Abstract
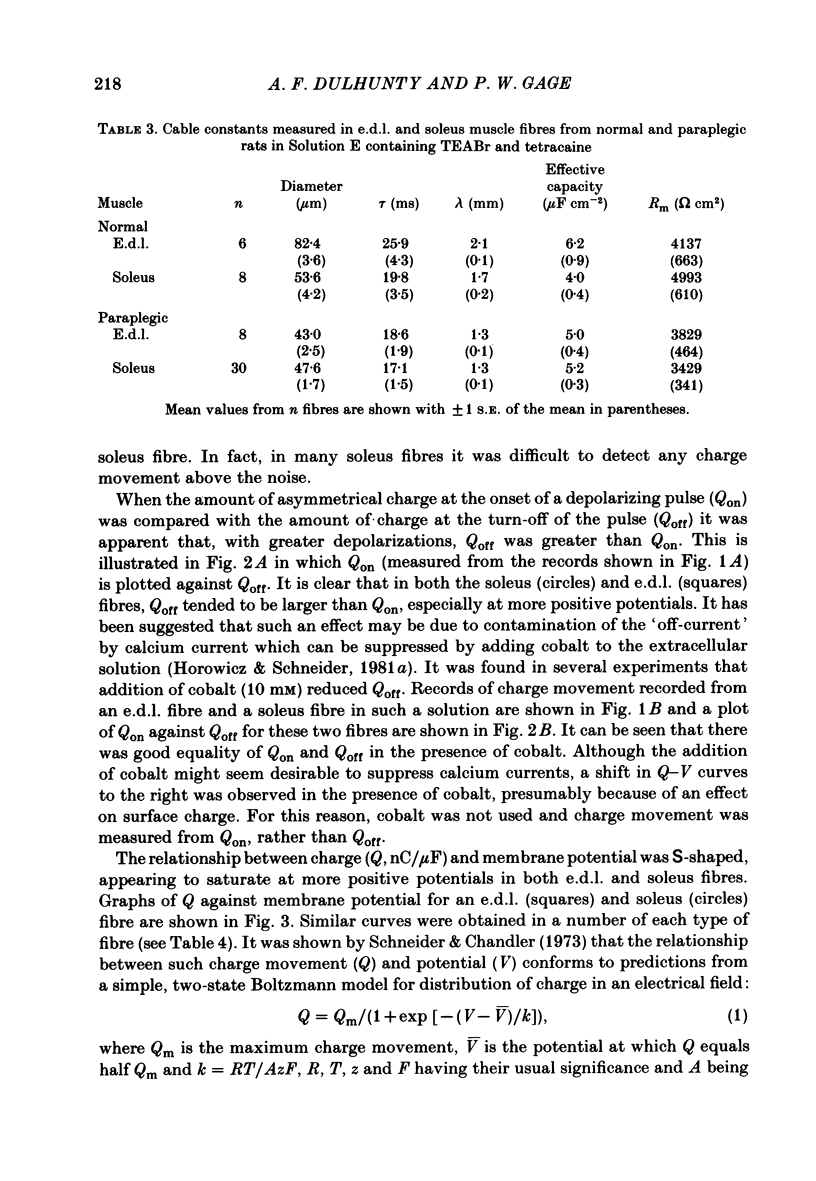
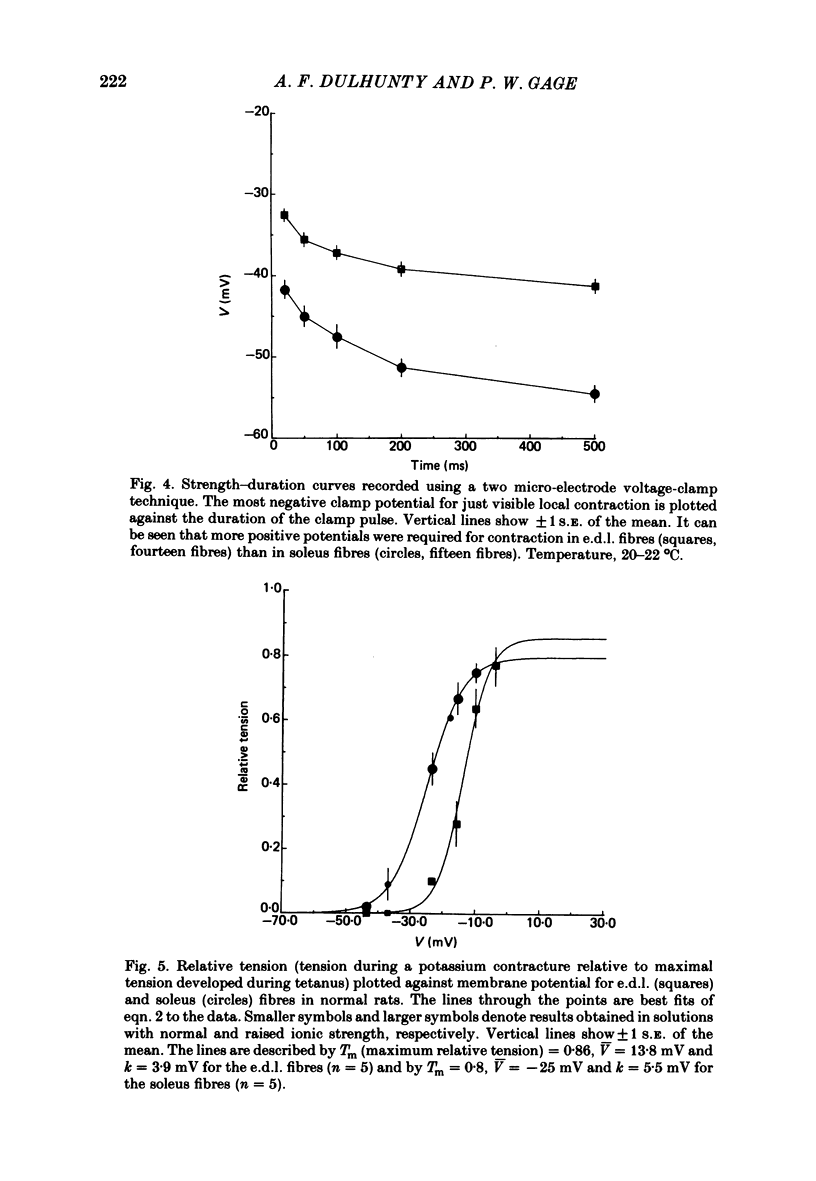
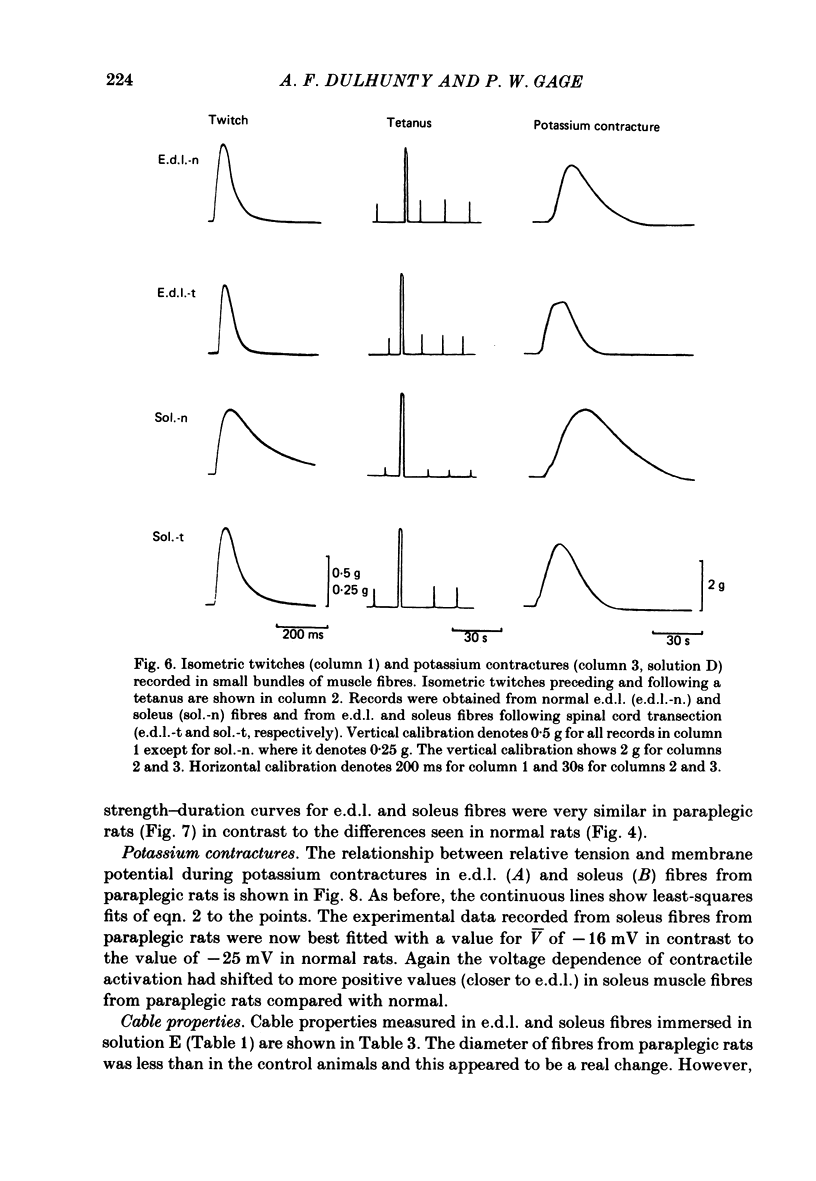
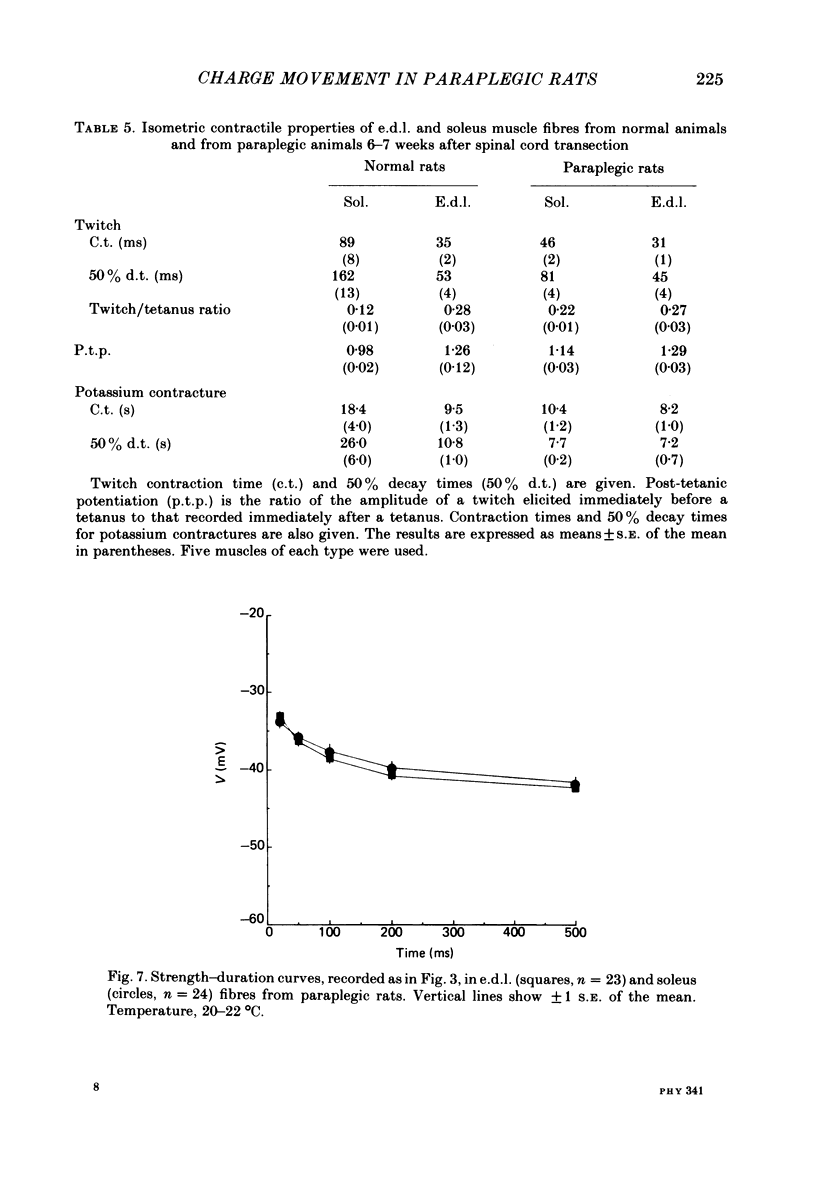
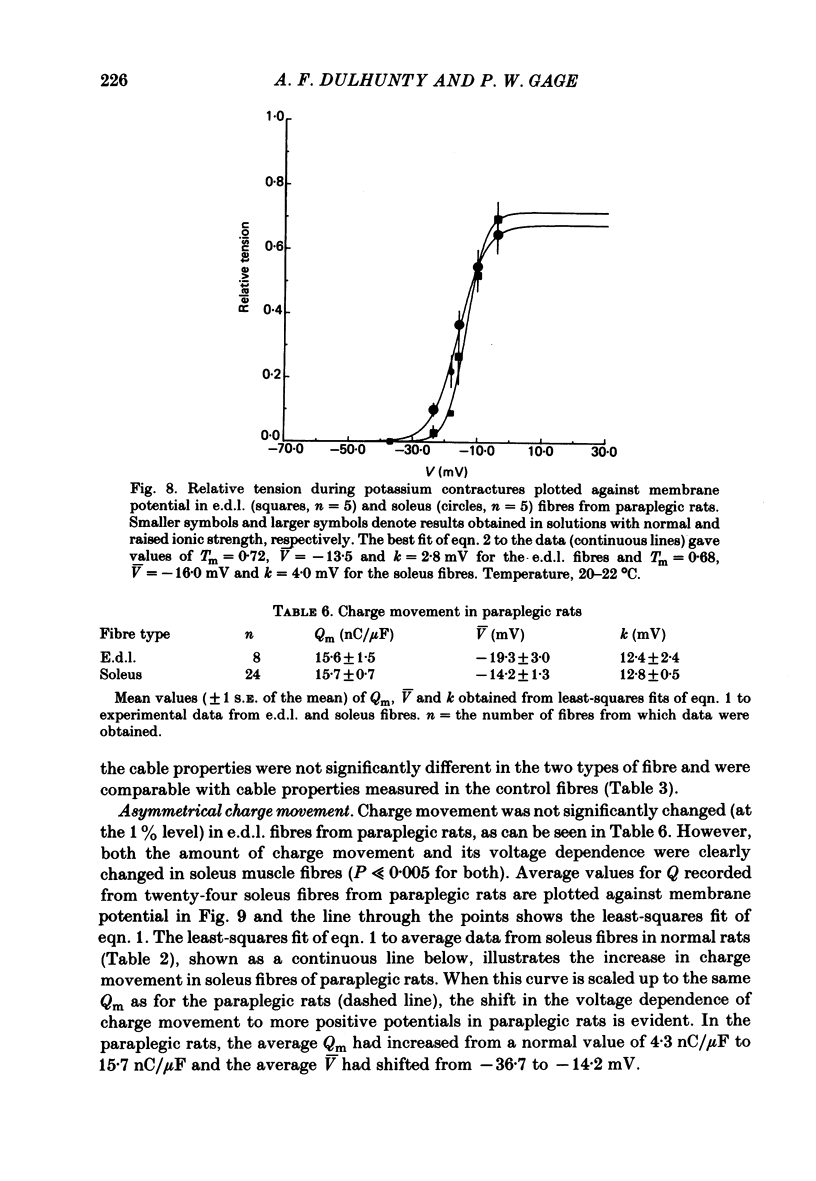
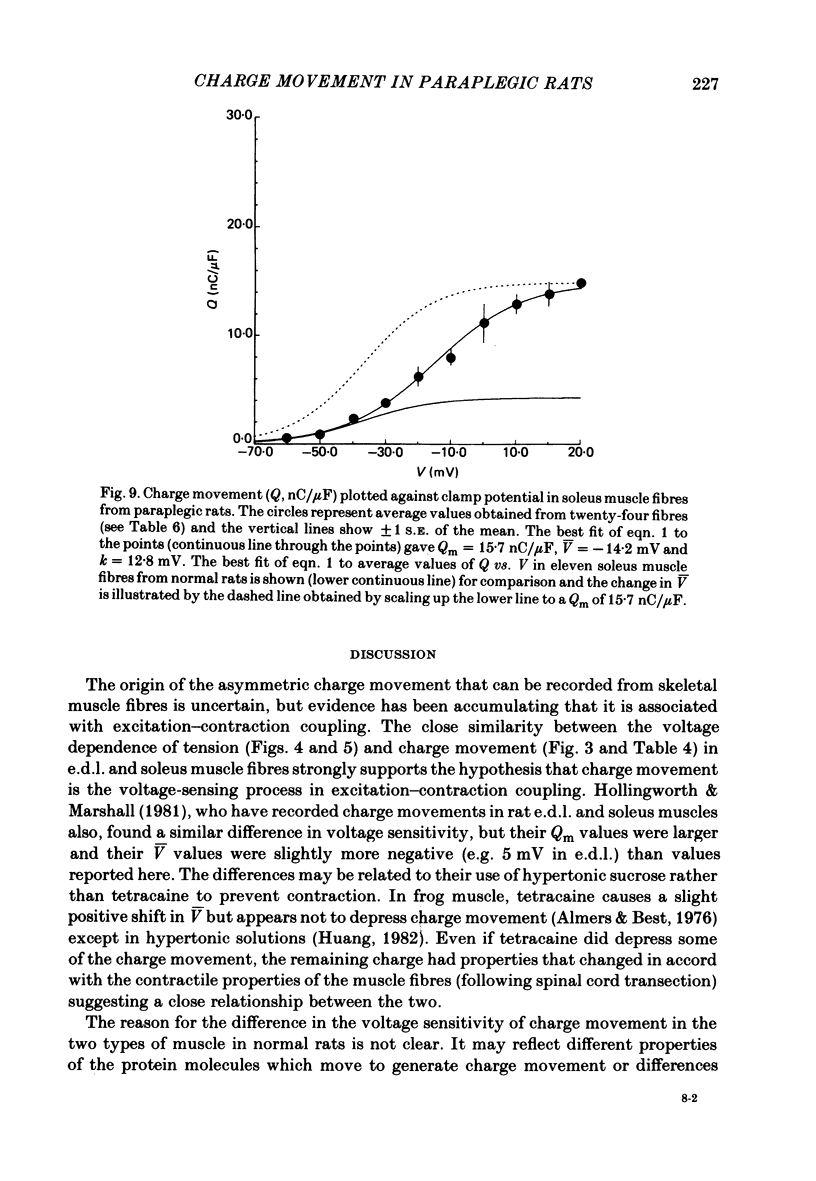
Asymmetrical charge movements (Q) were recorded from the voltage-clamped ends of muscle fibres in extensor digitorum longus (e.d.l.) and soleus muscles from rats. Tetracaine (2 mM) was added to solutions to prevent contraction. In both muscles the relationship between Q and membrane potential (V) was S-shaped and could be described by the Boltzmann-type equation Q = Qm/(1 + exp[-(v - V)/k]) where Qm was the maximum charge, V the membrane potential at which Q = Qm/2, and k a 'slope factor'. On average, Qm was 5-6 times greater in e.d..l. than in soleus fibres and charge movement occurred at more negative potentials in soleus than in e.d.l. fibres, V being -36.7 mV in the former and -19.0 mV in the latter, a difference of about 18 mV. The threshold for contraction, determined using a two-electrode voltage clamp, was more negative in soleus than in e.d.l. fibres. For 500 ms depolarizations, the difference was 12 mV. The relationship between tension and membrane potential during potassium contractures was S-shaped and, when fitted by the Boltzmann-type equation, gave V values of -25 mV for soleus and -14 mV for e.d.l. fibres. In paraplegic rats, the threshold for contraction in soleus fibres shifted about 12 mV to more positive potentials, but there was no change in e.d.l. fibres so that there was no significant difference between the two muscles. In paraplegic rats the relationship between tension and membrane potential during potassium contractures also shifted to more positive potentials in soleus fibres, whereas there was no change in e.d.l. fibres. These changes in the voltage sensitivity of contractile activation in soleus fibres from paraplegic rats were associated with a parallel shift in the voltage sensitivity of charge movement so that the average V shifted from -36.7 mV in normal rats to a value of -14.2 mV in paraplegic rats. There was also a four-fold increase in Qm in soleus fibres from paraplegic rats. The difference between the voltage sensitivity of contractile activation and charge movement in e.d.l. and soleus fibres in normal rats supports the hypothesis that the two are closely related: even stronger support comes from the observation of the parallel shift in the voltage sensitivity of contractile activation and charge movement in soleus fibres in paraplegic rats.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. The kinetics of mechanical activation in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):207–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):607–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Best P. M. Effects of tetracaine on displacement currents and contraction of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(3):583–611. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M. Interactions between motoneurones and muscles in respect of the characteristic speeds of their responses. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:417–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Arsenazo III signals in singly dissected frog twitch fibres [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:23P–24P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs F. N., Poland J. L., Solaro R. J. Relative capabilities of sarcoplasmic reticulum in fast and slow mammalian skeletal muscles. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(3):587–594. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C., Fernandez de Bolaños P. Membrane potential, contractile activation and relaxation rates in voltage clamped short muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:175–189. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. Effects of glycerol treatment and maintained depolarization on charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):285–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey D. F., Dunlop C., Hoh J. F., Wong S. Y. Contractile properties and ultrastructure of extensor digitorum longus and soleus muscles in spinal cord transected rats. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1981 Aug;59(4):393–404. doi: 10.1038/icb.1981.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F., Gage P. W., Valois A. A. Upper motor neurone modulation of the structure of the terminal cisternae in rat skeletal muscle fibres. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Dec 23;27(3):277–283. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90443-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F. Potassium contractures and mechanical activation in mammalian skeletal muscles. J Membr Biol. 1980 Dec 30;57(3):223–233. doi: 10.1007/BF01869590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg B. R., Kuda A. M. Discrimination between fiber populations in mammalian skeletal muscle by using ultrastructural parameters. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Jan;54(1):76–88. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg B. R., Kuda A. M., Peter J. B. Stereological analysis of mammalian skeletal muscle. I. Soleus muscle of the adult guinea pig. J Cell Biol. 1974 Mar;60(3):732–754. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.3.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg B. R., Kuda A. M. Stereological analysis of mammalian skeletal muscle. II. White vastus muscle of the adult guinea pig. J Ultrastruct Res. 1975 May;51(2):176–187. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(75)80146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisman M. H., Rash J. E., Staehelin L. A., Porter K. R. Studies of excitable membranes. II. A comparison of specializations at neuromuscular junctions and nonjunctional sarcolemmas of mammalian fast and slow twitch muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):752–774. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eusebi F., Miledi R., Takahashi T. Calcium transients in mammalian muscles. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):560–561. doi: 10.1038/284560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Dulhunty A. F. Upper motor neurone modulation of charge movement and mechanical activation in rat skeletal muscle fibres. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Dec 23;27(3):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90442-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Hui C. S. Mechanical activation in slow and twitch skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:137–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Hui C. S. Voltage-dependent charge movement in frog slow muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:175–190. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. Potassium contractures in single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:386–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingworth S., Marshall M. W. A comparative study of charge movement in rat and frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:583–602. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp014004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
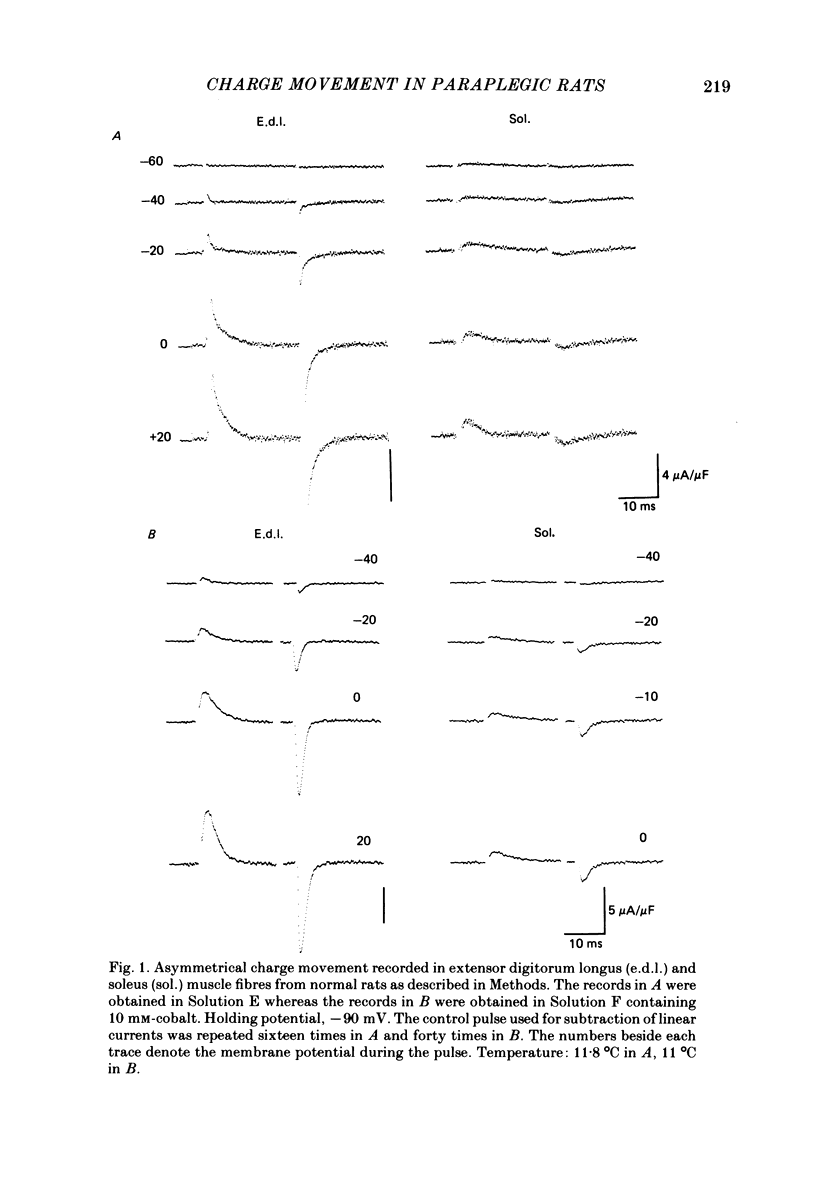
- Horowicz P., Schneider M. F. Membrane charge moved at contraction thresholds in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:595–633. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
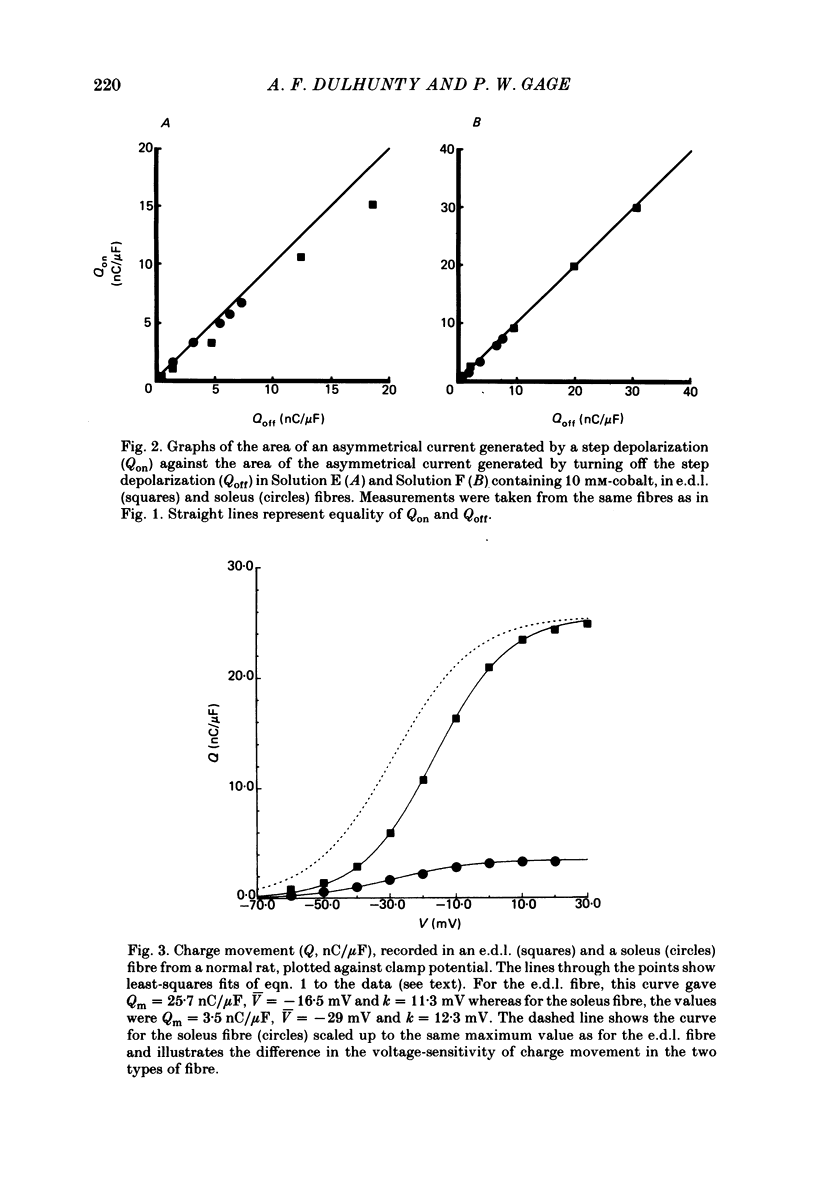
- Horowicz P., Schneider M. F. Membrane charge movement in contracting and non-contracting skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:565–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Pharmacological separation of charge movement components in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:375–387. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomo T., Westgaard R. H., Dahl H. A. Contractile properties of muscle: control by pattern of muscle activity in the rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1974 Aug 27;187(1086):99–103. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1974.0064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luff A. R., Atwood H. L. Membrane properties and contraction of single muscle fibers in the mouse. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jun;222(6):1435–1440. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.6.1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lännergren J. An intermediate type of muscle fibre in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1979 May 17;279(5710):254–256. doi: 10.1038/279254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmons S., Henriksson J. The adaptive response of skeletal muscle to increased use. Muscle Nerve. 1981 Mar-Apr;4(2):94–105. doi: 10.1002/mus.880040204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. B., Appel S. H. Isolation and characterization of the surface membranes of fast and slow mammalian skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 1;466(1):109–122. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90212-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. G., Williams D. A. Calcium-activated force responses in fast- and slow-twitch skinned muscle fibres of the rat at different temperatures. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:281–302. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



