Abstract
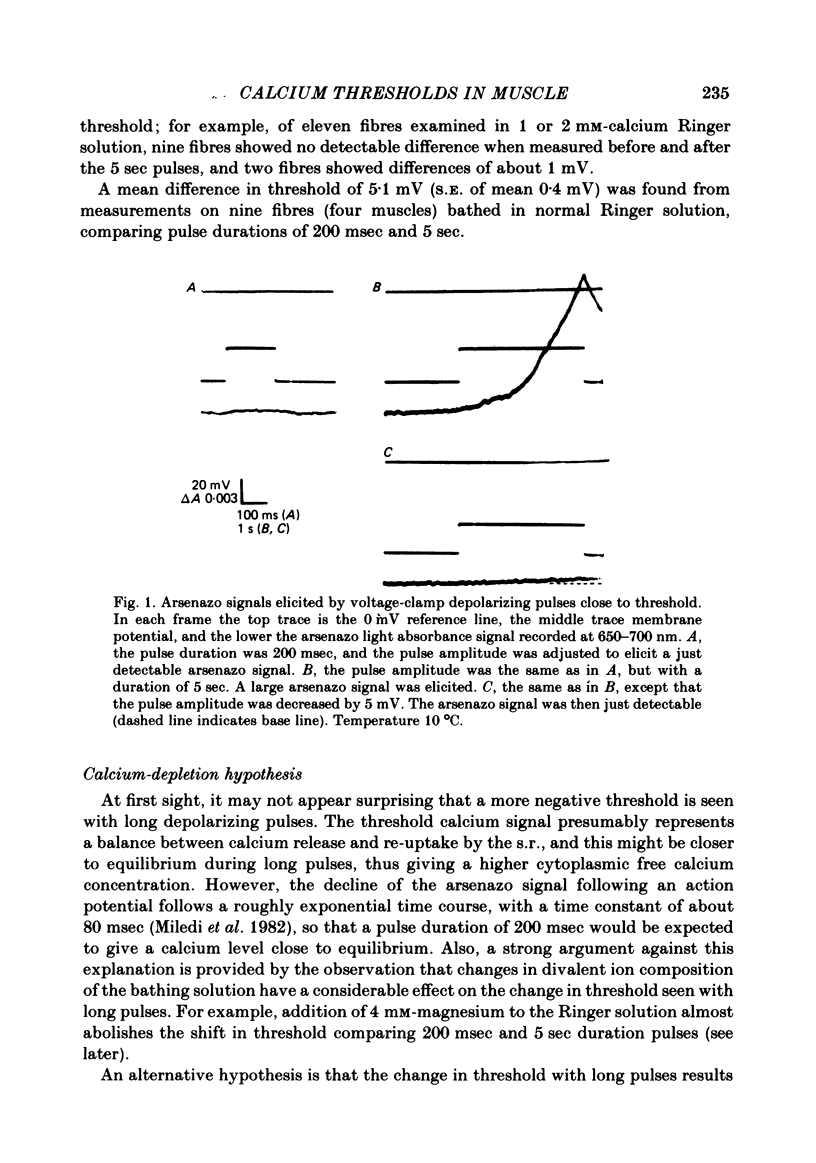
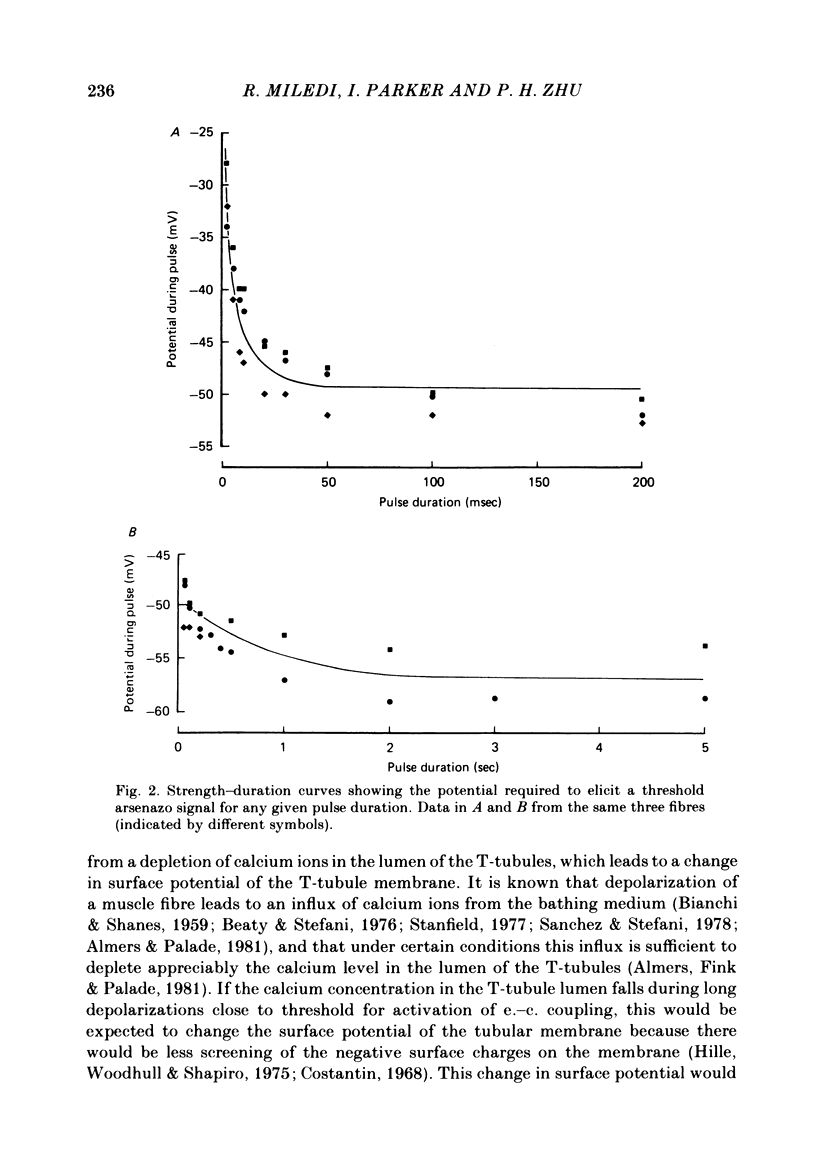
Strength-duration curves were measured for voltage-clamp depolarizations required to elicit a just detectable rise in intracellular calcium, as monitored using arsenazo III, in frog twitch muscle fibres. In normal Ringer solution, the threshold for a 5 sec duration depolarization was about 5 mV more negative than for a 200 msec duration pulse. The shift in threshold comparing 200 msec and 5 sec pulses was almost abolished in bathing solutions including magnesium or nickel (4 mM), or where the free calcium concentration was buffered. The shift in threshold was little changed by substitution of barium for calcium. These results can be explained by supposing that the 5 sec depolarization activates an inward calcium flux across the T-tubule membrane, which decreases the calcium concentration in the tubules, and hence alters the threshold for activation of excitation-contraction (e.-c.) coupling because of surface charge effects.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. The kinetics of mechanical activation in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):207–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Best P. M. Effects of tetracaine on displacement currents and contraction of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(3):583–611. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Fink R., Palade P. T. Calcium depletion in frog muscle tubules: the decline of calcium current under maintained depolarization. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:177–207. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Palade P. T. Slow calcium and potassium currents across frog muscle membrane: measurements with a vaseline-gap technique. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:159–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIANCHI C. P., SHANES A. M. Calcium influx in skeletal muscle at rest, during activity, and during potassium contracture. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Mar 20;42(4):803–815. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.4.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaty G. N., Stefani E. Calcium dependent electrical activity in twitch muscle fibres of the frog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Aug 27;194(1114):141–150. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantin L. L. The effect o f calcium on contraction and conductance thresholds in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(1):119–132. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács L., Schneider M. F. Contractile activation by voltage clamp depolarization of cut skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:483–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Zhu P. H. Calcium transients evoked by action potentials in frog twitch muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:655–679. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Zhu P. H. Calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres following conditioning stimuli. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:223–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Zhu P. H. Calcium transients studied under voltage-clamp control in frog twitch muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:649–680. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peachey L. D. The sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse tubules of the frog's sartorius. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3 Suppl):209–231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez J. A., Stefani E. Inward calcium current in twitch muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:197–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons T. J. The preparation of human red cell ghosts containing calcium buffers. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;256(1):209–225. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siri L. N., Sánchez J. A., Stefani E. Effect of glycerol treatment on the calcium current of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:87–96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. A calcium dependent inward current in frog skeletal muscle fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Apr 25;368(3):267–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00585206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. The effect of the tetraethylammonium ion on the delayed currents of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):209–229. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani E., Chiarandini D. J. Ionic channels in skeletal muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:357–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


