Abstract
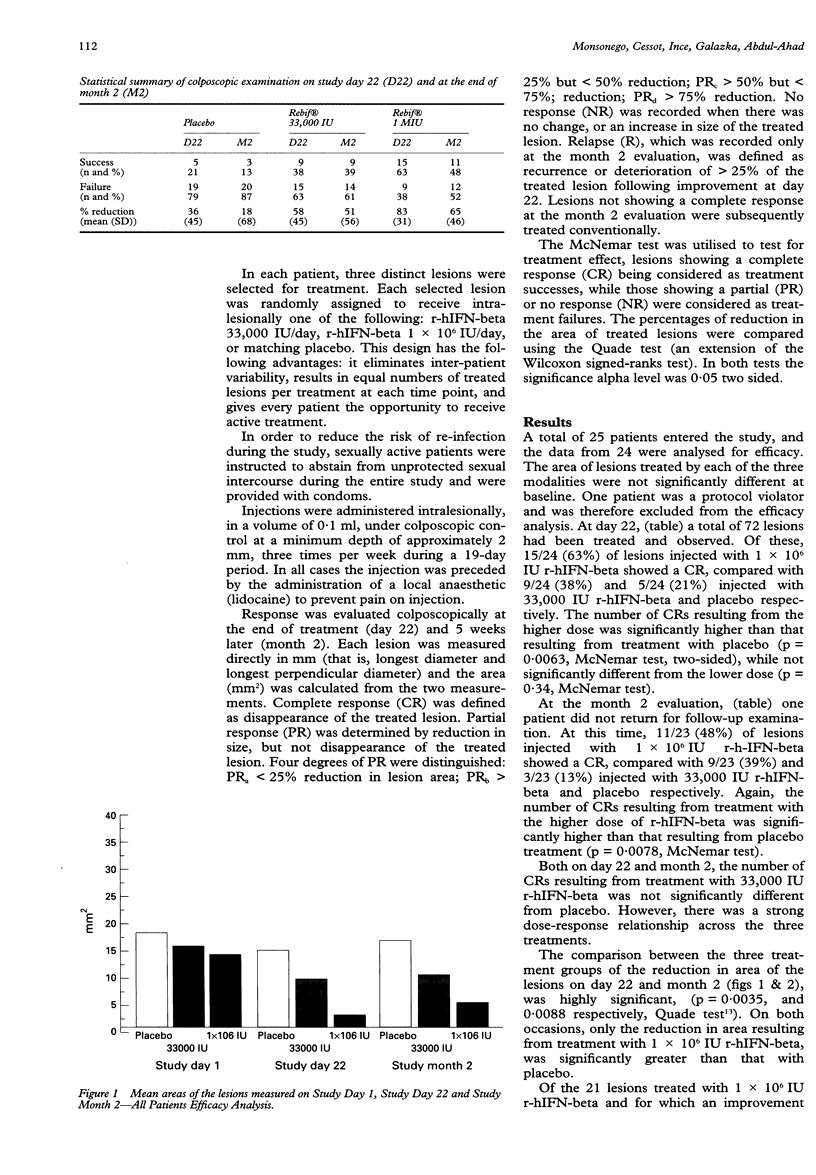
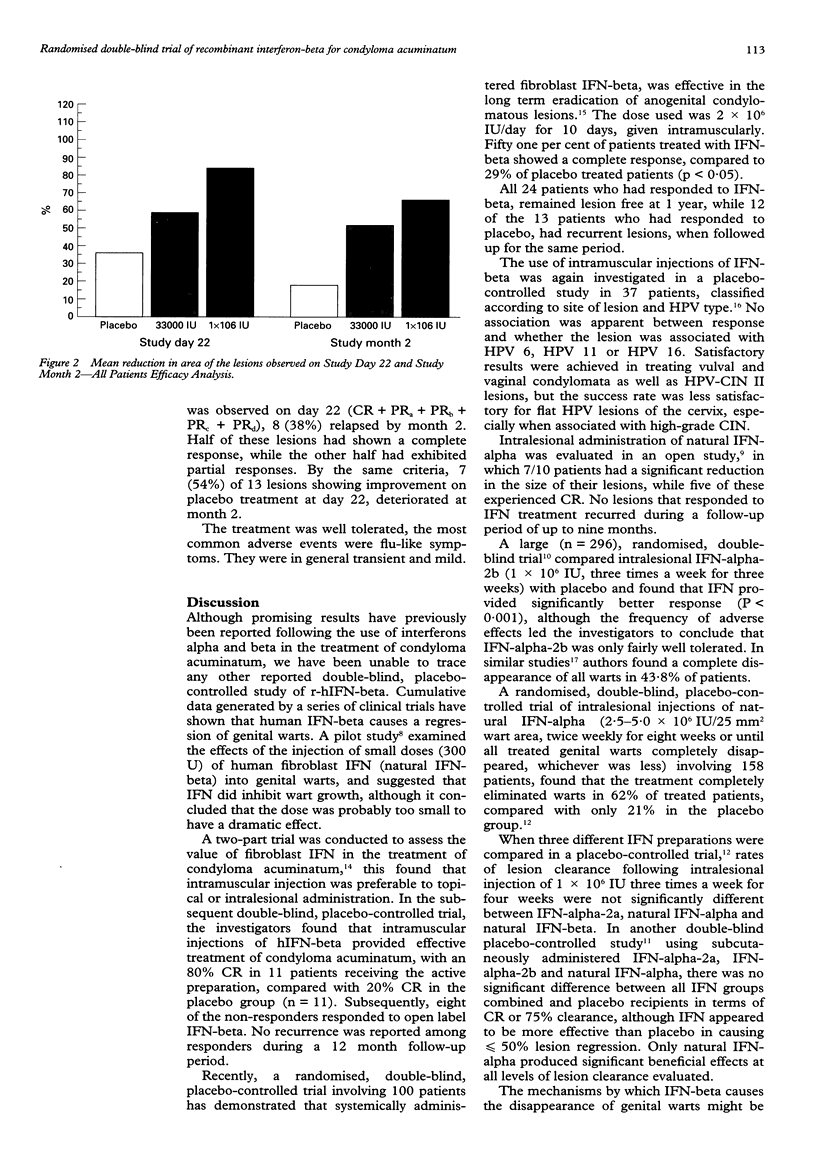
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of two intralesional doses of recombinant human interferon-beta (r-hIFN-beta: Rebif, Ares Serono), given 3 times a week for 3 weeks, in the treatment of condyloma acuminatum. DESIGN: A randomised, double-blind, within-patient, placebo-controlled study. SUBJECTS: 25 patients (24 males, 1 female) with a history of condyloma acuminatum. Twenty had failed previous treatment for condyloma acuminatum. In each patient, 3 distinct lesions were selected for treatment. Each selected lesion was randomly assigned to receive intralesionally one of the following: r-hIFN-beta 33,000 IU/day, r-hIFN-beta 1 x 10(6) IU/day, or matching placebo. SETTING: Institut Alfred Fournier, Paris, France. OUTCOME MEASURES: Response was evaluated colposcopically at the end of treatment (day 22) and 5 weeks later (month 2). Complete response (CR) was defined as disappearance of the treated lesion. Partial response (PR) was defined as at least a 50% reduction in size, but not disappearance of the treated lesion. RESULTS: The higher dose of 1 x 10(6) IU achieved significantly more complete and partial remissions than placebo, both by the end of treatment, and 5 weeks later. CONCLUSIONS: r-hIFN-beta appears to be safe and effective when administered intralesionally to patients with condyloma acuminatum. Most of the treated patients had failed previous treatments and were therefore a resistant population.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arany I., Rady P., Tyring S. K. Interferon treatment enhances the expression of underphosphorylated (biologically-active) retinoblastoma protein in human papilloma virus-infected cells through the inhibitory TGF beta 1/IFN beta cytokine pathway. Antiviral Res. 1994 Feb;23(2):131–141. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(94)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch F. X., Manos M. M., Muñoz N., Sherman M., Jansen A. M., Peto J., Schiffman M. H., Moreno V., Kurman R., Shah K. V. Prevalence of human papillomavirus in cervical cancer: a worldwide perspective. International biological study on cervical cancer (IBSCC) Study Group. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995 Jun 7;87(11):796–802. doi: 10.1093/jnci/87.11.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eron L. J., Judson F., Tucker S., Prawer S., Mills J., Murphy K., Hickey M., Rogers M., Flannigan S., Hien N. Interferon therapy for condylomata acuminata. N Engl J Med. 1986 Oct 23;315(17):1059–1064. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198610233151704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenczy A. Epidemiology and clinical pathophysiology of condylomata acuminata. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995 Apr;172(4 Pt 2):1331–1339. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(95)90399-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenczy A., Mitao M., Nagai N., Silverstein S. J., Crum C. P. Latent papillomavirus and recurring genital warts. N Engl J Med. 1985 Sep 26;313(13):784–788. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198509263131304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman-Kien A. E., Eron L. J., Conant M., Growdon W., Badiak H., Bradstreet P. W., Fedorczyk D., Trout J. R., Plasse T. F. Natural interferon alfa for treatment of condylomata acuminata. JAMA. 1988 Jan 22;259(4):533–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangemi J. D., Pirisi L., Angell M., Kreider J. W. HPV replication in experimental models: effects of interferon. Antiviral Res. 1994 Jul;24(2-3):175–190. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(94)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffen J. R., Klein R. J., Friedman-Kien A. E. Intralesional administration of large doses of human leukocyte interferon for the treatment of condylomata acuminata. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):612–615. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch K. D. Clinical appearance and treatment strategies for human papillomavirus: a gynecologic perspective. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995 Apr;172(4 Pt 2):1340–1344. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(95)90400-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby P. Interferon and genital warts: much potential, modest progress. JAMA. 1988 Jan 22;259(4):570–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuovo G. J., Blanco J. S., Leipzig S., Smith D. Human papillomavirus detection in cervical lesions nondiagnostic for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: correlation with Papanicolaou smear, colposcopy, and occurrence of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Jun;75(6):1006–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmos L., Vilata J., Rodríguez Pichardo A., Lloret A., Ojeda A., Calderón M. D. Double-blind, randomized clinical trial on the effect of interferon-beta in the treatment of condylomata acuminata. Int J STD AIDS. 1994 May-Jun;5(3):182–185. doi: 10.1177/095646249400500305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Alexander K. A. Antiviral therapy for human papillomaviruses: rational and prospects. Ann Intern Med. 1995 Sep 1;123(5):368–382. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-123-5-199509010-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichman R. C., Oakes D., Bonnez W., Greisberger C., Tyring S., Miller L., Whitley R., Carveth H., Weidner M., Krueger G. Treatment of condyloma acuminatum with three different interferons administered intralesionally. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1988 May;108(5):675–679. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-5-675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld A., Nitke S., Schattner A., Wallach D., Crespi M., Hahn T., Levavi H., Yarden O., Shoham J., Doerner T. Intramuscular human interferon-beta injections in treatment of condylomata acuminata. Lancet. 1984 May 12;1(8385):1038–1042. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91450-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott G. M., Csonka G. W. Effect of injections of small doses of human fibroblast interferon into genital warts. A pilot study. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Dec;55(6):442–445. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.6.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turek L. P., Byrne J. C., Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Friedman R. M., Howley P. M. Interferon induces morphologic reversion with elimination of extrachromosomal viral genomes in bovine papillomavirus-transformed mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7914–7918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance J. C., Bart B. J., Hansen R. C., Reichman R. C., McEwen C., Hatch K. D., Berman B., Tanner D. J. Intralesional recombinant alpha-2 interferon for the treatment of patients with condyloma acuminatum or verruca plantaris. Arch Dermatol. 1986 Mar;122(3):272–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


