Abstract
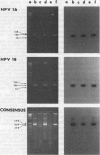
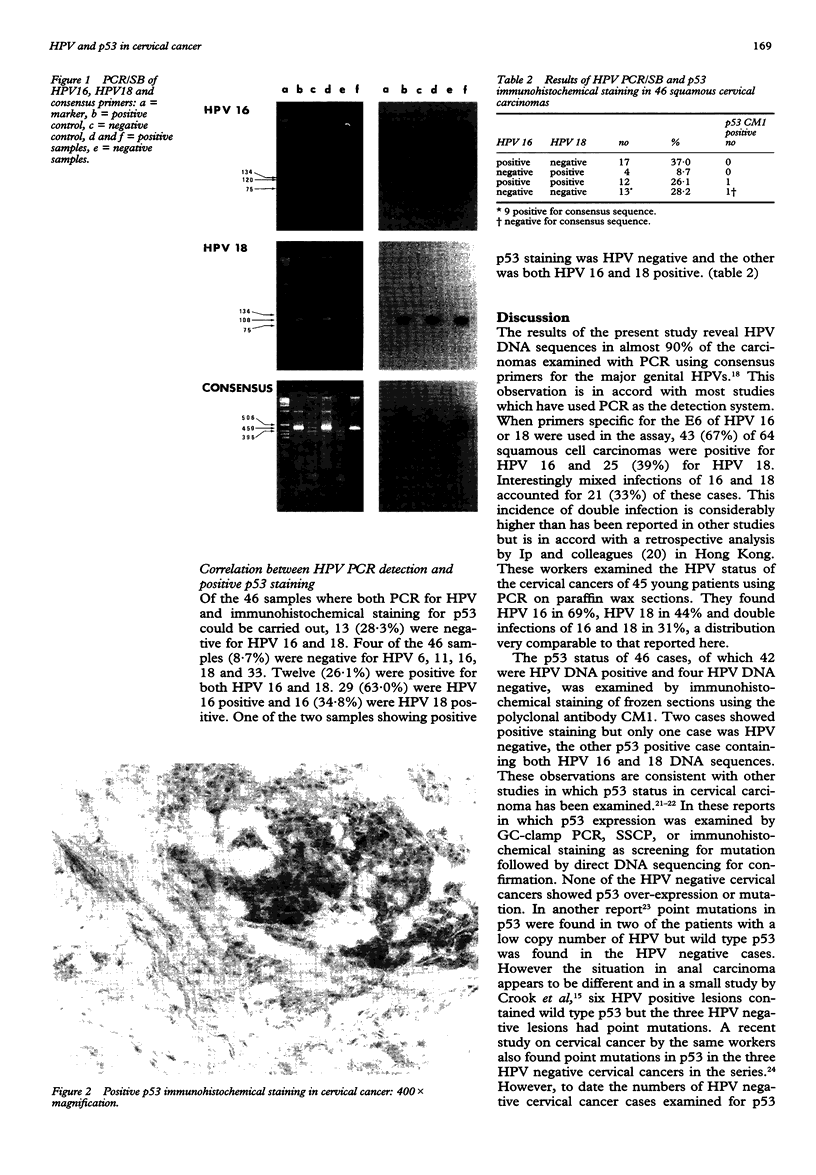
OBJECTIVE--To determine the prevalence of HPV 16 and 18 E6 by DNA detection and p53 abnormal protein expression in cervical cancers in Hong Kong. MATERIALS AND METHODS--Seventy-three squamous cell cervical cancer biopsy were analysed. Detection of HPV DNA was carried out by the polymerase chain reaction and Southern blotting (PCR/SB) technique using primers to the HPV16 & 18 E6 region and consensus primers to the L1 region. Abnormal expression of the p53 protein was detected by immunohistochemical staining (IHS) using the antibody CM1 on frozen sections of 55 cervical cancer samples. Forty-six samples were analysed for both the presence of HPV DNA and abnormal expression of p53. RESULTS--67.2% of the 64 samples showed the presence of HPV 16 E6 DNA and 39.1% showed the presence of HPV 18 E6 DNA. 32.8% showed the presence of both HPV 16 and 18 E6 DNA. No HPV DNA was shown in 10.9% of samples. Only 3.6% (2) of 55 samples showed positive IHS with CM1. One occurred in a HPV negative sample and the other in a HPV positive sample. CONCLUSION--A high prevalence of HPV DNA was detected in cervical cancer in Hong Kong using the PCR/SB technique. However, abnormal expression of p53 was uncommon amongst patients with or without HPV 16 or 18 infection.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Busby-Earle R. M., Steel C. M., Williams A. R., Cohen B., Bird C. C. Papillomaviruses, p53, and cervical cancer. Lancet. 1992 May 30;339(8805):1350–1350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Børresen A. L., Helland A., Nesland J., Holm R., Trope C., Kaern J. Papillomaviruses, p53, and cervical cancer. Lancet. 1992 May 30;339(8805):1350–1351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Tidy J. A., Vousden K. H. Degradation of p53 can be targeted by HPV E6 sequences distinct from those required for p53 binding and trans-activation. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):547–556. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90529-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Vousden K. H. Properties of p53 mutations detected in primary and secondary cervical cancers suggest mechanisms of metastasis and involvement of environmental carcinogens. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3935–3940. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05487.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Wrede D., Tidy J. A., Mason W. P., Evans D. J., Vousden K. H. Clonal p53 mutation in primary cervical cancer: association with human-papillomavirus-negative tumours. Lancet. 1992 May 2;339(8801):1070–1073. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90662-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Wrede D., Tidy J., Scholefield J., Crawford L., Vousden K. H. Status of c-myc, p53 and retinoblastoma genes in human papillomavirus positive and negative squamous cell carcinomas of the anus. Oncogene. 1991 Jul;6(7):1251–1257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Wrede D., Vousden K. H. p53 point mutation in HPV negative human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Oncogene. 1991 May;6(5):873–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Luca D., Costa S., Monini P., Rotola A., Terzano P., Savioli A., Grigioni W., Cassai E. Search for human papillomavirus, herpes simplex virus and c-myc oncogene in human genital tumors. Int J Cancer. 1989 Apr 15;43(4):570–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita M., Inoue M., Tanizawa O., Iwamoto S., Enomoto T. Alterations of the p53 gene in human primary cervical carcinoma with and without human papillomavirus infection. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 1;52(19):5323–5328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K. A., Kulesz-Martin M. F. Altered expression of wild-type p53 tumor suppressor gene during murine epithelial cell transformation. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 1;52(3):749–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins G. D., Phillips G. E., Smith L. A., Uzelin D. M., Burrell C. J. High prevalence of human papillomavirus transcripts in all grades of cervical intraepithelial glandular neoplasia. Cancer. 1992 Jul 1;70(1):136–146. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920701)70:1<136::aid-cncr2820700123>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbert N. L., Sedman S. A., Schiller J. T. Human papillomavirus type 16 E6 increases the degradation rate of p53 in human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6237–6241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6237-6241.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip E. W., Collins R. J., Srivastava G., Cheung A. N., Wong L. C. Human papillomavirus and its prognostic significance in invasive carcinoma of the cervix in young patients. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 1992 Oct;11(4):258–265. doi: 10.1097/00004347-199210000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koutsky L. A., Holmes K. K., Critchlow C. W., Stevens C. E., Paavonen J., Beckmann A. M., DeRouen T. A., Galloway D. A., Vernon D., Kiviat N. B. A cohort study of the risk of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or 3 in relation to papillomavirus infection. N Engl J Med. 1992 Oct 29;327(18):1272–1278. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199210293271804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox P. H., Jenkins D. 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APES): a new advance in section adhesion. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Oct;40(10):1256–1257. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.10.1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer C. J., van den Brule A. J., Snijders P. J., Helmerhorst T., Kenemans P., Walboomers J. M. Detection of human papillomavirus in cervical scrapes by the polymerase chain reaction in relation to cytology: possible implications for cervical cancer screening. IARC Sci Publ. 1992;(119):271–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz N., Bosch F. X., de Sanjosé S., Tafur L., Izarzugaza I., Gili M., Viladiu P., Navarro C., Martos C., Ascunce N. The causal link between human papillomavirus and invasive cervical cancer: a population-based case-control study in Colombia and Spain. Int J Cancer. 1992 Nov 11;52(5):743–749. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanczuk H., Villa L. L., Schlegel R., Howley P. M. The viral transcriptional regulatory region upstream of the E6 and E7 genes is a major determinant of the differential immortalization activities of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2739–2744. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2739-2744.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa L. L., Schlegel R. Differences in transformation activity between HPV-18 and HPV-16 map to the viral LCR-E6-E7 region. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):374–377. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90507-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers E. M. Heterogeneity of the human papillomavirus group. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4898–4903. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4898-4903.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Human papillomaviruses in the pathogenesis of anogenital cancer. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):9–13. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90816-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]