Abstract
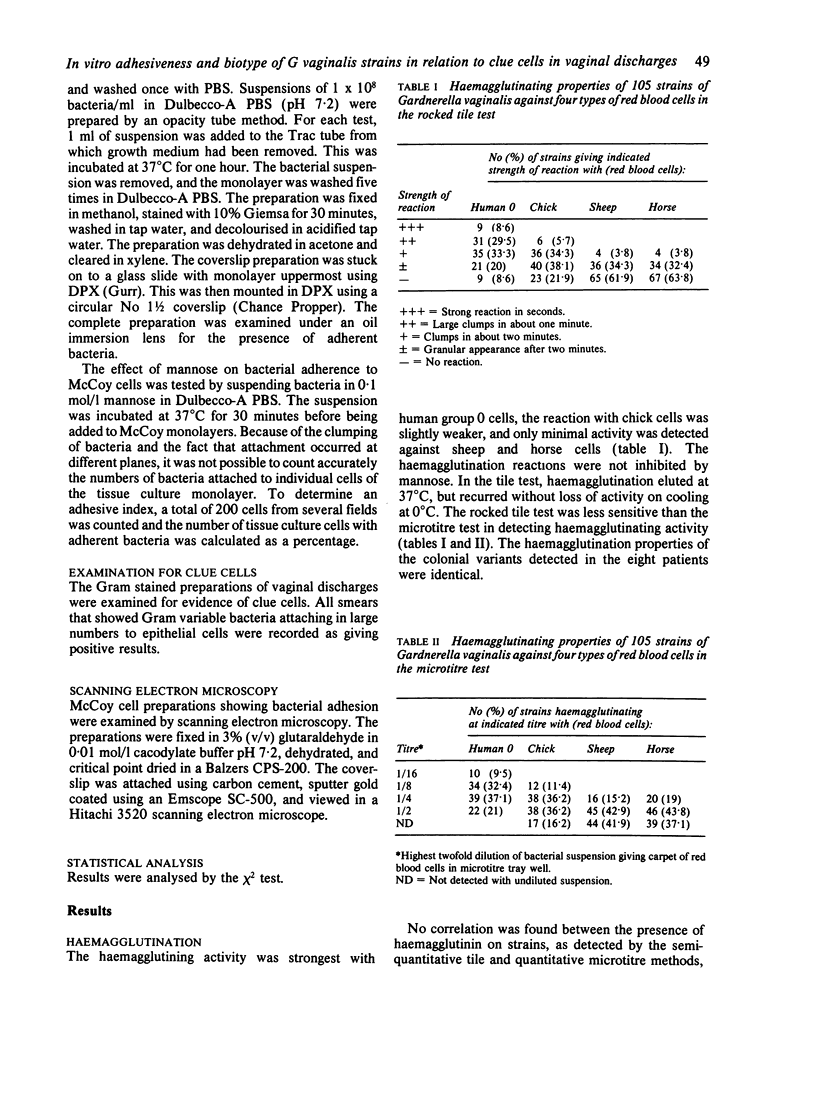
Haemagglutination and tissue culture adherence tests using a McCoy cell line were used to examine the adherence characteristics of 105 strains of Gardnerella vaginalis. Each strain represented one isolate per patient. For each patient, a direct smear of vaginal discharge was examined for clue cells. The relation between in vitro adherence and the presence of clue cells was examined. There seemed to be no appreciable relation between the presence of clue cells in smears and the haemagglutinating activity of strains. In contrast, adherence as judged by the McCoy tissue culture system showed a significant relation to the presence of clue cells (p less than 0.001). Though both adhesive characteristics were not inhibited by mannose, the mechanism of haemagglutination of human red cells appeared to differ from that of adherence of tissue culture cells. The findings imply that the clue cell phenomenon is due to attachment of adherent strains of G vaginalis to epithelial cells. Adherent strains of G vaginalis may play a part in the pathogenesis of bacterial vaginosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amsel R., Totten P. A., Spiegel C. A., Chen K. C., Eschenbach D., Holmes K. K. Nonspecific vaginitis. Diagnostic criteria and microbial and epidemiologic associations. Am J Med. 1983 Jan;74(1):14–22. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREWER J. I., HALPERN B., THOMAS G. Hemophilus vaginalis vaginitis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1957 Oct;74(4):834–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botta G. A. Hormonal and type-dependent adhesion of group B streptococci to human vaginal cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):1084–1086. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.1084-1086.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney F. E. Hemophilus vaginalis septicemia. Obstet Gynecol. 1973 Jan;41(1):78–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. P., Clegg S., Wilson M. I. The fimbrial and non-fimbrial haemagglutinins of Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1979 May;12(2):213–227. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. T., Woodland R. M. Detection of chlamydiae by isolation and direct examination. Br Med Bull. 1983 Apr;39(2):181–186. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairley K. F., Birch D. F. Unconventional bacteria in urinary tract disease: Gardnerella vaginalis. Kidney Int. 1983 Jun;23(6):862–865. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelhor R. S., Wolinsky E., Kim C. H., Tchou P., Frengley J. D. Gardnerella vaginalis perinephric abscess in a transplanted kidney. N Engl J Med. 1981 Apr 2;304(14):846–846. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198104023041418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredricsson B., Hagström B., Evaldson G., Nord C. E. Gardnerella-associated vaginitis and anaerobic bacteria. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1984;17(5):236–241. doi: 10.1159/000299155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., Jones G. W. Models for studying the role of bacterial attachment in virulence and pathogenesis. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S647–S658. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER H. L., DUKES C. D. Haemophilus vaginalis vaginitis: a newly defined specific infection previously classified non-specific vaginitis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1955 May;69(5):962–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafiz S., McEntegart M. G., Kinghorn G. R. Sheffield medium for cultivation of Haemophilus ducreyi. Br J Vener Dis. 1984 Jun;60(3):196–198. doi: 10.1136/sti.60.3.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ison C. A., Easmon C. S. Studies on the mechanism of adhesion of Gardnerella vaginalis to human erythrocytes. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 1984;86:191–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levison M. E., Trestman I., Quach R., Sladowski C., Floro C. N. Quantitative bacteriology of the vaginal flora in vaginitis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1979 Jan 15;133(2):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(79)90464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. F., O'Brien S. M., Ural U. M., Burke T. Corynebacterium vaginale vaginitis. Review of the literature and presentation of data based on vaginal cultures from 1,008 patients. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Jan 1;112(1):87–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loulergue J., Laudat P., Huten N., Raoult A., Boutault L. Upper urinary tract infection with Gardnerella vaginalis in a woman. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;3(3):270–270. doi: 10.1007/BF02014901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A. S., Dutta P., Dutta D., Ghose A. C. Antibacterial and antitoxin responses in the serum and milk of cholera patients. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.1-8.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. M., Hayes C. H., Rosner B., Evrard J. R., Crockett V. A., Alpert S., Zinner S. H. Vaginal colonization with Corynebacterium vaginale (Haemophilus vaginalis). J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):740–745. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monif G. R., Baer H. Haemophilus (Corynebacterium) vaginalis septicemia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Dec 15;120(8):1041–1045. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(74)90147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårdh P. A., Westtöm L. Adherence of bacterial to vaginal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):661–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.661-666.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pheifer T. A., Forsyth P. S., Durfee M. A., Pollock H. M., Holmes K. K. Nonspecific vaginitis: role of Haemophilus vaginalis and treatment with metronidazole. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 29;298(26):1429–1434. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806292982601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P., Van Dyck E., Godts P., Vanderheyden J. The vaginal microbial flora in non-specific vaginitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;1(5):301–306. doi: 10.1007/BF02019976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P., Van Dyck E., Peeters M., Hale J., Totten P. A., Holmes K. K. Biotypes of Gardnerella vaginalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):677–679. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.677-679.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer L. G., Reller L. B. Gardnerella vaginalis bacteremia: a review of thirty cases. Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Aug;64(2):170–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D., Myers P., Levison M. E., Kaye D. Comparison of bacterial and fungal adherence to vaginal exfoliated epithelial cells and human vaginal epithelial tissue culture cells. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):697–701. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.697-701.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F. Bacterial virulence and pathogenesis: an overview. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S637–S646. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel C. A., Amsel R., Eschenbach D., Schoenknecht F., Holmes K. K. Anaerobic bacteria in nonspecific vaginitis. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 11;303(11):601–607. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009113031102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel C. A., Amsel R., Holmes K. K. Diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis by direct gram stain of vaginal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.170-177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E., Blackwell A. L., Barlow D., Phillips I. Gardnerella vaginalis, anaerobes, and vaginal discharge. Lancet. 1982 Jun 19;1(8286):1376–1379. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92498-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E., Phillips I. The identification of Gardnerella vaginalis. J Med Microbiol. 1983 Feb;16(1):83–92. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks M., Thin R. N., Tabaqchali S. Quantitative bacteriology of the vaginal flora in genital disease. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Oct;18(2):217–231. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-2-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]