Abstract
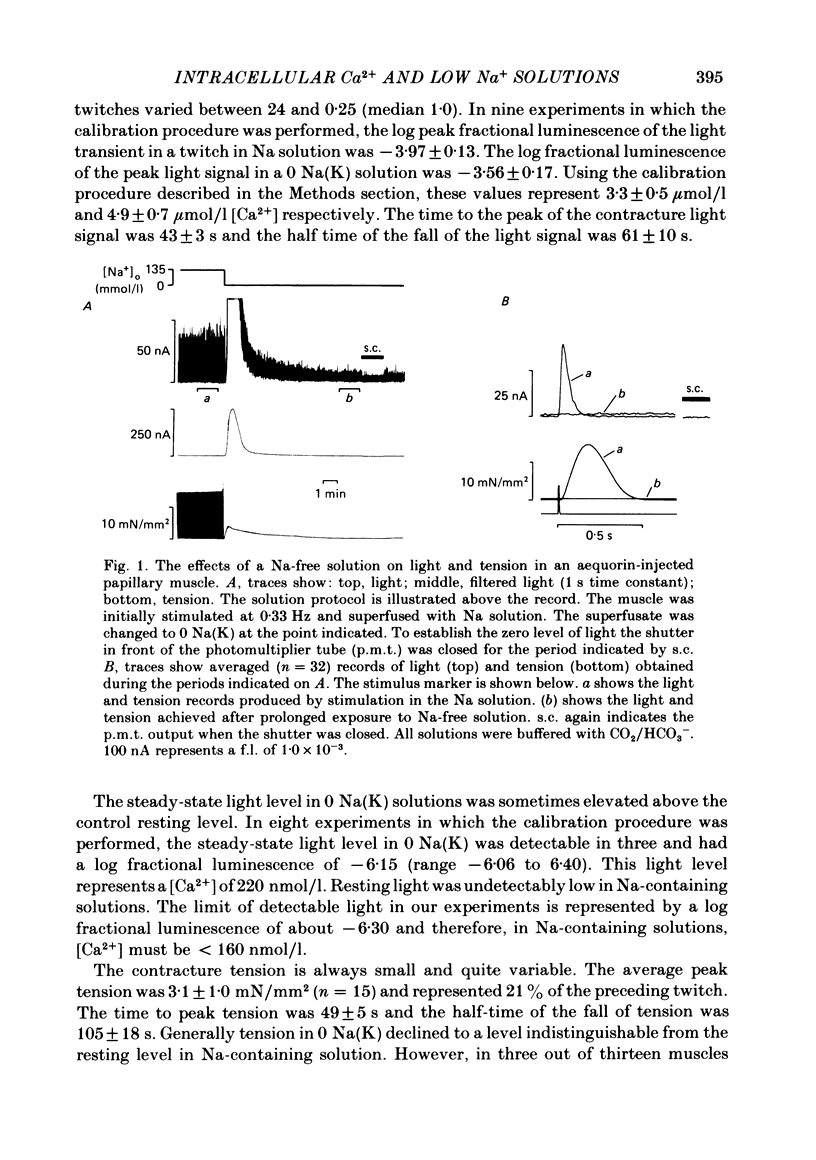
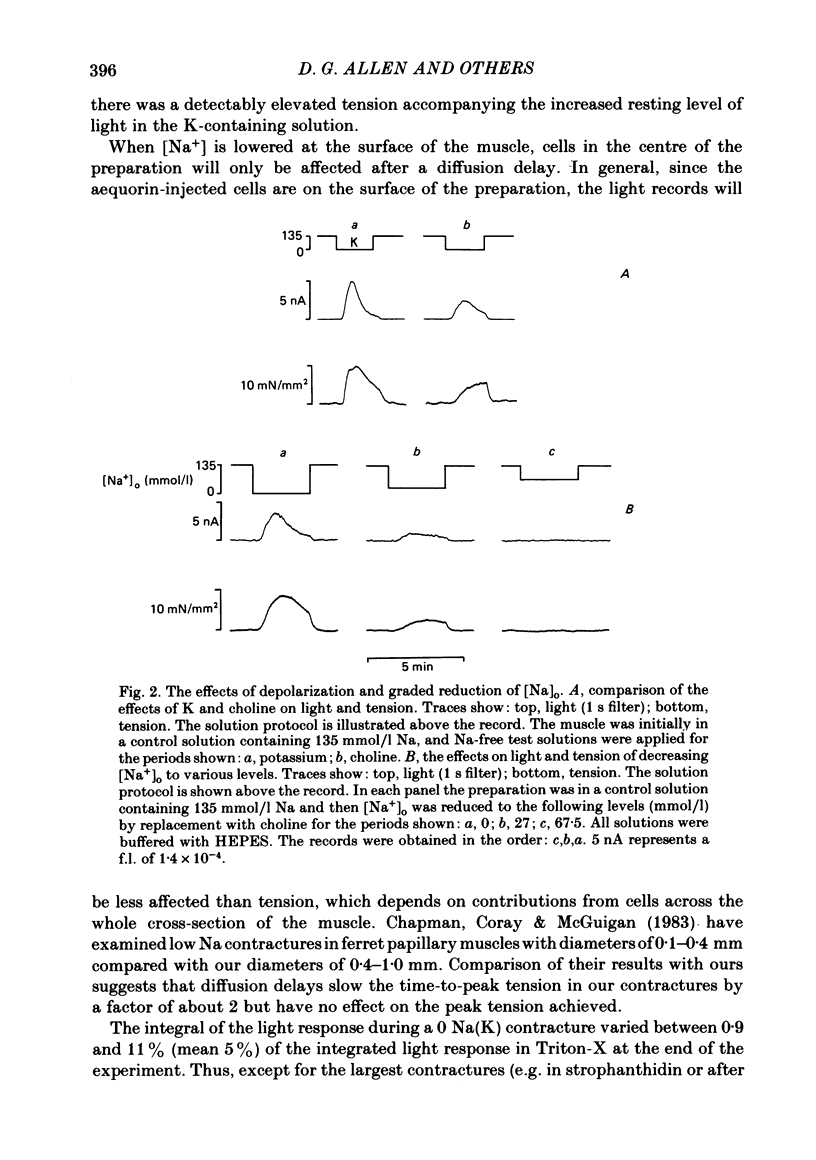
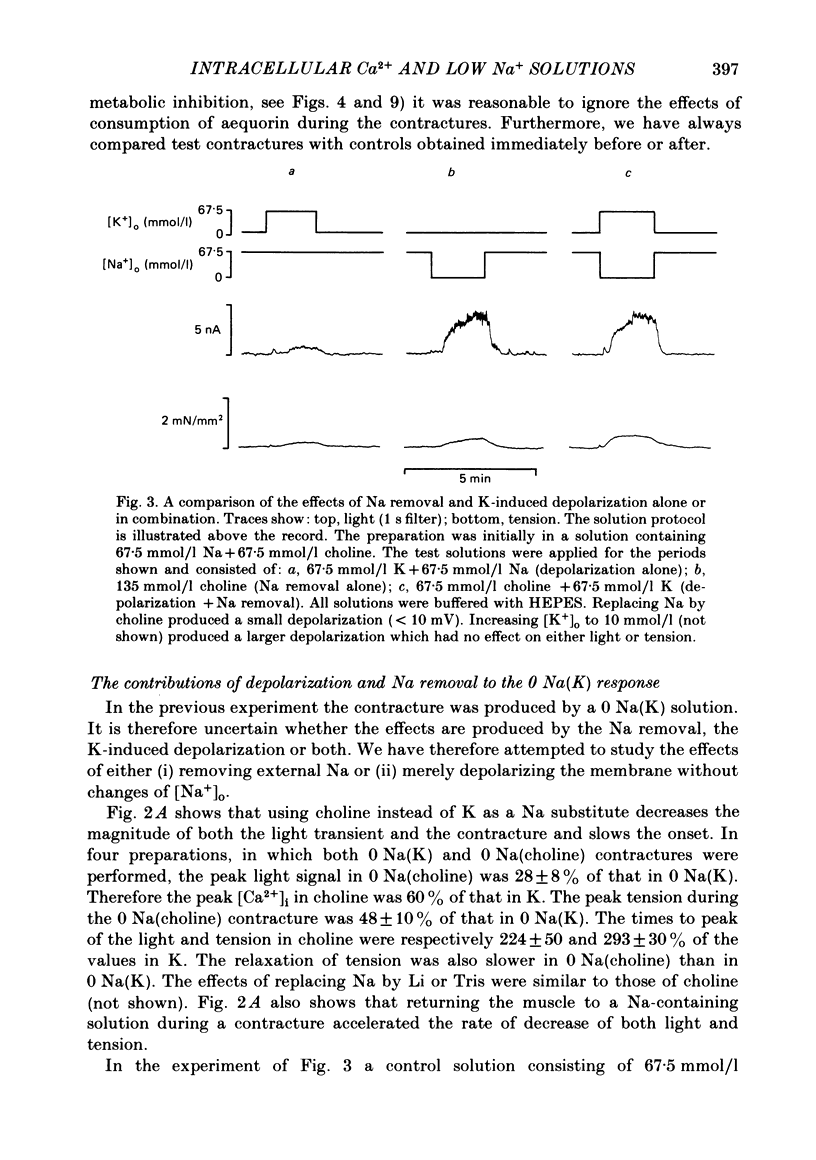
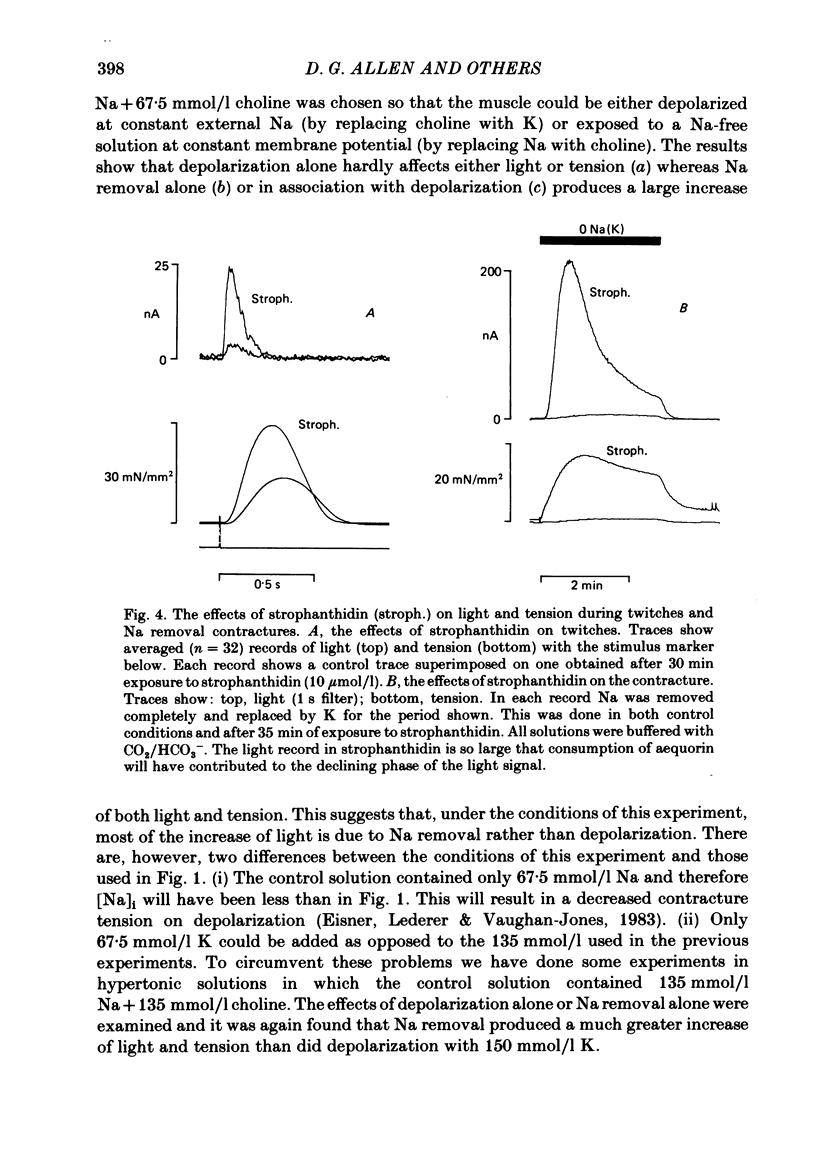
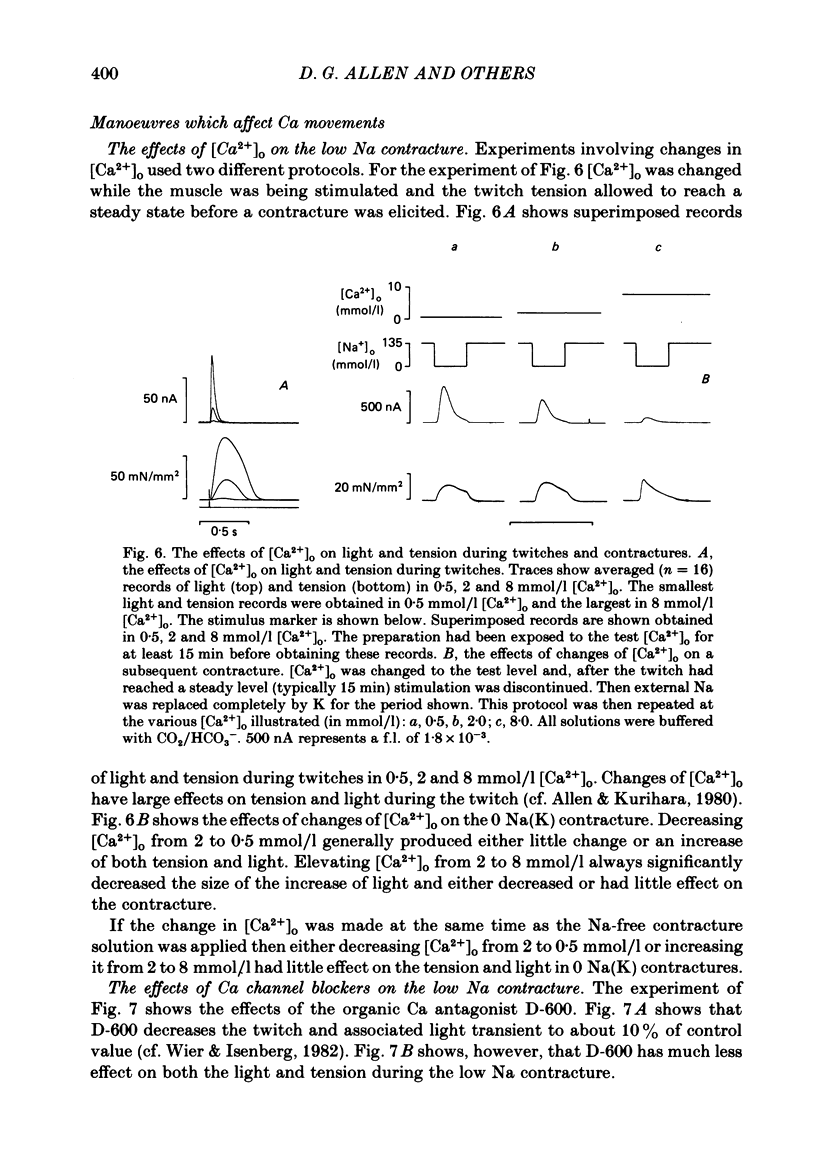
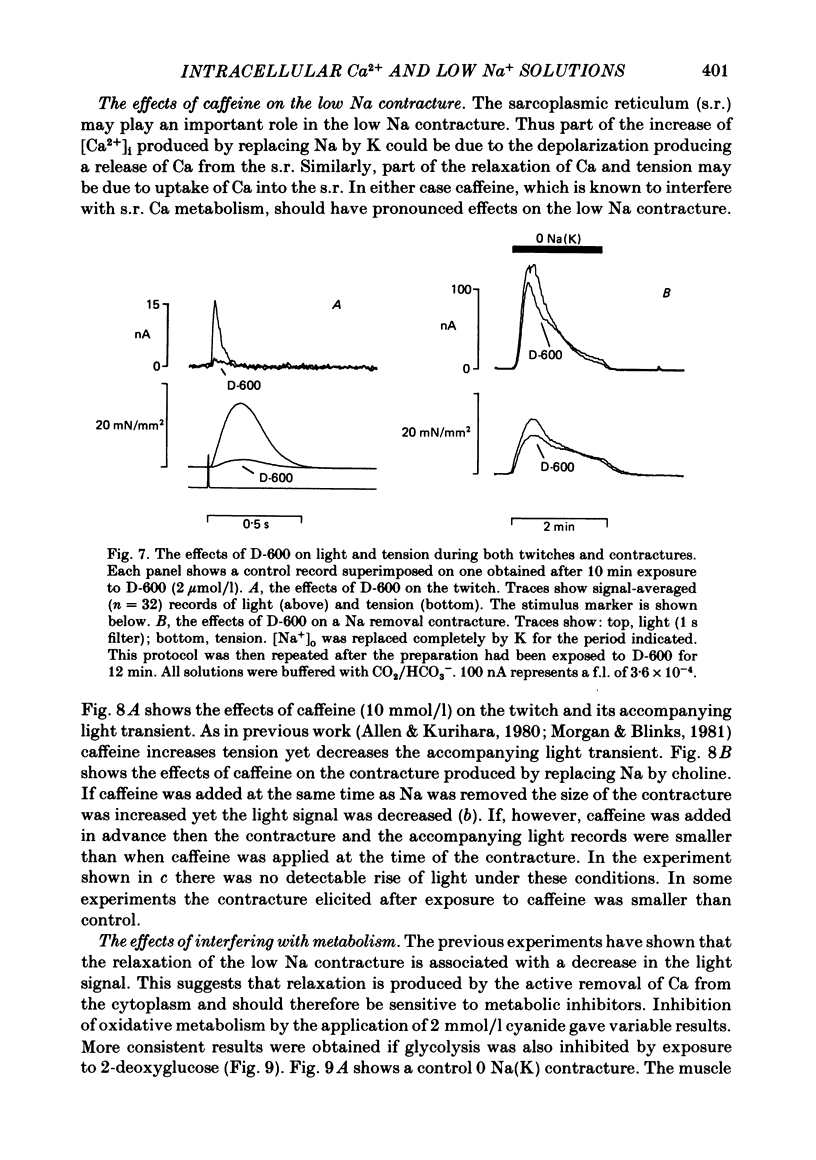
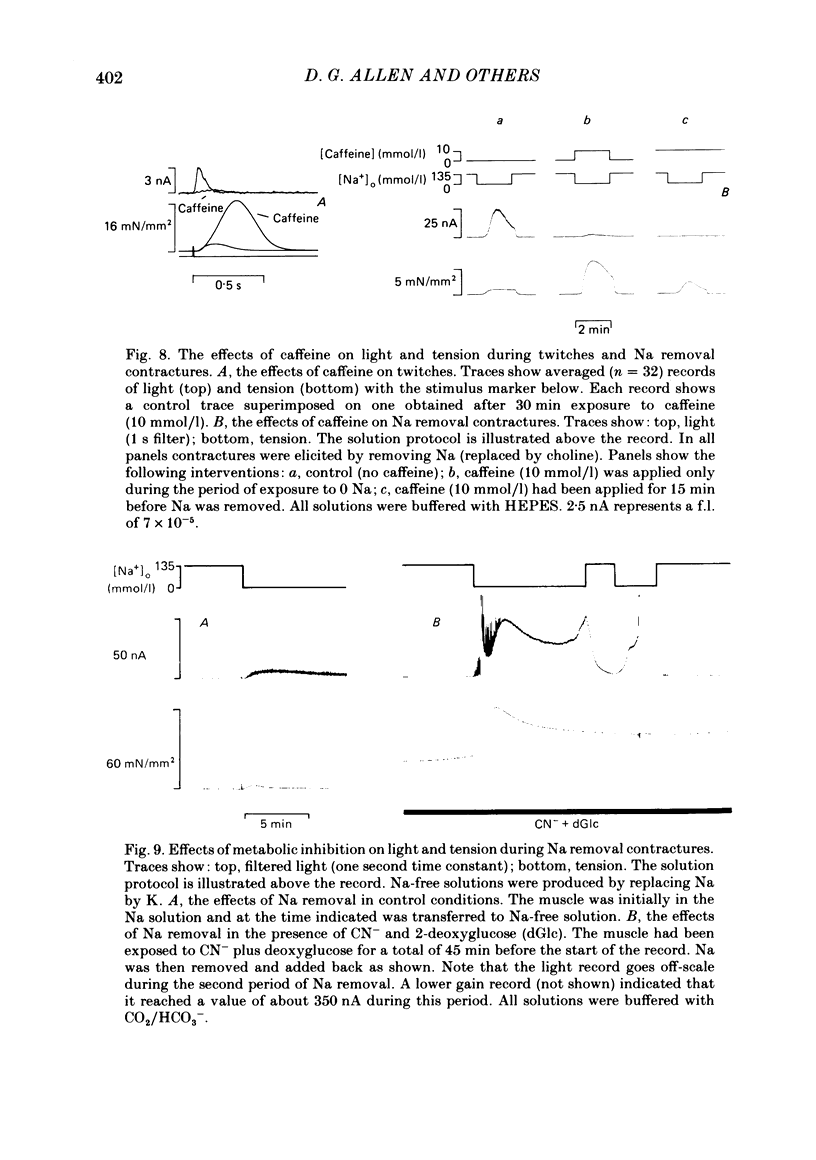
Papillary muscles from the right ventricles of ferrets were micro-injected with the photoprotein aequorin. Both tension and the light emitted by the aequorin, which is a measure of the free intracellular Ca concentration [( Ca2+]i), were monitored. Exposure of the papillary muscle to a solution in which all the Na had been replaced by K (0 Na(K) solution) resulted in an increase in tension which subsequently slowly decreased. This contracture was associated with a large increase in [Ca2+]i followed by a decrease to a steady-state-level which was often significantly greater than that in Na-containing solutions. If choline, Li or Tris was used instead of K as a substitute for Na, both the contracture and the associated increase of [Ca2+]i were reduced. The effects of depolarization alone (by raising external K at constant Na concentration) were compared with those of Na removal alone (at constant external K concentration). Na removal contributes more than depolarization to the effects of a Na-free, K-containing solution on the contracture and rise of [Ca2+]i. Increasing intracellular Na concentration [( Na+]i), by exposure to strophanthidin (10 mumol/l), increased the magnitude of both the contracture and [Ca2+]i in 0 Na(K) solutions. Conversely, decreasing [Na+]i by exposure to a solution containing a decreased extracellular Na concentration [( Na+]o), decreased the contracture and [Ca2+]i. When contractures were produced by solutions with various [Na+]o, the size of the resulting contracture and [Ca2+]i were inversely related to [Na+]o. No contracture was seen unless [Na+]o was reduced to below 70 mmol/l. A decrease in the extracellular Ca concentration [( Ca2+]o) from 2 to 0.5 mmol/l or an increase to 8 mmol/l produced, respectively, large decreases and increases of the twitch and accompanying Ca transient. However, if [Ca2+]o was changed at the same time as Na was replaced by K there was little effect on either the contracture or the rise of [Ca2+]i. If [Ca2+]o was changed before replacing Na by K then increasing [Ca2+]o from 2 to 8 mmol/l decreased, and decreasing [Ca2+]o from 2 to 0.5 mmol/l increased, the rise of [Ca2+]i produced by replacing Na by K. The difference between this result and that obtained when [Ca2+]o was changed at the same time as Na was removed may be due to changes of [Na+]i produced by prolonged exposure to an altered [Ca2+]o.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen D. G., Blinks J. R. Calcium transients in aequorin-injected frog cardiac muscle. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):509–513. doi: 10.1038/273509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen D. G., Blinks J. R., Prendergast F. G. Aequorin luminescence: relation of light emission to calcium concentration--a calcium-independent component. Science. 1977 Mar 11;195(4282):996–998. doi: 10.1126/science.841325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen D. G., Kurihara S. Calcium transients in mammalian ventricular muscle. Eur Heart J. 1980;Suppl A:5–15. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/1.suppl_1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen D. G., Orchard C. H. The effects of changes of pH on intracellular calcium transients in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:555–567. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P., Hodgkin A. L., Steinhardt R. A. The influence of calcium on sodium efflux in squid axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):431–458. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Ellis D. Intracellular calcium and sodium activity in sheep heart Purkinje fibres. Effect of changes of external sodium and intracellular pH. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Apr;393(2):171–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00582941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Wier W. G., Hess P., Prendergast F. G. Measurement of Ca2+ concentrations in living cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;40(1-2):1–114. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(82)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Carafoli E. An ATP-dependent Ca2+-pumping system in dog heart sarcolemma. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):765–767. doi: 10.1038/283765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. A. A study of the contractures induced in frog atrial trabeculae by a reduction of the bathing sodium concentration. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):295–313. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. A., Coray A., McGuigan J. A. Sodium/calcium exchange in mammalian ventricular muscle: a study with sodium-sensitive micro-electrodes. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:253–276. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W., Ellis D. Changes in the intracellular sodium activity of sheep heart Purkinje fibres produced by calcium and other divalent cations. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:437–453. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W., Ellis D. Interactions between the regulation of the intracellular pH and sodium activity of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:471–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner D. A., Lederer W. J., Vaughan-Jones R. D. The control of tonic tension by membrane potential and intracellular sodium activity in the sheep cardiac Purkinje fibre. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:723–743. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis D., Deitmer J. W. The relationship between the intra- and extracellular sodium activity of sheep heart Purkinje fibres during inhibition of the Na-K pump. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Nov 30;377(3):209–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00584274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Effects of magnesium on contractile activation of skinned cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):497–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Effects of pH on the myofilaments and the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned cells from cardiace and skeletal muscles. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:233–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons W. R., Fozzard H. A. High potassium and low sodium contractures in sheep cardiac muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Nov;58(5):483–510. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.5.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glitsch H. G., Reuter H., Scholz H. The effect of the internal sodium concentration on calcium fluxes in isolated guinea-pig auricles. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):25–43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUTTGAU H. C., NIEDERGERKE R. The antagonism between Ca and Na ions on the frog's heart. J Physiol. 1958 Oct 31;143(3):486–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakatta E. G., Lappé D. L. Diastolic scattered light fluctuation, resting force and twitch force in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:369–394. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClellan G. B., Winegrad S. Cyclic nucleotide regulation of the contractile proteins in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Mar;75(3):283–295. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. J., Moisescu D. G. The effects of very low external calcium and sodium concentrations on cardiac contractile strength and calcium-sodium antagonism. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(2):283–308. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mope L., McClellan G. B., Winegrad S. Calcium sensitivity of the contractile system and phosphorylation of troponin in hyperpermeable cardiac cells. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Mar;75(3):271–282. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Blinks J. R. Intracellular Ca2+ transients in the cat papillary muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Apr;60(4):524–528. doi: 10.1139/y82-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J., Requena J. The "late" Ca channel in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Dec;78(6):683–700. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.6.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Goodman D. B. Relationships between calcium and cyclic nucleotides in cell activation. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jul;57(3):421–509. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.3.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Seitz N. The dependence of calcium efflux from cardiac muscle on temperature and external ion composition. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):451–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheu S. S., Fozzard H. A. Transmembrane Na+ and Ca2+ electrochemical gradients in cardiac muscle and their relationship to force development. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Sep;80(3):325–351. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ventura-Clapier R., Vassort G. Rigor tension during metabolic and ionic rises in resting tension in rat heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):551–561. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(81)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Herz R. The relationship between caffeine contracture of intact muscle and the effect of caffeine on reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Nov;52(5):750–759. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.5.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wier W. G., Isenberg G. Intracellular [Ca2+] transients in voltage clamped cardiac Purkinje fibers. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Jan;392(3):284–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00584312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


