Abstract
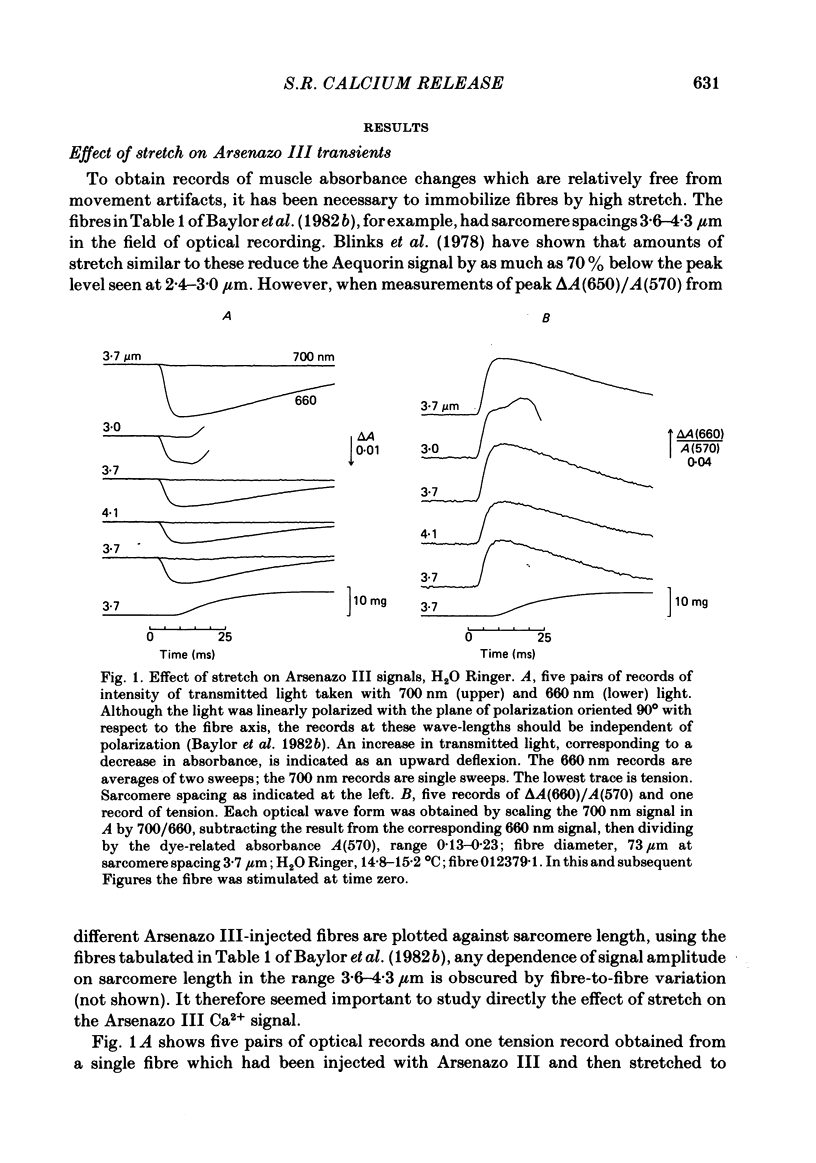
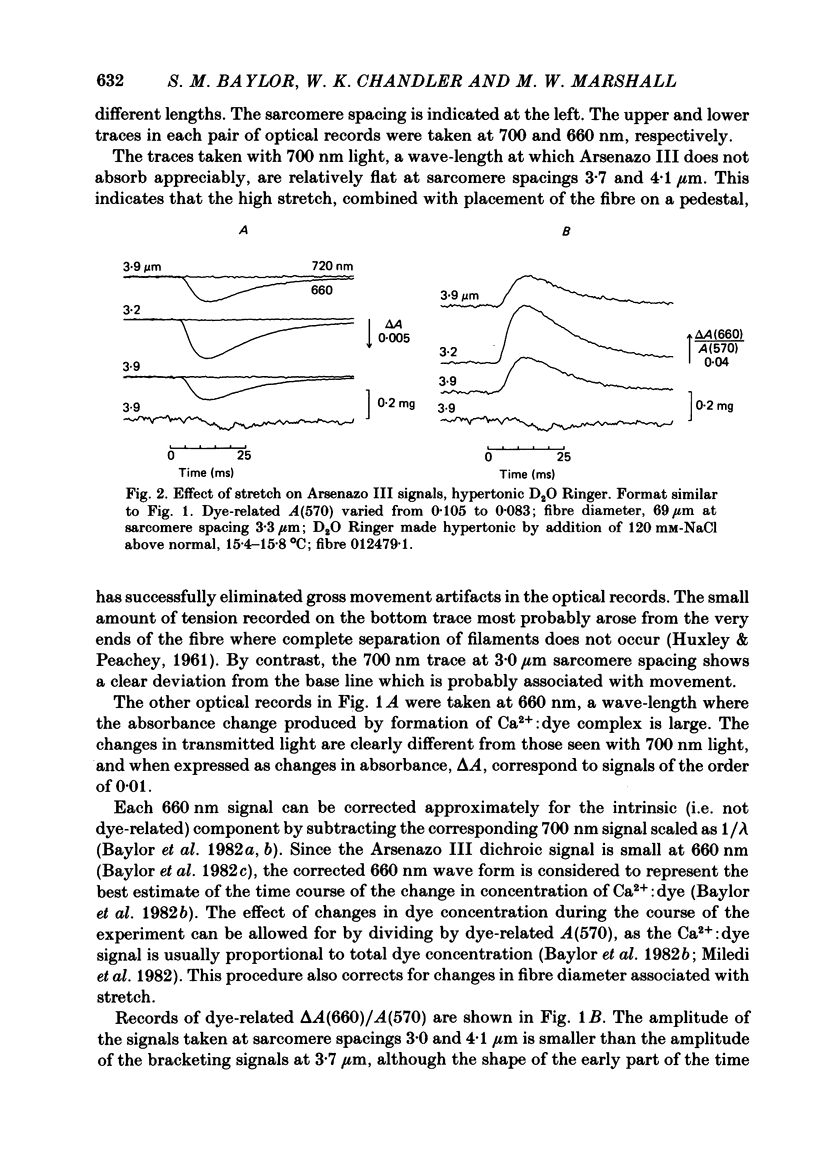
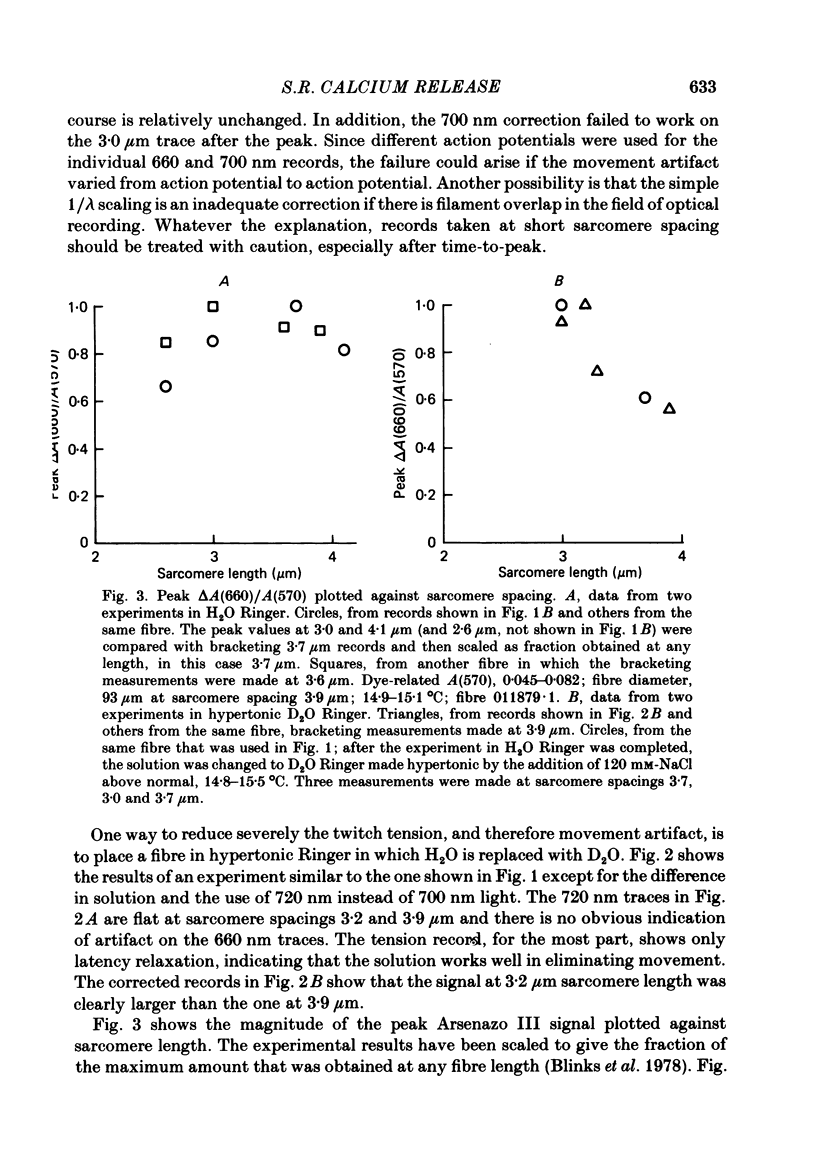
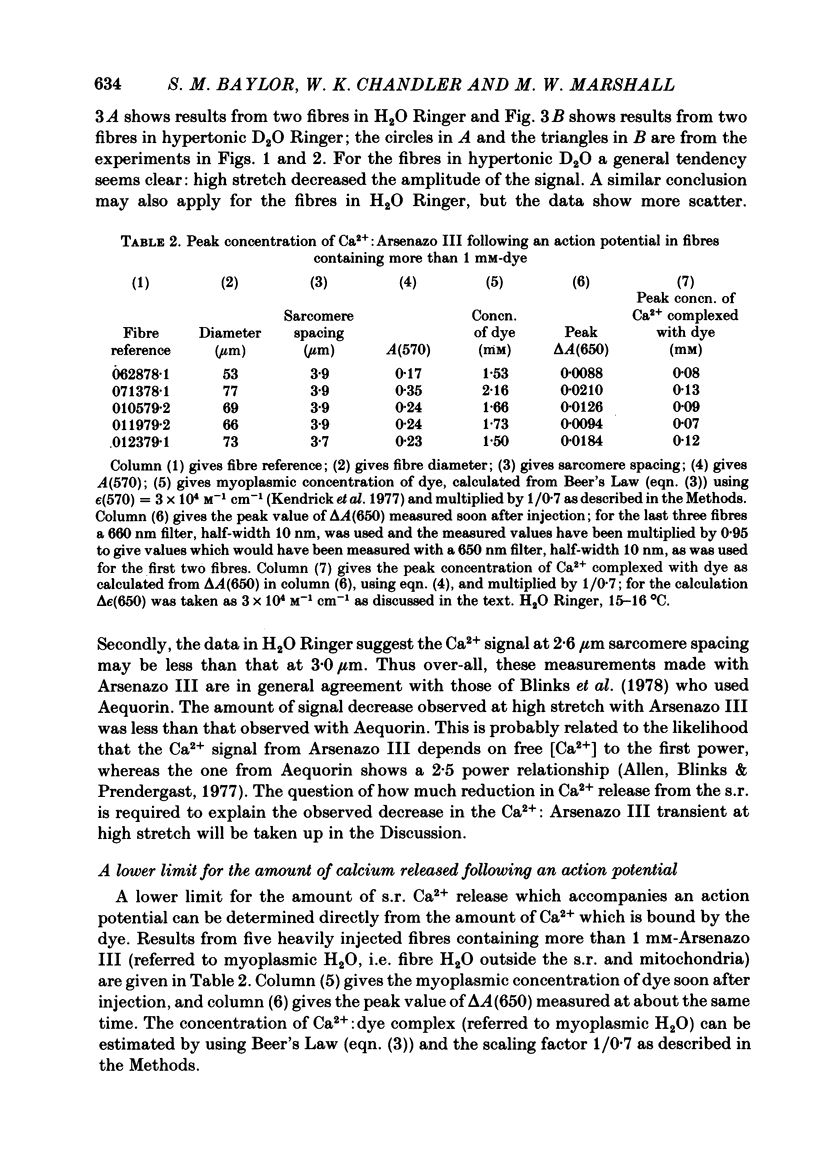
Single twitch fibres, dissected from frog muscle, were injected with the metallochromic dye Arsenazo III. Changes in dye-related absorbance measured at 650 or 660 nm were used to estimate the time course of myoplasmic free [Ca2+] following either action potential stimulation or voltage-clamp depolarization (temperature, 15-17 degrees C). The amplitude of the Ca2+ transient decreased when fibres were stretched to sarcomere spacings approaching 4 microns. The effect appeared to be less marked in H2O Ringer than in D2O Ringer, where a reduction of about 40% was observed in going from 3.0 microns to 3.7-3.9 microns. In fibres heavily injected with dye (1.5-2.2 mM-dye) at least 0.1 mM-Ca2+ was complexed with Arsenazo III following a single action potential, implying that at least 0.1 mM-Ca2+ was released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (s.r.) into the myoplasm. Computer simulations were carried out to estimate the flux of Ca2+ between the s.r. and myoplasm (in fibres containing no more that 0.8 mM-dye). The amounts and time courses of Ca2+ bound to the Ca2+-regulatory sites on troponin and to the Ca2+, Mg2+ sites on parvalbumin were estimated from the free [Ca2+] wave form and the law of mass action. In the computations the total myoplasmic [Ca2+] was taken as the total amount of Ca2+ existing either as free ion or as ion complexed with dye, troponin or parvalbumin. The time derivative of total myoplasmic [Ca2+] was used as an estimate of net Ca2+ flux (release minus uptake) from the s.r. into myoplasm. Rate constants for formation of cation: receptor complex were taken from published values. For the Ca2+-regulatory sites on troponin, three sets of rate constants, corresponding to two values of dissociation constant (0.2 and 2 microM) were used. Each set of three simulations was carried out both with and without parvalbumin. The simulations show that following action potential stimulation, 0.2-0.3 mM-Ca2+ enters the myoplasm from the s.r. The wave form of s.r. Ca2+ release is early and brief compared with the wave form of free [Ca2+]. Neither the selection of troponin rate constants nor the inclusion of parvalbumin has much effect on the shape of the release wave form; the main effect of varying these parameters is to change the magnitude. After the initial, rapid phase of Ca2+ release from the s.r. there is a longer, maintained period of Ca2+ uptake.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF









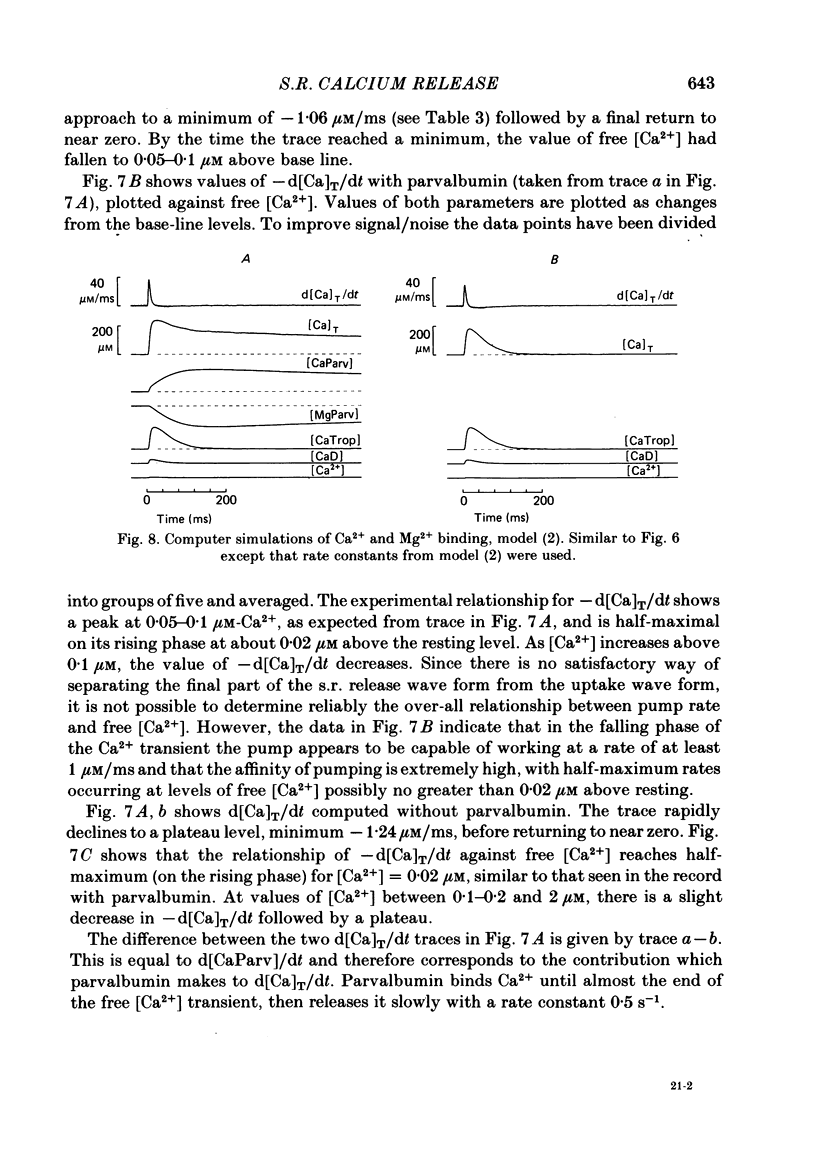
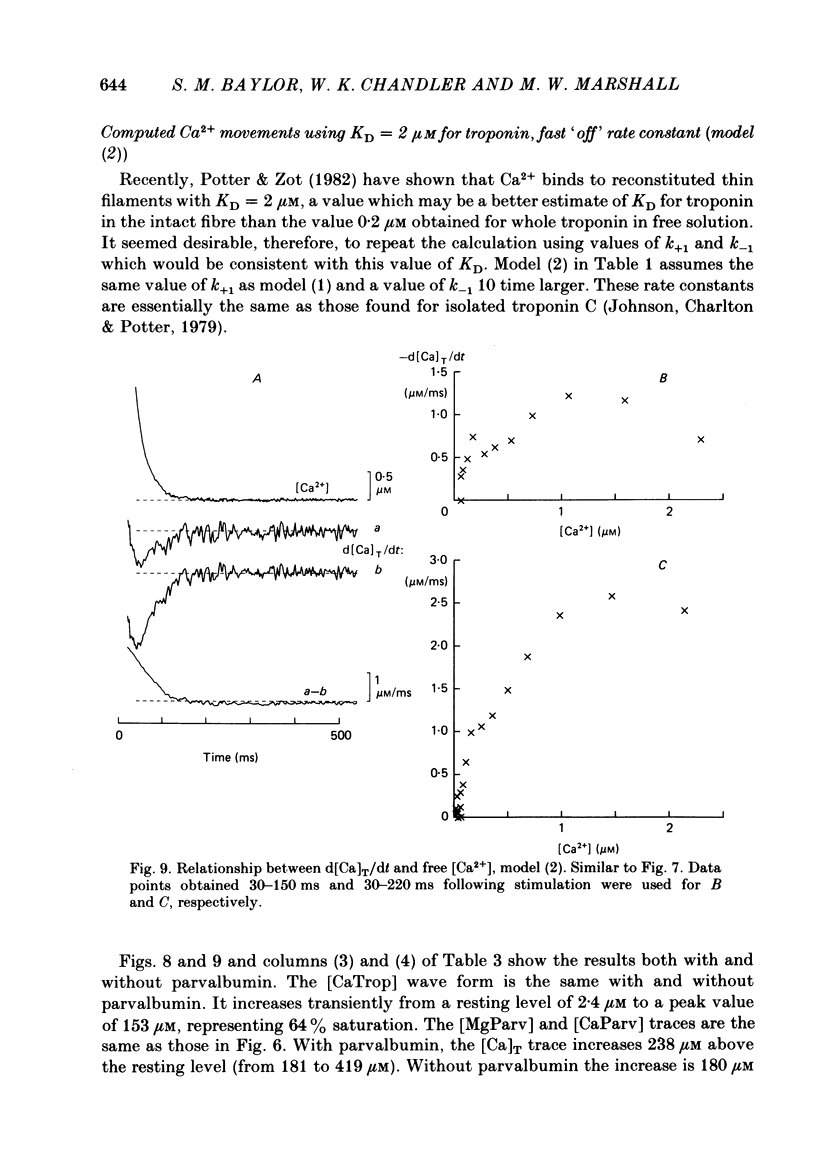
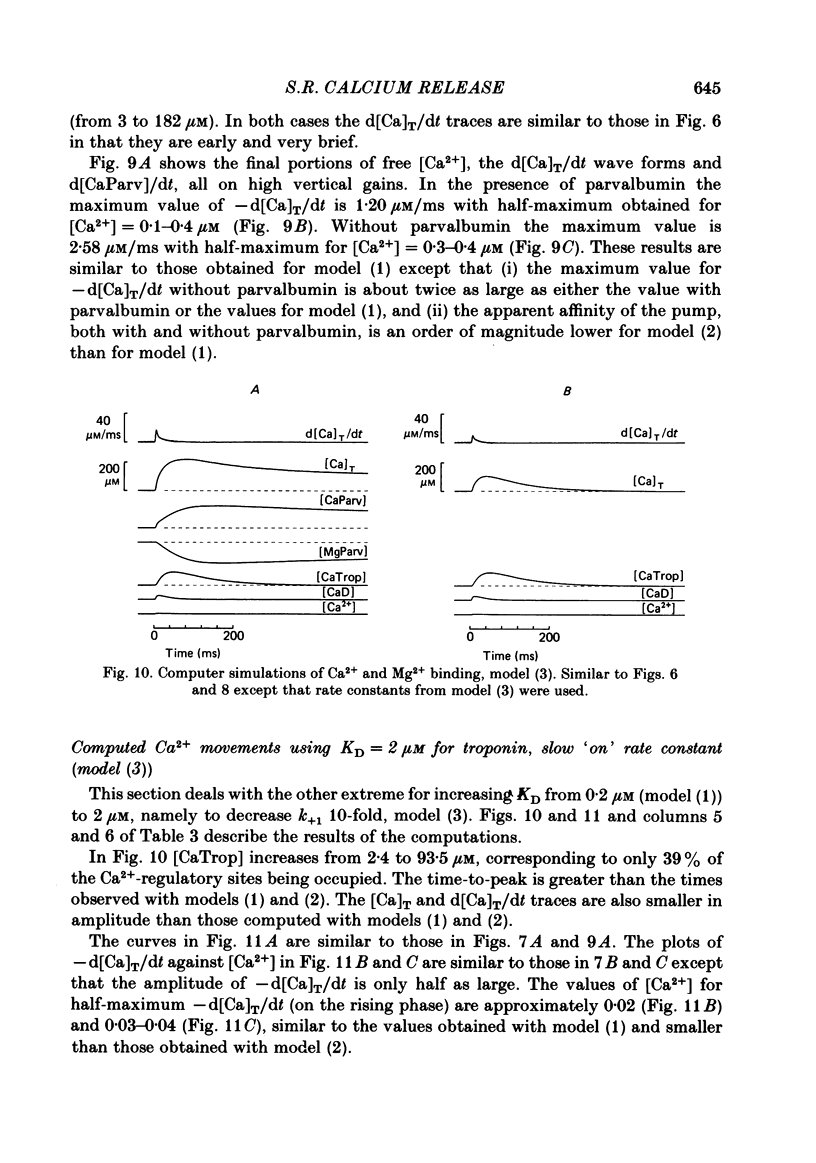
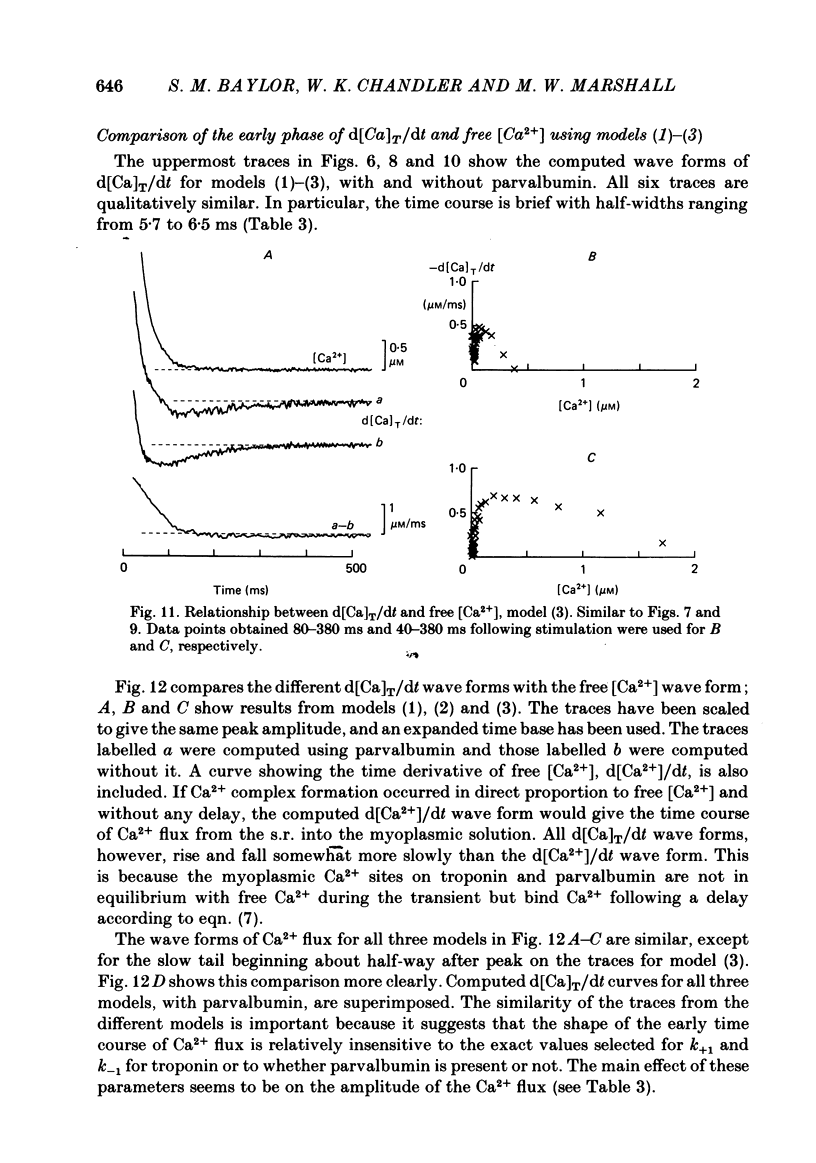












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen D. G., Blinks J. R., Prendergast F. G. Aequorin luminescence: relation of light emission to calcium concentration--a calcium-independent component. Science. 1977 Mar 11;195(4282):996–998. doi: 10.1126/science.841325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. M., Horowicz P. Twitches in the presence of ethylene glycol bis( -aminoethyl ether)-N,N'-tetracetic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 23;267(3):605–608. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Arsenazo III signals in singly dissected frog twitch fibres [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:23P–24P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Dichroic components of Arsenazo III and dichlorophosphonazo III signals in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:179–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Use of metallochromic dyes to measure changes in myoplasmic calcium during activity in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:139–177. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler T. J., Schibeci A., Martonosi A. The binding of arsenazo III to cell components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 7;629(2):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Rüdel R., Taylor S. R. Calcium transients in isolated amphibian skeletal muscle fibres: detection with aequorin. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:291–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P., Eckert R. Calcium entry leads to inactivation of calcium channel in Paramecium. Science. 1978 Dec 15;202(4373):1203–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.103199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DESMEDT J. E. Electrical activity and intracellular sodium concentration in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1953 Jul;121(1):191–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFuria R. R., Kushmerick M. J. ATP utilization associated with recovery metabolism in anaerobic frog muscle. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jan;232(1):C30–C36. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1977.232.1.C30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
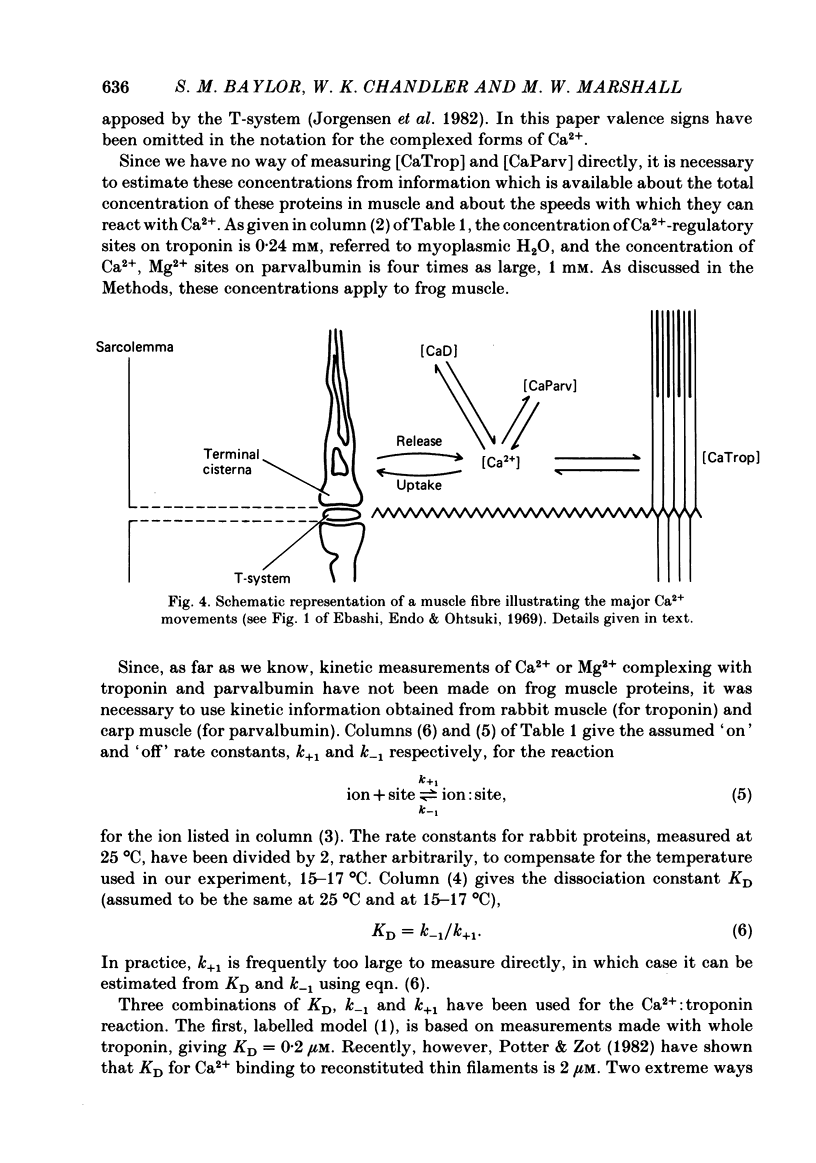
- Ebashi S., Endo M., Otsuki I. Control of muscle contraction. Q Rev Biophys. 1969 Nov;2(4):351–384. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg B. R., Eisenberg R. S. The T-SR junction in contracting single skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jan;79(1):1–19. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg B. R., Kuda A. M. Discrimination between fiber populations in mammalian skeletal muscle by using ultrastructural parameters. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Jan;54(1):76–88. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C. Membrane particles and transmission at the triad. Fed Proc. 1975 Apr;34(5):1382–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C. STUDIES OF THE TRIAD : I. Structure of the Junction in Frog Twitch Fibers. J Cell Biol. 1970 Nov 1;47(2):488–499. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerday C., Gillis J. M. Proceedings: The possible role of parvalbumins in the control of contraction. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;258(2):96P–97P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis J. M., Piront A., Gosselin-Rey C. Parvalbumins. Distribution and physical state inside the muscle cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 4;585(3):444–450. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis J. M., Thomason D., Lefèvre J., Kretsinger R. H. Parvalbumins and muscle relaxation: a computer simulation study. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1982 Dec;3(4):377–398. doi: 10.1007/BF00712090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosselin-rey C., Gerday C. Parvalbumins from frog skeletal muscle (Rana temporaria L.). Isolation and characterization. Structural modifications associated with calcium binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 27;492(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F., PEACHEY L. D. The maximum length for contraction in vertebrate straiated muscle. J Physiol. 1961 Apr;156:150–165. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Charlton S. C., Potter J. D. A fluorescence stopped flow analysis of Ca2+ exchange with troponin C. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3497–3502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen A. O., Shen A. C., MacLennan D. H., Tokuyasu K. T. Ultrastructural localization of the Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum in rat skeletal muscle by immunoferritin labeling of ultrathin frozen sections. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):409–416. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jöbsis F. F., O'Connor M. J. Calcium release and reabsorption in the sartorius muscle of the toad. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Oct 20;25(2):246–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90588-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick N. C., Ratzlaff R. W., Blaustein M. P. Arsenazo III as an indicator for ionized calcium in physiological salt solutions: its use for determination of the CaATP dissociation constant. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):433–450. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs L., Rios E., Schneider M. F. Measurement and modification of free calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres by a metallochromic indicator dye. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:161–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács L., Ríos E., Schneider M. F. Calcium transients and intramembrane charge movement in skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):391–396. doi: 10.1038/279391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Conner G. E., Fleischer S. Isolation of sarcoplasmic reticulum by zonal centrifugation and purification of Ca 2+ -pump and Ca 2+ -binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 16;298(2):246–269. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Nakajima S., Parker I., Takahashi T. Effects of membrane polarization on sarcoplasmic calcium release in skeletal muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Sep 17;213(1190):1–13. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Schalow G. Measurement of calcium transients in frog muscle by the use of arsenazo III. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Aug 22;198(1131):201–210. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Zhu P. H. Calcium transients evoked by action potentials in frog twitch muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:655–679. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley B. A., Eisenberg B. R. Sizes of components in frog skeletal muscle measured by methods of stereology. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jul;66(1):31–45. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Harafuji H., Kurebayashi N. Comparison of the characteristics of four metallochromic dyes as potential calcium indicators for biological experiments. J Biochem. 1980 May;87(5):1293–1303. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y. Some properties of fragmented frog sarcoplasmic reticulum with particular reference to its response to caffeine. J Biochem. 1970 May;67(5):667–683. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade P., Vergara J. Arsenazo III and antipyrylazo III calcium transients in single skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Apr;79(4):679–707. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.4.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peachey L. D. The sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse tubules of the frog's sartorius. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3 Suppl):209–231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pechère J. F., Derancourt J., Haiech J. The participation of parvalbumins in the activation-relaxation cycle of vertebrate fast skeletal-muscle. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. D., Gergely J. The calcium and magnesium binding sites on troponin and their role in the regulation of myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4628–4633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch B., von Chak D., Hasselbach W. An estimate of the kinetics of calcium binding and dissociation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum transport ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1978 Sep 1;93(1):65–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80806-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. P., Johnson J. D., Potter J. D. The time-course of Ca2+ exchange with calmodulin, troponin, parvalbumin, and myosin in response to transient increases in Ca2+. Biophys J. 1981 Jun;34(3):559–569. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84868-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E., Schneider M. F. Stoichiometry of the reactions of calcium with the metallochromic indicator dyes antipyrylazo III and arsenazo III. Biophys J. 1981 Dec;36(3):607–621. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84755-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdel R., Taylor S. R. Aequorin luminescence during contraction of amphibian skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Aug;233(1):5P–6P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scales D., Giuseppeinesi Assembly of ATPase protein in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biophys J. 1976 Jul;16(7):735–751. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85725-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Gonzalez-Serratos H. G., Shuman H., McClellan G., Somlyo A. P. Calcium release and ionic changes in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of tetanized muscle: an electron-probe study. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):577–594. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. V. Arsenazo III forms 2:1 complexes with Ca and 1:1 complexes with Mg under physiological conditions. Estimates of the apparent dissociation constants. Biophys J. 1979 Mar;25(3):541–548. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85322-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D. Inactivation of Ca conductance dependent on entry of Ca ions in molluscan neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1497–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J. M., Ierokomas A., Nakamura H., Martonosi A. Fluorescence energy transfer between Ca2+ transport ATPase molecules in artificial membranes. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 5;16(7):1262–1267. doi: 10.1021/bi00626a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verjovski-Almeida S., Inesi G. Fast-kinetic evidence for an activating effect of ATP on the Ca2+ transport of sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):18–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Tonomura Y. Reaction mechanism of the Ca++ -dependent ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum from skeletal muscle. I. Kinetic studies. J Biochem. 1967 Nov;62(5):558–575. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikami S., Hagins W. A. Calcium in excitation of vertebrate rods and cones: retinal efflux of calcium studied with dichlorophosphonazo III. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:545–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


