Abstract
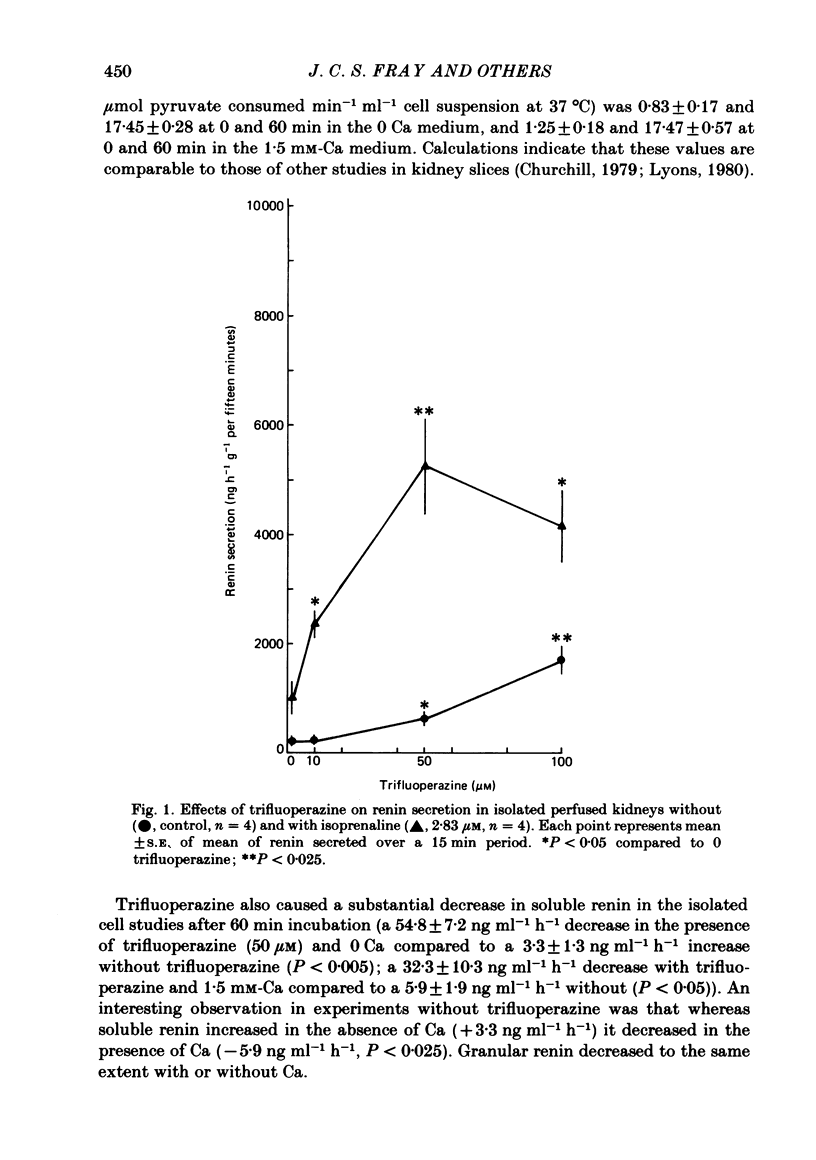
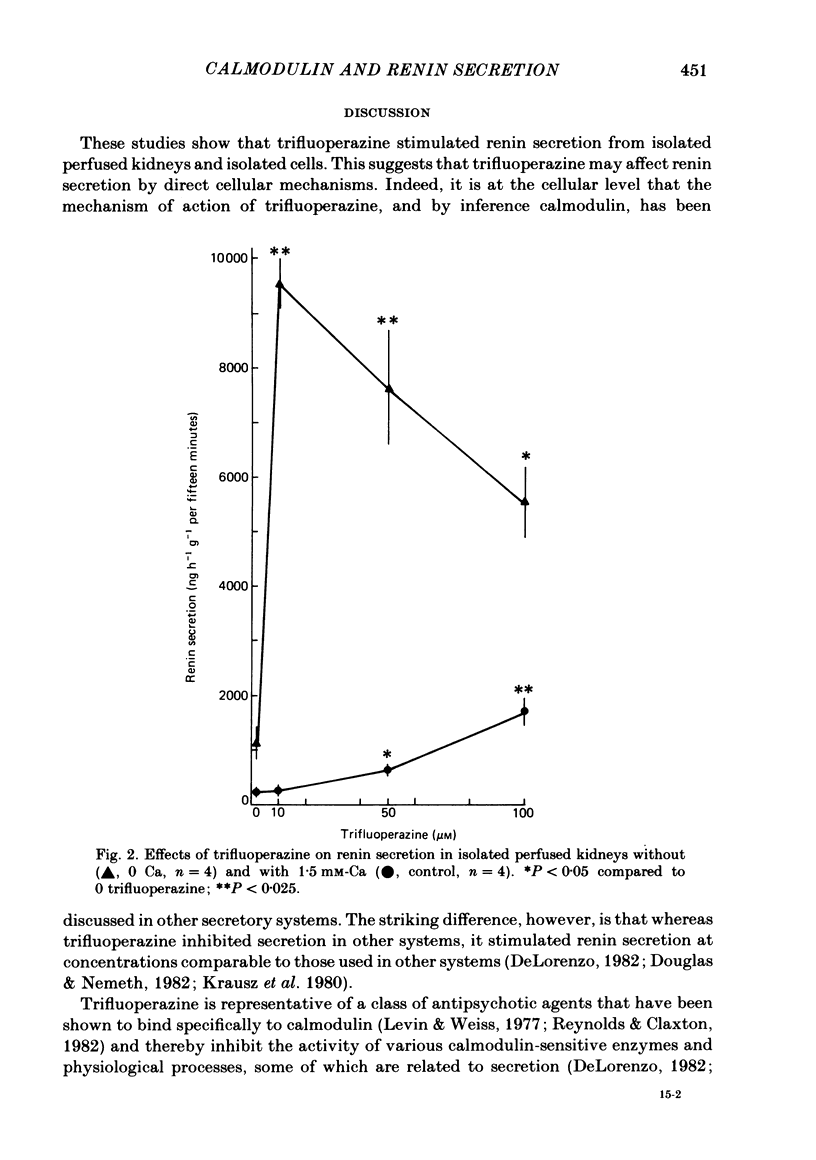
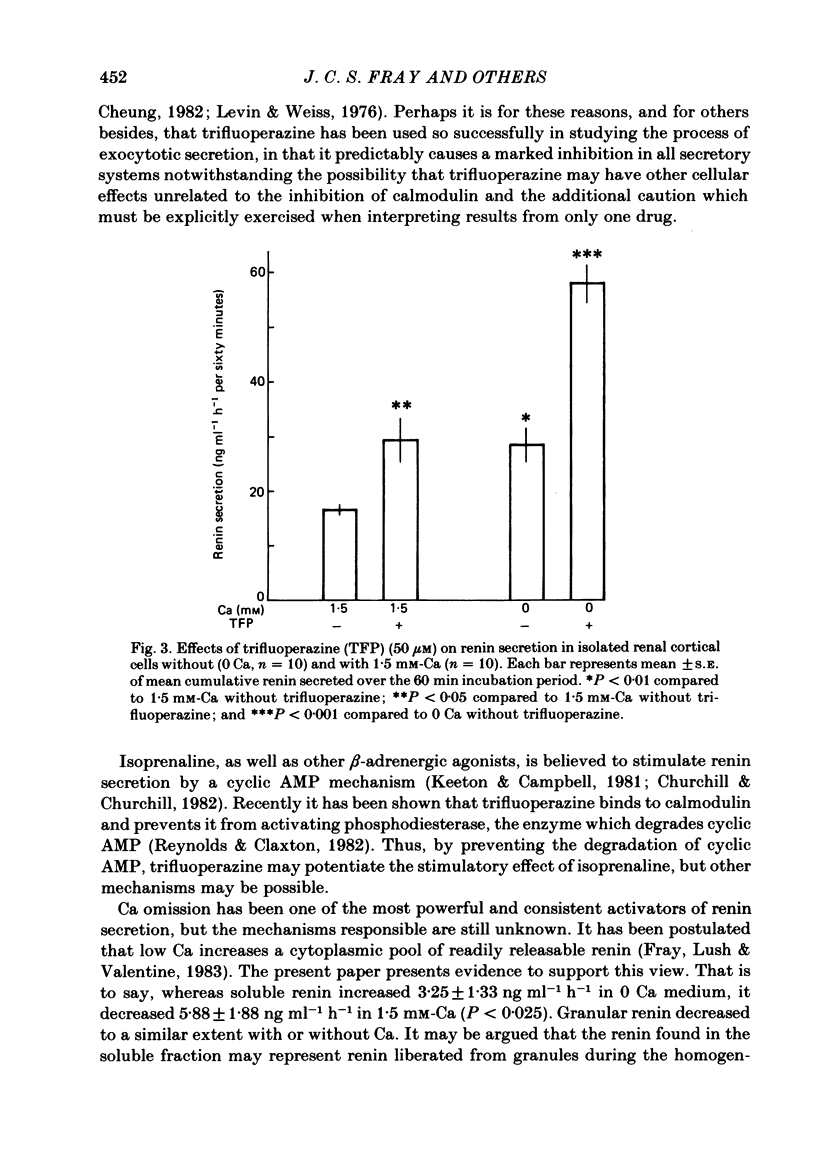
Trifluoperazine, an inhibitor of calmodulin and calmodulin-directed secretion, was used to examine a possible role of calmodulin in renin secretion from isolated perfused kidneys and renal cortical cells. In isolated perfused kidneys trifluoperazine stimulated basal renin secretion in a dose-dependent manner, with 10 microM causing no stimulation and 50 microM causing 167% increase. Trifluoperazine potentiated the elevated renin secretion induced by isoprenaline and low Ca in isolated kidneys. In renal cortical cells trifluoperazine increased basal renin secretion and potentiated the secretion induced by Ca omission. Cells homogenized immediately after 1 h exposure to trifluoperazine had a substantial reduction in soluble renin without any effect on the change in granular renin. In the absence of trifluoperazine, soluble renin increased with O Ca and decreased with 1.5 mM-Ca. It is concluded that trifluoperazine stimulates renin secretion by a cellular mechanism possibly at the level of the juxtaglomerular cell. It is suggested that the role of trifluoperazine, and by inference calmodulin, in the secretion of renin may be quite different from its role in secretion of several other substances.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgoyne R. D., Geisow M. J., Barron J. Dissection of stages in exocytosis in the adrenal chromaffin cell with use of trifluoperazine. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Aug 23;216(1202):111–115. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D. S., Poisner A. M. Direct stimulation of renin release by calcium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Sep;152(4):565–567. doi: 10.3181/00379727-152-39441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin: an overview. Fed Proc. 1982 May;41(7):2253–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill P. C., Churchill M. C. Isoproterenol-stimulated renin secretion in the rat: second messenger roles of Ca and cyclic AMP. Life Sci. 1982 Apr 12;30(15):1313–1319. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90694-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill P. C. Possible mechanism of the inhibitory effect of ouabain on renin secretion from rat renal cortical slices. J Physiol. 1979 Sep;294:123–134. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorenzo R. J. Calmodulin in neurotransmitter release and synaptic function. Fed Proc. 1982 May;41(7):2265–2272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorenzo R. J., Freedman S. D., Yohe W. B., Maurer S. C. Stimulation of Ca2+-dependent neurotransmitter release and presynaptic nerve terminal protein phosphorylation by calmodulin and a calmodulin-like protein isolated from synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1838–1842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Nemeth E. F. On the calcium receptor activating exocytosis: inhibitory effects of calmodulin-interacting drugs on rat mast cells. J Physiol. 1982 Feb;323:229–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W. Stimulus-secretion coupling: the concept and clues from chromaffin and other cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):451–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb08474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C., Laurens N. J. Mechanism by which albumin stimulates renin secretion in isolated kidneys and juxtaglomerular cells. J Physiol. 1981 Nov;320:31–39. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C. Stimulus-secretion coupling of renin. Role of hemodynamic and other factors. Circ Res. 1980 Oct;47(4):485–492. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.4.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C. Stretch receptor model for renin release with evidence from perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):936–944. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krausz Y., Wollheim C. B., Siegel E., Sharp G. W. Possible role for calmodulin in insulin release. Studies with trifluoperazine in rat pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):603–607. doi: 10.1172/JCI109893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester G. E., Rubin R. P. The role of calcium in renin secretion from the isolated perfused cat kidney. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(1):93–108. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin R. M., Weiss B. Binding of trifluoperazine to the calcium-dependent activator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Jul;13(4):690–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin R. M., Weiss B. Mechanism by which psychotropic drugs inhibit adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase of brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;12(4):581–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons H. J. Studies on the mechanism of renin release from rat kidney slices: calcium, sodium and metabolic inhibition. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:99–108. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peart W. S. The kidney as an endocrine organ. Lancet. 1977 Sep 10;2(8037):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. H., Claxton P. T. Inhibition of calmodulin-activated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase: multiple binding-sites for tricyclic drugs on calmodulin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 1;31(3):419–421. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. P. The role of calcium in the release of neurotransmitter substances and hormones. Pharmacol Rev. 1970 Sep;22(3):389–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagnella G. A., Peart W. S. Studies on the isolation and properties of renin granules from the rat kidney cortex. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):301–309. doi: 10.1042/bj1820301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhardt R. A., Alderton J. M. Calmodulin confers calcium sensitivity on secretory exocytosis. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):154–155. doi: 10.1038/295154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


