Abstract
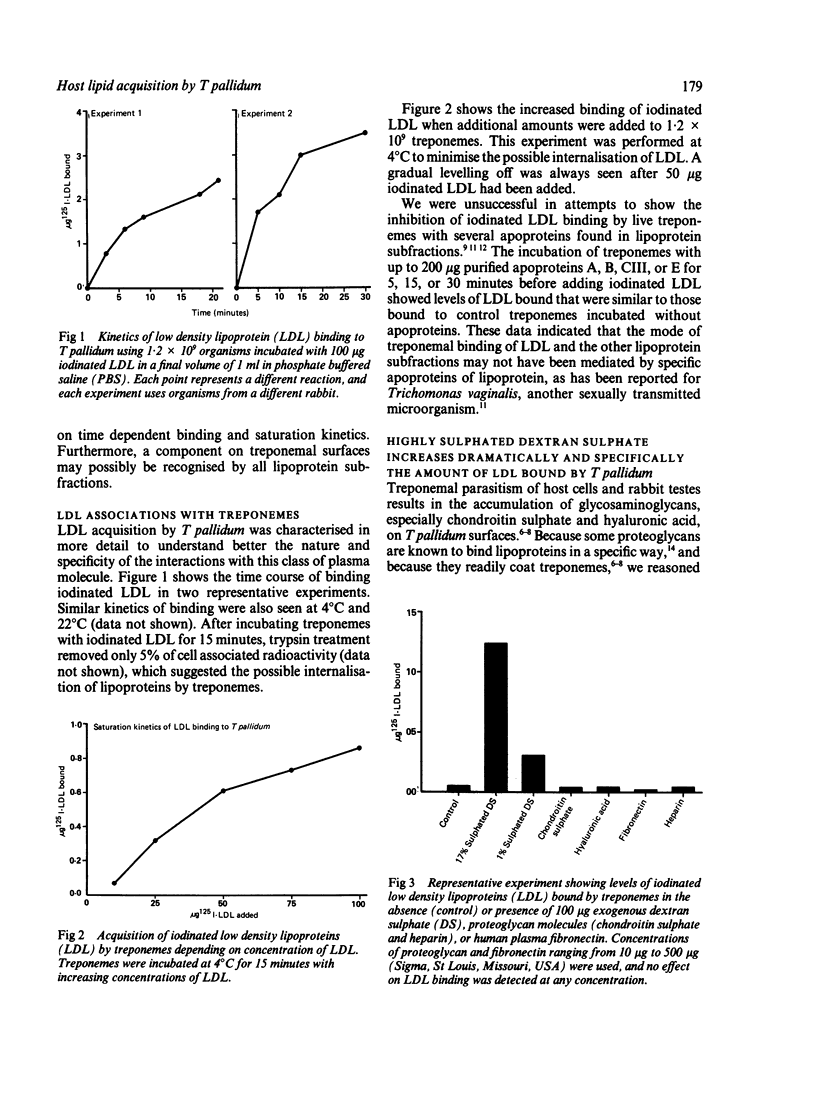
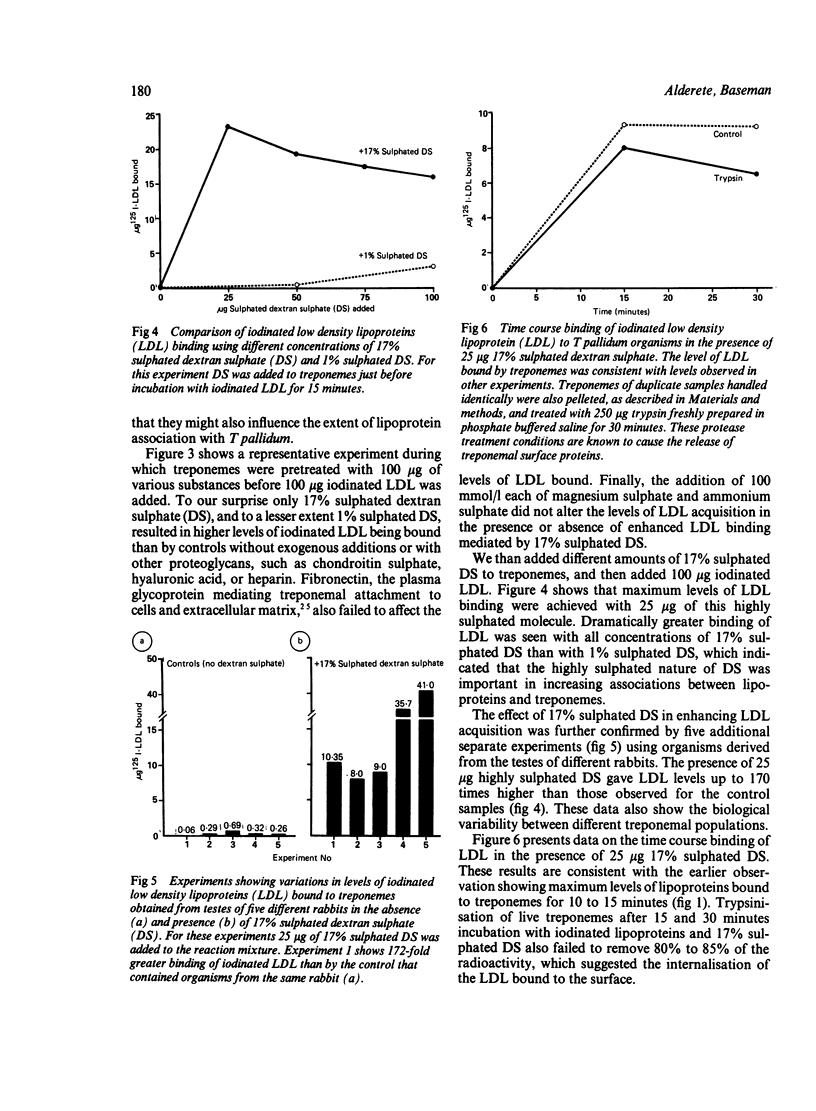
Acquisition by the syphilis spirochaete, Treponema pallidum, of radioiodinated total human plasma lipoprotein and lipoprotein subfractions was examined. Time dependent and saturation binding kinetics were observed for total lipoproteins and subfractions, including high density lipoproteins, low density lipoproteins (LDL), and very low density lipoproteins. All subfractions competed equally well in binding iodinated total lipoproteins and individual subfractions, but apoproteins common to all subfractions were ineffective in inhibiting lipoprotein acquisition. The interaction of LDL with T pallidum was studied further and, interestingly, the presence of 17% sulphated dextran sulphate (DS) in the reaction mixture containing treponemes and LDL resulted in up to 172 times more LDL being bound by live treponemes. Biological variability was observed in the extent of increased LDL bound in the presence of 17% sulphated DS by preparations of T pallidum isolated from different infected rabbits. Saturation kinetics of iodinated LDL acquisition was obtained in the presence of 17% sulphated DS but not 1% sulphated DS. Other proteoglycan molecules, such as chondroitin sulphate, hyaluronic acid and heparin, and fibronectin, the extracellular matrix protein targeted by treponemes in parasitism of host cells and tissues neither diminished nor enhanced LDL binding by live treponemes. Only 5% and 10% of associated radioactivity was released from treponemal surfaces after T pallidum was incubated with iodinated LDL and 17% sulphated-DS for 15 and 30 minutes, respectively. These data show binding and possible internalisation of host lipoproteins by T pallidum, which may be mediated by sulphated proteoglycan. Sulphated proteoglycans accumulate during T pallidum infections of host cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface characterization of virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):814–823. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.814-823.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface-associated host proteins on virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1048–1056. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1048-1056.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Peterson K. M., Baseman J. B. Affinities of Treponema pallidum for human lactoferrin and transferrin. Genitourin Med. 1988 Dec;64(6):359–363. doi: 10.1136/sti.64.6.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieldsteel A. H., Becker F. A., Stout J. G. Prolonged survival of virulent Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in cell-free and tissue culture systems. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):173–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.173-182.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C. Mucopolysaccharidase of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):261–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.261-268.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C., Ritzi D. M. Relationship of Treponema pallidum to acidic mucopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):252–260. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.252-260.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Miller J. N., Repesh L. A., Rice M., Urquhart A. Binding of glycosaminoglycans to the surface of Treponema pallidum and subsequent effects on complement interactions between antigen and antibody. Genitourin Med. 1985 Feb;61(1):13–20. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIMM G. E., ALLEN R. H., MORTON H. J., MORGAN J. F. Studies on the in vitro survival of virulent Treponema pallidum. I. Methodology and basal synthetic medium. Am J Hyg. 1962 May;75:339–346. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews H. M., Jenkin H. M., Crilly K., Sandok P. L. Effects of fatty acids on motility retention by Treponema pallidum in vitro. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):814–821. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.814-821.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews H. M., Yang T. K., Jenkin H. M. Unique lipid composition of Treponema pallidum (Nichols virulent strain). Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):713–719. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.713-719.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin T. A., Guest W. J., Geller R. C. Response of Treponema pallidum to certain nutrilites. Br J Vener Dis. 1968 Dec;44(4):274–276. doi: 10.1136/sti.44.4.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Alderete J. F. Trichomonas vaginalis is dependent on uptake and degradation of human low density lipoproteins. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1261–1272. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Treponema pallidum receptor binding proteins interact with fibronectin. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1958–1970. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller N. L., Cox C. D. Catabolism of glucose and fatty acids by virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):60–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.60-68.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Fibronectin mediates Treponema pallidum cytadherence through recognition of fibronectin cell-binding domain. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):514–525. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Sluis J. J., van Dijk G., Boer M., Stolz E., van Joost T. Mucopolysaccharides in suspensions of Treponema pallidum extracted from infected rabbit testes. Genitourin Med. 1985 Feb;61(1):7–12. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


