Abstract
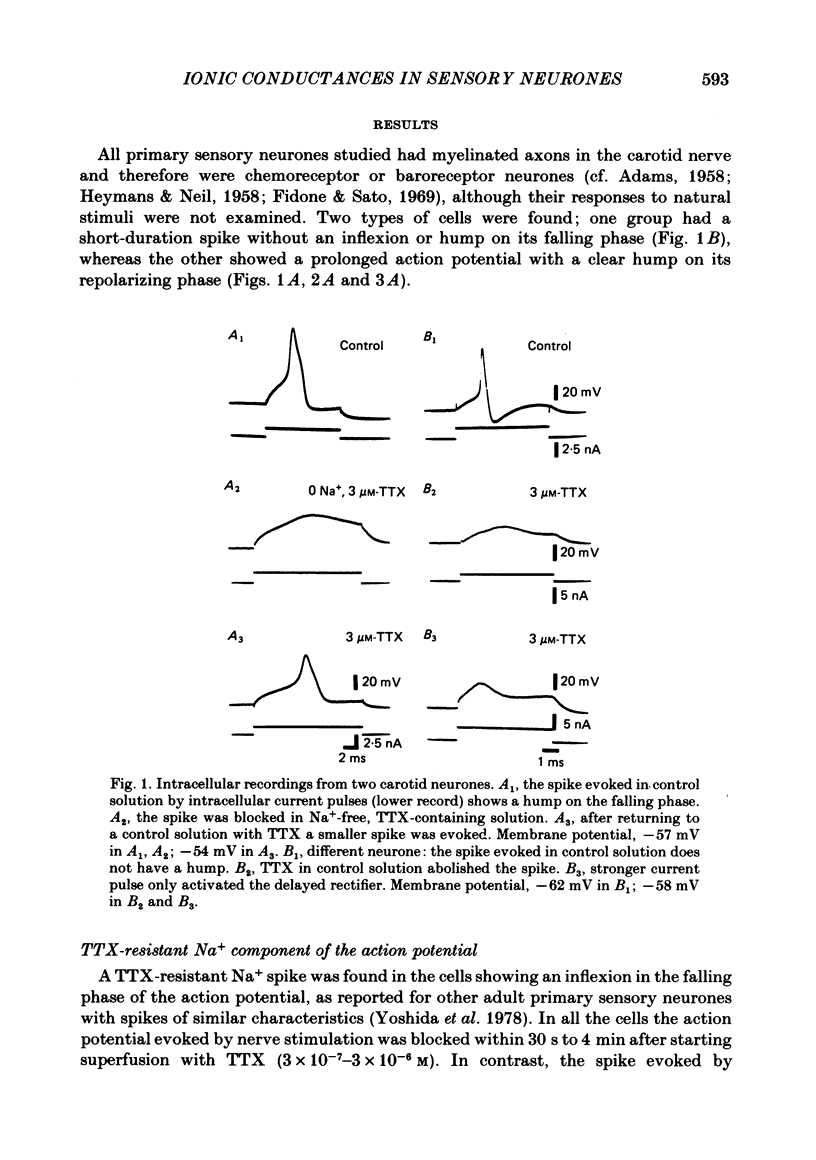
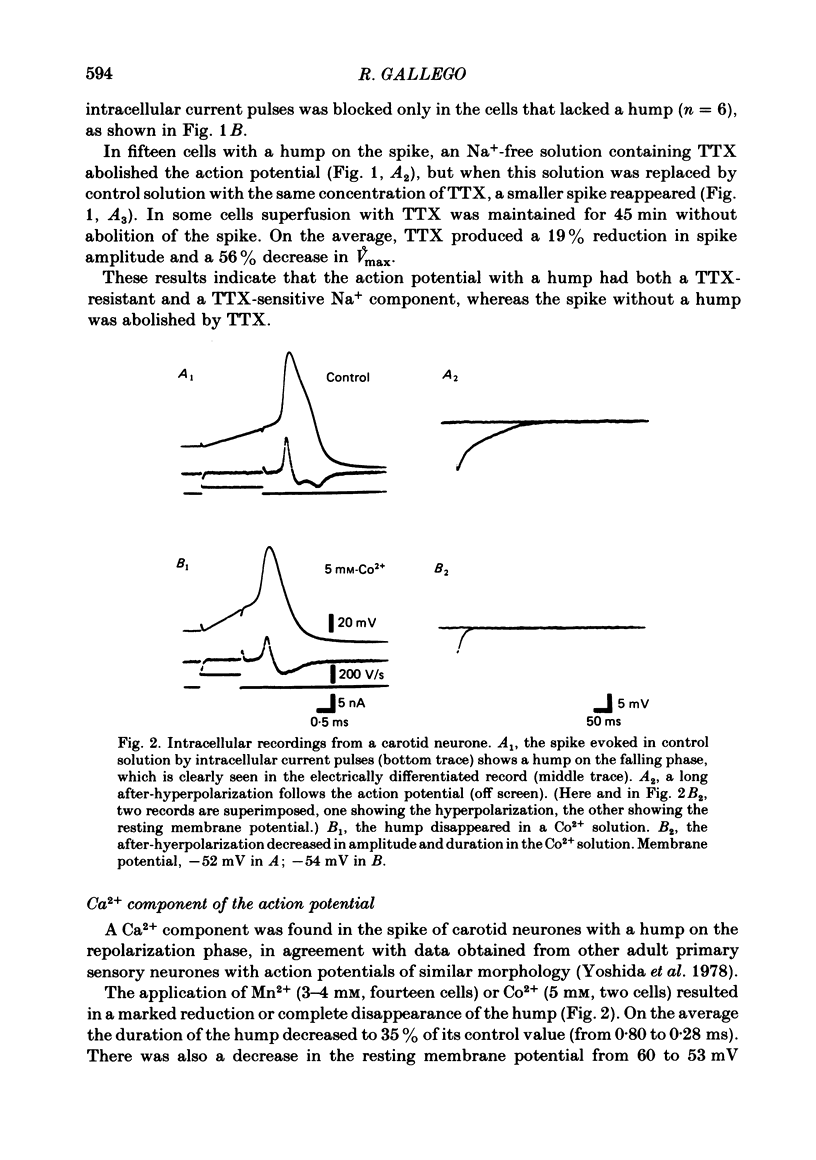
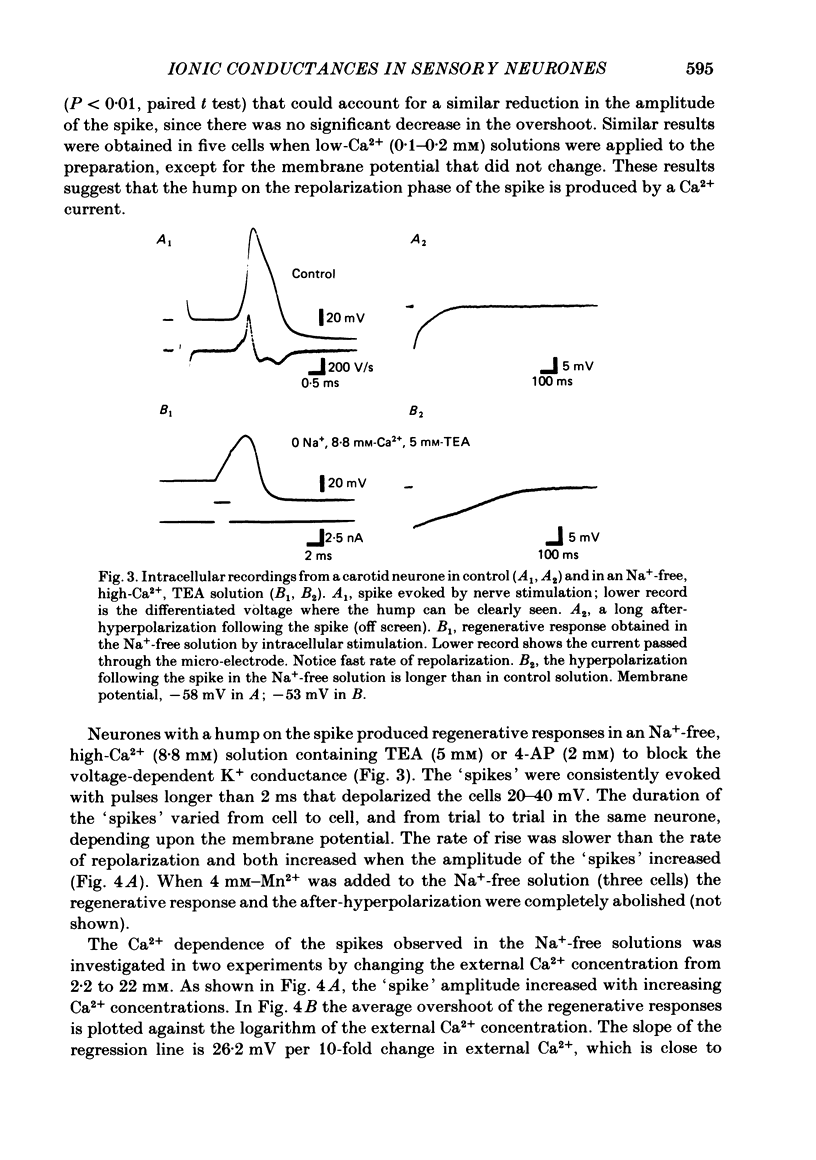
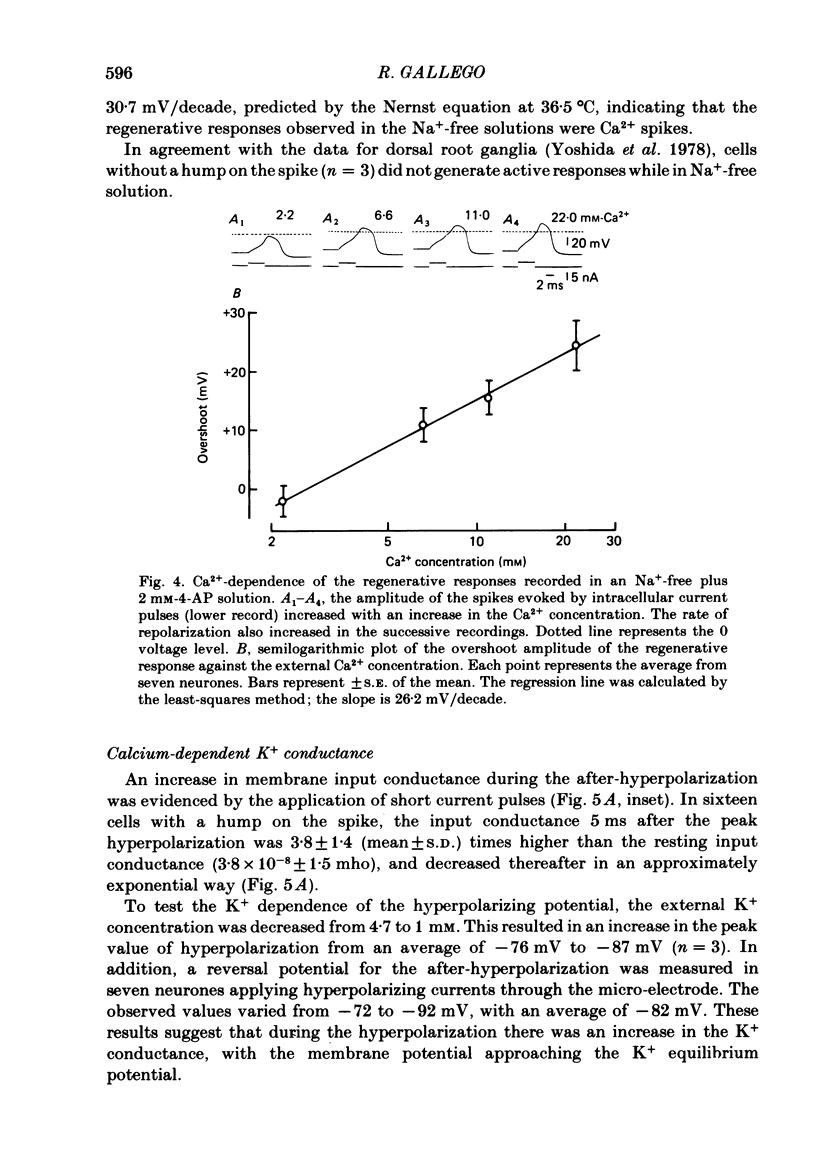
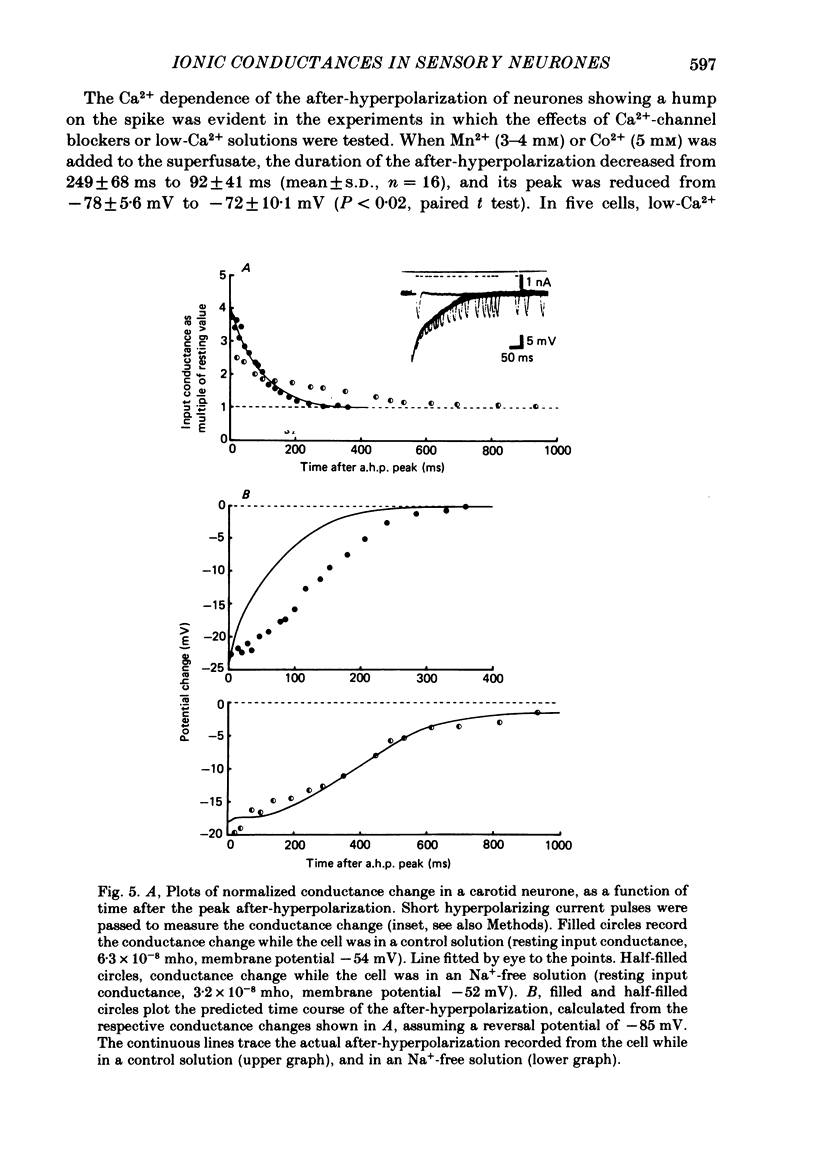
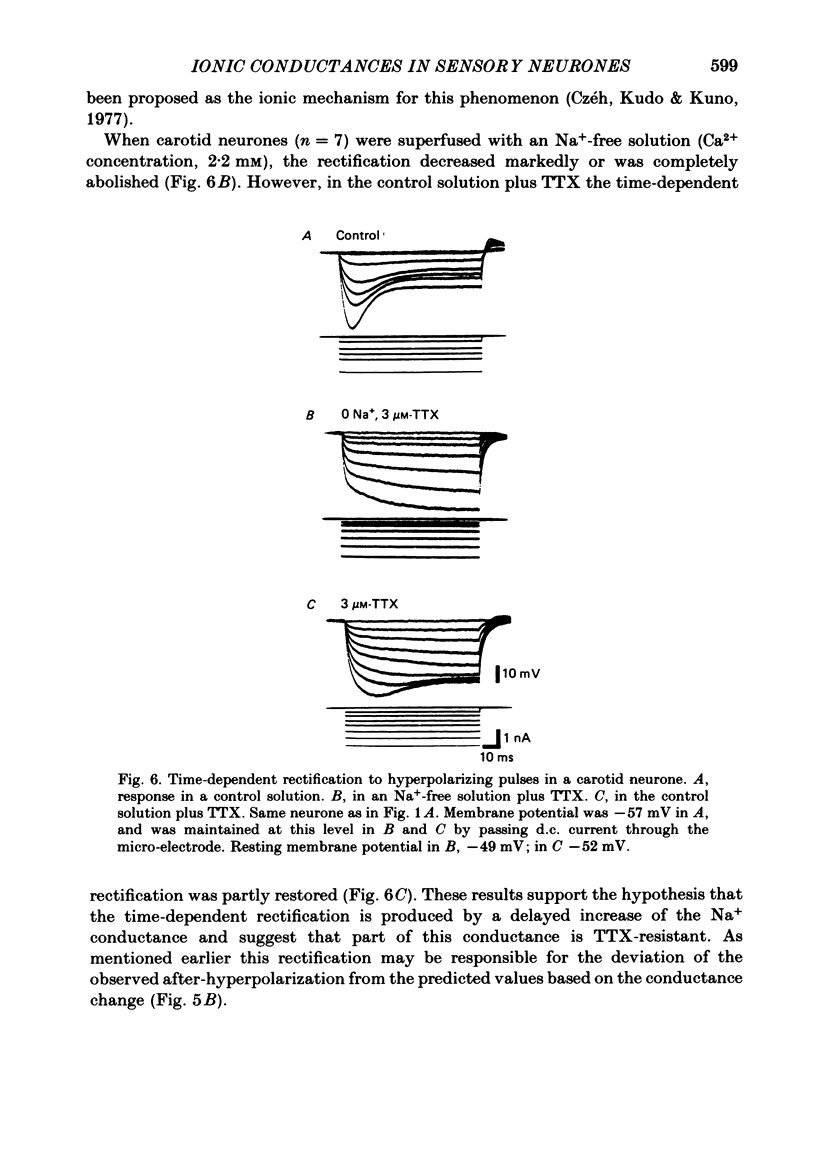
The ionic conductances underlying the action potential and after-hyperpolarization of the cat petrosal ganglion neurones with myelinated axons in the carotid nerve were studied in vitro. Neurones were divided into two groups based on the presence or absence of an inflexion or hump on the spike falling phase. The application of tetrodotoxin (TTX, 3 X 10(-7)-3 X 10(-6) M) revealed the presence of a TTX-resistant component in spikes with a hump, which was abolished in Na+-free solution. The action potential without a hump was blocked by TTX. The spike hump decreased or was abolished when Ca2+-channel blockers (Mn2+, 3-4 mM or Co2+, 5 mM) or low-Ca2+ solutions (0.1-0.2 mM) were applied to the preparation. In neurones with a hump on the spike, regenerative responses were obtained in Na+-free, high-Ca2+ (8.8 mM) solution; these responses were antagonized by Mn2+, and their amplitude was proportional to the external Ca2+ concentration. It is concluded that the action potential with a hump was produced by an Na+ current, a part of which was TTX-resistant, and by a Ca2+ current which is responsible for the hump. Neurones without a hump had a TTX-sensitive Na+ spike. The spike with a hump was followed by a long-lasting after-hyperpolarization which reversed polarity at about -82 mV. During the hyperpolarization an increase in membrane conductance was observed. The amplitude and duration of the long hyperpolarizing potential decreased when Ca2+-channel blockers or low-Ca2+ solutions were applied. In Na+-free solution, regenerative responses were followed by a long hyperpolarization associated with an increase in membrane conductance. It is concluded that the long after-hyperpolarization is produced by activation of the Ca2+-dependent K+ conductance.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Constanti A., Brown D. A., Clark R. B. Intracellular Ca2+ activates a fast voltage-sensitive K+ current in vertebrate sympathetic neurones. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):746–749. doi: 10.1038/296746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccaglini P. I. Action potentials of embryonic dorsal root ganglion neurones in Xenopus tadpoles. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:585–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Barret J. N. Separation of two voltage-sensitive potassium currents, and demonstration of a tetrodotoxin-resistant calcium current in frog motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):737–774. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Barrett E. F., Dribin L. B. Calcium-dependent slow potassium conductance in rat skeletal myotubes. Dev Biol. 1981 Mar;82(2):258–266. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90450-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belmonte C., Gallego R. Membrane properties of cat sensory neurones with chemoreceptor and baroreceptor endings. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:603–614. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czéh G., Kudo N., Kuno M. Membrane properties and conduction velocity in sensory neurones following central or peripheral axotomy. J Physiol. 1977 Aug;270(1):165–180. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichter M. A., Fischbach G. D. The action potential of chick dorsal root ganglion neurones maintained in cell culture. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):281–298. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidone S. J., Sato A. A study of chemoreceptor and baroreceptor A and C-fibres in the cat carotid nerve. J Physiol. 1969 Dec;205(3):527–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda J., Kameyama M. Tetrodotoxin-sensitive and tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels in tissue-cultured spinal ganglion neurons from adult mammals. Brain Res. 1980 Jan 20;182(1):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90844-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallego R., Eyzaguirre C. Membrane and action potential characteristics of A and C nodose ganglion cells studied in whole ganglia and in tissue slices. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Sep;41(5):1217–1232. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.5.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görke K., Pierau F. K. Spike potentials and membrane properties of dorsal root ganglion cells in pigeons. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Jul;386(1):21–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00584182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann A., Gorman A. L. Effects of tetraethylammonium on potassium currents in a molluscan neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jul;78(1):87–110. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Lux H. D. Control of the delayed outward potassium currents in bursting pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):349–382. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer E. J., Macdonald R. L. Calcium- and sodium-dependent action potentials of mouse spinal cord and dorsal root ganglion neurons in cell culture. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Apr;47(4):641–655. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.47.4.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotson J. R., Prince D. A. A calcium-activated hyperpolarization follows repetitive firing in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Feb;43(2):409–419. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.43.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITO M. The electrical activity of spinal ganglion cells investigated with intracellular microelectrodes. Jpn J Physiol. 1957 Dec 20;7(4):297–323. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.7.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H. Evidence for initiation of calcium spikes in C-cells of the rabbit nodose ganglion. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Aug;394(2):106–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00582910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Doroshenko P. A., Tsyndrenko A. Y. Calcium-dependent potassium conductance studied on internally dialysed nerve cells. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2187–2192. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S., Fedulova S. A. Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons-II. Calcium currents. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2431–2437. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90089-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S., Tsyndrenko A. Y. Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons-I. Sodium currents. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2423–2430. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Yoshida S., Yonezawa T. A Ca- dependent regenerative response in rodent dorsal root ganglion cells cultured in vitro. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 15;115(2):334–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Yoshida S., Yonezawa T. Tetrodotoxin sensitivity and Ca component of action potentials of mouse dorsal root ganglion cells cultured in vitro. Brain Res. 1978 Oct 6;154(1):69–82. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)91052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAfee D. A., Yarowsky P. J. Calcium-dependent potentials in the mammalian sympathetic neurone. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):507–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Holz R. W. Ionic determinants of excitability in cultured mouse dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord cells. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 18;136(3):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer N. C. Ion channels in development. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1979;2:363–397. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.02.030179.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Matsuda Y. Responses dependent on alkaline earth cations (Ca, Sr, Ba) in dorsal root ganglion cells of the adult mouse. Brain Res. 1980 Apr 28;188(2):593–597. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Matsuda Y., Samejima A. Tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium and calcium components of action potentials in dorsal root ganglion cells of the adult mouse. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Sep;41(5):1096–1106. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.5.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Matsuda Y. Studies on sensory neurons of the mouse with intracellular-recording and horseradish peroxidase-injection techniques. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Jul;42(4):1134–1145. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.4.1134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


