Abstract
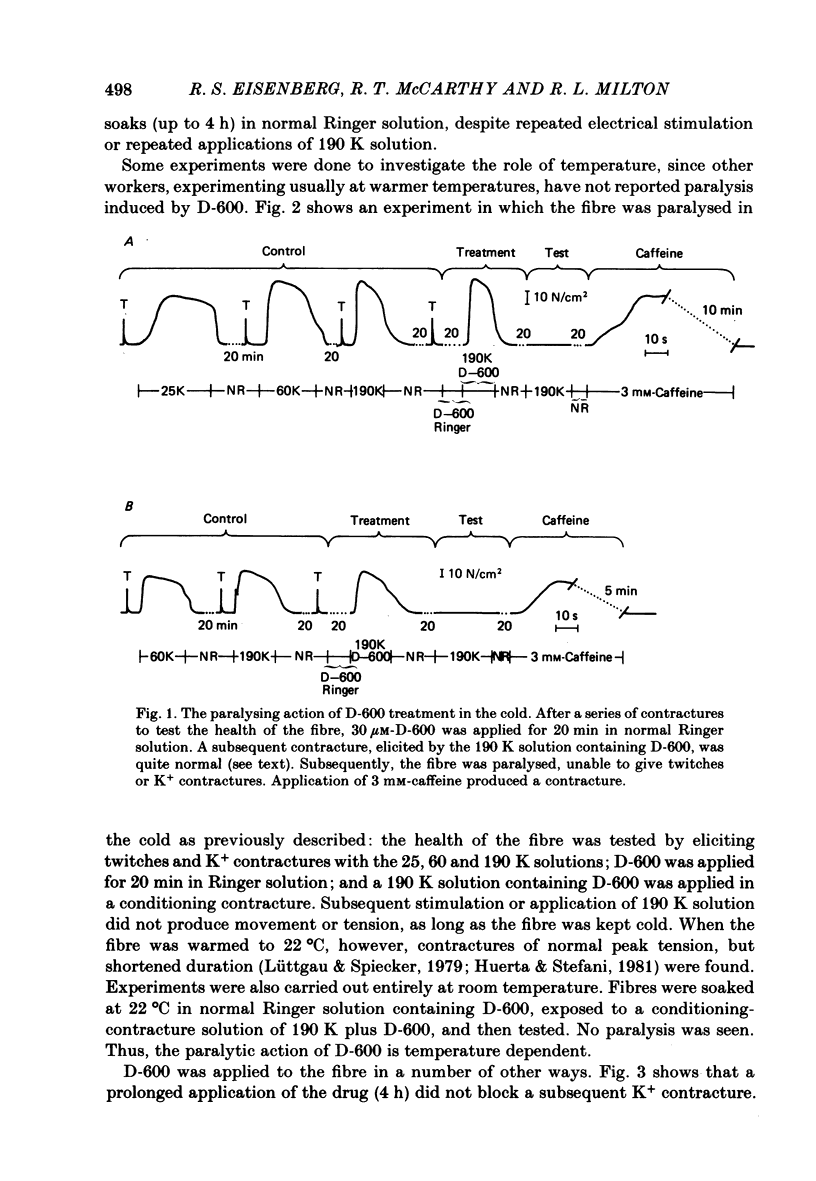
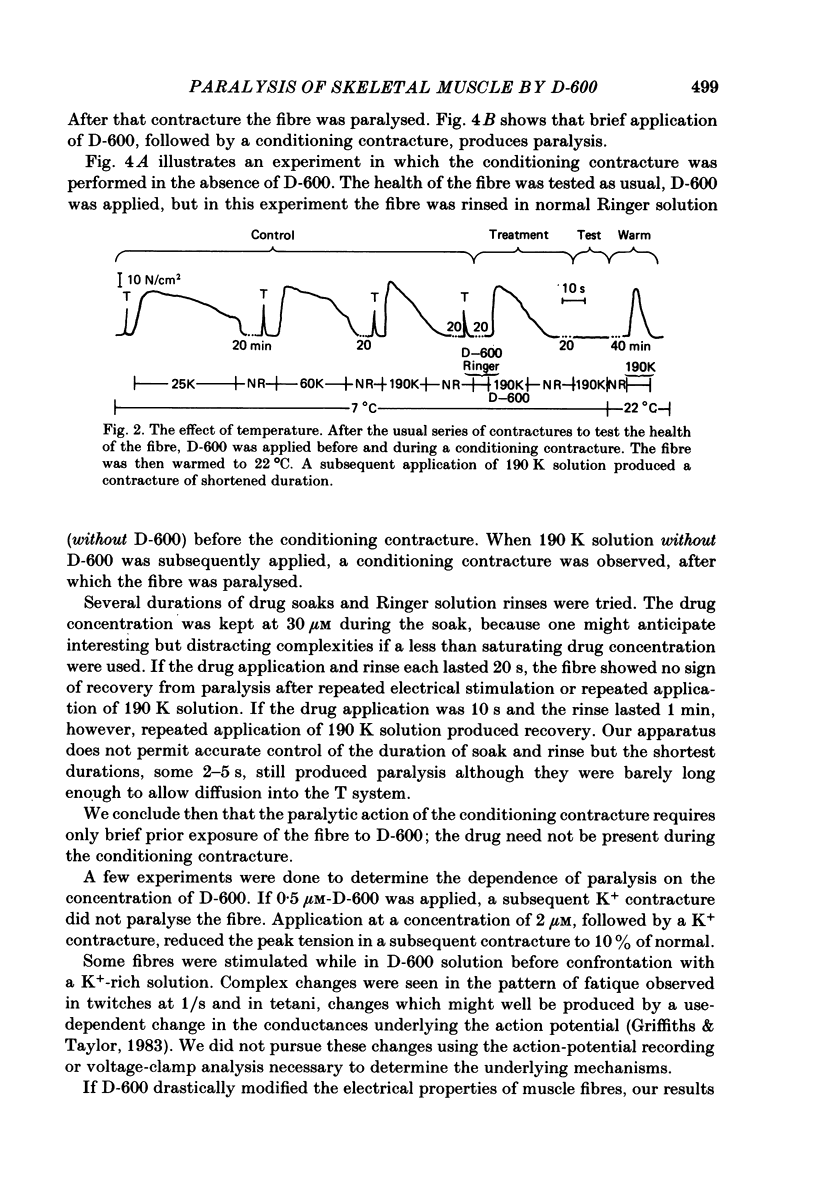
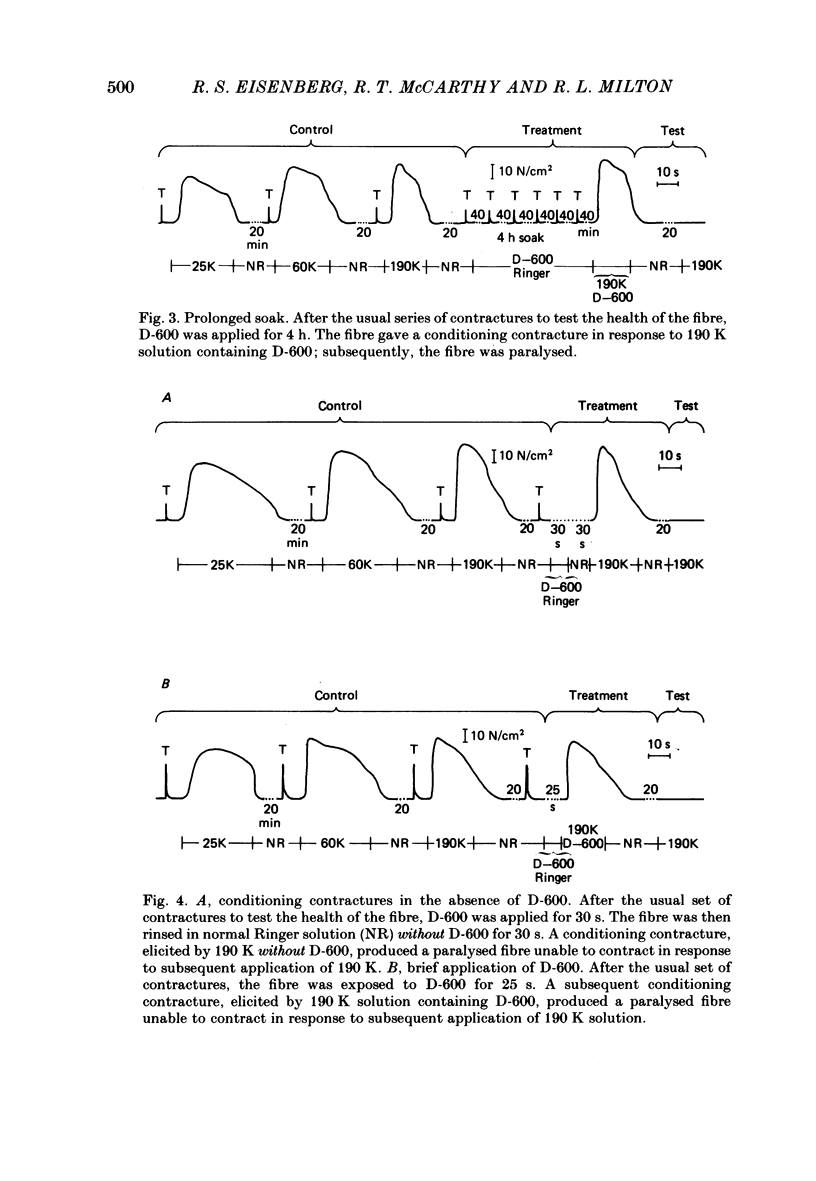
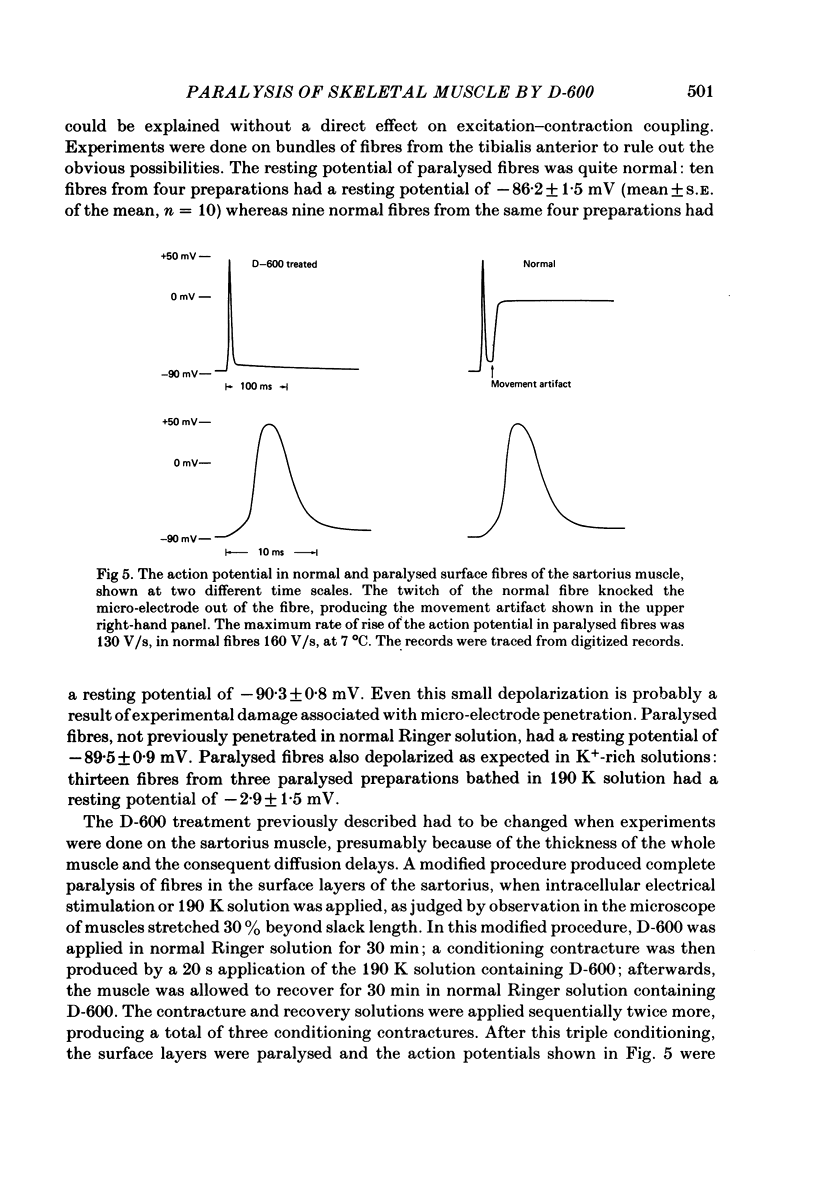
The Ca2+ channel blocker D-600 (methoxyverapamil) paralyses single muscle fibres of the frog: fibres exposed to the drug at 7 degrees C give a single K+ contracture after which they are paralysed, unable to contract in response to electrical stimulation or further applications of K+. Paralysed fibres contract in response to caffeine and have normal resting potentials and action potentials. Fibres treated with D-600 at 22 degrees C are not paralysed. Paralysed fibres warmed to 22 degrees C recover contractile properties: they twitch and give K+ contractures. Other workers have shown that D-600 blocks a Ca2+ channel at room temperature; thus, the paralytic action of D-600 is probably mediated by a different membrane protein, perhaps a different Ca2+ channel from that blocked at room temperature. These results suggest that the binding of D-600 can disrupt the mechanism coupling electrical potential changes across the T membrane to Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almers W., Fink R., Palade P. T. Calcium depletion in frog muscle tubules: the decline of calcium current under maintained depolarization. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:177–207. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Palade P. T. Slow calcium and potassium currents across frog muscle membrane: measurements with a vaseline-gap technique. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:159–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi C. P. Some historical aspects of excitation--contraction coupling. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Apr;60(4):415–416. doi: 10.1139/y82-061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C. Excitation and contraction processes in muscle. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:63–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C. The time course of potassium contractures of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(2):483–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. Effects of glycerol treatment and maintained depolarization on charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):285–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cota G., Stefani E. Effects of external calcium reduction on the kinetics of potassium contractures in frog twitch muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:303–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörrscheidt-Käfer M. The action of D600 on frog skeletal muscle: facilitation of excitation-contraction coupling. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Jul 19;369(3):259–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00582193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg B. R., Eisenberg R. S. The T-SR junction in contracting single skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jan;79(1):1–19. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg B. R., Mathias R. T., Gilai A. Intracellular localization of markers within injected or cut frog muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jul;237(1):C50–C55. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.237.1.C50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Mathias R. T. Structural analysis of electrical properties of cells and tissues. Crit Rev Bioeng. 1980;4(3):203–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Serratos H., Valle-Aguilera R., Lathrop D. A., Garcia M. C. Slow inward calcium currents have no obvious role in muscle excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):292–294. doi: 10.1038/298292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. Potassium contractures in single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:386–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The effect of sudden changes in ionic concentrations on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:370–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Pelzer D., Trube G., Trautwein W. Does the organic calcium channel blocker D600 act from inside or outside on the cardiac cell membrane? Pflugers Arch. 1982 Jun;393(4):287–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00581411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowicz P., Schneider M. F. Membrane charge movement in contracting and non-contracting skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:565–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Pharmacological separation of charge movement components in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:375–387. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huerta M., Stefani E. Potassium and caffeine contractures in fast and slow muscles of the chicken. J Physiol. 1981 Sep;318:181–189. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. S. Pharmacological dissection of charge movement in frog skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1982 Jul;39(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84498-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumann A. J., Uchitel O. D. Reversible Inhibition of Potassium Contractures by optical isomers of verapamil and D 600 on slow muscle fibres of the frog. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976;292(1):21–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00506485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Spiecker W. The effects of calcium deprivation upon mechanical and electrophysiological parameters in skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:411–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias R. T., Levis R. A., Eisenberg R. S. Electrical models of excitation-contraction coupling and charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Jul;76(1):1–31. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias R. T., Rae J. L., Eisenberg R. S. Electrical properties of structural components of the crystalline lens. Biophys J. 1979 Jan;25(1):181–201. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85284-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I. Blocking of acetylcholine-induced channels by extracellular or intracellular application of D600. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Dec 31;211(1182):143–150. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto H., Racker E. Mechanism of calcium release from skeletal sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Membr Biol. 1982;66(3):193–201. doi: 10.1007/BF01868494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelzer D., Trautwein W., McDonald T. F. Calcium channel block and recovery from block in mammalian ventricular muscle treated with organic channel inhibitors. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Aug;394(2):97–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00582909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez J. A., Stefani E. Inward calcium current in twitch muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:197–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow A. Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1965 Sep;17(3):265–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V. Bridging structures spanning the junctioning gap at the triad of skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1979 Mar;80(3):743–750. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. R., Lopez J. R., Griffiths P. J., Trube G., Cecchi G. Calcium in excitation--contraction coupling of frog skeletal muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Apr;60(4):489–502. doi: 10.1139/y82-068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


