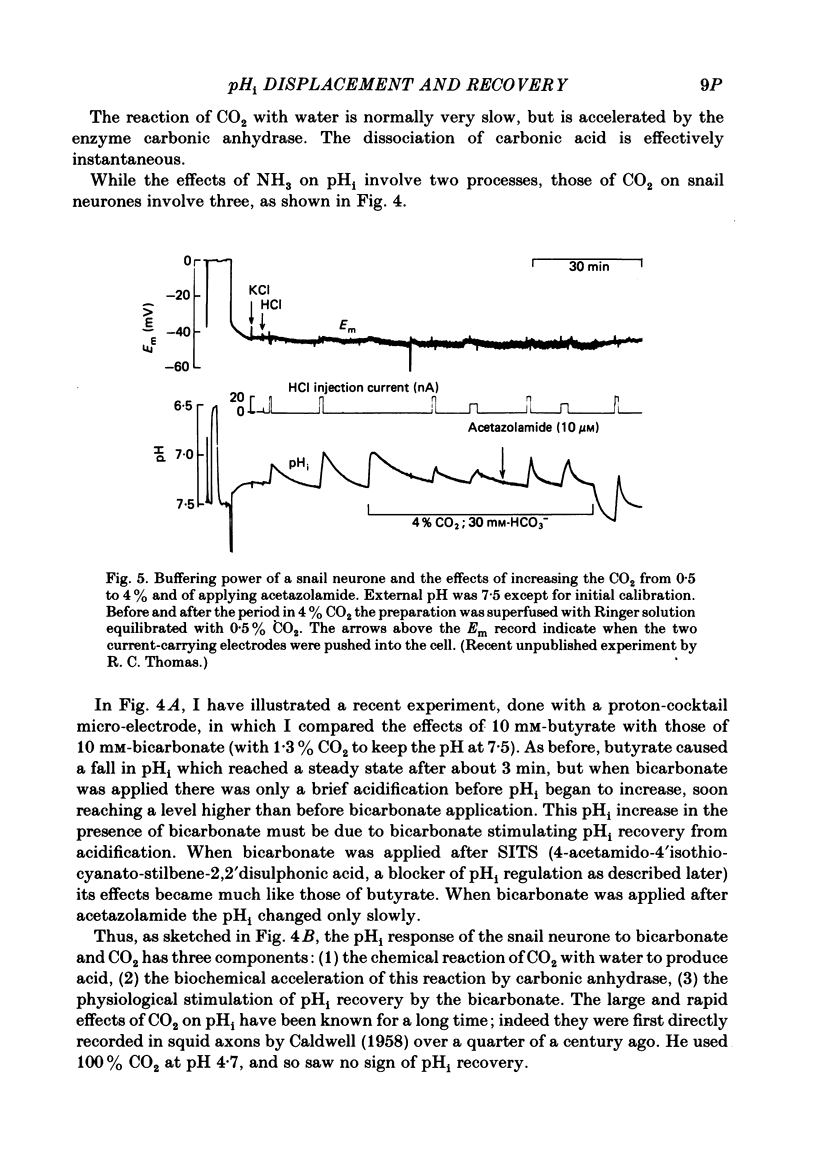
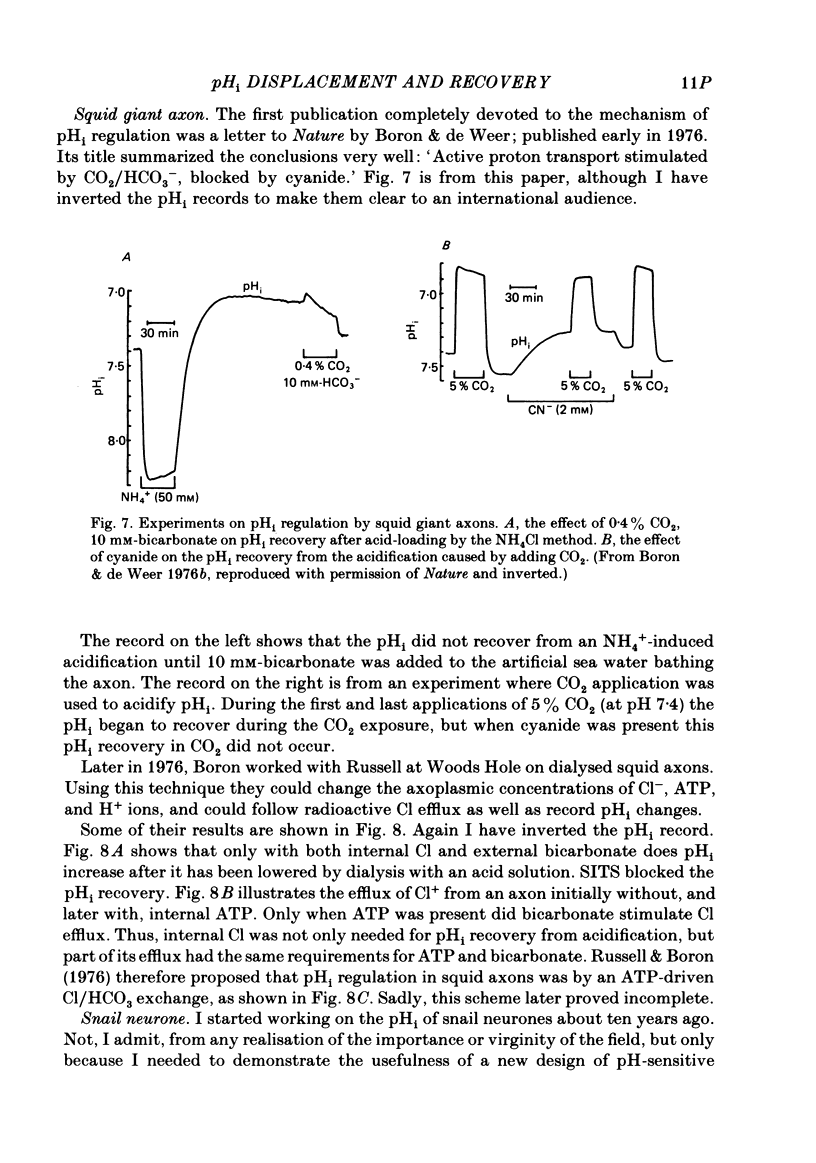
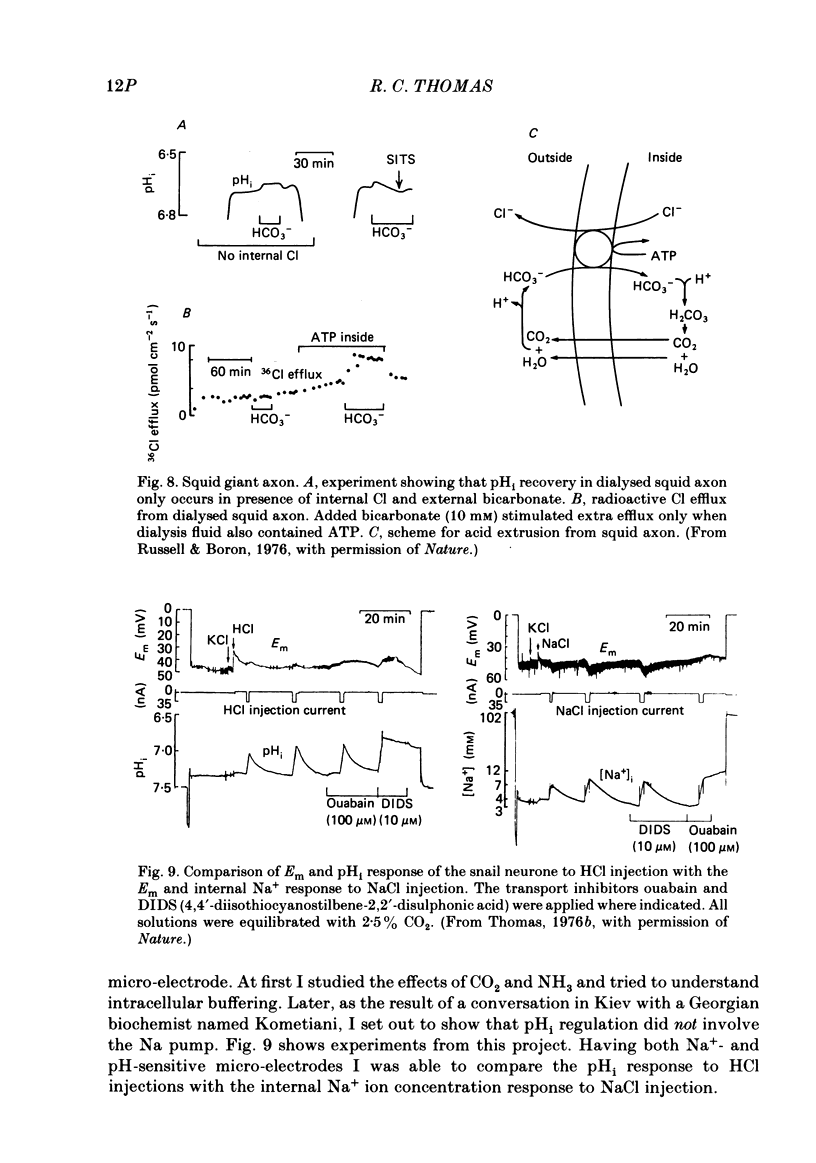
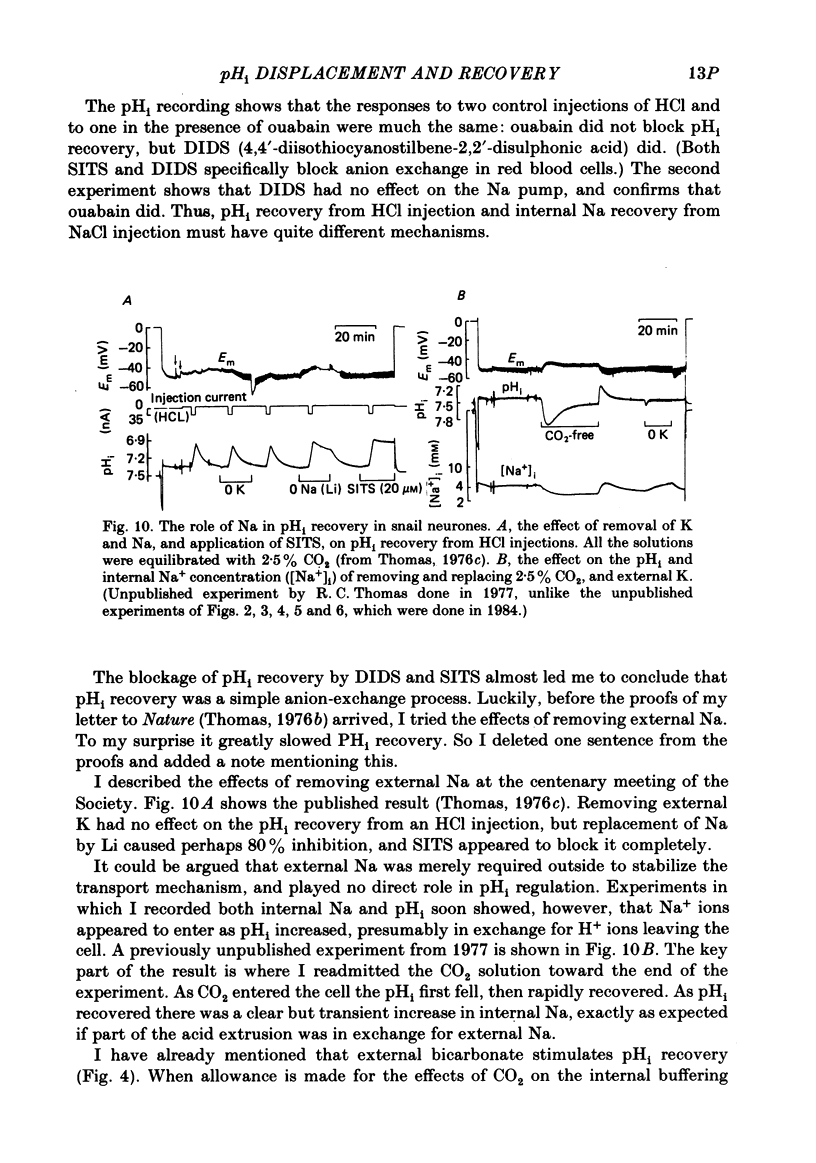
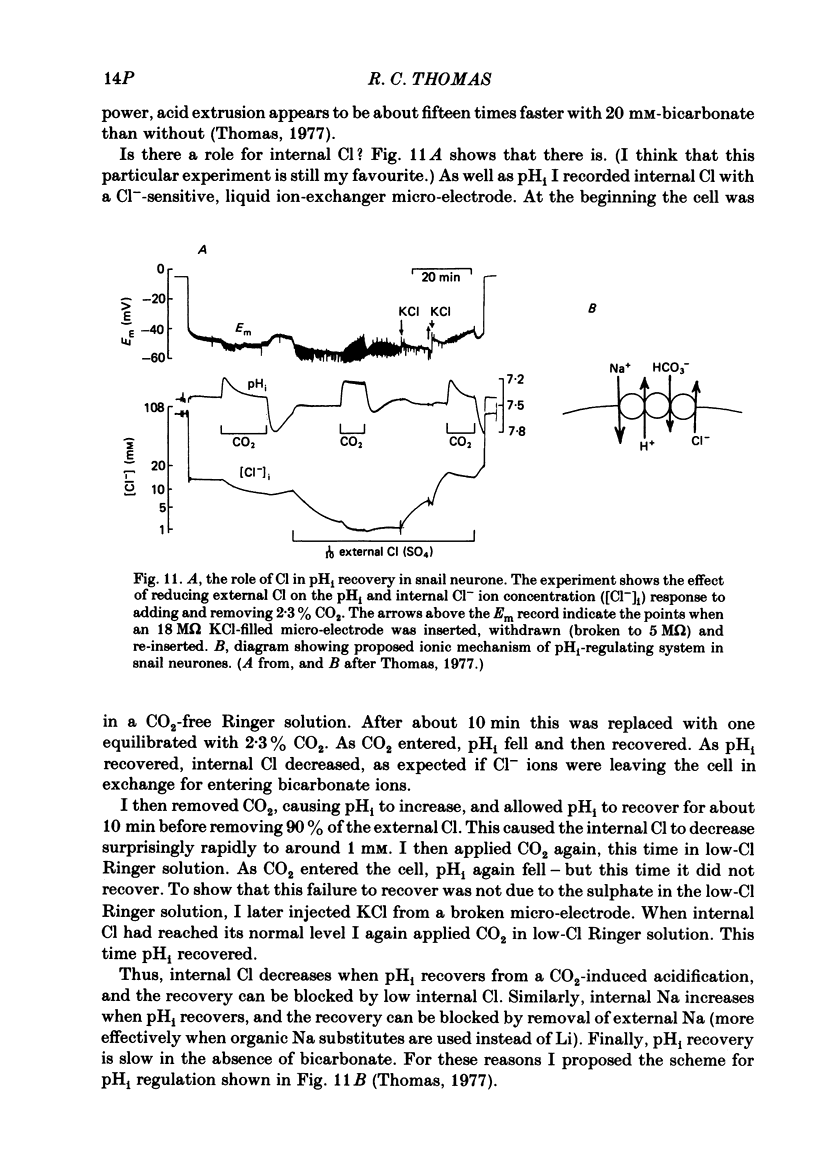
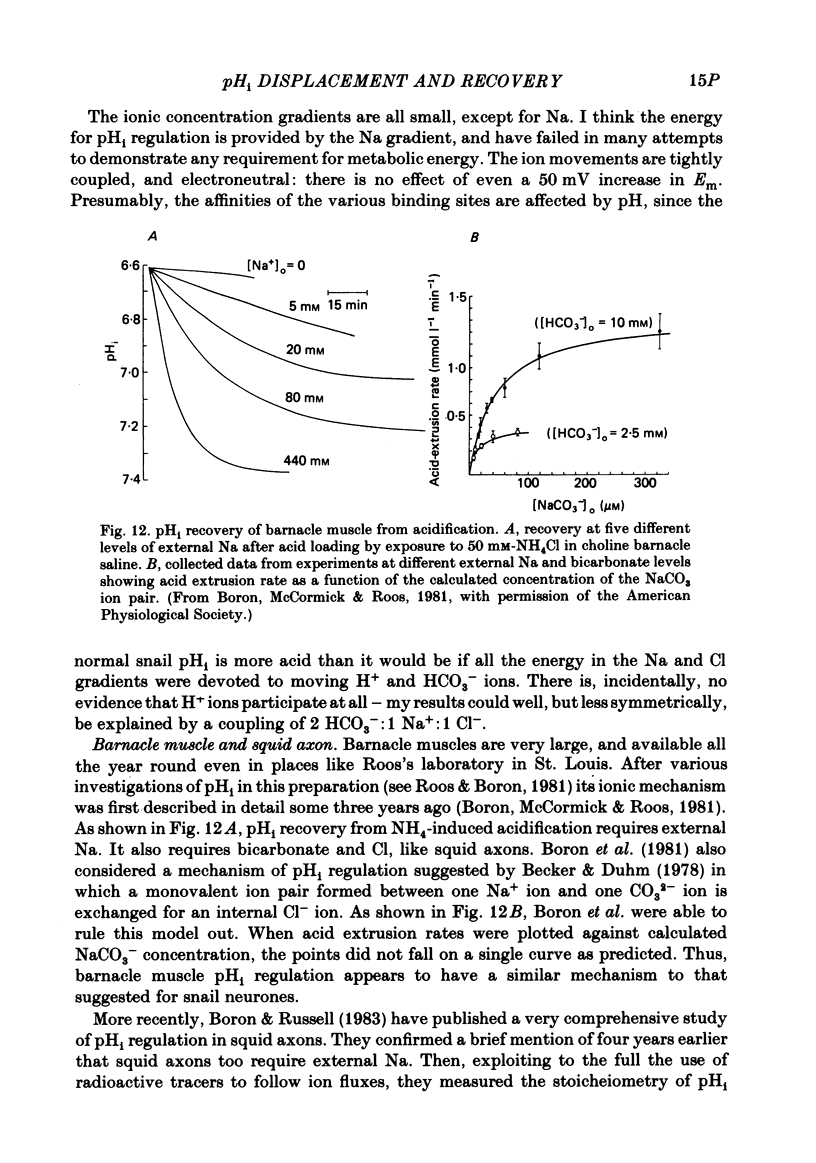
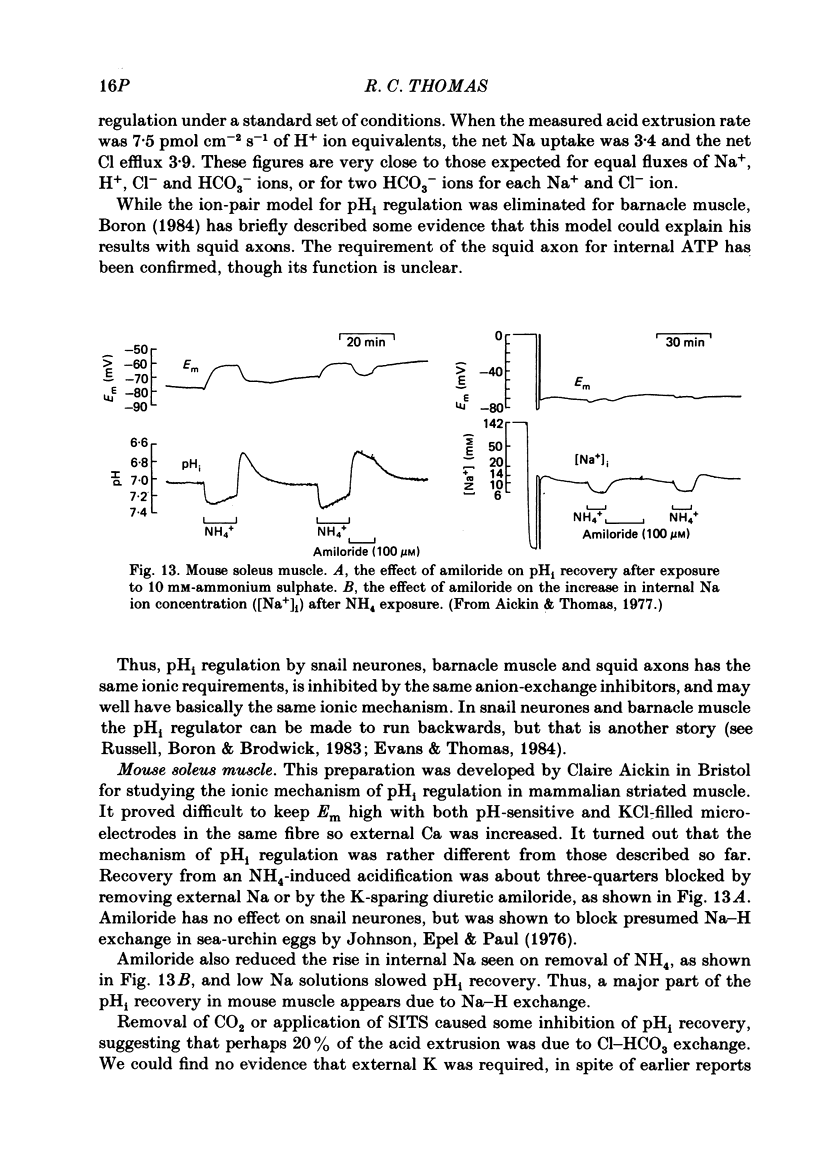
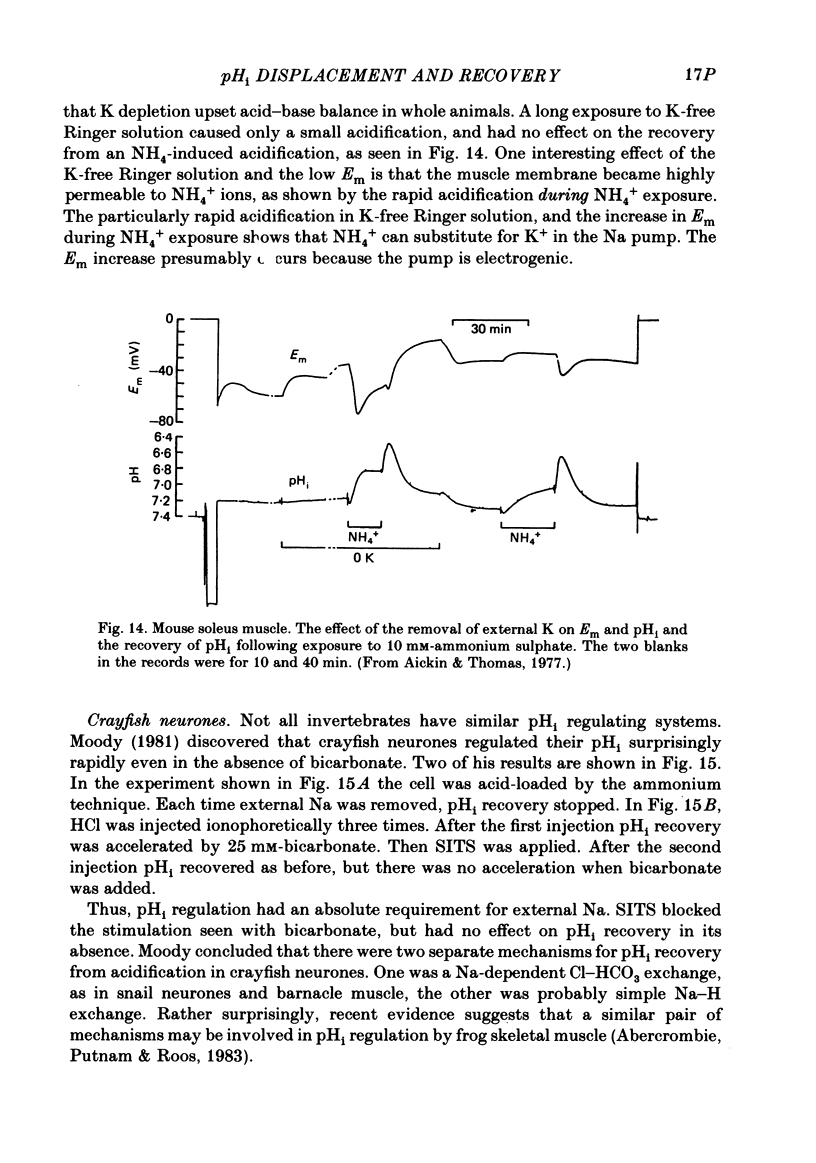
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abercrombie R. F., Putnam R. W., Roos A. The intracellular pH of frog skeletal muscle: its regulation in isotonic solutions. J Physiol. 1983 Dec;345:175–187. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aickin C. C. Direct measurement of intracellular pH and buffering power in smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:571–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aickin C. C., Thomas R. C. An investigation of the ionic mechanism of intracellular pH regulation in mouse soleus muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):295–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammann D., Lanter F., Steiner R. A., Schulthess P., Shijo Y., Simon W. Neutral carrier based hydrogen ion selective microelectrode for extra- and intracellular studies. Anal Chem. 1981 Dec;53(14):2267–2269. doi: 10.1021/ac00237a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker B. F., Duhm J. Evidence for anionic cation transport of lithium, sodium and potassium across the human erythrocyte membrane induced by divalent anions. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:149–168. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Boulpaep E. L. Intracellular pH regulation in the renal proximal tubule of the salamander. Na-H exchange. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jan;81(1):29–52. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., De Weer P. Active proton transport stimulated by CO2/HCO3-, blocked by cyanide. Nature. 1976 Jan 22;259(5540):240–241. doi: 10.1038/259240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., De Weer P. Intracellular pH transients in squid giant axons caused by CO2, NH3, and metabolic inhibitors. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jan;67(1):91–112. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Russell J. M. Stoichiometry and ion dependencies of the intracellular-pH-regulating mechanism in squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Mar;81(3):373–399. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F. Transport of H+ and of ionic weak acids and bases. J Membr Biol. 1983;72(1-2):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF01870311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALDWELL P. C. Studies on the internal pH of large muscle and nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1958 Jun 18;142(1):22–62. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W., Ellis D. Interactions between the regulation of the intracellular pH and sodium activity of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:471–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. G., Thomas R. C. Acid influx into snail neurones caused by reversal of the normal pHi-regulating system. J Physiol. 1984 Jan;346:143–154. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelin C., Vigne P., Lazdunski M. The amiloride-sensitive Na+/H+ antiport in 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6272–6276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Cohen S., Rothstein A. Cytoplasmic pH regulation in thymic lymphocytes by an amiloride-sensitive Na+/H+ antiport. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):341–369. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Epel D. Intracellular pH and activation of sea urchin eggs after fertilisation. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):661–664. doi: 10.1038/262661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody W. J., Jr The ionic mechanism of intracellular pH regulation in crayfish neurones. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:293–308. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Tsien R. Y., van der Saag P. T., de Laat S. W. Na+/H+ exchange and cytoplasmic pH in the action of growth factors in human fibroblasts. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):645–648. doi: 10.1038/304645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. M., Boron W. F., Brodwick M. S. Intracellular pH and Na fluxes in barnacle muscle with evidence for reversal of the ionic mechanism of intracellular pH regulation. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jul;82(1):47–78. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. M., Boron W. F. Role of choloride transport in regulation of intracellular pH. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):73–74. doi: 10.1038/264073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp A. P., Thomas R. C. The effects of chloride substitution on intracellular pH in crab muscle. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:71–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Intracellular pH of snail neurones measured with a new pH-sensitive glass mirco-electrode. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):159–180. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Ionic mechanism of the H+ pump in a snail neurone. Nature. 1976 Jul 1;262(5563):54–55. doi: 10.1038/262054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. The effect of carbon dioxide on the intracellular pH and buffering power of snail neurones. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):715–735. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. The role of bicarbonate, chloride and sodium ions in the regulation of intracellular pH in snail neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):317–338. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan-Jones R. D. Chloride activity and its control in skeletal and cardiac muscle. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 1;299(1097):537–548. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Tetraethylammonium contains an impurity which alkalizes cytoplasm and reduce calcium buffering in neurons. Brain Res. 1981 Mar 16;208(2):473–478. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Hemptinne A., Marrannes R., Vanheel B. Influence of organic acids on intracellular pH. Am J Physiol. 1983 Sep;245(3):C178–C183. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.3.C178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



