Abstract
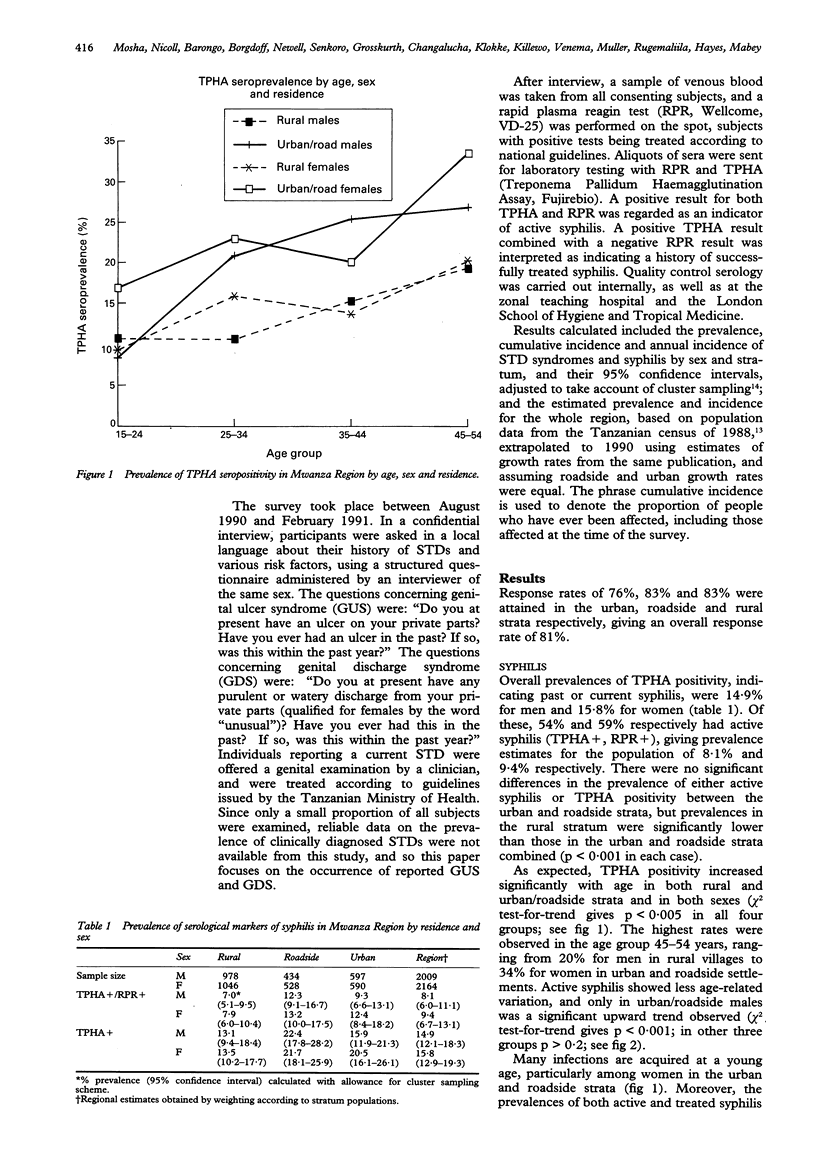
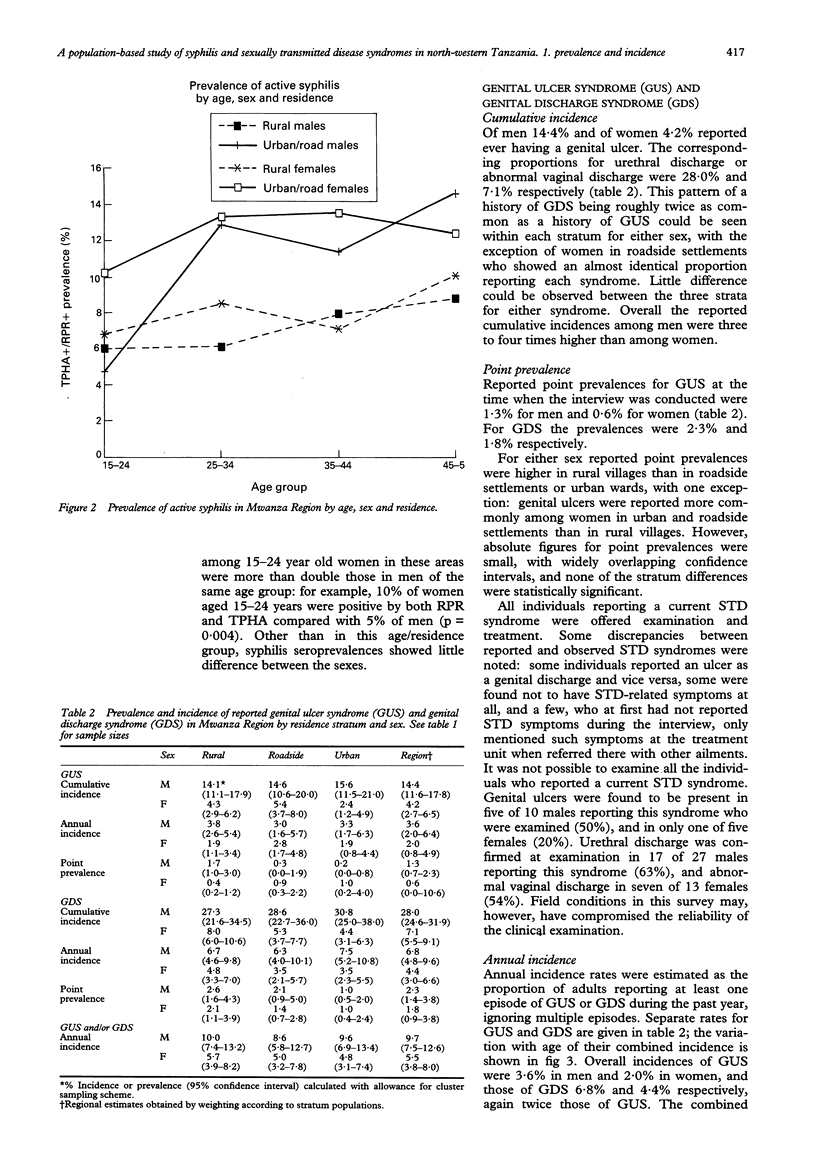
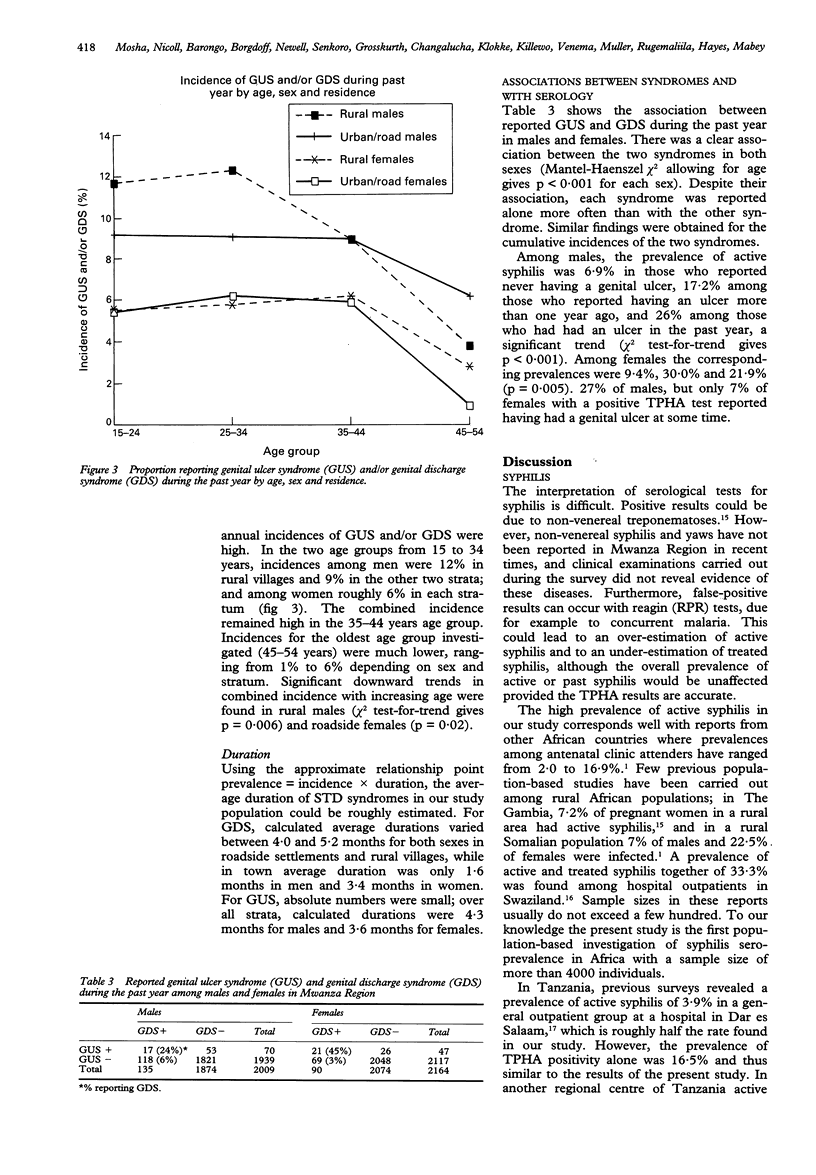
OBJECTIVE--To determine the prevalence of syphilis and the prevalence and incidence of self-reported STD syndromes in the population of Mwanza Region, North-Western Tanzania. METHODS--A population-based random cluster sample survey, stratified by rural, roadside or urban residence, of 4173 individuals aged 15-54 years was performed in 1990-91. The seroprevalence of syphilis (using TPHA and RPR) and the prevalence and incidence of self-reported genital ulcer syndrome (GUS) and genital discharge syndrome (GDS) were determined. RESULTS--Active syphilis was detected in 9% of the adult population, while 15% had serological evidence of past or current infection. Seroprevalence was significantly lower in the rural than in the roadside and urban populations, but there was little difference between men and women. Amongst men, a history of GDS was reported by 28%, and a history of GUS by 14%, with point prevalences of 2.3% and 1.3% respectively. Annual incidence among men were 6.8% for GDS and 3.6% for GUS. Women reported these conditions less frequently. There was little difference between the strata in the prevalence or incidence of reported STD syndromes. CONCLUSION--Sexually transmitted diseases represent a major public health problem in both the rural and urban populations of Mwanza Region.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya O. P., Nsanzumuhire H., Taber S. R. Clinical, cultural, and demographic aspects of gonorrhoea in a rural community in Uganda. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;49(6):587–595. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barongo L. R., Borgdorff M. W., Mosha F. F., Nicoll A., Grosskurth H., Senkoro K. P., Newell J. N., Changalucha J., Klokke A. H., Killewo J. Z. The epidemiology of HIV-1 infection in urban areas, roadside settlements and rural villages in Mwanza Region, Tanzania. AIDS. 1992 Dec;6(12):1521–1528. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199212000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett S., Woods T., Liyanage W. M., Smith D. L. A simplified general method for cluster-sample surveys of health in developing countries. World Health Stat Q. 1991;44(3):98–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron D. W., Simonsen J. N., D'Costa L. J., Ronald A. R., Maitha G. M., Gakinya M. N., Cheang M., Ndinya-Achola J. O., Piot P., Brunham R. C. Female to male transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: risk factors for seroconversion in men. Lancet. 1989 Aug 19;2(8660):403–407. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90589-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J., Mann J. Global surveillance and forecasting of AIDS. Bull World Health Organ. 1989;67(1):1–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper-Poole B. Prevalence of syphilis in Mbeya, Tanzania--the validity of the VDRL as a screening test. East Afr Med J. 1986 Oct;63(10):646–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Costa L. J., Plummer F. A., Bowmer I., Fransen L., Piot P., Ronald A. R., Nsanze H. Prostitutes are a major reservoir of sexually transmitted diseases in Nairobi, Kenya. Sex Transm Dis. 1985 Apr-Jun;12(2):64–67. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198504000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Schryver A., Meheus A. Epidemiology of sexually transmitted diseases: the global picture. Bull World Health Organ. 1990;68(5):639–654. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast M. V., D'Costa L. J., Nsanze H., Piot P., Curran J., Karasira P., Mirza N., Maclean I. W., Ronald A. R. The clinical diagnosis of genital ulcer disease in men in the tropics. Sex Transm Dis. 1984 Apr-Jun;11(2):72–76. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198404000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabey D. C., Wall R. A., Bello C. S. Aetiology of genital ulceration in the Gambia. Genitourin Med. 1987 Oct;63(5):312–315. doi: 10.1136/sti.63.5.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meheus A., Ballard R., Dlamini M., Ursi J. P., Van Dyck E., Piot P. Epidemiology and aetiology of urethritis in Swaziland. Int J Epidemiol. 1980 Sep;9(3):239–245. doi: 10.1093/ije/9.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meheus A., Friedman F., Van Dyck E., Guyver T. Genital infections in prenatal and family planning attendants in Swaziland. East Afr Med J. 1980 Mar;57(3):212–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens T. E., Hayes R. J., Smith P. G. Epidemiological methods to study the interaction between HIV infection and other sexually transmitted diseases. AIDS. 1990 Jan;4(1):57–65. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199001000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepin J., Plummer F. A., Brunham R. C., Piot P., Cameron D. W., Ronald A. R. The interaction of HIV infection and other sexually transmitted diseases: an opportunity for intervention. AIDS. 1989 Jan;3(1):3–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P., Plummer F. A., Mhalu F. S., Lamboray J. L., Chin J., Mann J. M. AIDS: an international perspective. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):573–579. doi: 10.1126/science.3277271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer F. A., Simonsen J. N., Cameron D. W., Ndinya-Achola J. O., Kreiss J. K., Gakinya M. N., Waiyaki P., Cheang M., Piot P., Ronald A. R. Cofactors in male-female sexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):233–239. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz K. F., Cates W., Jr, O'Mara P. R. Pregnancy loss, infant death, and suffering: legacy of syphilis and gonorrhoea in Africa. Genitourin Med. 1987 Oct;63(5):320–325. doi: 10.1136/sti.63.5.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen J. N., Cameron D. W., Gakinya M. N., Ndinya-Achola J. O., D'Costa L. J., Karasira P., Cheang M., Ronald A. R., Piot P., Plummer F. A. Human immunodeficiency virus infection among men with sexually transmitted diseases. Experience from a center in Africa. N Engl J Med. 1988 Aug 4;319(5):274–278. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198808043190504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


