Abstract
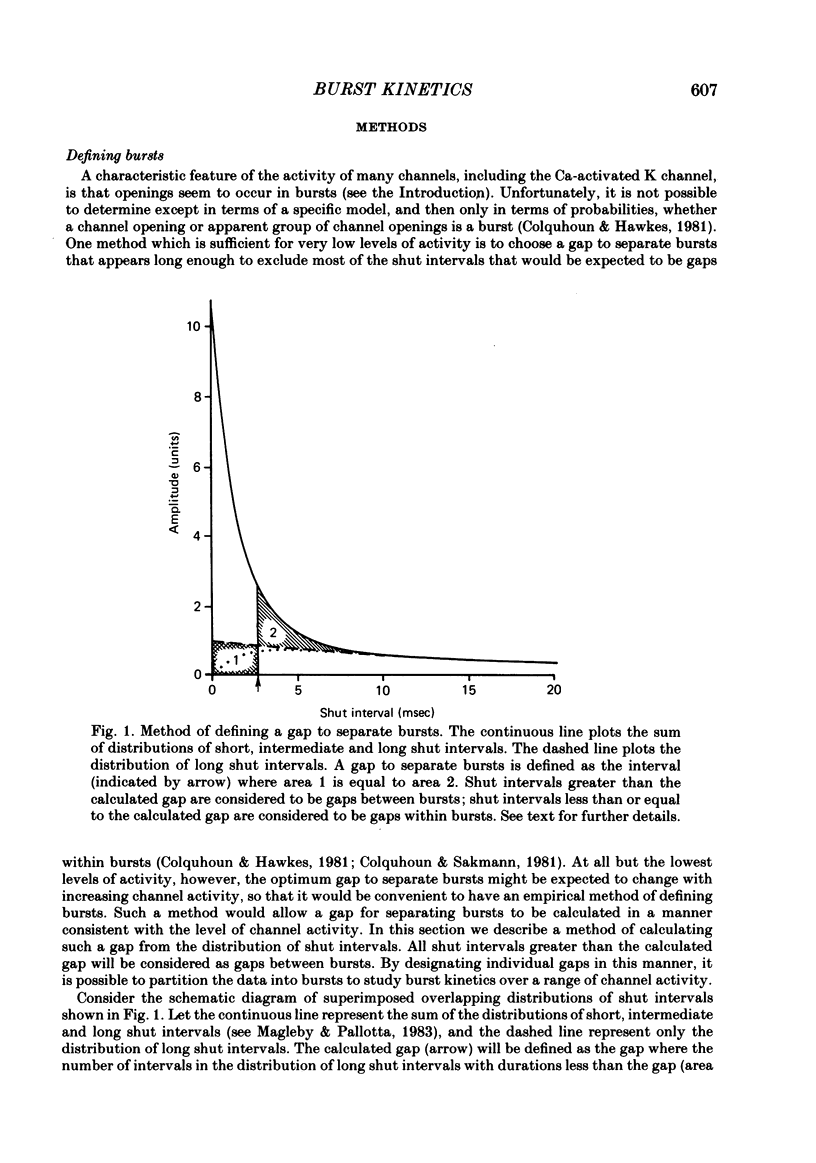
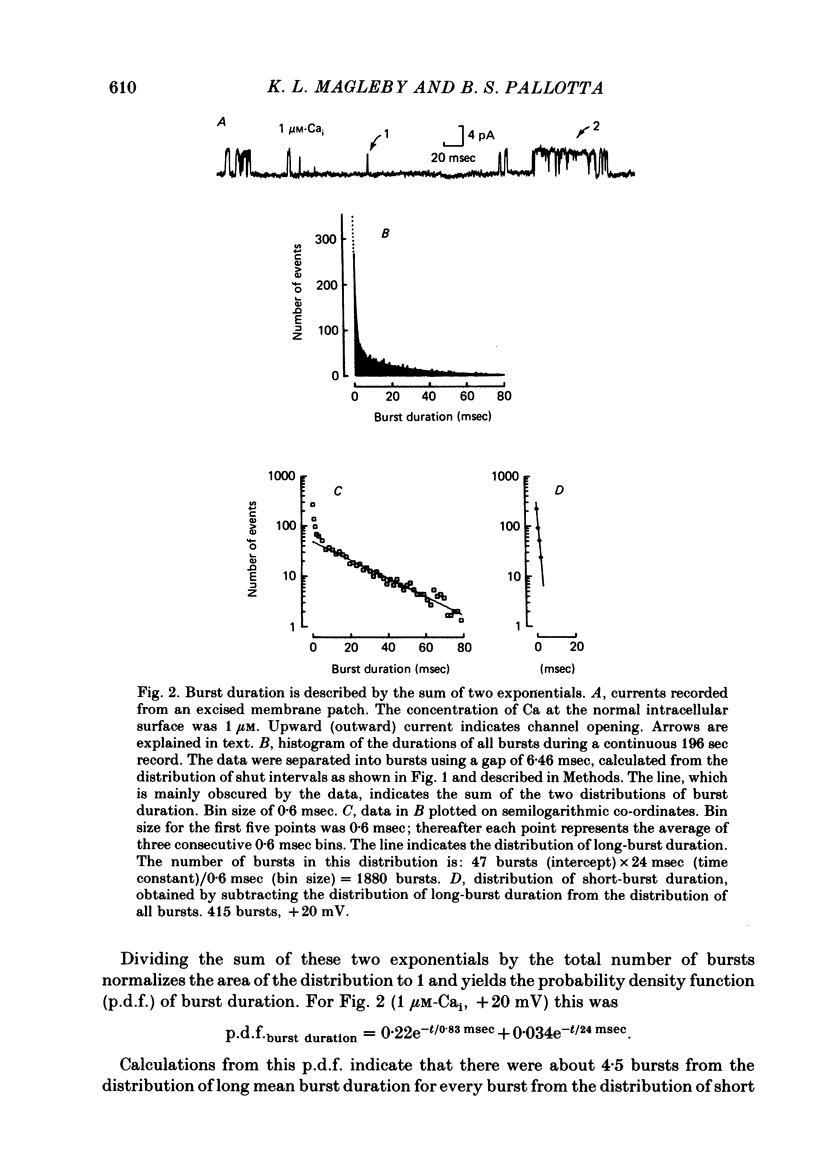
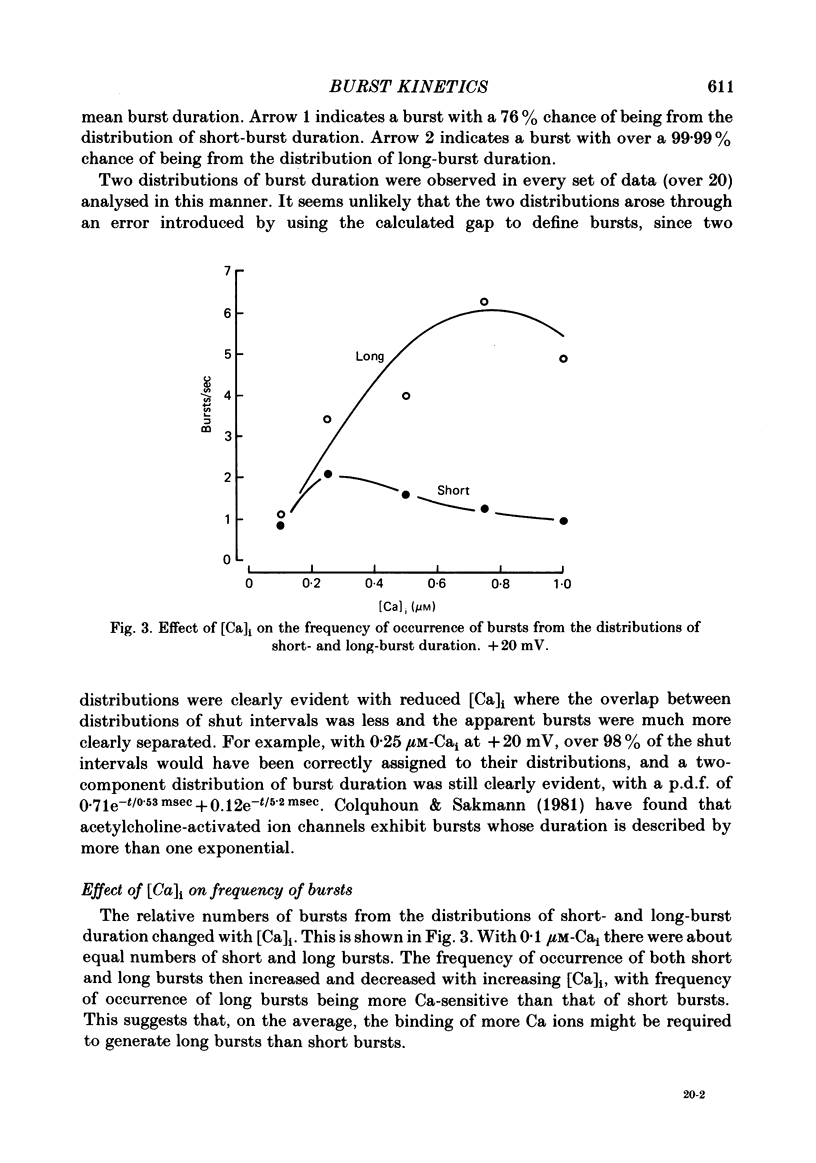
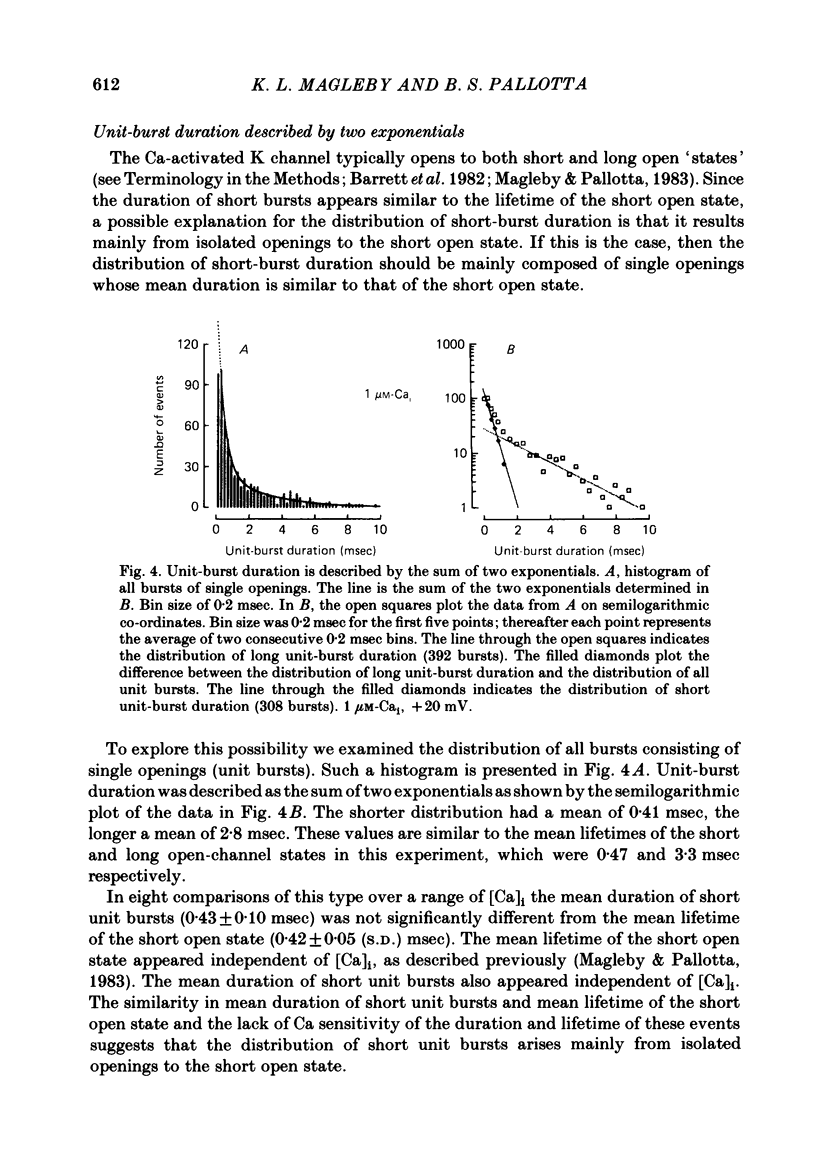
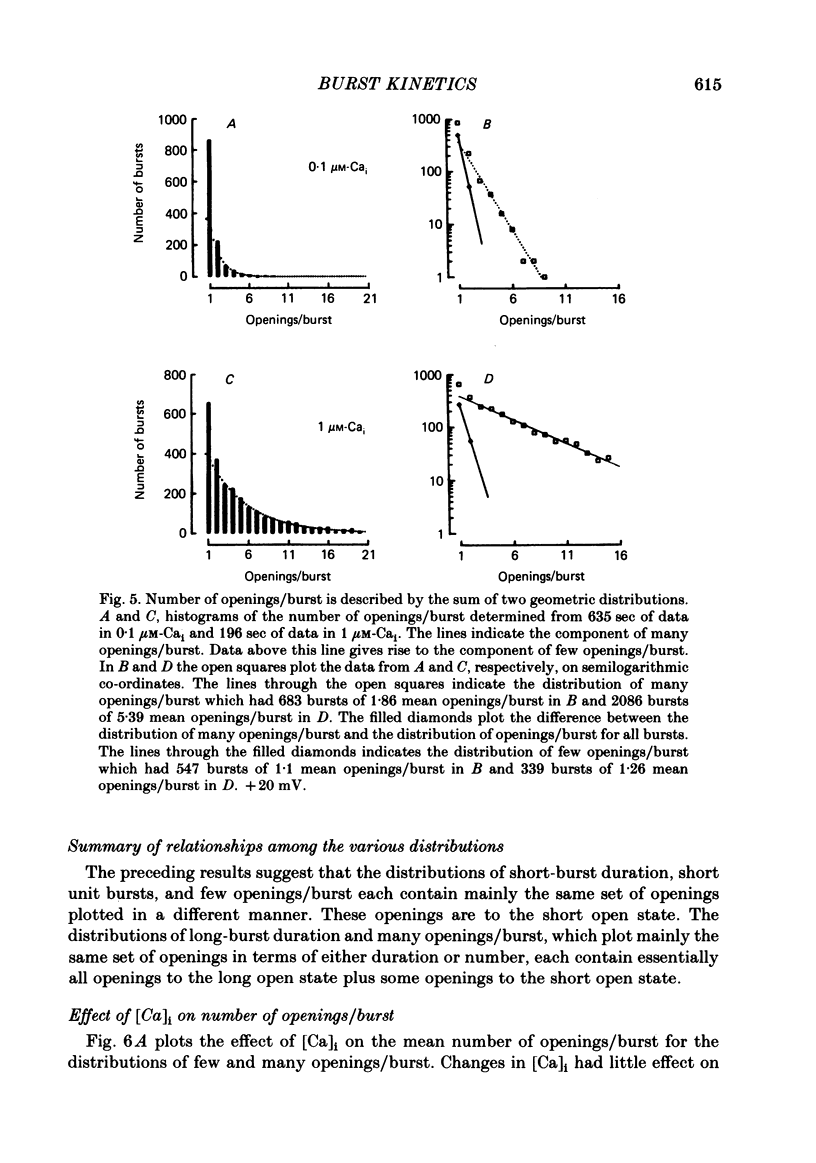
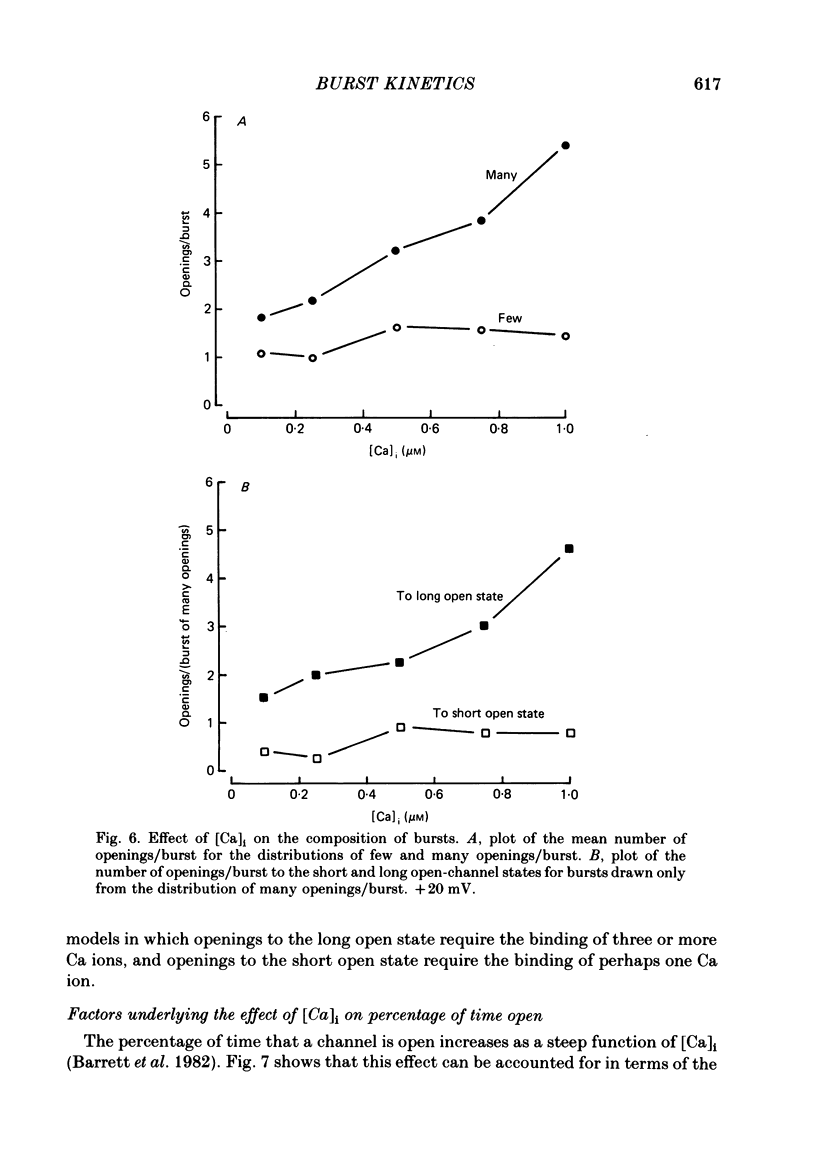
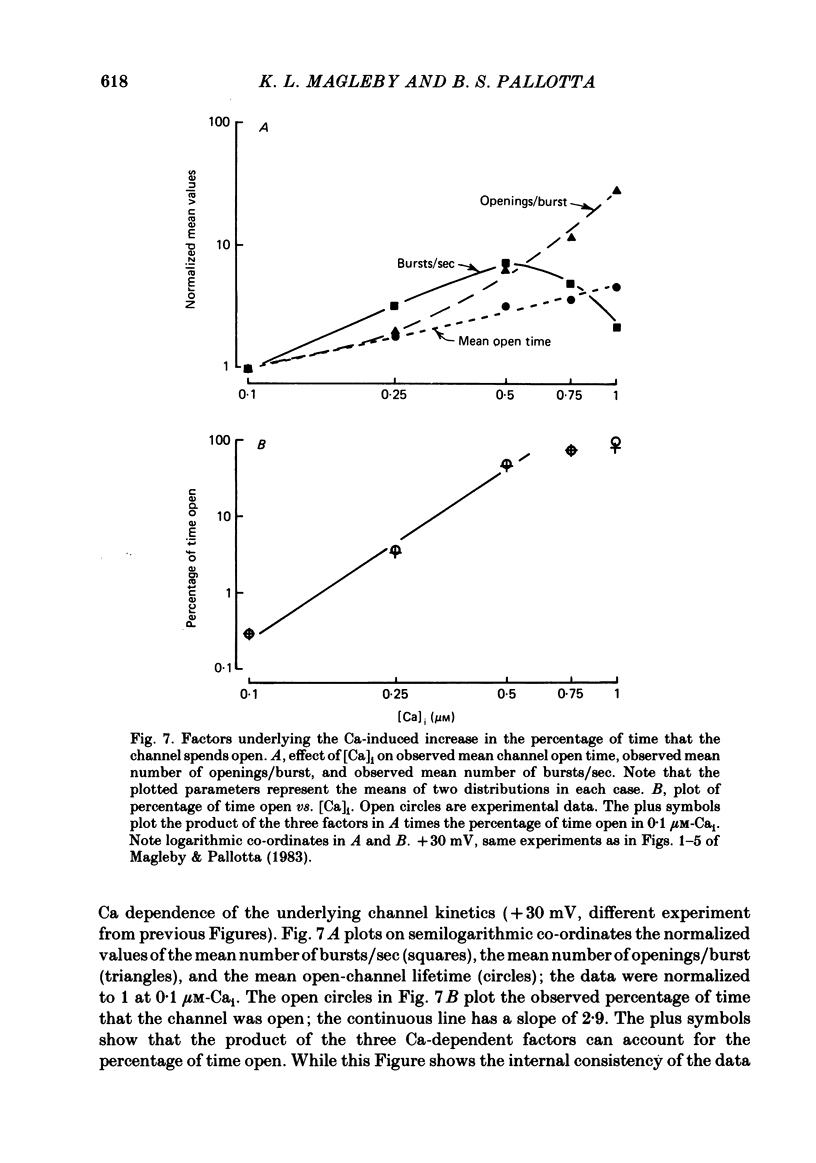
Burst kinetics of single Ca-activated K channels in excised patches of surface membrane from cultured rat muscle were studied using the patch-clamp technique. Channel activity was separated into bursts using a calculated gap derived from the distribution of shut intervals. Shut intervals greater than the calculated gap were taken as gaps between bursts. The distribution of burst duration was described as the sum of two exponentials with mean durations of about 0.8 and 24 msec (1 microM-Cai, + 20 mV), suggesting two classes of bursts (short and long). The composition of short and long bursts was determined from comparisons of the distributions of open intervals, unit bursts (bursts of single openings), and openings/burst. Short bursts consisted mainly of single openings to the open channel state of short mean lifetime. Long bursts consisted of one or more openings to the (compound) open-channel state of long mean lifetime, plus, in fewer than 70% of the long bursts, one or more openings to the short open-channel state. The frequency of occurrence of bursts from each class first increased and then decreased with increasing [Ca]i, with the number of long bursts increasing at a greater rate than the number of short bursts. The number of openings/short burst was relatively independent of [Ca]i, while the number of openings/long burst increased, often more than linearly, with increasing [Ca]i. This increase arose almost entirely from an increase in openings to the long open state. These results suggest that openings to the long open state typically require the binding of three or more Ca ions, and openings to the short open state typically require the binding of at least one Ca ion. This is the case whether the openings occur in isolation as bursts of single openings or in bursts composed of both types of openings. An obvious burst of channel activity would occur when the channel opens and closes several times without losing all its bound Ca. The power relationship between [Ca]i and the percentage of time spent in the open state is accounted for in terms of the effects of [Ca]i upon mean channel open time, openings/burst, and burst rate. A model is presented that describes quantitatively many features of the burst kinetics of the Ca-activated K channel for constant [Ca]i.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett J. N., Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:211–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of bursts of single ion channel openings and of clusters of bursts. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 24;300(1098):1–59. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of single ion channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Mar 6;211(1183):205–235. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. Relaxation and fluctuations of membrane currents that flow through drug-operated channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):231–262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fluctuations in the microsecond time range of the current through single acetylcholine receptor ion channels. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):464–466. doi: 10.1038/294464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti F., Neher E. Single channel recordings of K+ currents in squid axons. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):140–143. doi: 10.1038/285140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Miledi R., Parker I. Single glutamate-activated channels recorded from locust muscle fibres with perfused patch-clamp electrodes. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:195–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Parker I. Rapid kinetics of single glutamate-receptor channels. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):410–412. doi: 10.1038/295410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E. The kinetics of slow muscle acetylcholine-operated channels in the garter snake. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:159–190. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B., Lecar H. Single postsynaptic channel currents in tissue cultured muscle. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):863–864. doi: 10.1038/282863a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Calcium dependence of open and shut interval distributions from calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:585–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):497–500. doi: 10.1038/291497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Single-channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):799–802. doi: 10.1038/260799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. J., Sachs F. Single ionic channels observed in tissue-cultured muscle. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):861–863. doi: 10.1038/282861a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallotta B. S., Magleby K. L., Barrett J. N. Single channel recordings of Ca2+-activated K+ currents in rat muscle cell culture. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):471–474. doi: 10.1038/293471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B., Gration K. A., Usherwood P. N. Single glutamate-activated channels in locust muscle. Nature. 1979 Apr 12;278(5705):643–645. doi: 10.1038/278643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Patlak J., Neher E. Single acetylcholine-activated channels show burst-kinetics in presence of desensitizing concentrations of agonist. Nature. 1980 Jul 3;286(5768):71–73. doi: 10.1038/286071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Single Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channels in neuroblastoma. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):357–359. doi: 10.1038/296357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


