Abstract
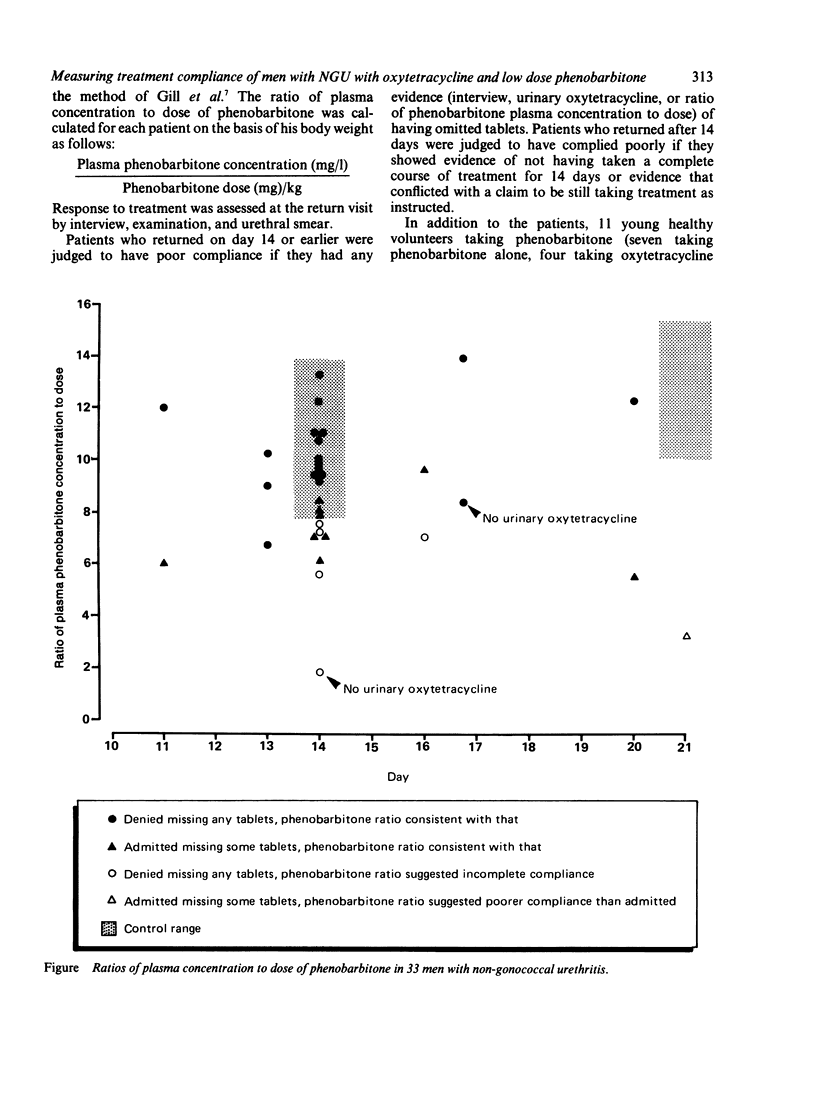
Of 62 men with non-gonococcal urethritis who entered a study to assess compliance with treatment with oxytetracycline, only 33 could be evaluated. Traditional methods (interview and the absence of oxytetracycline in the urine) showed incomplete compliance in nine. Use of low dose phenobarbitone as a pharmacological marker showed incomplete compliance in a further five patients. In addition, phenobarbitone concentrations gave information on the extent to which individual patients had omitted treatment and provided direct, as opposed to circumstantial, evidence of good compliance by most (18) of those studied. Only three of the 33 patients whose compliance was assessed had evidence of continuing infection at follow up, and there was evidence of incomplete compliance in only one of these patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGMAN A. B., WERNER R. J. Failure of children to receive penicillin by mouth. N Engl J Med. 1963 Jun 13;268:1334–1338. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196306132682404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L., Spelman M. The problem of non-compliance with drug therapy. Drugs. 1983 Jan;25(1):63–76. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198325010-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feely M., Cooke J., Price D., Singleton S., Mehta A., Bradford L., Calvert R. Low-dose phenobarbitone as an indicator of compliance with drug therapy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;24(1):77–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1987.tb03139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasagna L. Fault and default. N Engl J Med. 1973 Aug 2;289(5):267–268. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197308022890511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar M. R., Langdale P. Simple microbiological method for the identification of antimicrobial agents prescribed in general practice. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):741–744. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.741-744.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. E., Mehta A., Park B. K., Hay A., Feely M. P. The effect of low-dose phenobarbitone on three indices of hepatic microsomal enzyme induction. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;22(6):744–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb02970.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


