Abstract
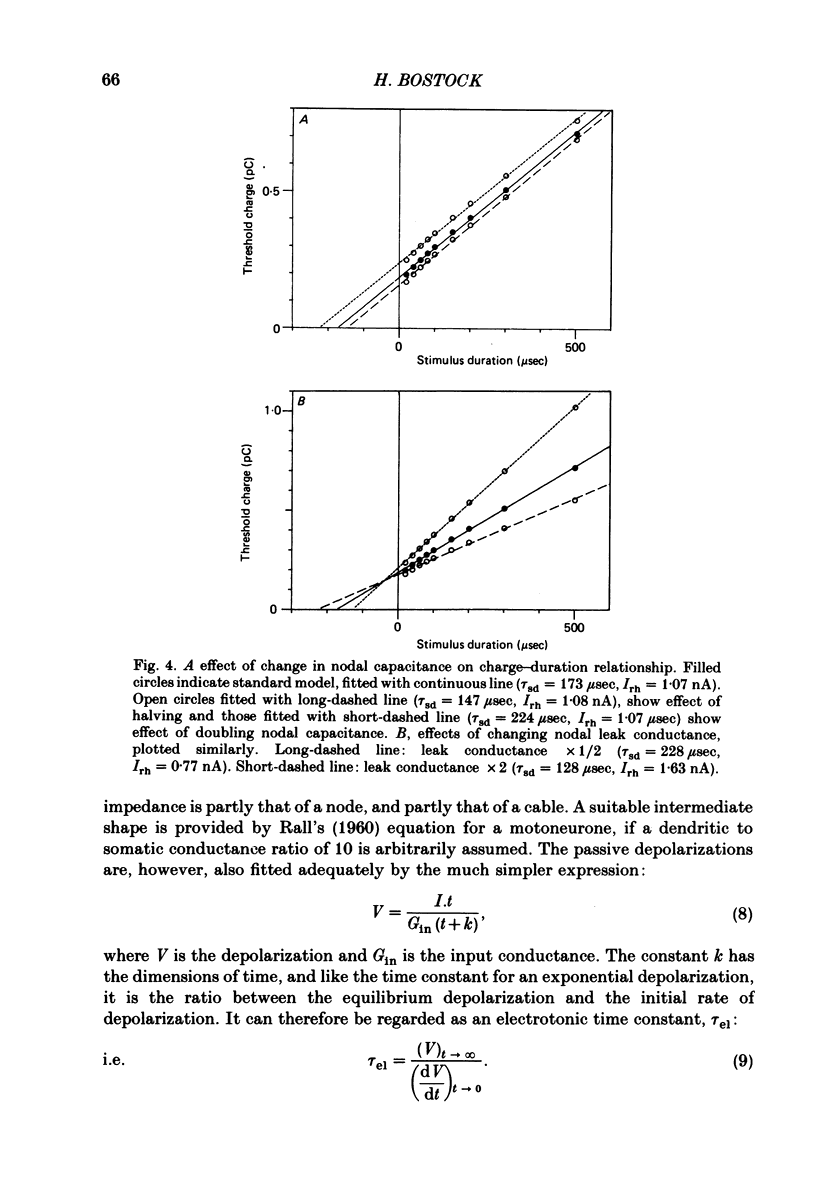
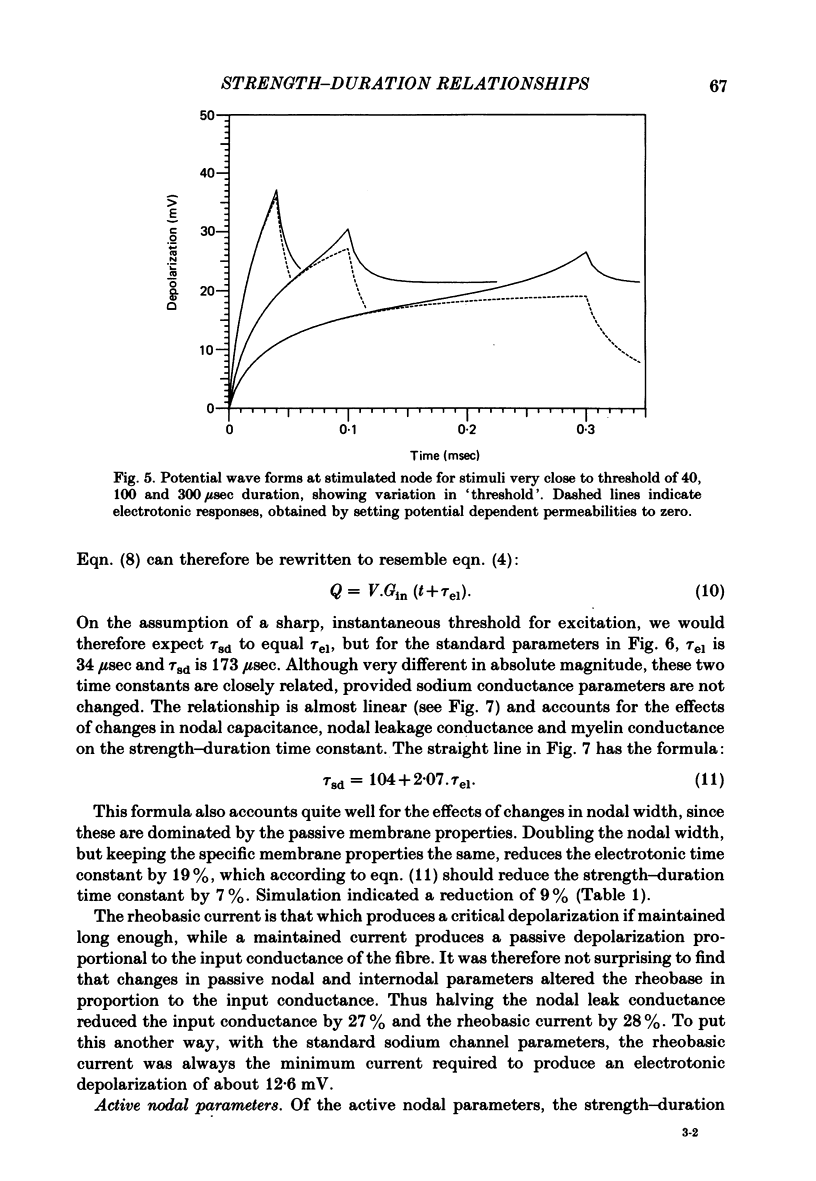
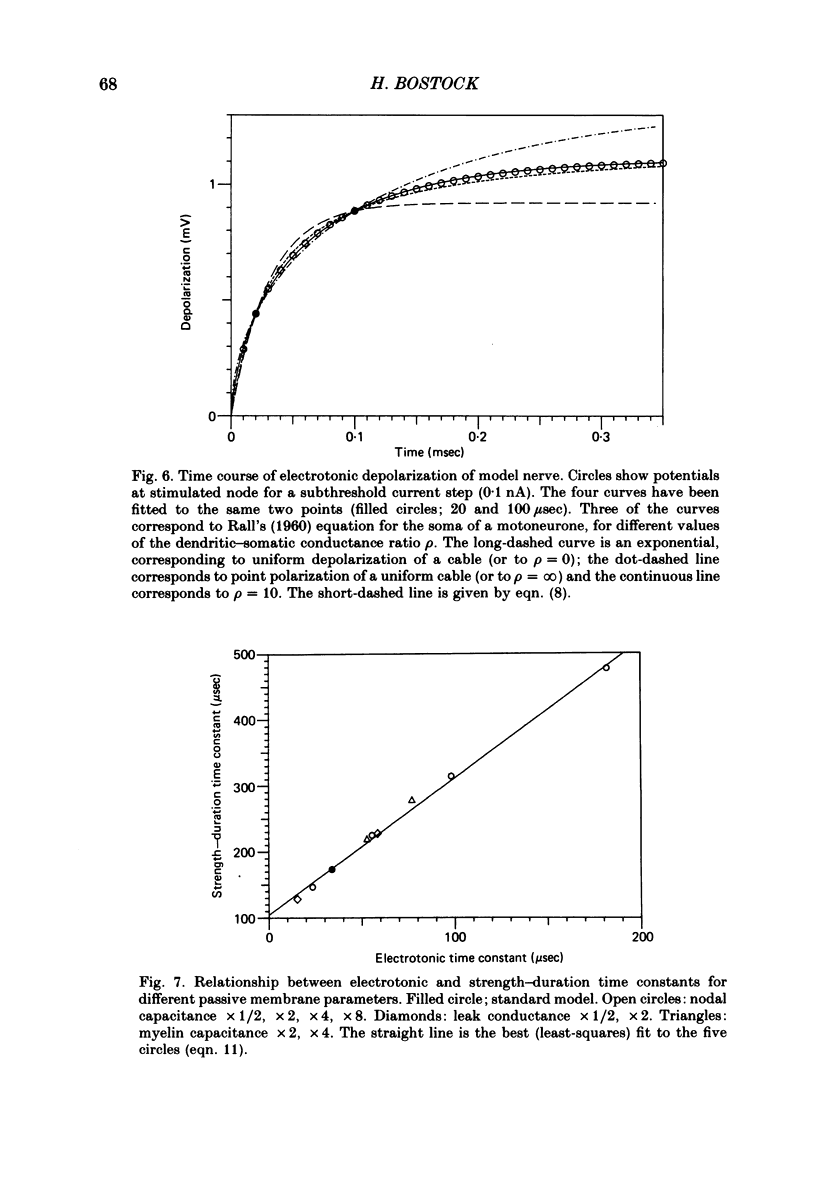
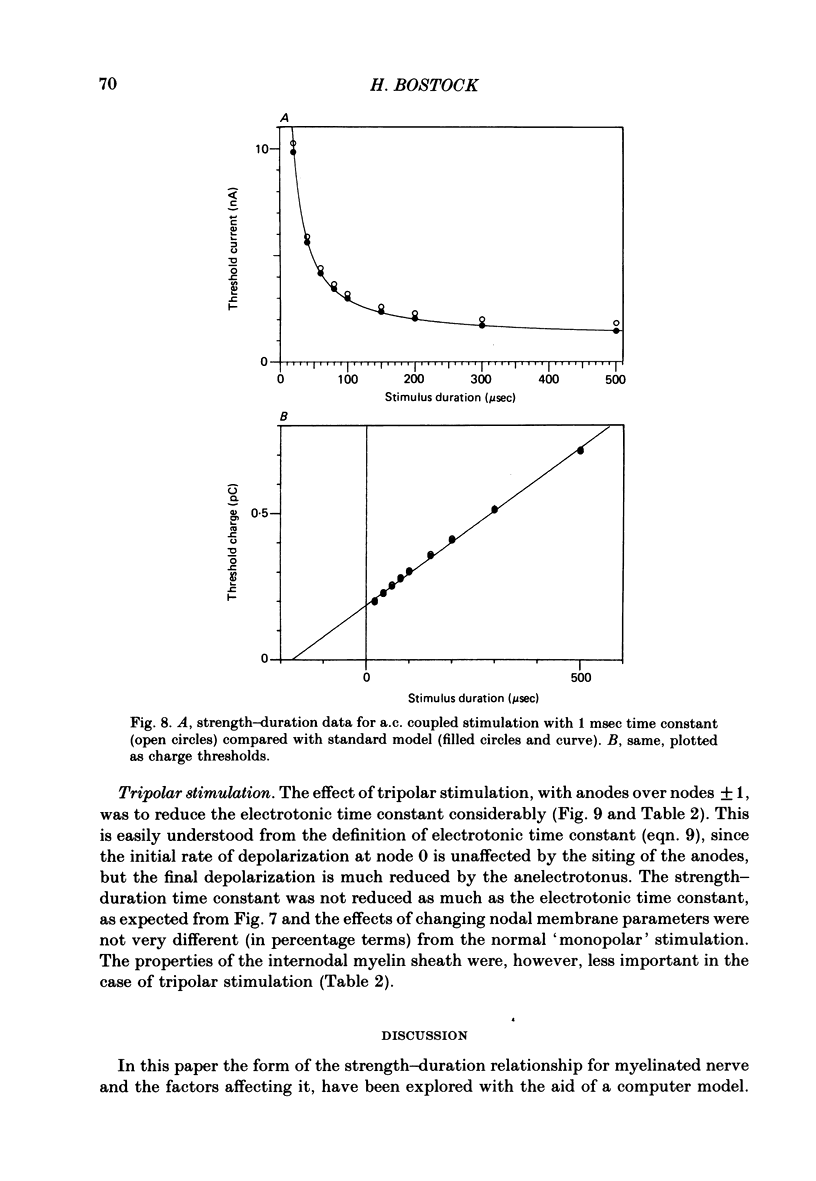
Thresholds to applied current pulses have been determined for the myelinated nerve model of Goldman & Albus (1968). Strength-duration curves have been plotted, and compared with three strength-duration equations that have been proposed in the past. The simple, linear relation between stimulus charge and stimulus duration proposed by Weiss (1901) provided the best fit to the computed data. The effects on the strength-duration relationship of changes in twelve parameters of the model were determined and expressed in terms of the strength-duration time constant and rheobasic current. The rheobase depended primarily on conductances, whereas the strength-duration time constant depended on the electrotonic time constant and also on the rate of sodium activation. The model predicts strength-duration curves of the same form, for extracellular or intracellular stimulation where the external resistance is low and uniform. Tripolar stimulation, with anodes over adjacent rather than remote nodes, is predicted to result in much shorter strength-duration time constants, but with a similar sensitivity to nodal membrane parameters. The limitations of strength-duration measurements on myelinated nerves are discussed in the light of these simulations.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bostock H., Sears T. A., Sherratt R. M. The spatial distribution of excitability and membrane current in normal and demyelinated mammalian nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:41–58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar T. Electrical properties of isolated demyelinated rat nerve fibres. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Oct;113(2):161–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y., Ritchie J. M., Rogart R. B., Stagg D. A quantitative description of membrane currents in rabbit myelinated nerve. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:149–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
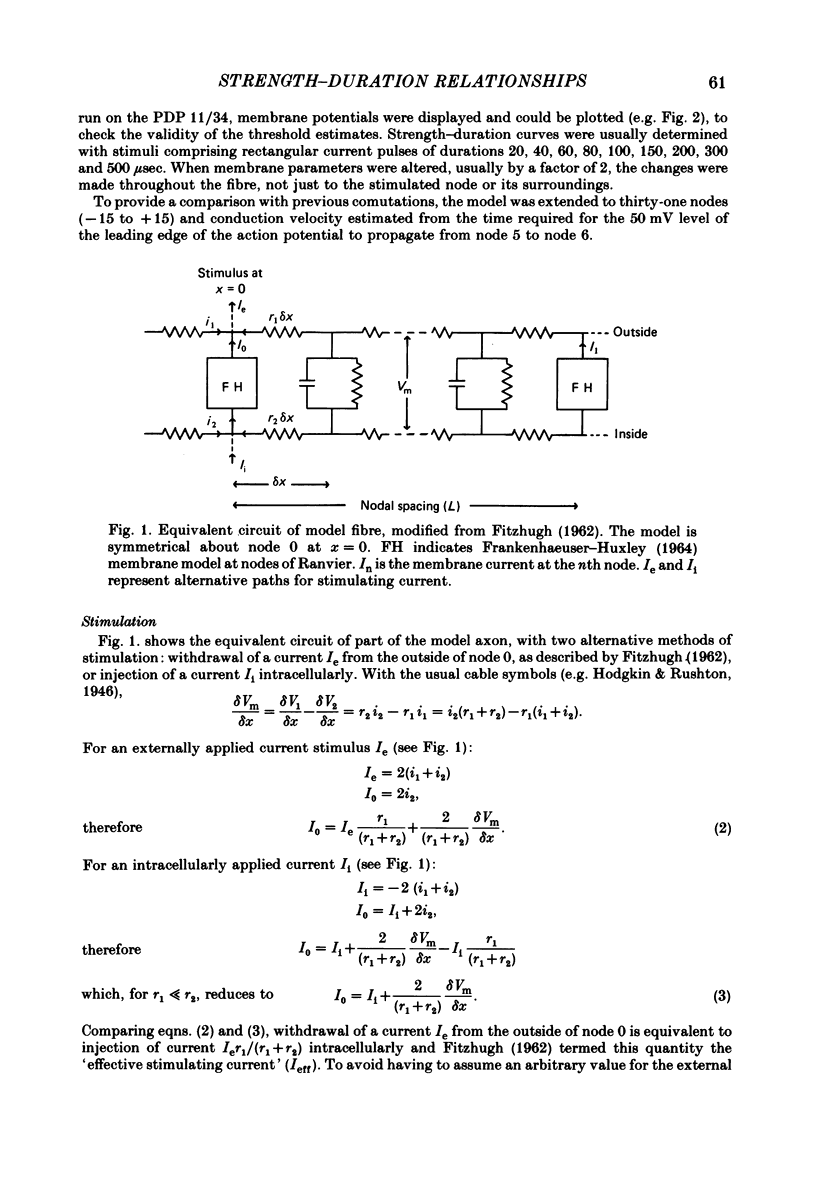
- FITZHUGH R. Computation of impulse initiation and saltatory conduction in a myelinated nerve fiber. Biophys J. 1962 Jan;2:11–21. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86837-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HUXLEY A. F. THE ACTION POTENTIAL IN THE MYELINATED NERVE FIBER OF XENOPUS LAEVIS AS COMPUTED ON THE BASIS OF VOLTAGE CLAMP DATA. J Physiol. 1964 Jun;171:302–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., MOORE L. E. THE EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE SODIUM AND POTASSIUM PERMEABILITY CHANGES IN MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES OF XENOPUS LAEVIS. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:431–437. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., WALTMAN B. Membrane resistance and conduction velocity of large myelinated nerve fibres from Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:677–682. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenhaeuser B. Computed action potential in nerve from Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):780–787. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L., Albus J. S. Computation of impulse conduction in myelinated fibers; theoretical basis of the velocity-diameter relation. Biophys J. 1968 May;8(5):596–607. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(68)86510-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundfest H. Excitability of the single fibre nerve-muscle complex. J Physiol. 1932 Sep 16;76(1):95–115. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1932.sp002913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson N. A., Koles Z. J., Smith R. S. Conduction velocity in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1970 Jun;208(2):279–289. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koles Z. J., Rasminsky M. A computer simulation of conduction in demyelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):351–364. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
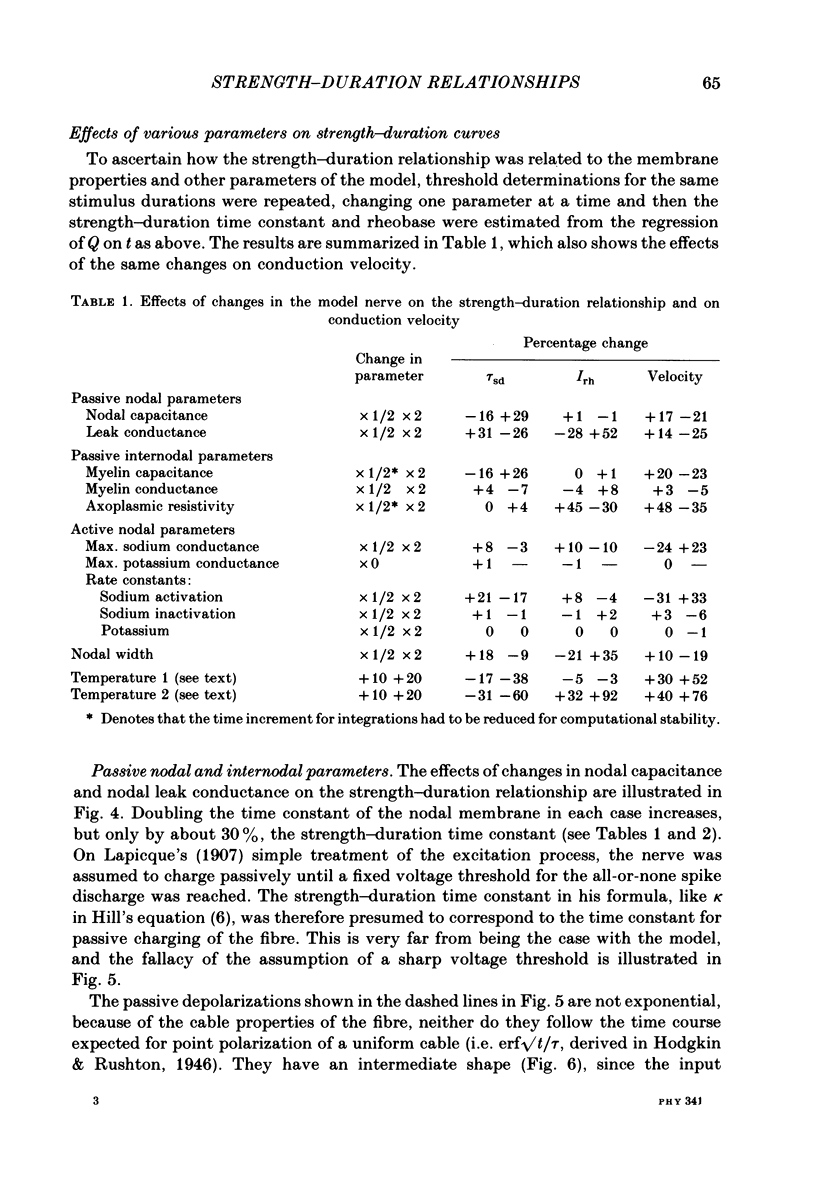
- Moore J. W., Joyner R. W., Brill M. H., Waxman S. D., Najar-Joa M. Simulations of conduction in uniform myelinated fibers. Relative sensitivity to changes in nodal and internodal parameters. Biophys J. 1978 Feb;21(2):147–160. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85515-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
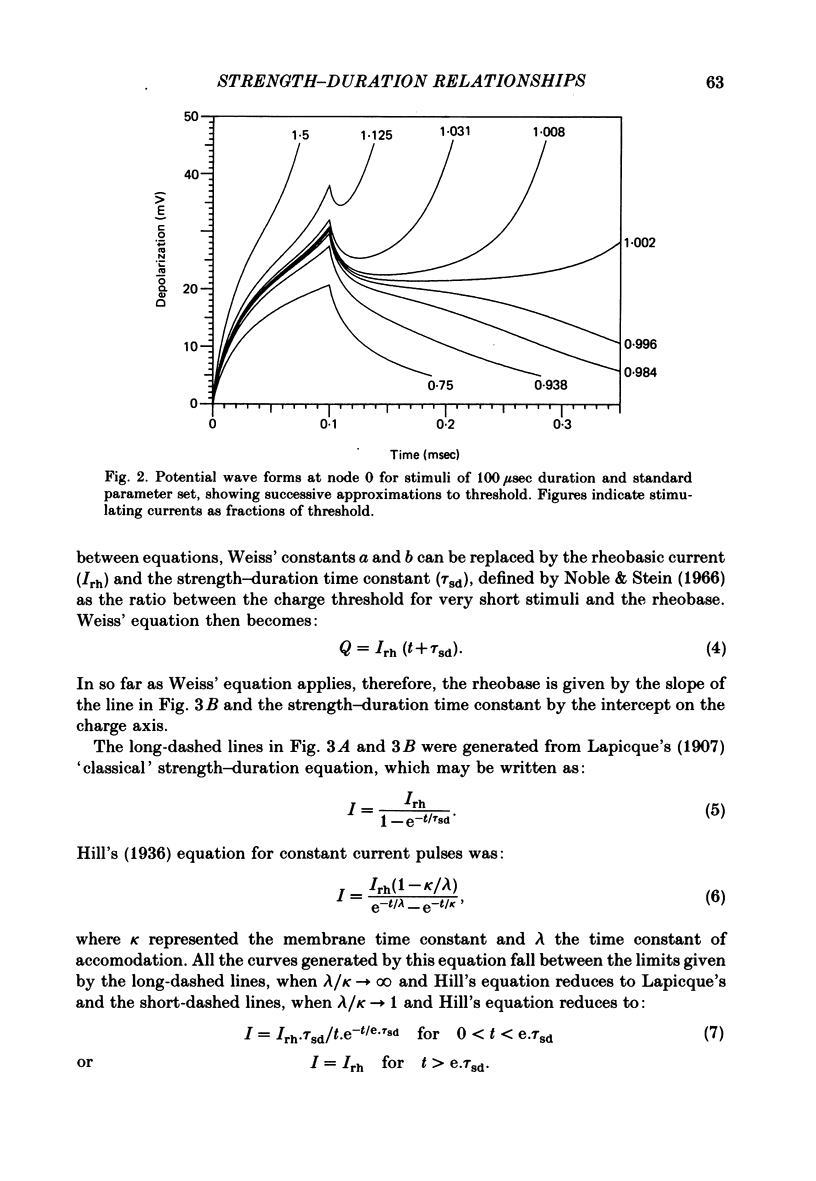
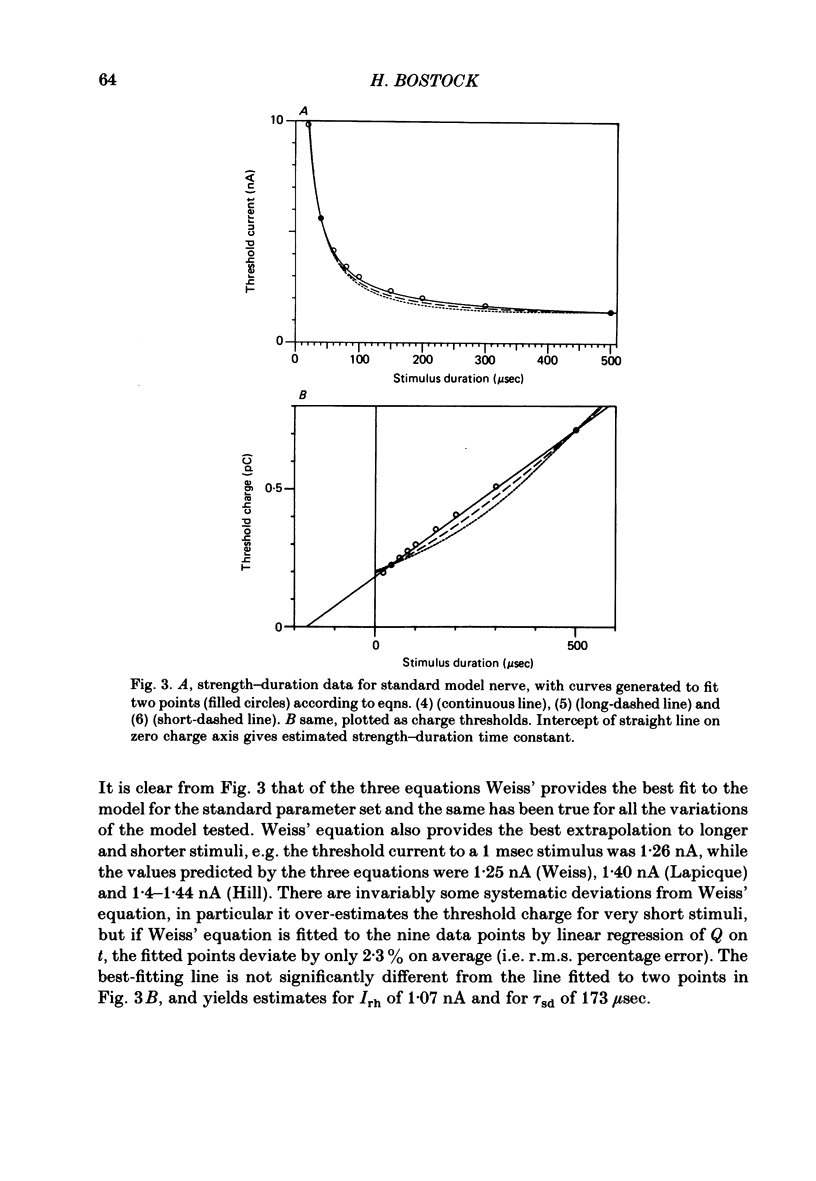
- Noble D., Stein R. B. The threshold conditions for initiation of action potentials by excitable cells. J Physiol. 1966 Nov;187(1):129–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL W. Membrane potential transients and membrane time constant of motoneurons. Exp Neurol. 1960 Oct;2:503–532. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(60)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L., Davis F. A. Impulse conduction in multiple sclerosis: a theoretical basis for modification by temperature and pharmacological agents. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Feb;37(2):152–161. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.2.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. S., Koles Z. J. Myelinated nerve fibers: computed effect of myelin thickness on conduction velocity. Am J Physiol. 1970 Nov;219(5):1256–1258. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.5.1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I. New measurements of the capacity and the resistance of the myelin sheath and the nodal membrane of the isolated frog nerve fiber. Am J Physiol. 1955 Jun;181(3):639–650. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.181.3.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


