Abstract
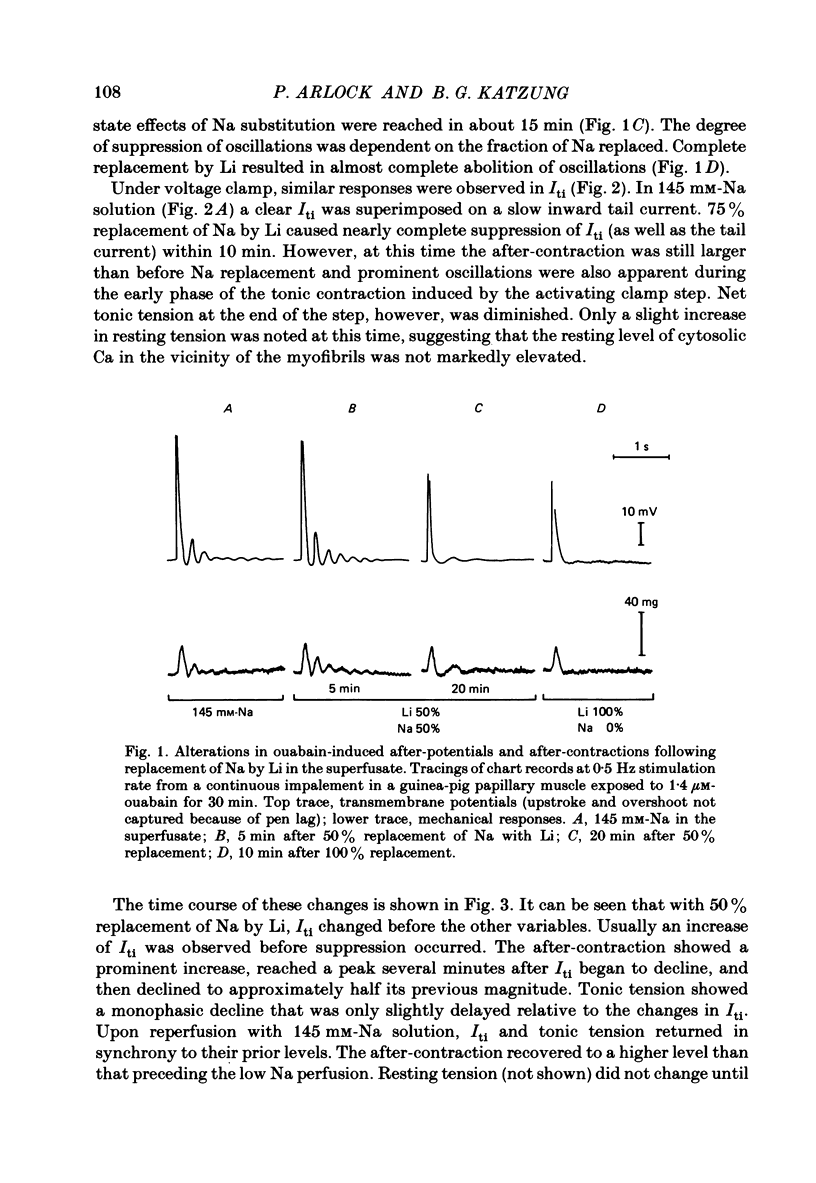
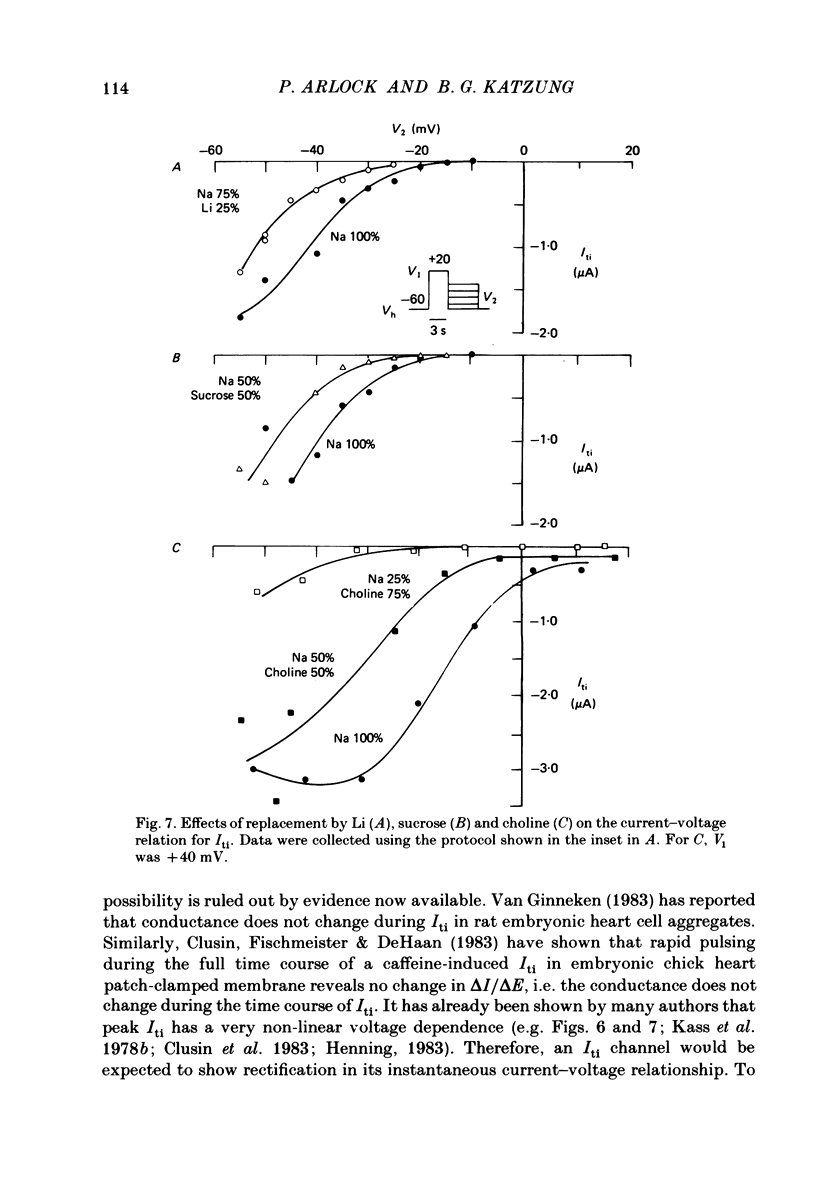
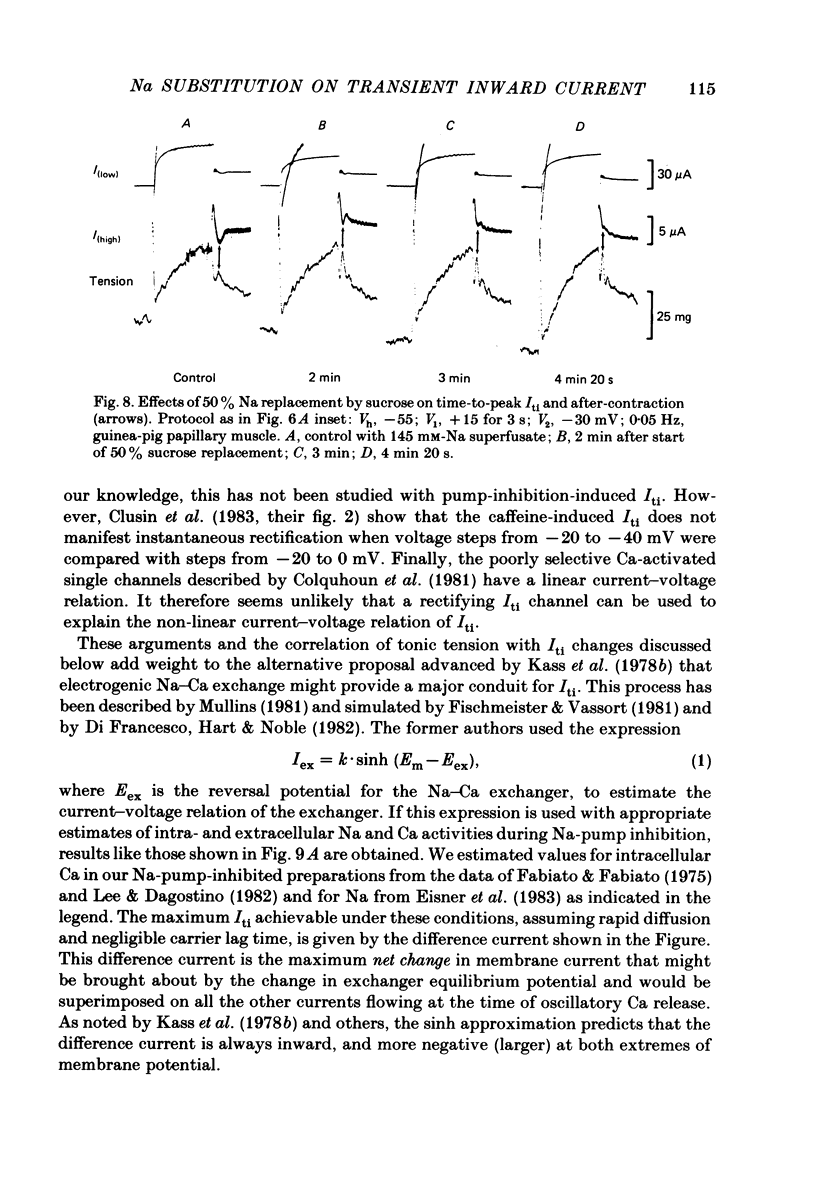
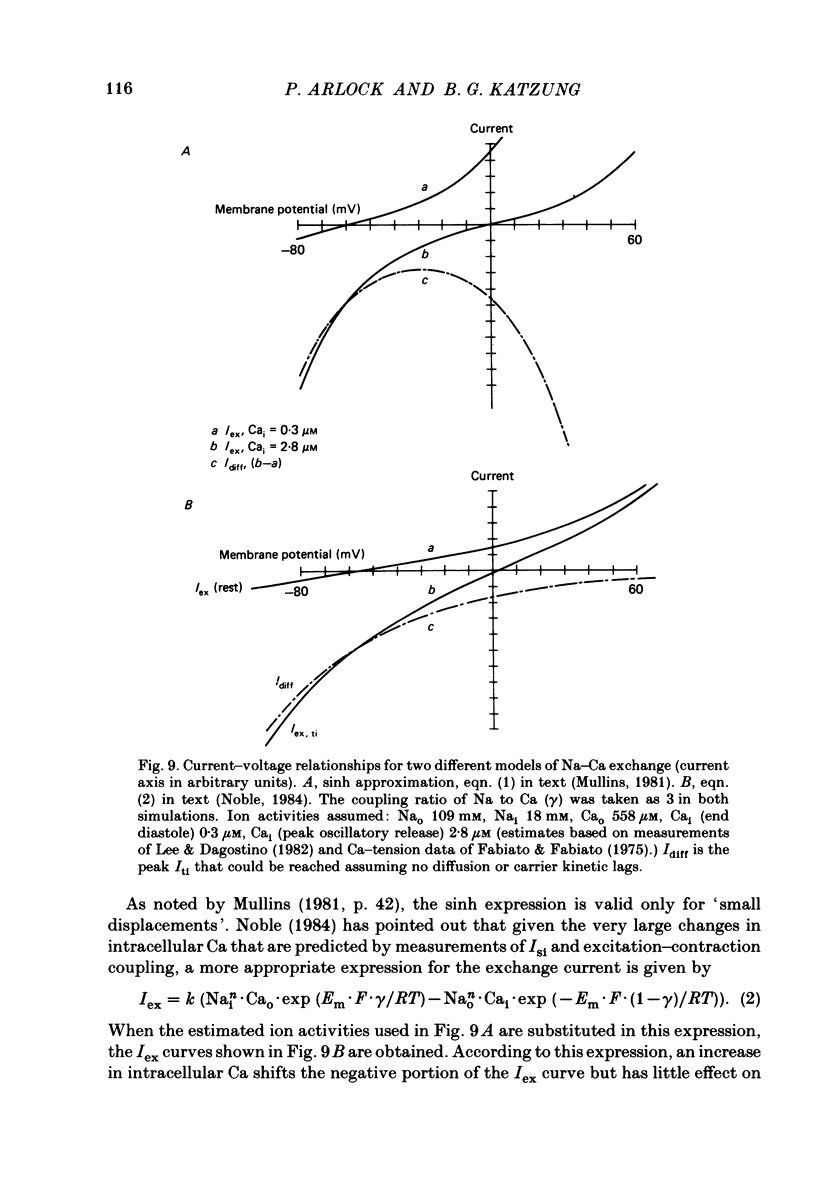
We used ouabain-treated guinea-pig and ferret papillary muscles to study transient inward current (Iti), after-contractions, and tonic tension development during voltage-clamp pulses. Li, sucrose and choline were used isosmotically as Na substitutes to evaluate the effect of altering the Na equilibrium potential. We were unable to detect outward Iti at any potential up to +30 mV in normal or Na-depleted solutions. However, reduction of Na had a biphasic effect on Iti, initially increasing it and then reducing it at all clamp potentials from -50 to +20 mV. After-contractions were also initially increased and, in sufficiently Na-depleted solutions, decreased by reduction of extracellular Na. However, the peak in the after-contraction always occurred later than the increase in Iti and frequently coincided with the maximum suppression of the current. Complete suppression of after-contractions was not often achieved and always required more complete Na replacement than Iti suppression. Tonic tension responses were reduced by Na replacement, usually in synchrony with the reduction of Iti. The responses of Iti to Na replacement are consistent with a model of electrogenic Na-Ca exchange over the potential range positive to -50 mV. The responses deviate from the predictions of the model at more negative potentials. The results are consistent with the previous proposal that oscillatory changes in internal free Ca concentration underlie both Iti and after-contractions.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arlock P., Katzung B. G. Effects of sodium substitutes on ouabain induced transient inward current. Proc West Pharmacol Soc. 1982;25:57–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosteels S., Vleugels A., Carmeliet E. Choline permeability in cardiac muscle cells of the cat. J Gen Physiol. 1970 May;55(5):602–619. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.5.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. A. Excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1979;35(1):1–52. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(80)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clusin W. T., Fischmeister R., DeHaan R. L. Caffeine-induced current in embryonic heart cells: time course and voltage dependence. Am J Physiol. 1983 Sep;245(3):H528–H532. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.245.3.H528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Neher E., Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):752–754. doi: 10.1038/294752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coraboeuf E. Editorial: Membrane electrical activity and double component contraction in cardiac tissue. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1974 Jun;6(3):215–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(74)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner D. A., Lederer W. J. Inotropic and arrhythmogenic effects of potassium-depleted solutions on mammalian cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Sep;294:255–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner D. A., Lederer W. J., Vaughan-Jones R. D. The control of tonic tension by membrane potential and intracellular sodium activity in the sheep cardiac Purkinje fibre. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:723–743. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Contractions induced by a calcium-triggered release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of single skinned cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):469–495. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier G. R. Digitalis arrhythmias: role of oscillatory afterpotentials. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1977 May-Jun;19(6):459–474. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(77)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischmeister R., Vassort G. The electrogenic Na-Ca exchange and the cardiac electrical activity. I--Simulation on Purkinje fibre action potential. J Physiol (Paris) 1981 Sep;77(6-7):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karagueuzian H. S., Katzung B. G. Voltage-clamp studies of transient inward current and mechanical oscillations induced by ouabain in ferret papillary muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:255–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass R. S., Lederer W. J., Tsien R. W., Weingart R. Role of calcium ions in transient inward currents and aftercontractions induced by strophanthidin in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:187–208. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass R. S., Tsien R. W., Weingart R. Ionic basis of transient inward current induced by strophanthidin in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:209–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi Y. The effects of intracellular protons on the electrical activity of single ventricular cells. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Sep;394(3):264–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00589102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer W. J., Tsien R. W. Transient inward current underlying arrhythmogenic effects of cardiotonic steroids in Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(2):73–100. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. O., Dagostino M. Effect of strophanthidin on intracellular Na ion activity and twitch tension of constantly driven canine cardiac Purkinje fibers. Biophys J. 1982 Dec;40(3):185–198. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84474-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. I., Vassalle M. Role of sodium in strophanthidin toxicity of Purkinje fibers. Am J Physiol. 1978 Apr;234(4):H477–H486. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1978.234.4.H477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Noma A., Kurachi Y., Irisawa H. Transient depolarization and spontaneous voltage fluctuations in isolated single cells from guinea pig ventricles. Calcium-mediated membrane potential fluctuations. Circ Res. 1982 Aug;51(2):142–151. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.2.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade P., Mitchell R. D., Fleischer S. Spontaneous calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum. General description and effects of calcium. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8098–8107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritchie J. M. On the electrogenic sodium pump in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres and its activation by various external cations. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):183–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Kass R. S., Weingart R. Calcium ions and membrane current changes induced by digitals in cardiac Purkinje fibers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:483–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41978.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Kass R. S., Weingart R. Cellular and subcellular mechanisms of cardiac pacemaker oscillations. J Exp Biol. 1979 Aug;81:205–215. doi: 10.1242/jeb.81.1.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wier W. G., Hess P. Excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac Purkinje fibers. Effects of cardiotonic steroids on the intracellular [Ca2+] transient, membrane potential, and contraction. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):395–415. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




