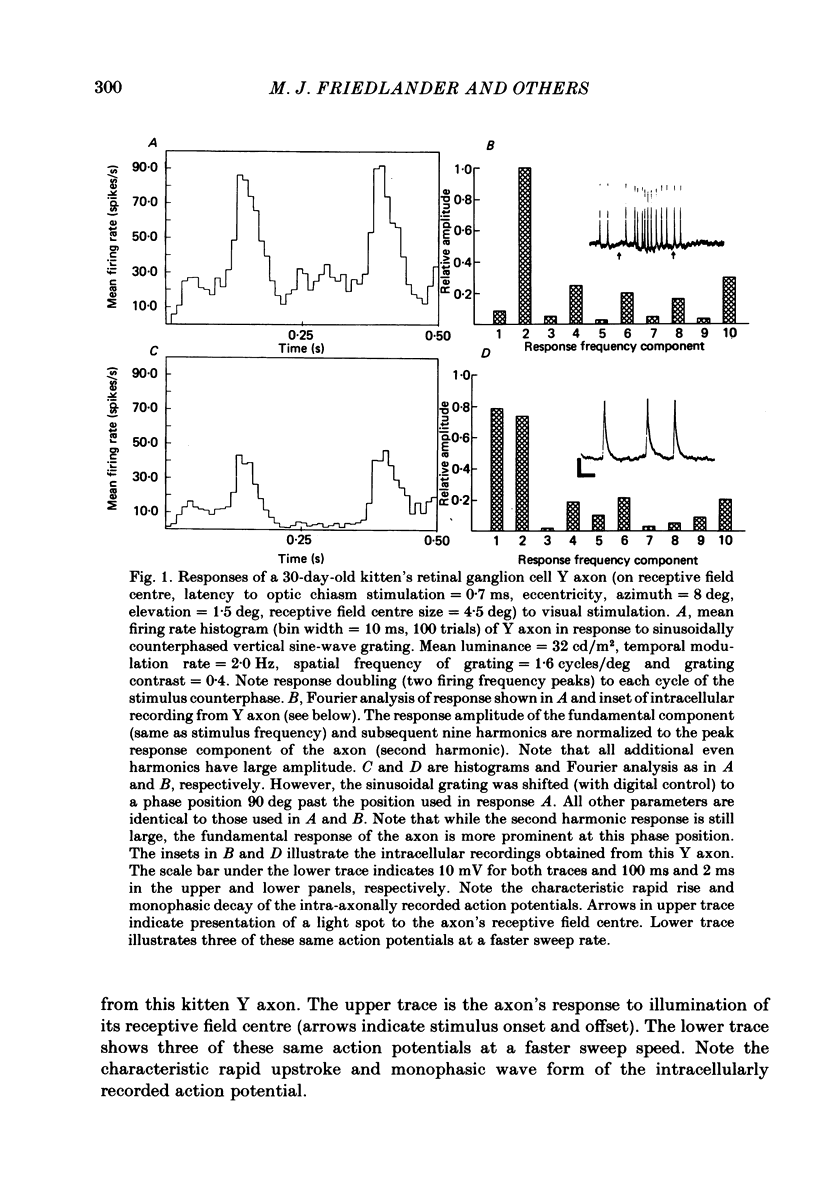
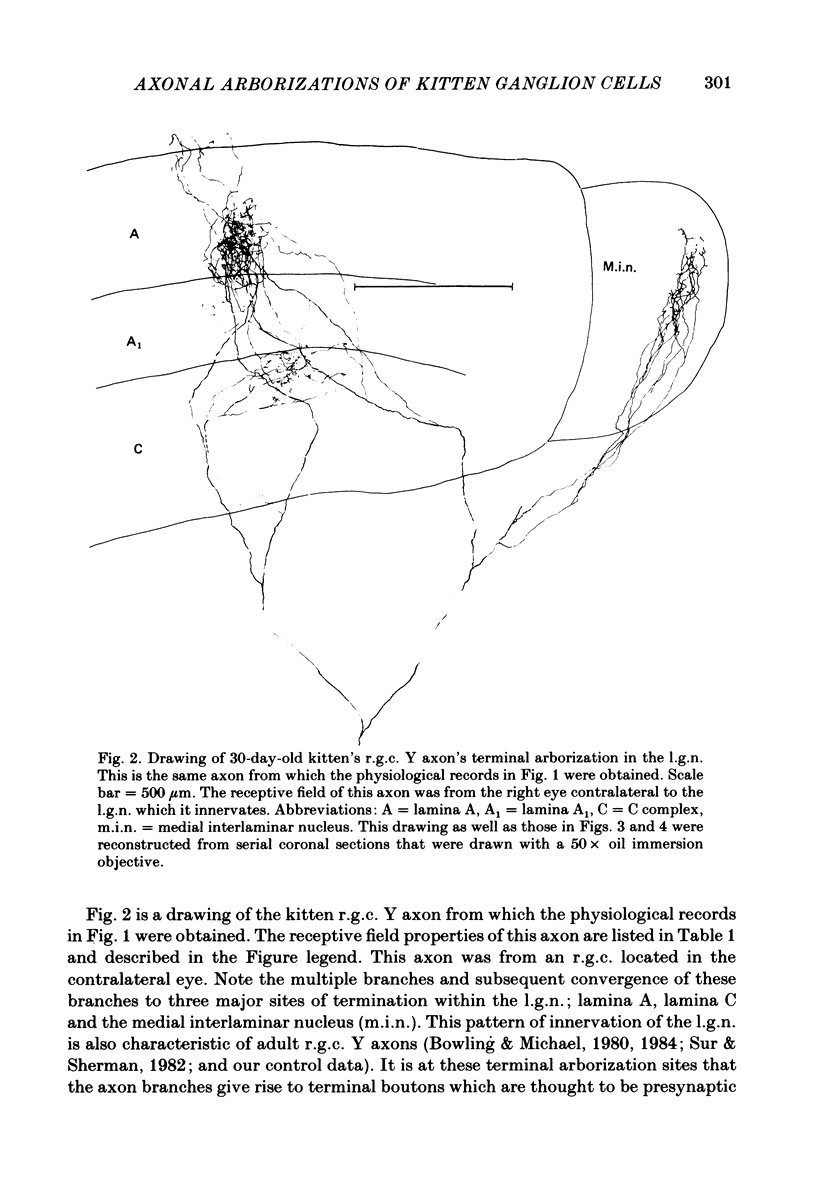
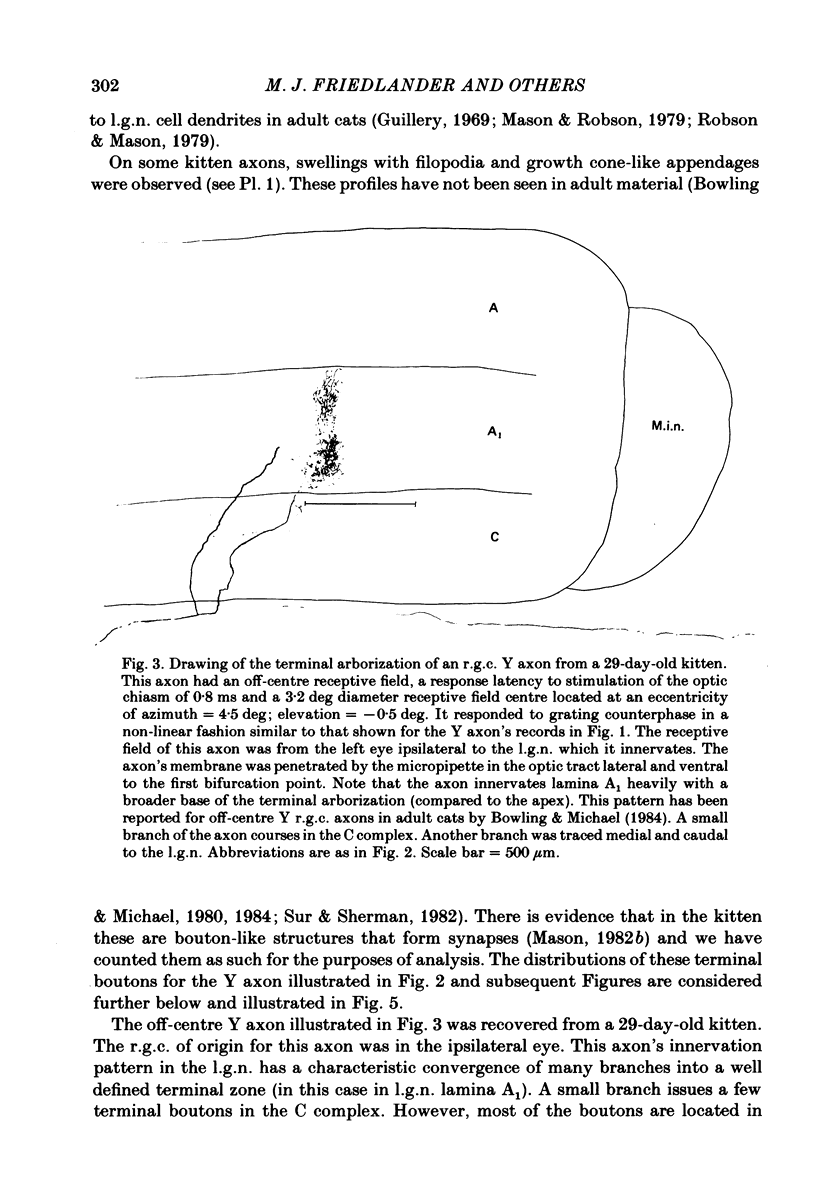
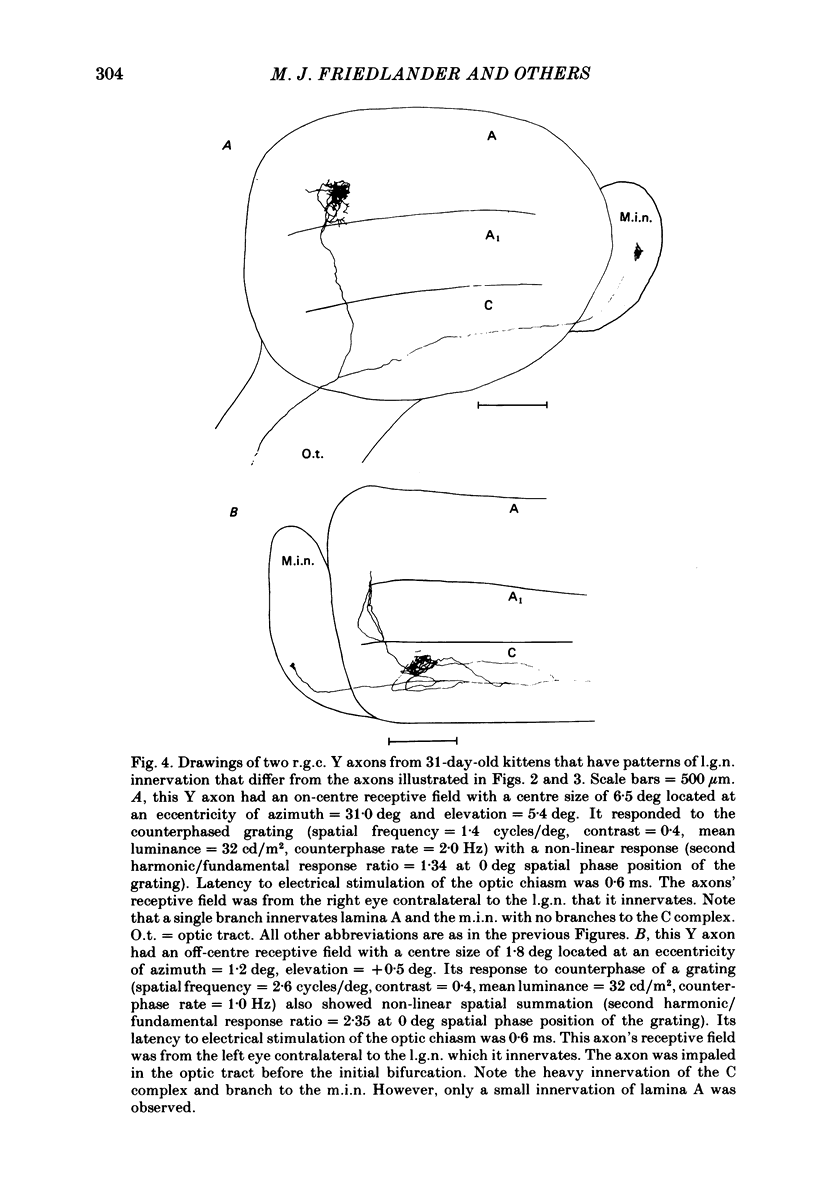
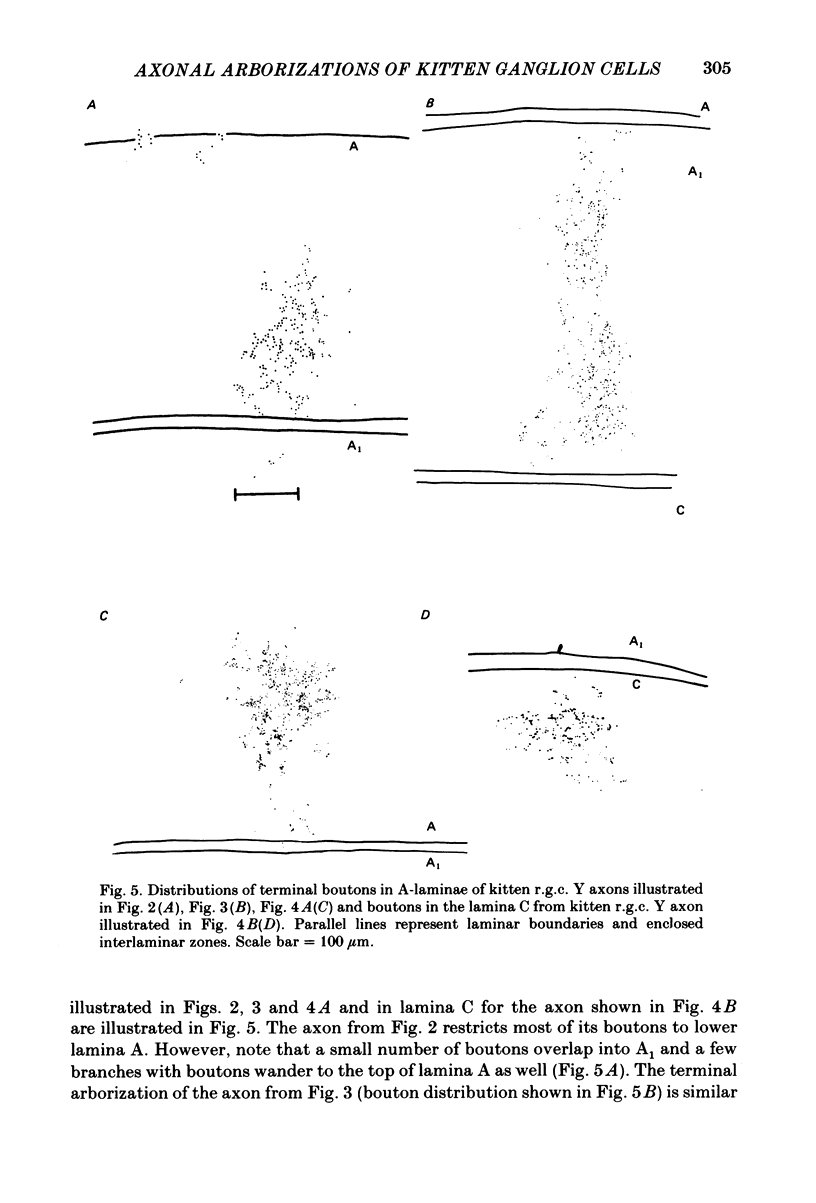
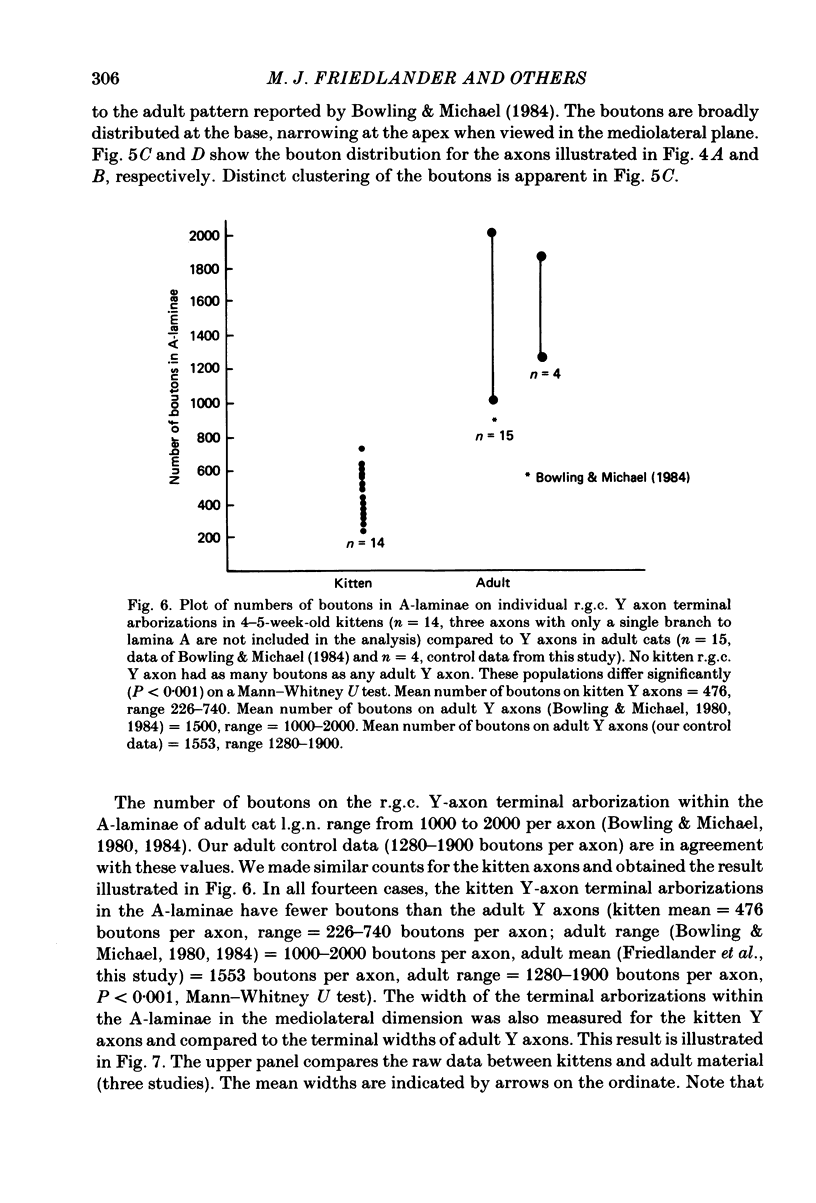
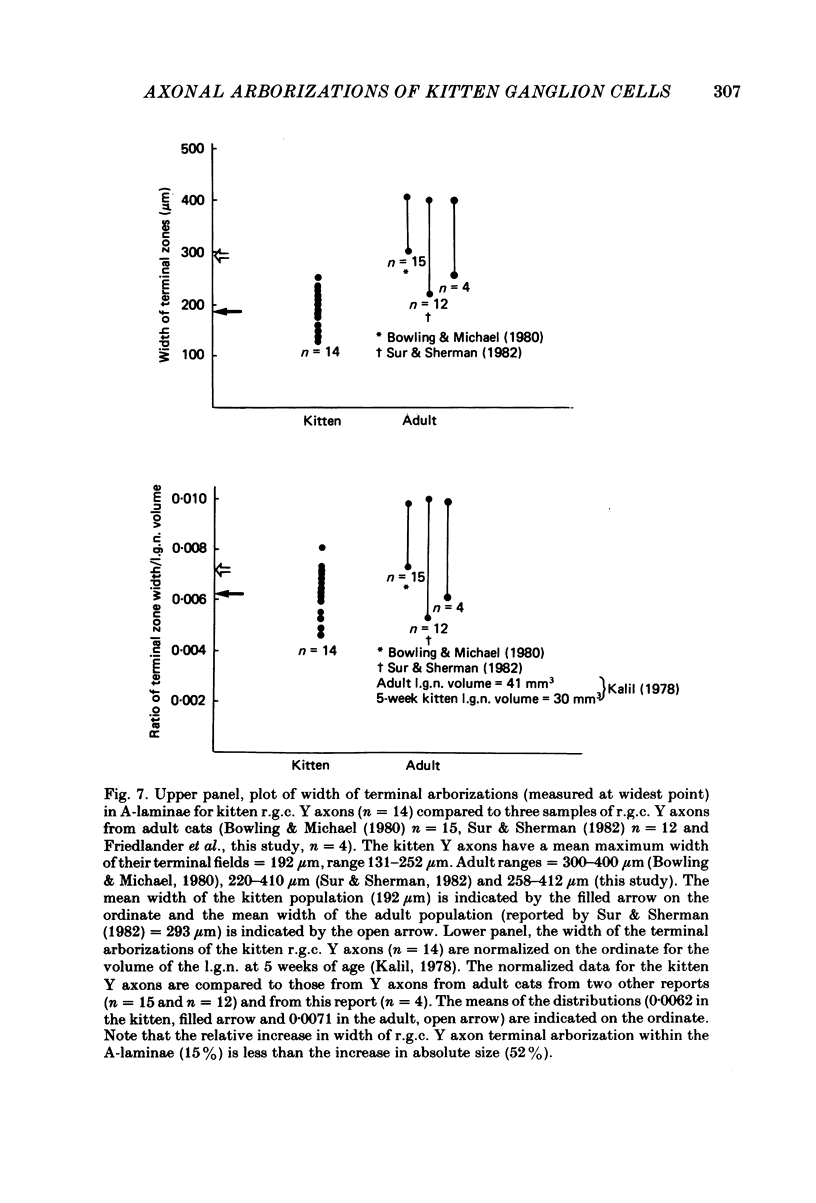
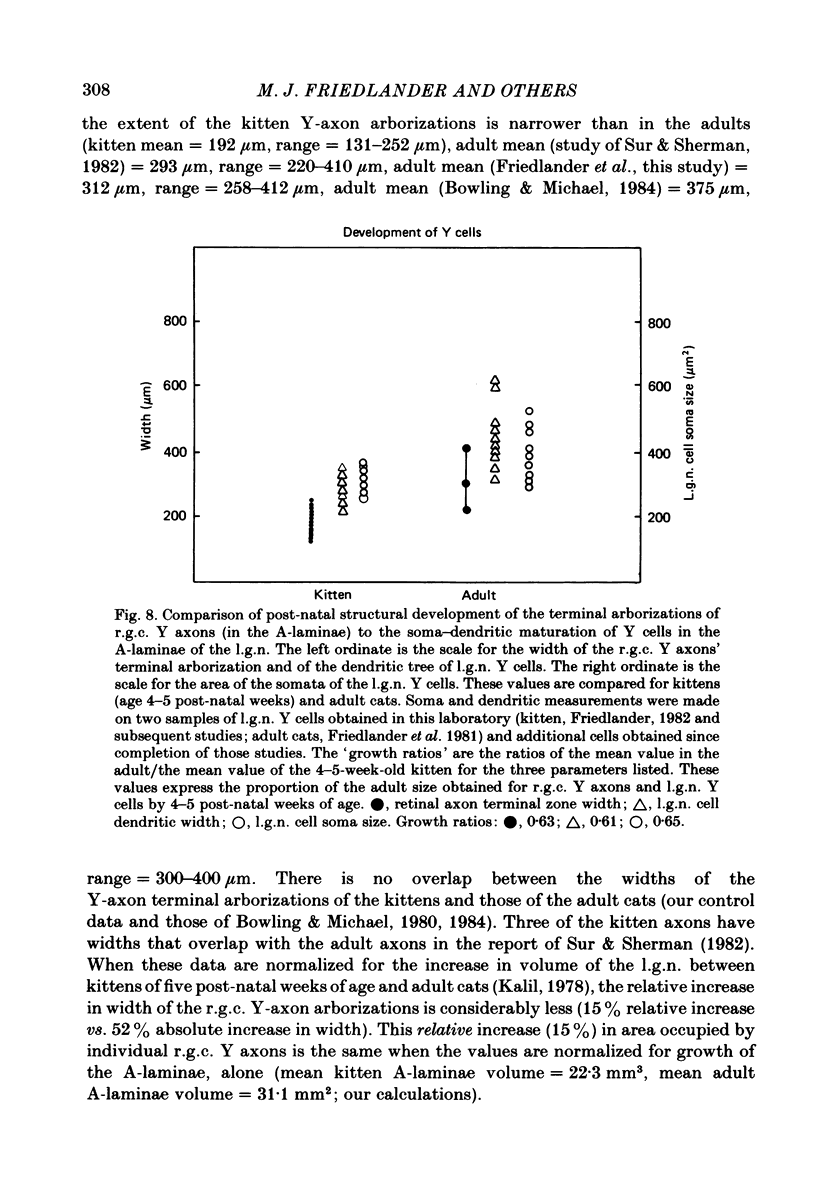
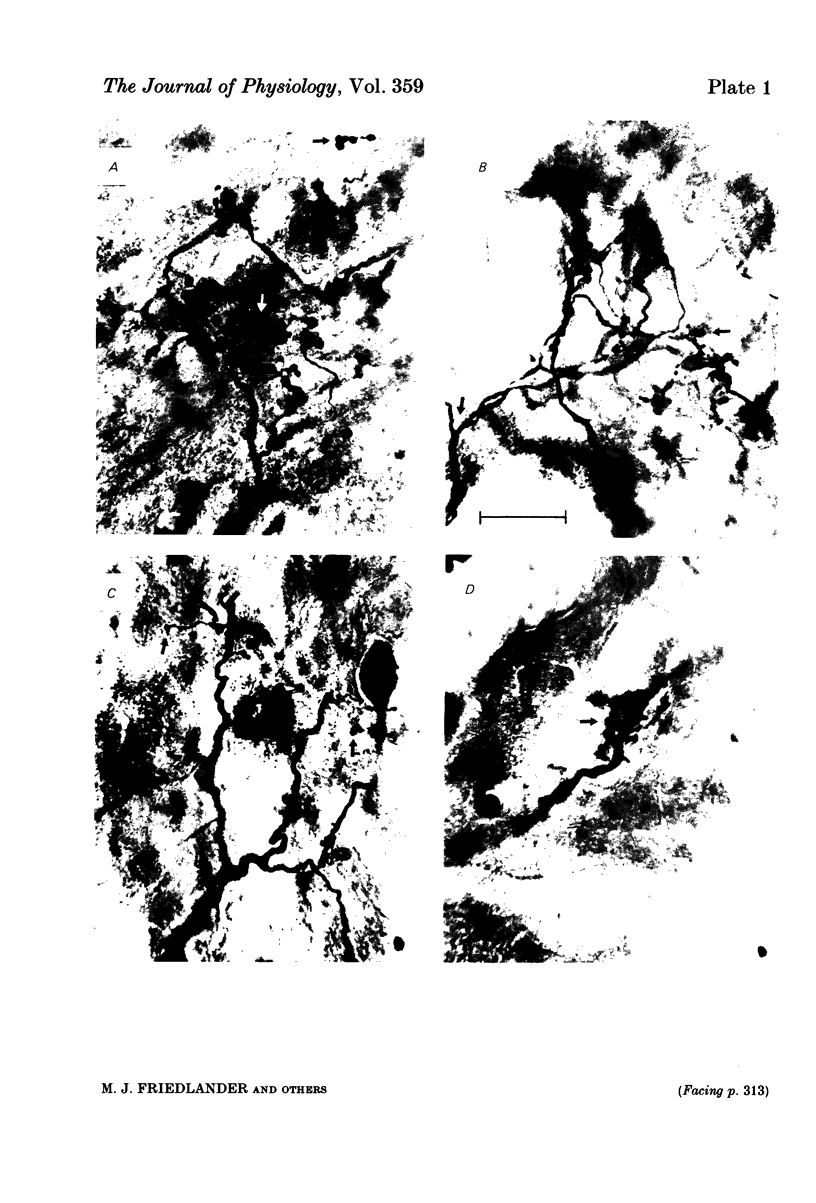
Retinal ganglion cell (r.g.c.) axons (n = 17) in the optic tract of 4-5 week-old kittens and adult cats (n = 4, this study, n = 27 from other reports) were studied both physiologically and morphologically. Axons were initially classified during extracellular recording with a battery of physiological tests that included Fourier analysis of the response to a sinusoidally counterphased sine-wave grating. Y axons had a significant second harmonic response component (greater than twice the fundamental) present independent of the spatial phase position of the grating. These axons were then recorded from intracellularly and subsequently filled ionophoretically with horseradish peroxidase (HRP). The HRP filled the axons' terminal arborizations in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (l.g.n.). The innervation pattern and and structure of the terminal arborizations of the kitten r.g.c. Y axons were compared to those of the adult. The kitten Y axons innervated the l.g.n. in a pattern similar to that of the adult (individual branches from a single axon always innervated lamina A or A1 and may also have innervated lamina C, the medial interlaminar nucleus (m.i.n.) and/or sent branches that coursed medial to the l.g.n.). Fourteen of seventeen of these Y axons in the kitten innervated either of the A-laminae heavily (greater than 200 terminal boutons per axon). The remaining three r.g.c. Y axons in the kitten had only small arborizations within lamina A (less than fifty terminal boutons per axon) but heavily innervated lamina C. The structure of the terminal boutons on the kitten r.g.c. Y axons was highly variable when compared to axons of adult cats. Some of the boutons were spherical or crenulated as in the adult. Many others had filopodia and growth cone-like terminals with fine extensions. This variable maturation of terminal boutons was seen both between axons and on individual axons. The number of boutons on the kitten r.g.c. Y axons in the A-laminae was significantly less than that of adult Y axons. The mean numbers of boutons per axon were 476 and 1553 in the kittens and adult cats, respectively (P less than 0.001, Mann-Whitney U test). The width of the terminal arborization of individual Y axons in the A-laminae of the kittens was considerably smaller than in adult cats (mean widths of the terminal arborizations are 192 and 293 micron in the kittens and adult cats, respectively).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C. Technical considerations on the use of horseradish peroxidase as a neuronal marker. Neuroscience. 1977;2(1):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonds A. B., Freeman R. D. Development of optical quality in the kitten eye. Vision Res. 1978;18(4):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(78)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowling D. B., Michael C. R. Projection patterns of single physiologically characterized optic tract fibres in cat. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):899–902. doi: 10.1038/286899a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowling D. B., Michael C. R. Terminal patterns of single, physiologically characterized optic tract fibers in the cat's lateral geniculate nucleus. J Neurosci. 1984 Jan;4(1):198–216. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-01-00198.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cragg B. G. The development of synapses in the visual system of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Mar 15;160(2):147–166. doi: 10.1002/cne.901600202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels J. D., Pettigrew J. D., Norman J. L. Development of single-neuron responses in kitten's lateral geniculate nucleus. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Nov;41(6):1373–1393. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.6.1373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enroth-Cugell C., Robson J. G. The contrast sensitivity of retinal ganglion cells of the cat. J Physiol. 1966 Dec;187(3):517–552. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famiglietti E. V., Jr Dendro-dendritic synapses in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. Brain Res. 1970 Jun 3;20(2):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. D., Lai C. E. Development of the optical surfaces of the kitten eye. Vision Res. 1978;18(4):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(78)90049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. D., Wong S., Zezula S. Optical development of the kitten cornea. Vision Res. 1978;18(4):409–414. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(78)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander M. J., Lin C. S., Stanford L. R., Sherman S. M. Morphology of functionally identified neurons in lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jul;46(1):80–129. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.46.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander M. J., Stanford L. R. Effects of monocular deprivation on the distribution of cell types in the LGNd: a sampling study with fine-tipped micropipettes. Exp Brain Res. 1984;53(2):451–461. doi: 10.1007/BF00238175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander M. J., Stanford L. R., Sherman S. M. Effects of monocular deprivation on the structure-function relationship of individual neurons in the cat's lateral geniculate nucleus. J Neurosci. 1982 Mar;2(3):321–330. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-03-00321.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander M. J. Structure of physiologically classified neurones in the kitten dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):180–183. doi: 10.1038/300180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garey L. J., Fisken R. A., Powell T. P. Effects of experimental deafferentation on cells in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. Brain Res. 1973 Mar 30;52:363–369. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90672-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillery R. W., Stelzner D. J. The differential effects of unilateral lid closure upon the monocular and binocular segments of the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1970 Aug;139(4):413–421. doi: 10.1002/cne.901390403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillery R. W. The organization of synaptic interconnections in the laminae of the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969;96(1):1–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00321474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamasaki D. I., Sutija V. G. Development of X- and Y-cells in kittens. Exp Brain Res. 1979 Mar 9;35(1):9–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00236781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson A. Electron microscopic radioautography: identification of origin of synaptic terminals in normal nervous tissue. Science. 1969 Jul 11;165(3889):194–196. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3889.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey T. L. Development of the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus in normal and visually deprived cats. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Feb 1;189(3):467–481. doi: 10.1002/cne.901890304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstein S., Shapley R. M. Linear and nonlinear spatial subunits in Y cat retinal ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):265–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstein S., Shapley R. M. Quantitative analysis of retinal ganglion cell classifications. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):237–264. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ide L. S. The fine structure of the perigeniculate nucleus in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Oct 1;210(4):317–334. doi: 10.1002/cne.902100402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innocenti G. M. Growth and reshaping of axons in the establishment of visual callosal connections. Science. 1981 May 15;212(4496):824–827. doi: 10.1126/science.7221566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalil R. Development of the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Nov 15;182(2):265–291. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalil R. Quantitative study of the effects of monocular enucleation and deprivation on cell growth in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Feb 1;189(3):483–524. doi: 10.1002/cne.901890305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratz K. E., Sherman S. M., Kalil R. Lateral geniculate nucleus in dark-reared cats: loss of Y cells without changes in cell size. Science. 1979 Mar 30;203(4387):1353–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.424758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman J. W., Purves D. The elimination of redundant preganglionic innervation to hamster sympathetic ganglion cells in early post-natal life. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:213–228. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangel S. C., Wilson J. R., Sherman S. M. Development of neuronal response properties in the cat dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus during monocular deprivation. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Jul;50(1):240–264. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.1.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason C. A. Development of terminal arbors of retino-geniculate axons in the kitten--I. Light microscopical observations. Neuroscience. 1982 Mar;7(3):541–559. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90063-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason C. A. Development of terminal arbors of retino-geniculate axons in the kitten--II. Electron microscopical observations. Neuroscience. 1982 Mar;7(3):561–582. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason C. A., Gregory E. Postnatal maturation of cerebellar mossy and climbing fibers: transient expression of dual features on single axons. J Neurosci. 1984 Jul;4(7):1715–1735. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-07-01715.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason C. A., Robson J. A. Morphology of retino-geniculate axons in the cat. Neuroscience. 1979;4(1):79–97. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry V. H., Henderson Z., Linden R. Postnatal changes in retinal ganglion cell and optic axon populations in the pigmented rat. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Sep 20;219(3):356–368. doi: 10.1002/cne.902190309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raper J. A., Bastiani M., Goodman C. S. Pathfinding by neuronal growth cones in grasshopper embryos. I. Divergent choices made by the growth cones of sibling neurons. J Neurosci. 1983 Jan;3(1):20–30. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-01-00020.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson J. A., Mason C. A. The synaptic organization of terminals traced from individual labeled retino-geniculate axons in the cat. Neuroscience. 1979;4(1):99–111. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusoff A. C., Dubin M. W. Development of receptive-field properties of retinal ganglion cells in kittens. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Sep;40(5):1188–1198. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.5.1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatz C. J. The prenatal development of the cat's retinogeniculate pathway. J Neurosci. 1983 Mar;3(3):482–499. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-03-00482.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. M., Hoffmann K. P., Stone J. Loss of a specific cell type from dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus in visually deprived cats. J Neurophysiol. 1972 Jul;35(4):532–541. doi: 10.1152/jn.1972.35.4.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. M., Spear P. D. Organization of visual pathways in normal and visually deprived cats. Physiol Rev. 1982 Apr;62(2):738–855. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.2.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sur M., Humphrey A. L., Sherman S. M. Monocular deprivation affects X- and Y-cell retinogeniculate terminations in cats. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):183–185. doi: 10.1038/300183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sur M., Sherman S. M. Retinogeniculate terminations in cats: morphological differences between X and Y cell axons. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):389–389. doi: 10.1126/science.7123239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorn F., Gollender M., Erickson P. The development of the kittens visual optics. Vision Res. 1976;16(10):1145–1149. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(76)90255-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIESEL T. N., HUBEL D. H. EFFECTS OF VISUAL DEPRIVATION ON MORPHOLOGY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF CELLS IN THE CATS LATERAL GENICULATE BODY. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Nov;26:978–993. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.6.978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. R., Friedlander M. J., Sherman S. M. Fine structural morphology of identified X- and Y-cells in the cat's lateral geniculate nucleus. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Jun 22;221(1225):411–436. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield D. A., Hiorns R. W., Powell T. P. A quantitative electron-microscopical study of the postnatal development of the lateral geniculate nucleus in normal kittens and in kittens with eyelid suture. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Nov 19;210(1179):211–234. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield D. A., Powell T. P. An electron-microscopical study of the postnatal development of the lateral geniculate nucleus in the normal kitten and after eyelid suture. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Nov 19;210(1179):197–210. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]