Abstract
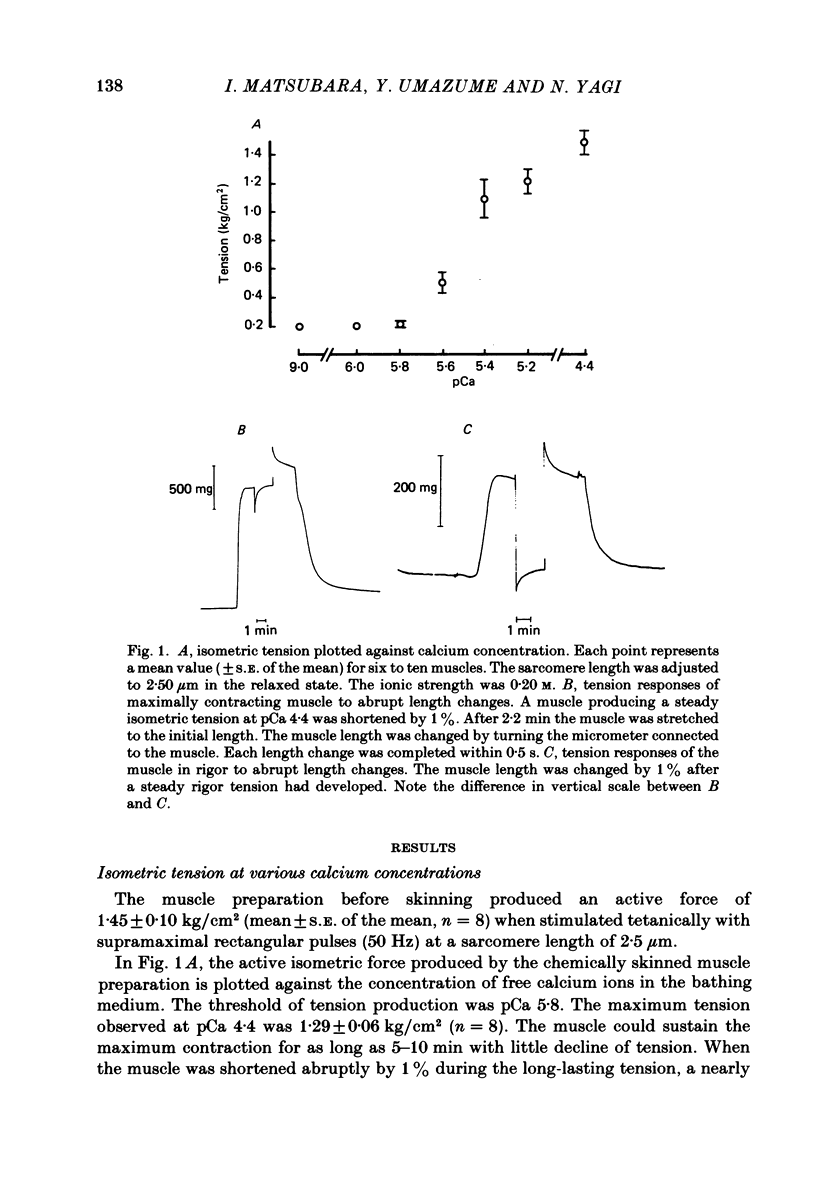
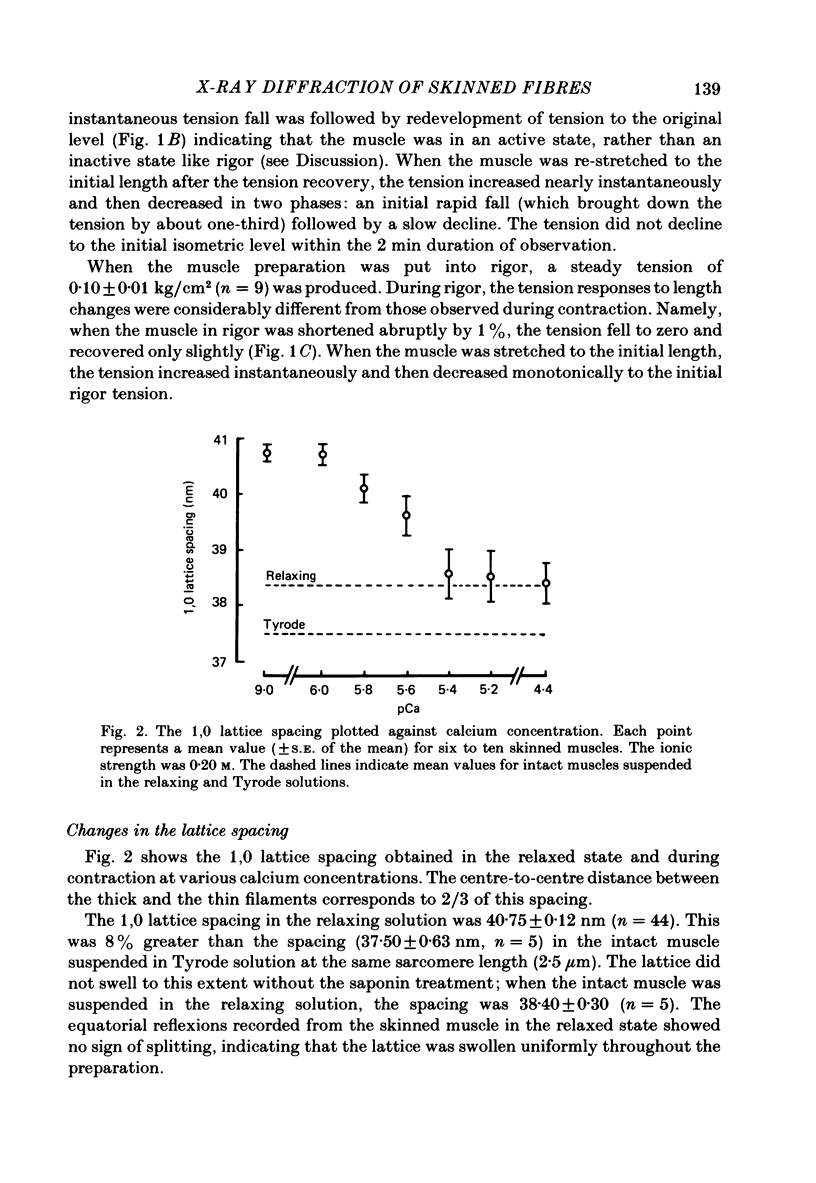
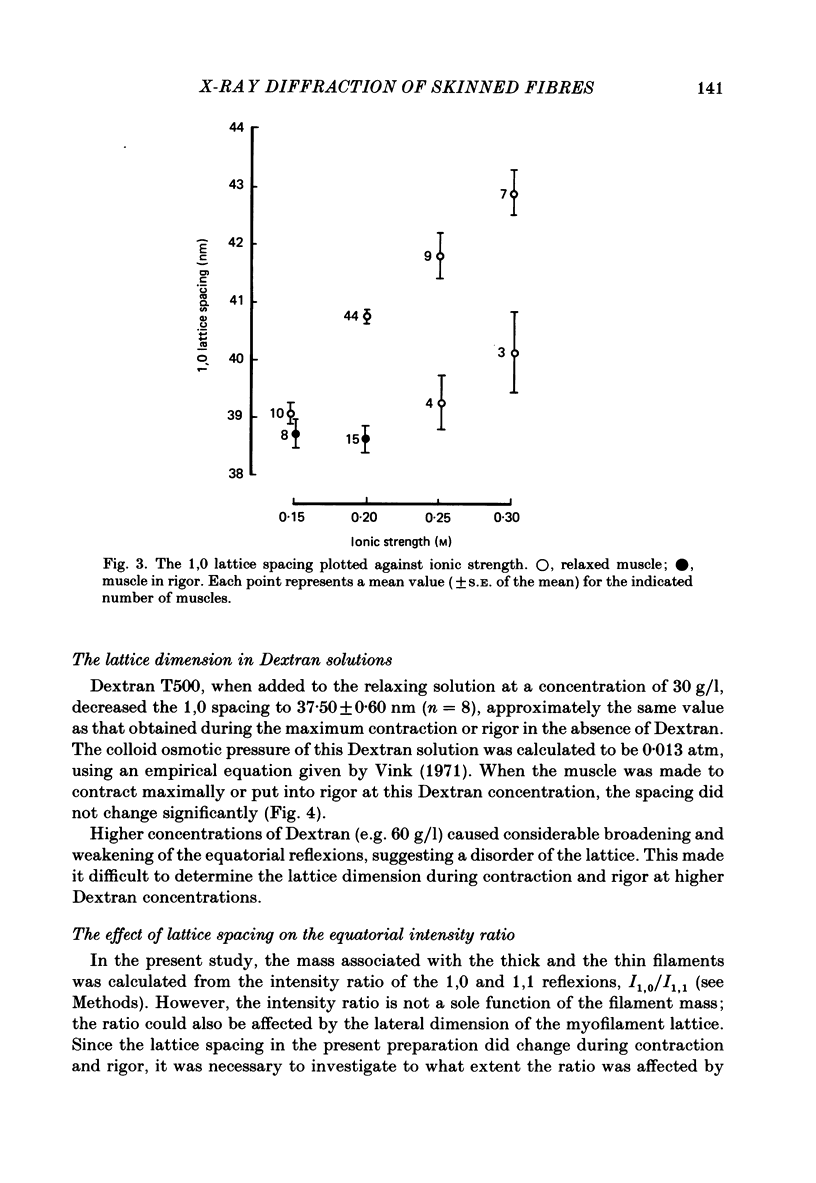
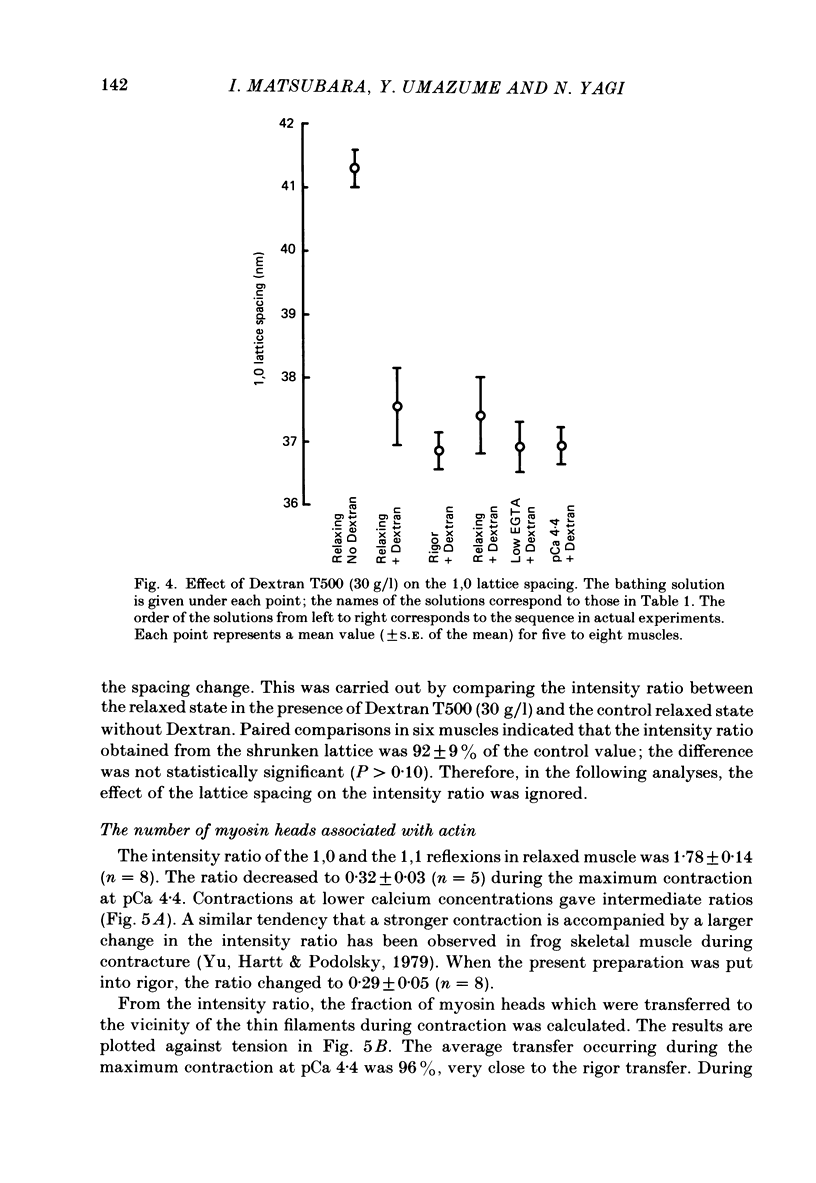
A mouse toe muscle was chemically skinned with saponin and the 1,0 spacing of the hexagonal myofilament lattice at a sarcomere length of 2.5 micron was measured with the X-ray-diffraction method. In the relaxed state, the 1,0 spacing was 40.8 nm. When the muscle was maximally activated at pCa 4.4, the spacing decreased to 38.4 nm. During contractions at lower calcium concentrations, the spacing decreased less. In rigor, the spacing decreased to almost the same extent as during maximum contraction, although the rigor tension was only 8% of the maximum tension. When the spacing in relaxed muscle had been adjusted osmotically to about 38 nm, activation caused no further decrease in the spacing. The results support the view that the force responsible for the lattice shrinkage during contraction is produced by cross-bridges displaced from their optimum lateral positions.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ELLIOTT G. F., WORTHINGTON C. R. A SMALL-ANGLE OPTICALLY FOCUSING X-RAY DIFFRACTION CAMERA IN BIOLOGICAL RESEARCH. I. J Ultrastruct Res. 1963 Aug;49:166–170. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(63)80044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott G. F. Force-balances and stability in hexagonally-packed polyelectrolyte systems. J Theor Biol. 1968 Oct;21(1):71–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(68)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M., Iino M. Specific perforation of muscle cell membranes with preserved SR functions by saponin treatment. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1980 Mar;1(1):89–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00711927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenczi M. A., Goldman Y. E., Simmons R. M. The dependence of force and shortening velocity on substrate concentration in skinned muscle fibres from Rana temporaria. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:519–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godt R. E., Maughan D. W. Influence of osmotic compression on calcium activation and tension in skinned muscle fibers of the rabbit. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Oct;391(4):334–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00581519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Matsubara I., Simmons R. M. Lateral filamentary spacing in frog skinned muscle fibres in the relaxed and rigor states [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:80P–81P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harafuji H., Ogawa Y. Re-examination of the apparent binding constant of ethylene glycol bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid with calcium around neutral pH. J Biochem. 1980 May;87(5):1305–1312. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselgrove J. C., Huxley H. E. X-ray evidence for radial cross-bridge movement and for the sliding filament model in actively contracting skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jul 15;77(4):549–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90222-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E., Brown W. The low-angle x-ray diagram of vertebrate striated muscle and its behaviour during contraction and rigor. J Mol Biol. 1967 Dec 14;30(2):383–434. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. Structural difference between resting and rigor muscle; evidence from intensity changes in the lowangle equatorial x-ray diagram. J Mol Biol. 1968 Nov 14;37(3):507–520. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara I., Elliott G. F. X-ray diffraction studies on skinned single fibres of frog skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):657–669. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90183-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
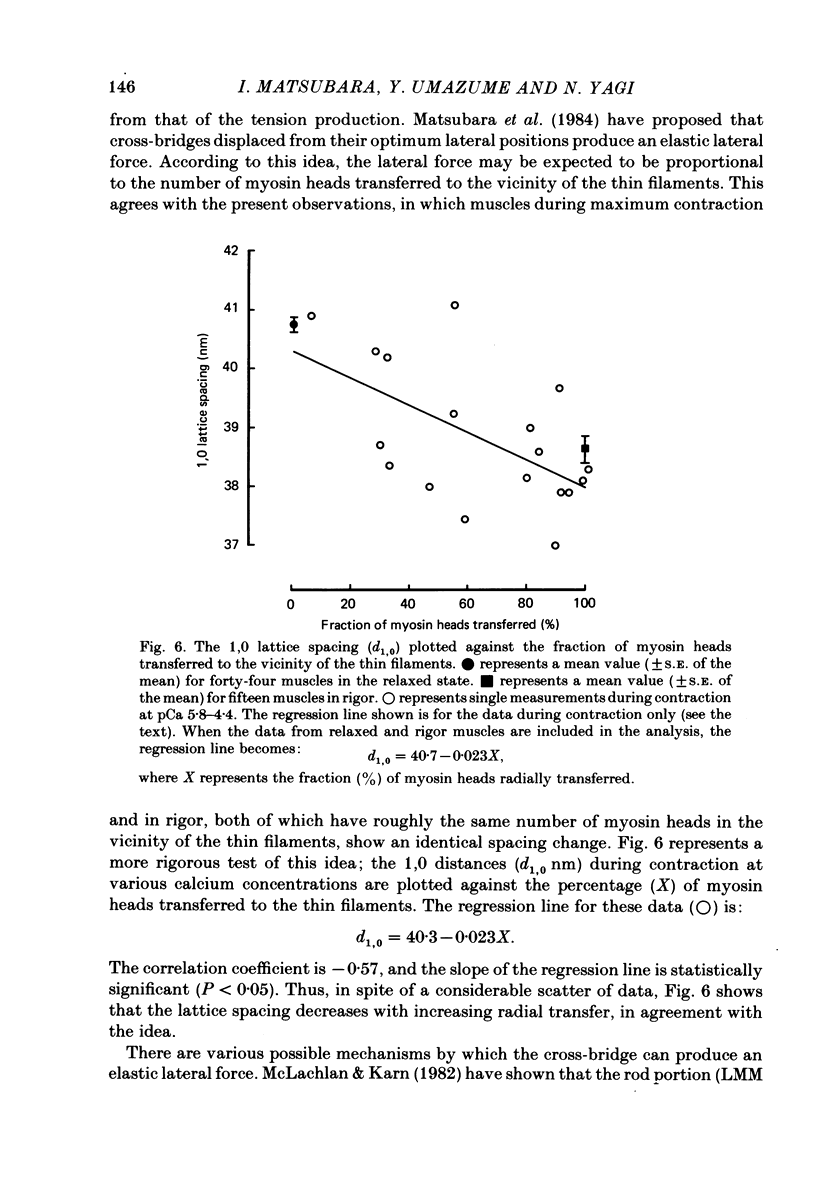
- Matsubara I., Goldman Y. E., Simmons R. M. Changes in the lateral filament spacing of skinned muscle fibres when cross-bridges attach. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 15;173(1):15–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara I., Yagi N., Hashizume H. Use of an X-ray television for diffraction of the frog striated muscle. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):728–729. doi: 10.1038/255728a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maughan D. W., Godt R. E. Radial forces within muscle fibers in rigor. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jan;77(1):49–64. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Karn J. Periodic charge distributions in the myosin rod amino acid sequence match cross-bridge spacings in muscle. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):226–231. doi: 10.1038/299226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moisescu D. G. Kinetics of reaction in calcium-activated skinned muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):610–613. doi: 10.1038/262610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
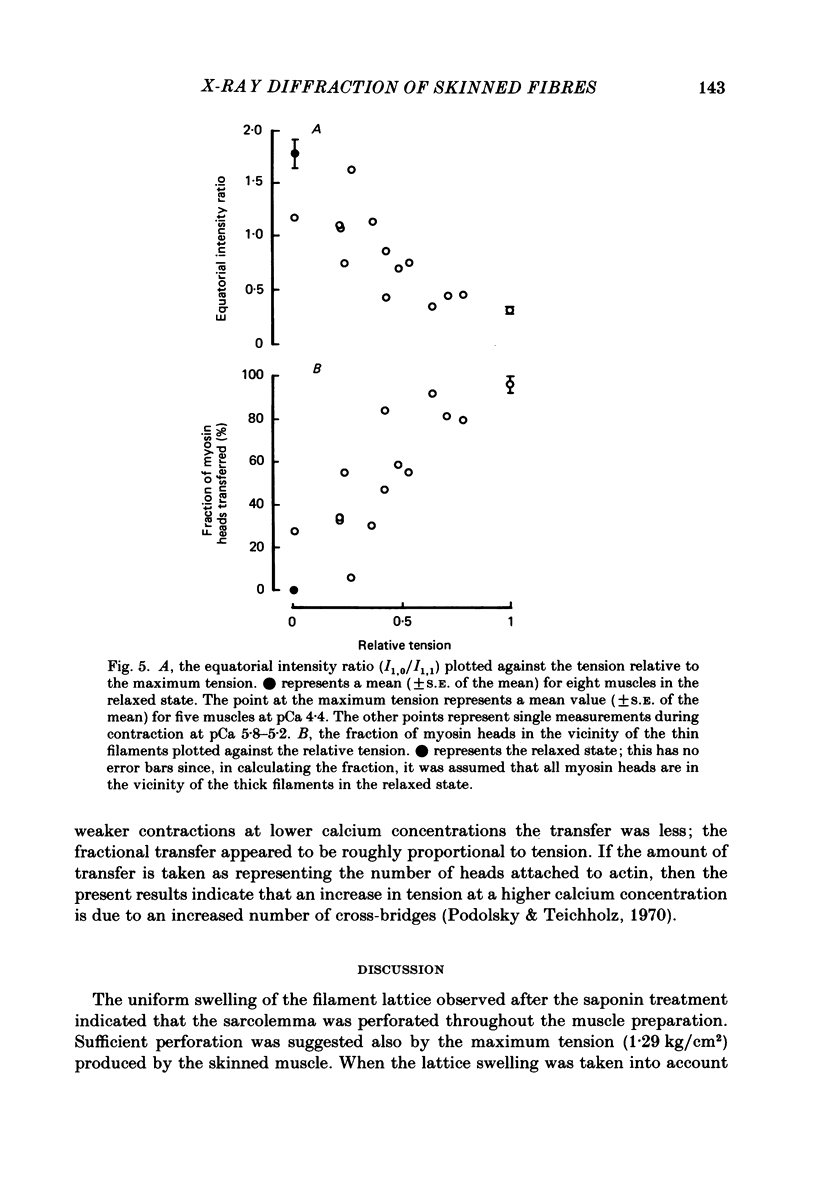
- Podolsky R. J., Teichholz L. E. The relation between calcium and contraction kinetics in skinned muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;211(1):19–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rome E. Light and X-ray diffraction studies of the filament lattice of glycerol-extracted rabbit psoas muscle. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 14;27(3):591–602. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rome E. Relaxation of glycerinated muscle: low-angle x-ray diffraction studies. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 28;65(2):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rome E. X-ray diffraction studies of the filament lattice of striated muscle in various bathing media. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 28;37(2):331–344. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg M. Geometrical factors influencing muscle force development. II. Radial forces. Biophys J. 1980 Apr;30(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85077-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L. P., Hartt J. E., Podolsky R. J. Equatorial x-ray intensities and isometric force levels in frog sartorius muscle. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 25;132(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90495-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



