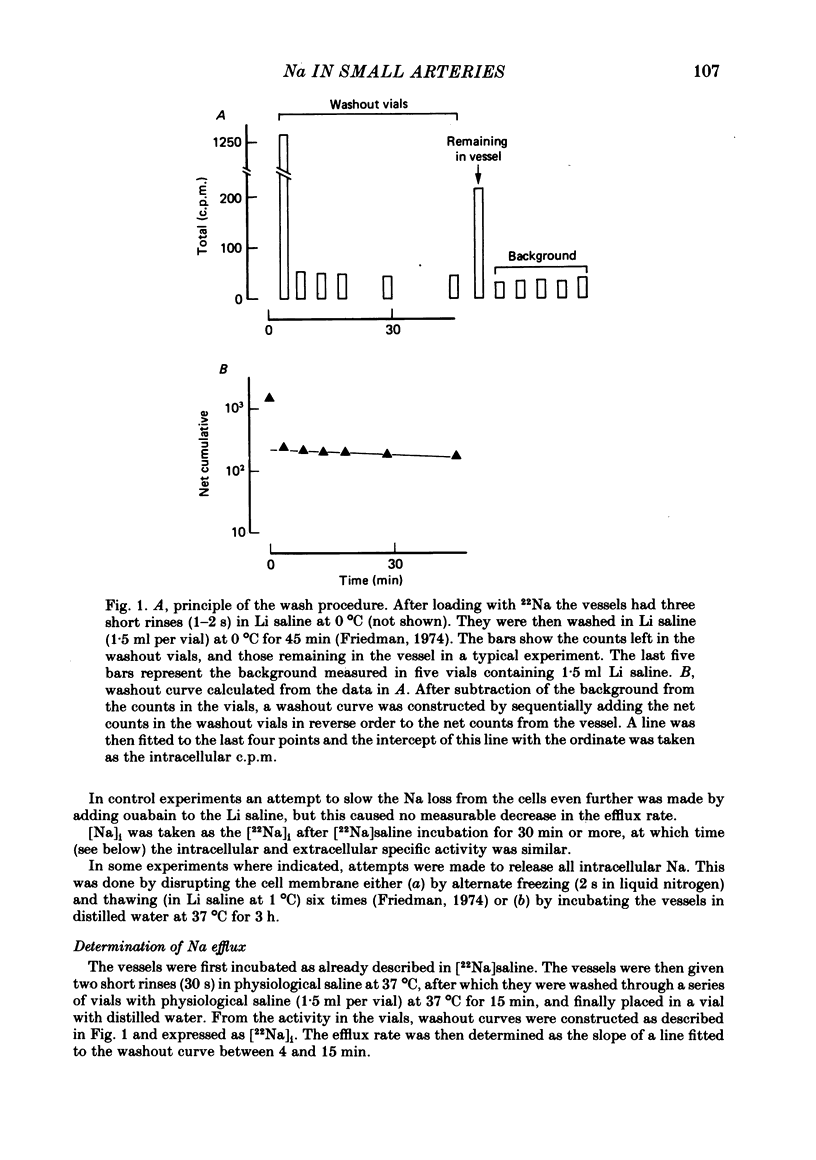
Abstract
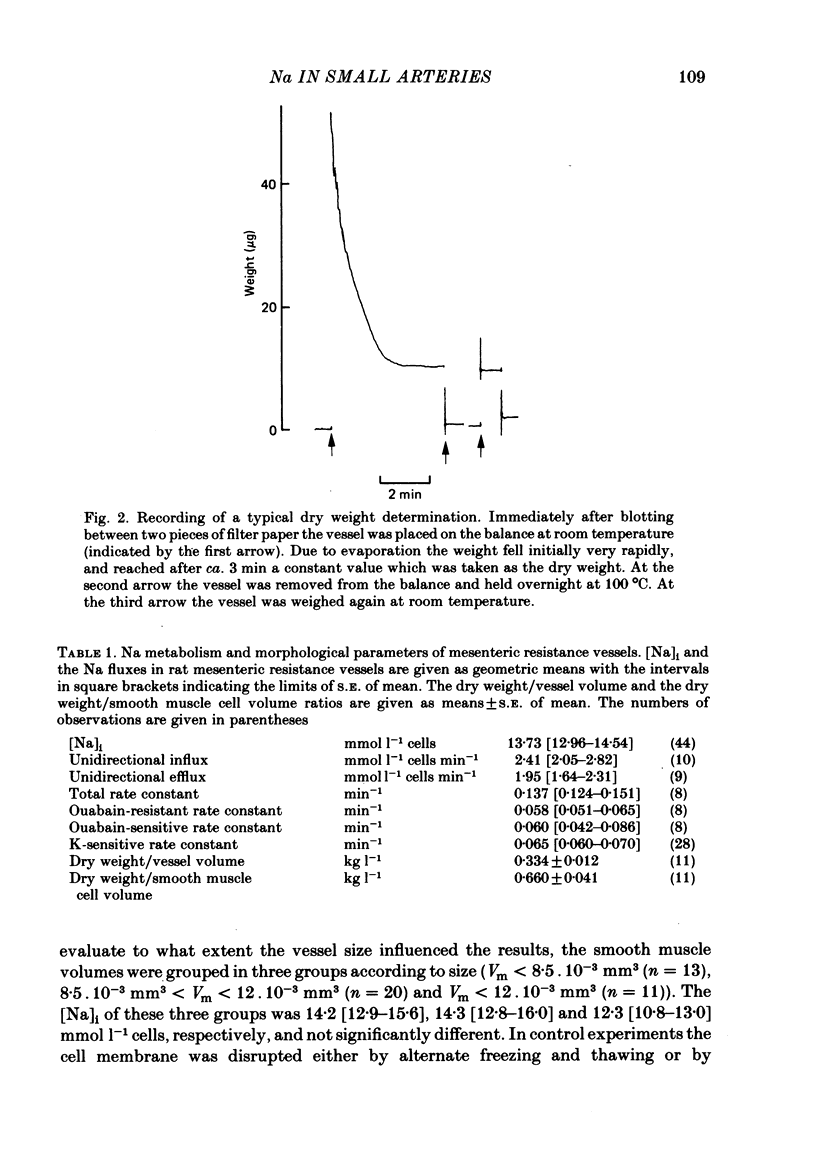
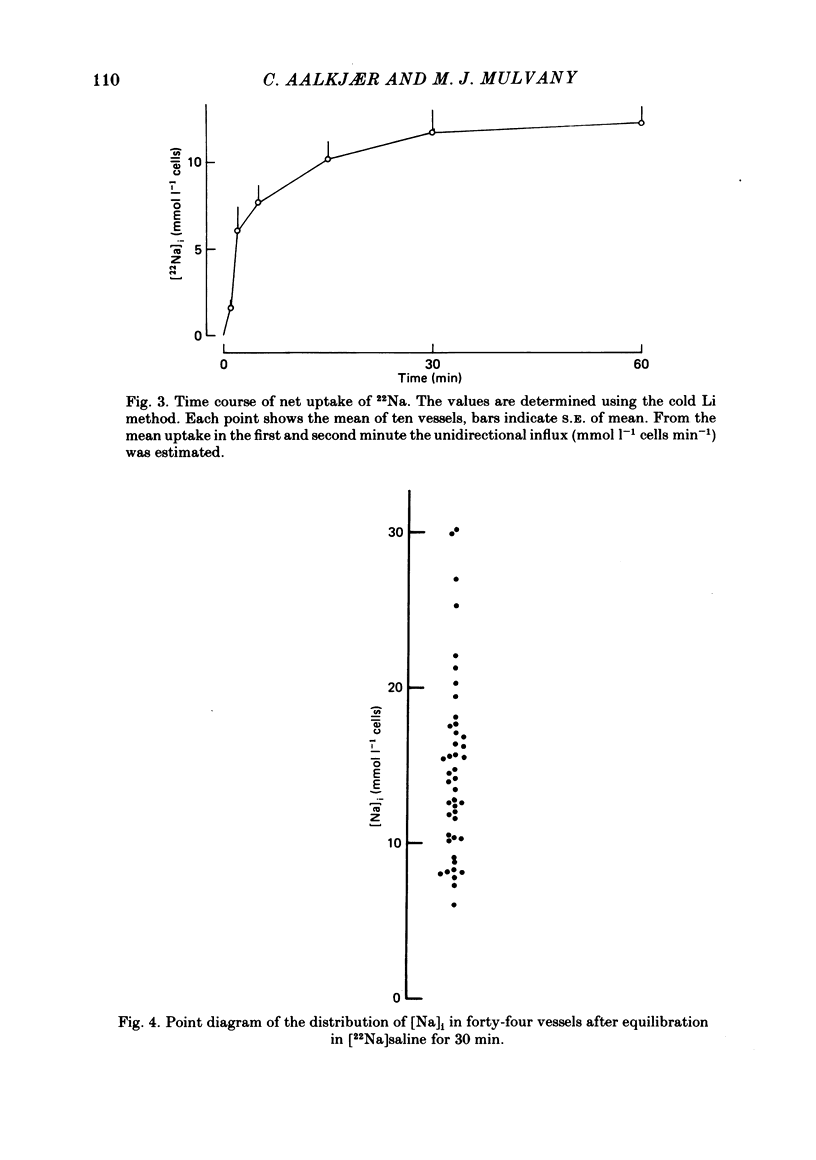
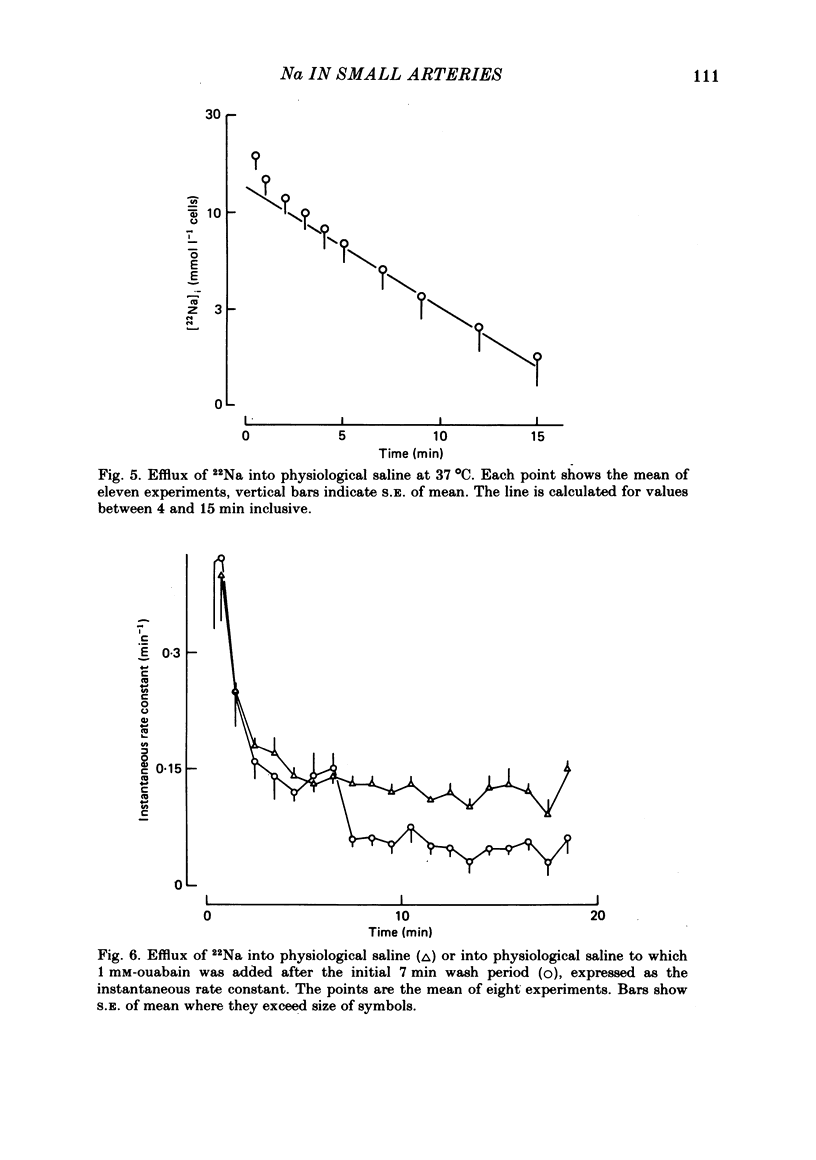
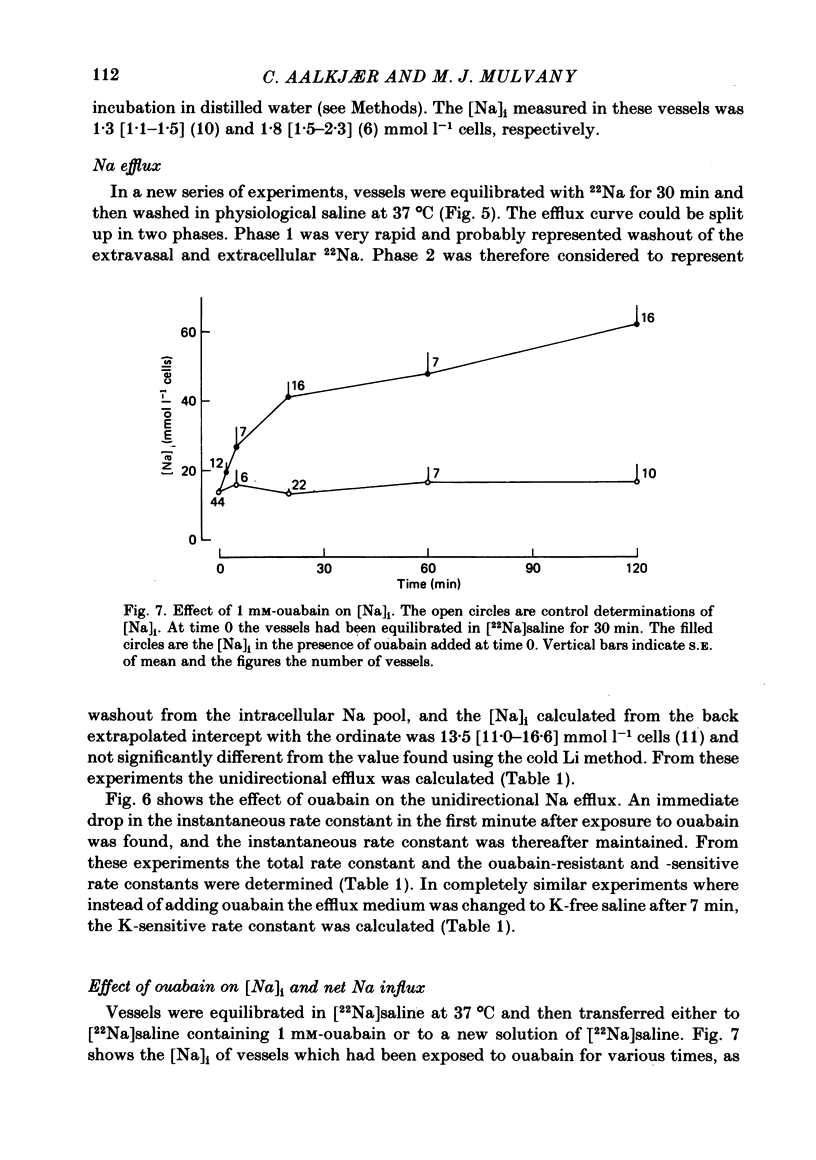
Using 22Na we have investigated the Na metabolism in rat mesenteric resistance vessels (internal diameter about 200 micron). The intracellular Na content was determined by washing the vessels at 0 degrees C in saline with Li substituted for Na, and was related to smooth muscle volume determined from measurements of media thickness and internal diameter using light microscopy. On this basis an internal Na concentration of 13.7 mmol l-1 cells was found. The efflux of Na into saline at 37 degrees C consists of two phases, a fast one and a slow one, where the slow phase was considered to be intracellular. It had a rate constant of 0.137 min-1, which was decreased by 50% if 1 mM-ouabain was added to or K withdrawn from the efflux medium. The gain of cell Na after addition of 1 mM-ouabain was much faster than would be expected from the decrease in efflux, indicating that 1 mM-ouabain increases the permeability to Na.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aalkjaer C., Mulvany M. J. Human and rat resistance vessels: a comparison of their morphological and pharmacological characteristics. Gen Pharmacol. 1983;14(1):85–87. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(83)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brading A. F. Ion distribution and the role of calcium in cellular function. Ion distribution and ion movements in smooth muscle. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Mar 15;265(867):35–46. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1973.0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa M., Adragna N., Solomon H. S., Connolly T. M., Tosteson D. C. Increased sodium-lithium countertransport in red cells of patients with essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1980 Apr 3;302(14):772–776. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198004033021403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detweiler D. K. Comparative pharmacology of cardiac glycosides. Fed Proc. 1967 Jul-Aug;26(4):1119–1124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droogmans G., Raeymaekers L., Casteels R. Electro- and pharmacomechanical coupling in the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit ear artery. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Aug;70(2):129–148. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkow B., Hallbäck M., Jones J. V., Sutter M. Dependence on external calcium for the noradrenaline contractility of the resistance vessels in spontaneously hypertensive and renal hypertensive rats, as compared with normotensive controls. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Sep;101(1):84–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb05986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. M., Friedman C. L. Cell permeability, sodium transport, and the hypertensive process in the rat. Circ Res. 1976 Sep;39(3):433–441. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.3.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. M. Lithium substitution and the distribution of sodium in the rat tail artery. Circ Res. 1974 Feb;34(2):168–175. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.2.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. M., Mar M., Nakashima M. Lithium substitution analysis of Na and K phases in a small artery. Blood Vessels. 1974;11(1-2):55–64. doi: 10.1159/000157999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Dagher G., Pernollet M. G., Devynck M. A., Meyer P. Inherited defect in a Na+, K-co-transport system in erythrocytes from essential hypertensive patients. Nature. 1980 Mar 20;284(5753):281–283. doi: 10.1038/284281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Moura A. M., Osborne-Pellegrin M. J., Papadimitriou A., Worcel M. Identification of different sodium compartments from smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts and endothelial cells, in arteries and tissue culture. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:213–229. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P., Villamil M. F., Zadunaisky J. A. Sodium exchange and distribution in the arterial wall. Am J Physiol. 1965 Nov;209(5):955–960. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.5.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickx H., Casteels R. Electrogenic sodium pump in arterial smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1974;346(4):299–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00596185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. W. Altered ion transport in vascular smooth muscle from spontaneously hypertensive rats. Influences of aldosterone, norepinephrine, and angiotensin. Circ Res. 1973 Nov;33(5):563–572. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.5.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. W. Reactivity of ion fluxes in rat aorta during hypertension and circulatory control. Fed Proc. 1974 Feb;33(2):133–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keatinge W. R. Sodium flux and electrical activity of arterial smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):183–200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvany M. J., Halpern W. Contractile properties of small arterial resistance vessels in spontaneously hypertensive and normotensive rats. Circ Res. 1977 Jul;41(1):19–26. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvany M. J., Halpern W. Mechanical properties of vascular smooth muscle cells in situ. Nature. 1976 Apr 15;260(5552):617–619. doi: 10.1038/260617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvany M. J., Hansen O. K., Aalkjaer C. Direct evidence that the greater contractility of resistance vessels in spontaneously hypertensive rats is associated with a narrowed lumen, a thickened media, and an increased number of smooth muscle cell layers. Circ Res. 1978 Dec;43(6):854–864. doi: 10.1161/01.res.43.6.854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvany M. J., Nilsson H., Flatman J. A., Korsgaard N. Potentiating and depressive effects of ouabain and potassium-free solutions on rat mesenteric resistance vessels. Circ Res. 1982 Oct;51(4):514–524. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.4.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V., Shuman H. Electron probe analysis of vascular smooth muscle. Composition of mitochondria, nuclei, and cytoplasm. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):316–335. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]