Abstract
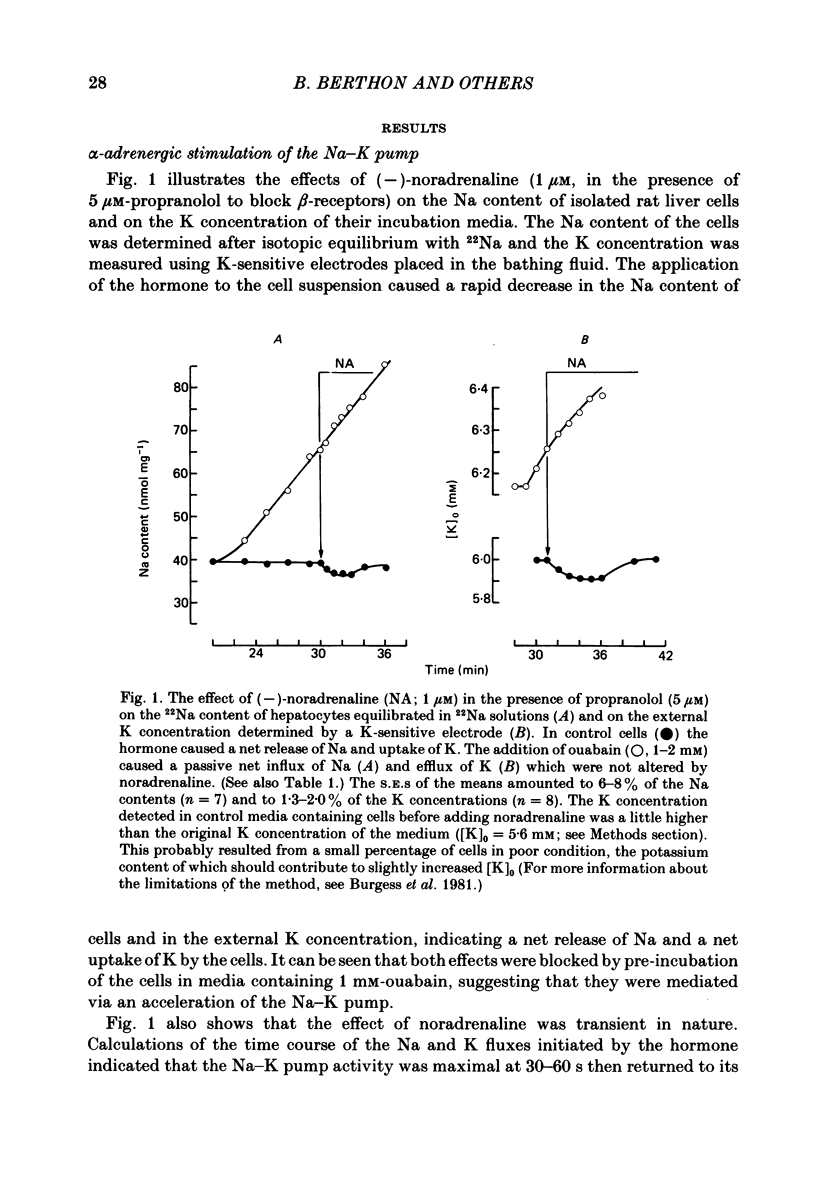
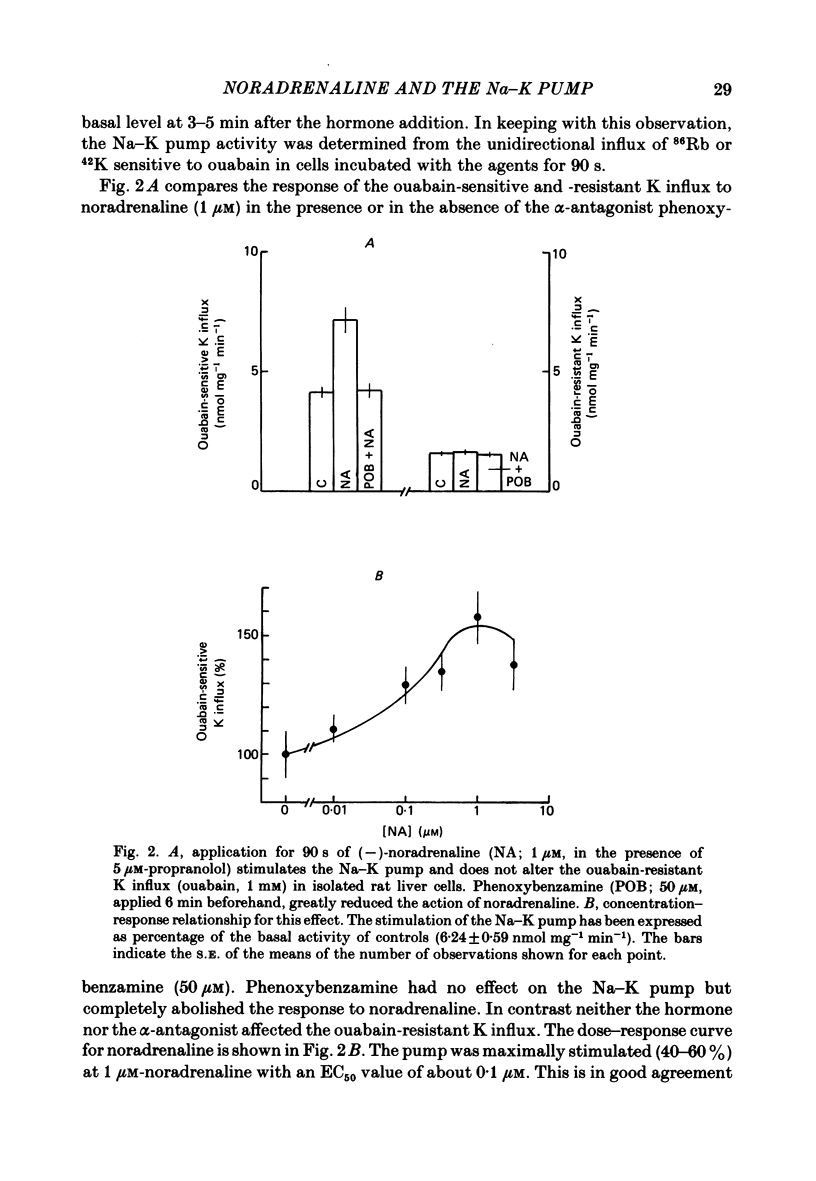
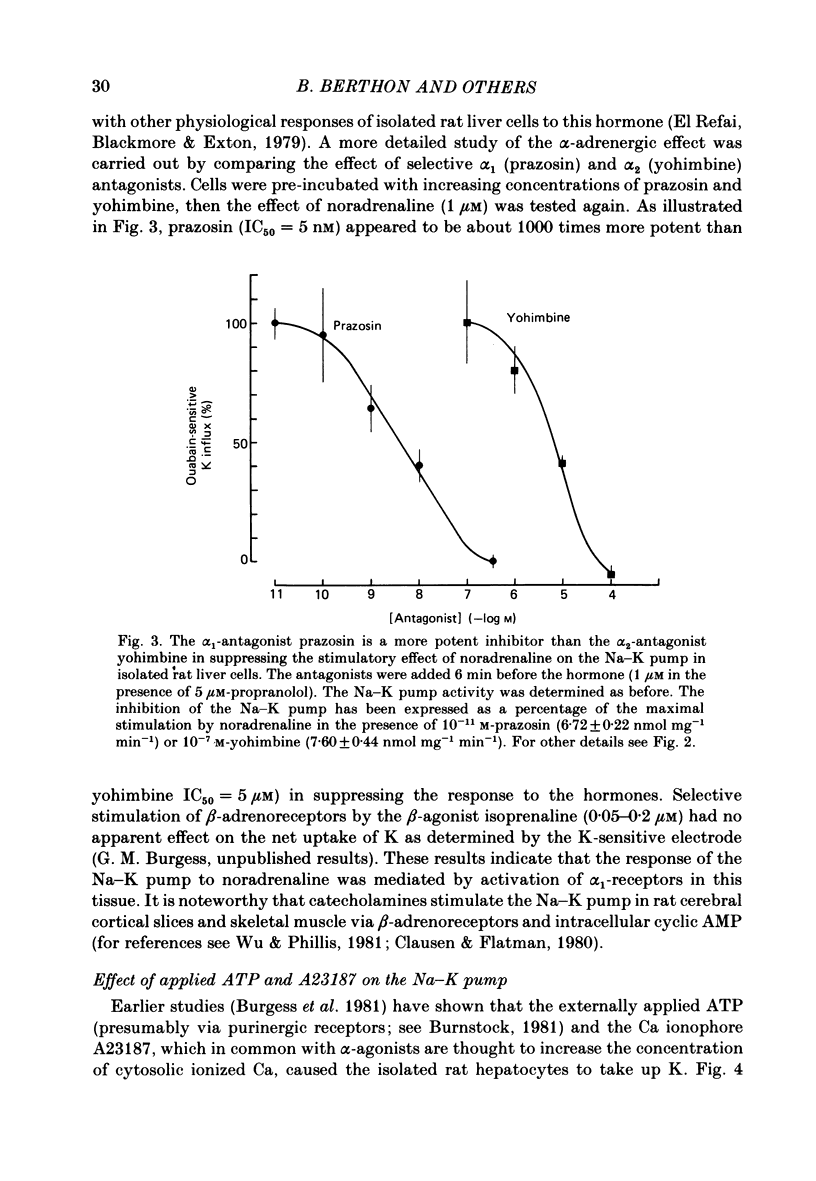
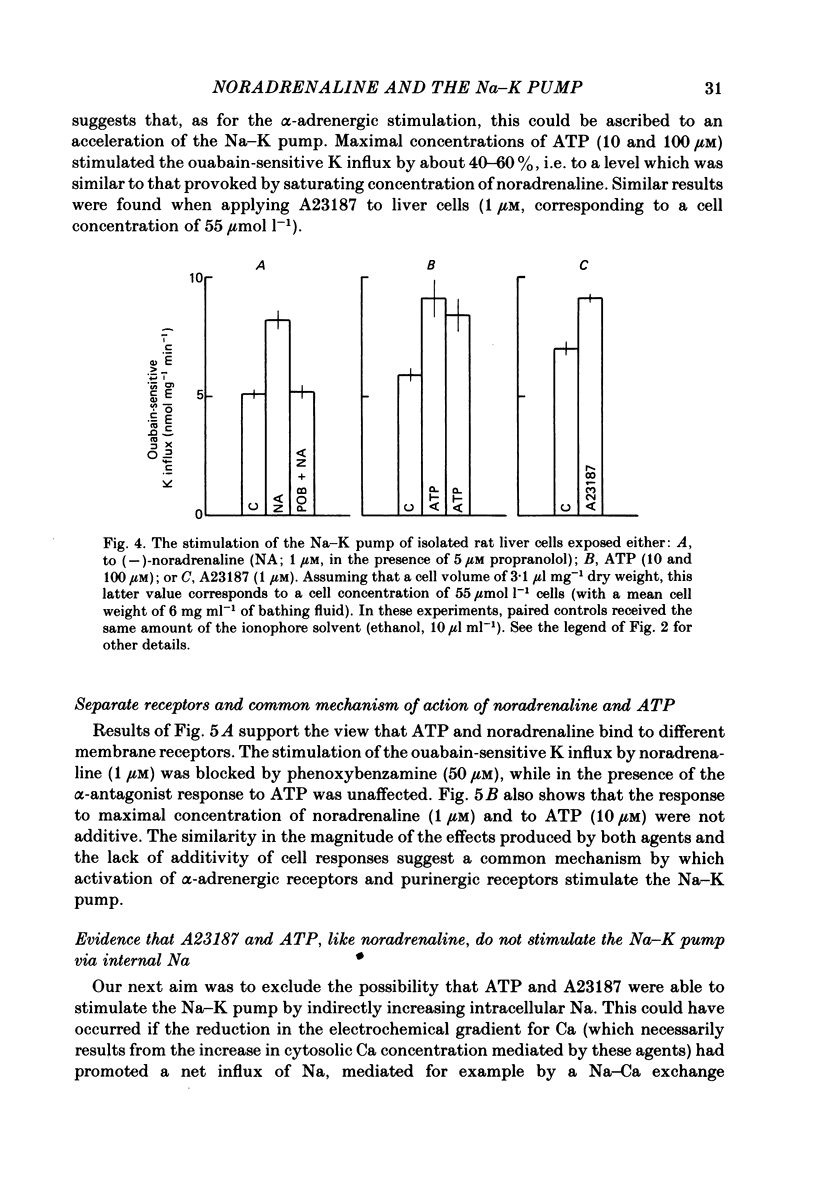
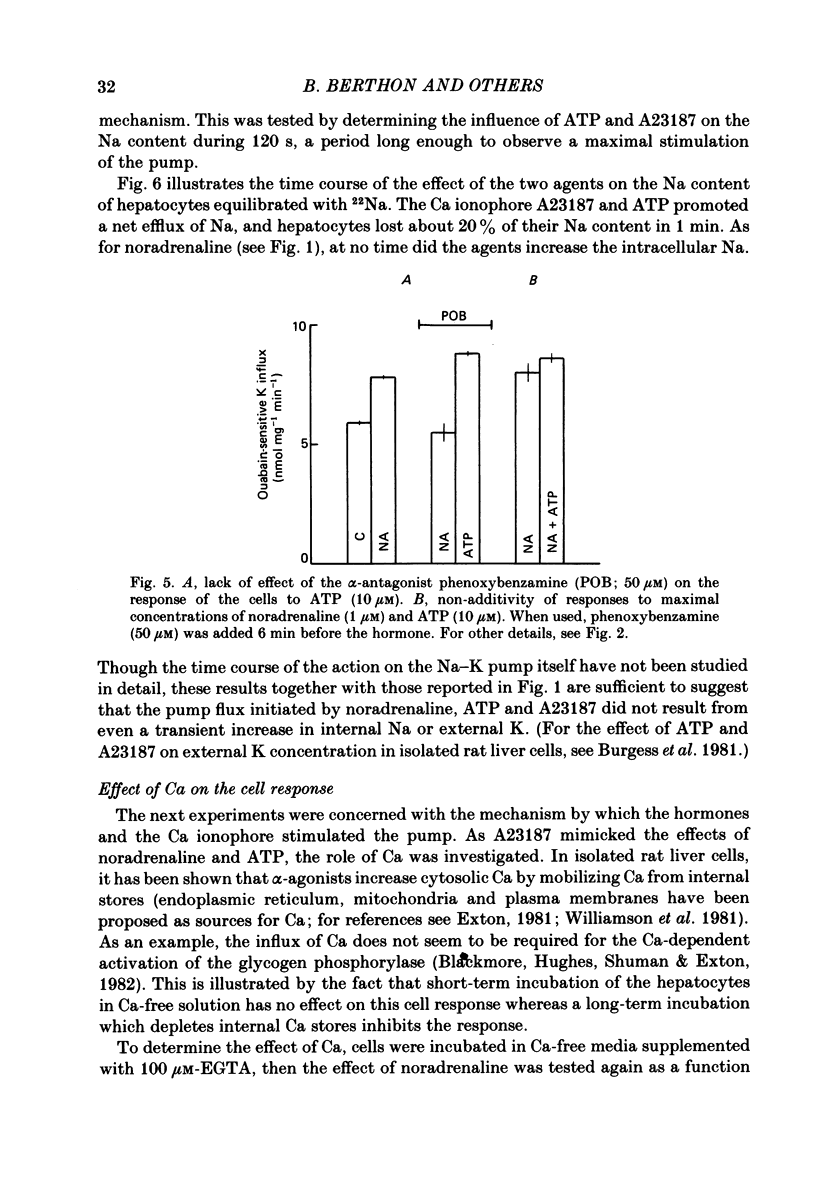
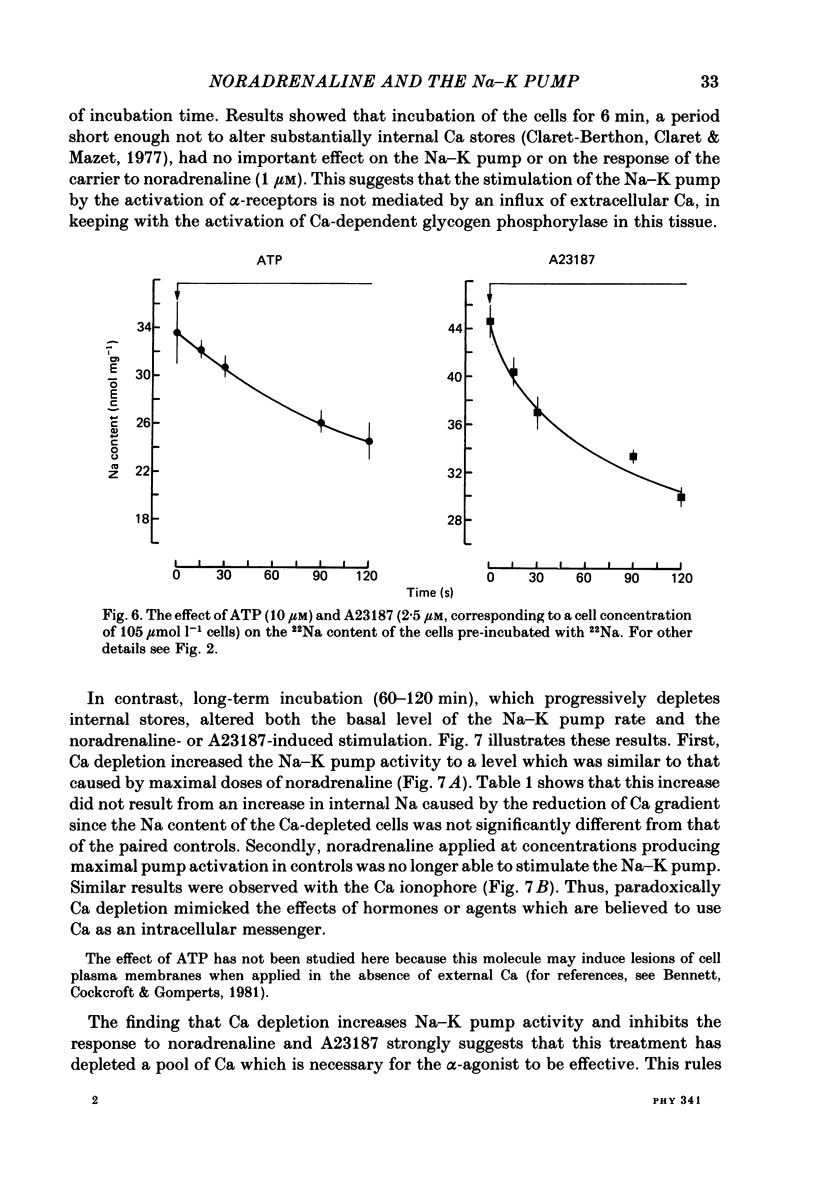
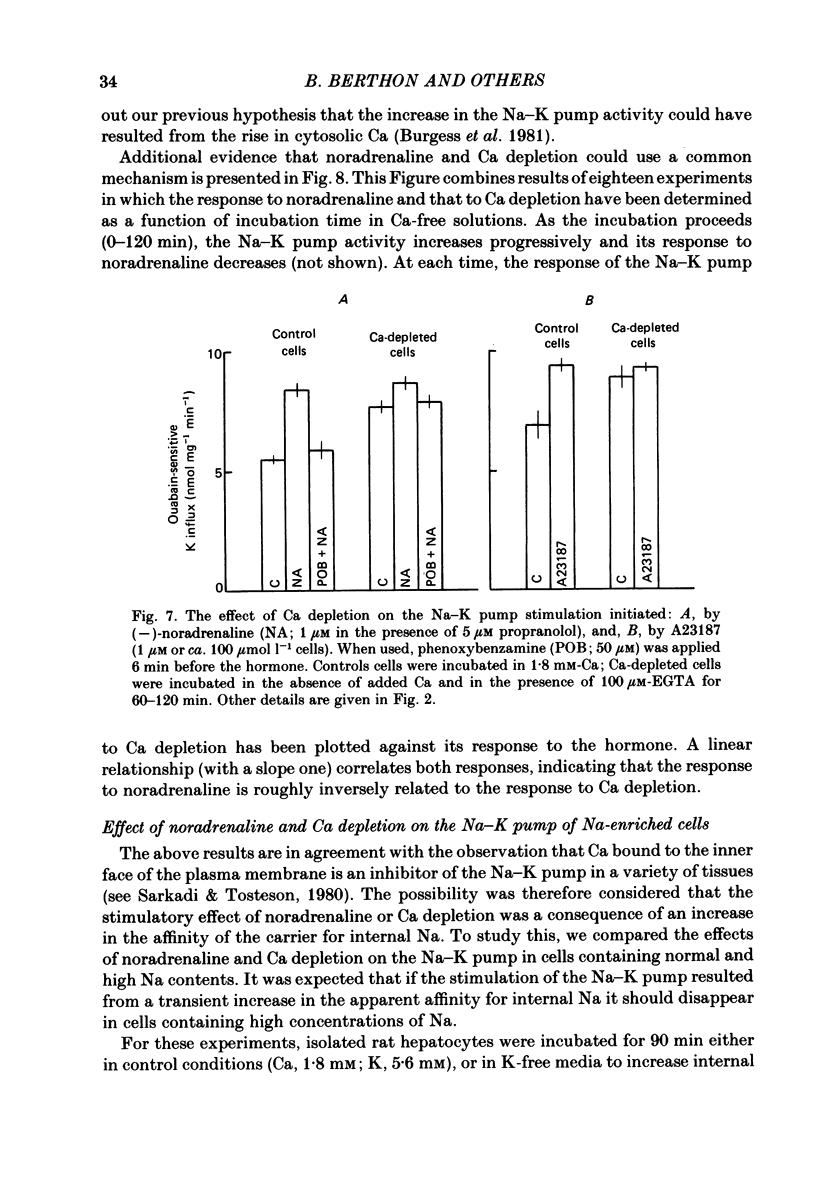
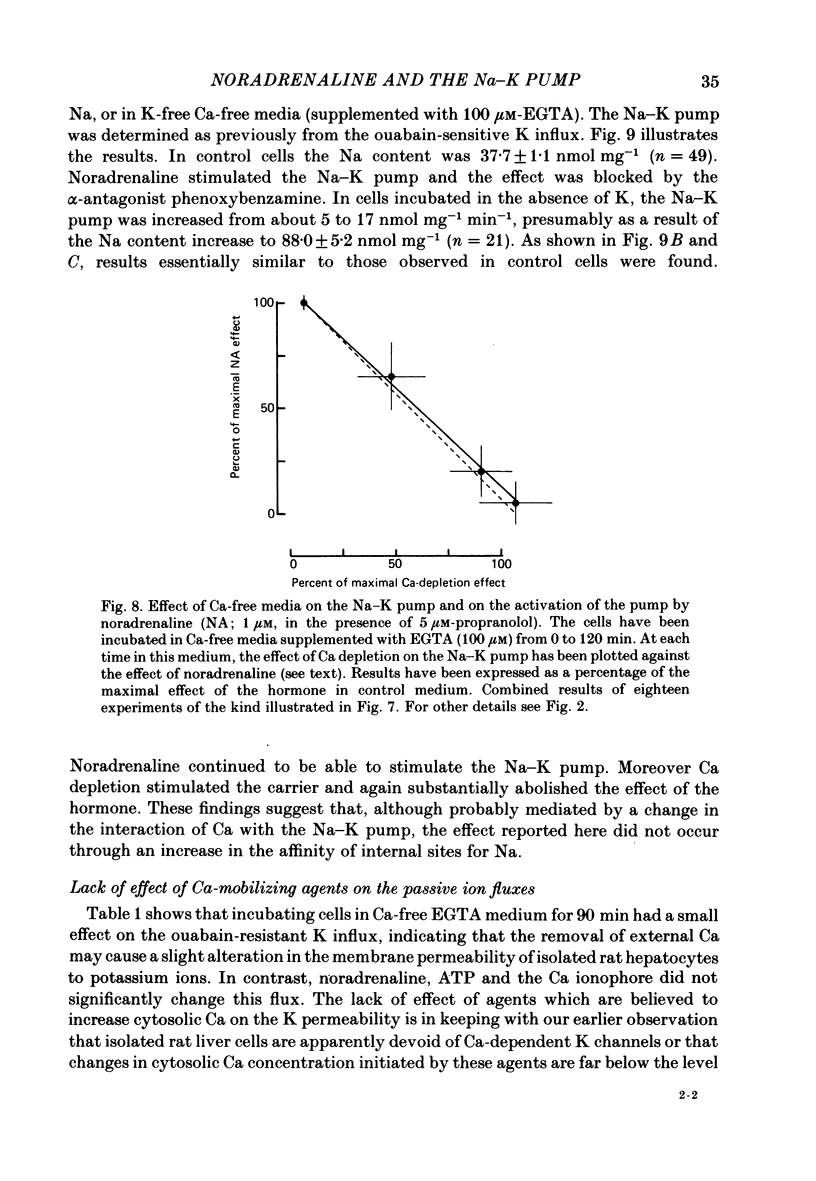
Noradrenaline, which mobilizes Ca from intracellular stores, stimulated the Na-K pump in isolated rat liver cells. This resulted in transient decreases in internal Na content and external K concentration. The effect of the hormones was observed in the presence of the beta-adrenergic antagonist propranolol and was blocked by the alpha-antagonist phenoxybenzamine. Prazosin appeared to be 1000 times more potent than yohimbine in suppressing the cell response to the hormone, suggesting that the effect is mediated by an activation of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors. Externally applied ATP and the Ca ionophore A23187 which, in common with alpha-agonists, deplete internal Ca stores in this tissue, similarly stimulated the Na-K pump and transiently decreased internal Na and external K. The effects of noradrenaline and ATP were not additive. Moreover, the cell response to ATP was observed in the presence of the alpha-antagonist phenoxybenzamine, indicating that though acting via separate receptors, noradrenaline and ATP use a common mechanism to alter the carrier. The effect of noradrenaline and A23187 on the Na-K pump was not dependent on the presence of extracellular Ca. In contrast, when the hepatocytes were incubated in Ca-free medium for long periods (cell Ca depletion) the activity of the Na-K pump was increased to a level corresponding to that induced by maximal doses of noradrenaline. In these conditions, noradrenaline and A23187 did not increase the pump activity further. In cells in which the Na content was raised, leading to a 3-fold increase in the Na-K pump activity, noradrenaline continued to be able to stimulate the pump. Again long-term incubations in Ca-free medium increased the pump activity and the effect of noradrenaline was greatly reduced. It is proposed that in isolated rat liver cells alpha-agonists and applied ATP influence the Na-K pump by releasing Ca bound to plasma membranes, thus removing the inhibitory effect of this ion on the Na pump.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. P., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Rat mast cells permeabilized with ATP secrete histamine in response to calcium ions buffered in the micromolar range. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:335–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
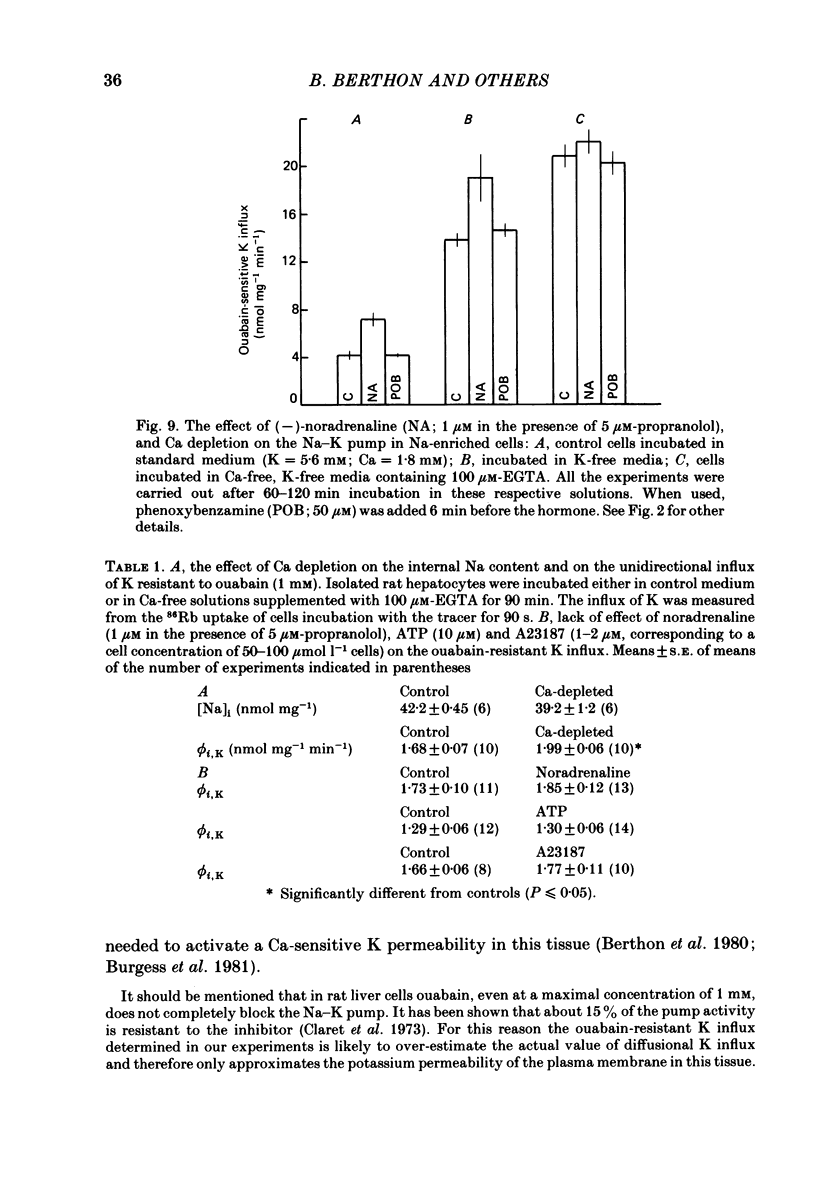
- Berthon B., Claret M., Mazet J. L., Poggioli J. Volume- and temperature-dependent permeabilities in isolated rat liver cells. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:267–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Dehaye J. P., Exton J. H. Studies on alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. The role of mitochondrial calcium release in alpha-adrenergic activation of phosphorylase in perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6945–6950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Hughes B. P., Shuman E. A., Exton J. H. alpha-Adrenergic activation of phosphorylase in liver cells involves mobilization of intracellular calcium without influx of extracellular calcium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):190–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blouin A., Bolender R. P., Weibel E. R. Distribution of organelles and membranes between hepatocytes and nonhepatocytes in the rat liver parenchyma. A stereological study. J Cell Biol. 1977 Feb;72(2):441–455. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Claret M., Jenkinson D. H. Effects of quinine and apamin on the calcium-dependent potassium permeability of mammalian hepatocytes and red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:67–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Review lecture. Neurotransmitters and trophic factors in the autonomic nervous system. J Physiol. 1981;313:1–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capiod T., Berthon B., Poggioli J., Burgess G. M., Claret M. The effect of Ca2+ -mobilising hormones on the Na+ --K+ pump in isolated rat liver hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1982 May 3;141(1):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claret-Berthon B., Claret M., Mazet J. L. Fluxes and distribution of calcium in rat liver cells: kinetic analysis and identification of pools. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):529–552. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claret B., Claret M., Mazet J. L. Ionic transport and membrane potential of rat liver cells in normal and low-chloride solutions. J Physiol. 1973 Apr;230(1):87–101. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claret M., Mazet J. L. Ionic fluxes and permeabilities of cell membranes in rat liver. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(2):279–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Flatman J. A. Beta 2-adrenoceptors mediate the stimulating effect of adrenaline on active electrogenic Na-K-transport in rat soleus muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Apr;68(4):749–755. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10868.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desaiah D., Ho I. K. Kinetics of catecholamine sensitive Na+-K+ ATPase activity in mouse brain synaptosomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Nov 1;26(21):2029–2035. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Refai M. F., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Evidence for two alpha-adrenergic binding sites in liver plasma membranes. Studies with [3H]epinephrine and [3H]dihydroergocryptine. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4375–4386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Molecular mechanisms involved in alpha-adrenergic responses. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Sep;23(3):233–264. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann N., Park C. R. Early effects of 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate on the fluxes of calcium end potassium in the perfused liver of normal and adrenalectomized rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):504–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gervais A., Lane L. K., Anner B. M., Lindenmayer G. E., Schwartz A. A possible molecular mechanism of the action of digitalis: ouabain action on calcium binding to sites associated with a purified sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase from kidney. Circ Res. 1977 Jan;40(1):8–14. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupte S. S., Lane L. K., Johnson J. D., Wallick E. T., Schwartz A. The interaction of divalent cations with (Na,K)-ATPase. A lipid-bound fluorescence probe study. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5099–5103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems D. A., Whitton P. D. Control of hepatic glycogenolysis. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jan;60(1):1–50. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hexum T. D. The effect of catecholamines on transport (Na,K) adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Jul 1;26(13):1221–1227. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakob A., Diem S. Metabolic responses of perfused rat livers to alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonists, glucagon and cyclic AMP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 8;404(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90147-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai M., Hawthorne J. N. Physiological significance of polyphosphoinositides in brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Oct 17;165(2):761–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. L., Phillis J. W. Stimulation of cerebral cortical synaptosomal Na-K-ATPase by biogenic amines. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;55(4):961–964. doi: 10.1139/y77-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrop G. Effects of adrenergic blocking agents on epinephrine- and 3',5'-amp-induced responses in the perfused rat liver. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Jan;159(1):22–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawas A. H., Gilbert J. C. Effects of adrenergic agonists and antagonists and of the catechol nucleus on the Na+, K+-ATPase and Mg2+-ATPase activities of synaptosomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 1;30(13):1799–1803. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachtenberg M. C., Packey D. J., Sweeney T. In vivo functioning of the Na+, K+-activated ATPase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;19:159–217. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152819-5.50022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S. Na+-K+-activated adenosinetriphosphatase as a trigger in transmitter release. Neuroscience. 1978;3(4-5):367–384. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Cooper R. H., Hoek J. B. Role of calcium in the hormonal regulation of liver metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 30;639(3-4):243–295. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(81)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu P. H., Phillis J. W. The effect of noradrenaline on Na-K transport in rat cerebral cortical slices. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Feb 19;69(4):529–531. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90463-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Krogt J. A., Belfroid R. D. Characterization and localization of catecholamine-susceptible Na-K ATPase activity of rat striatum: studies using catecholamine receptor (ant)agonists and lesion techniques. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Mar 15;29(6):857–868. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90215-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


