Abstract
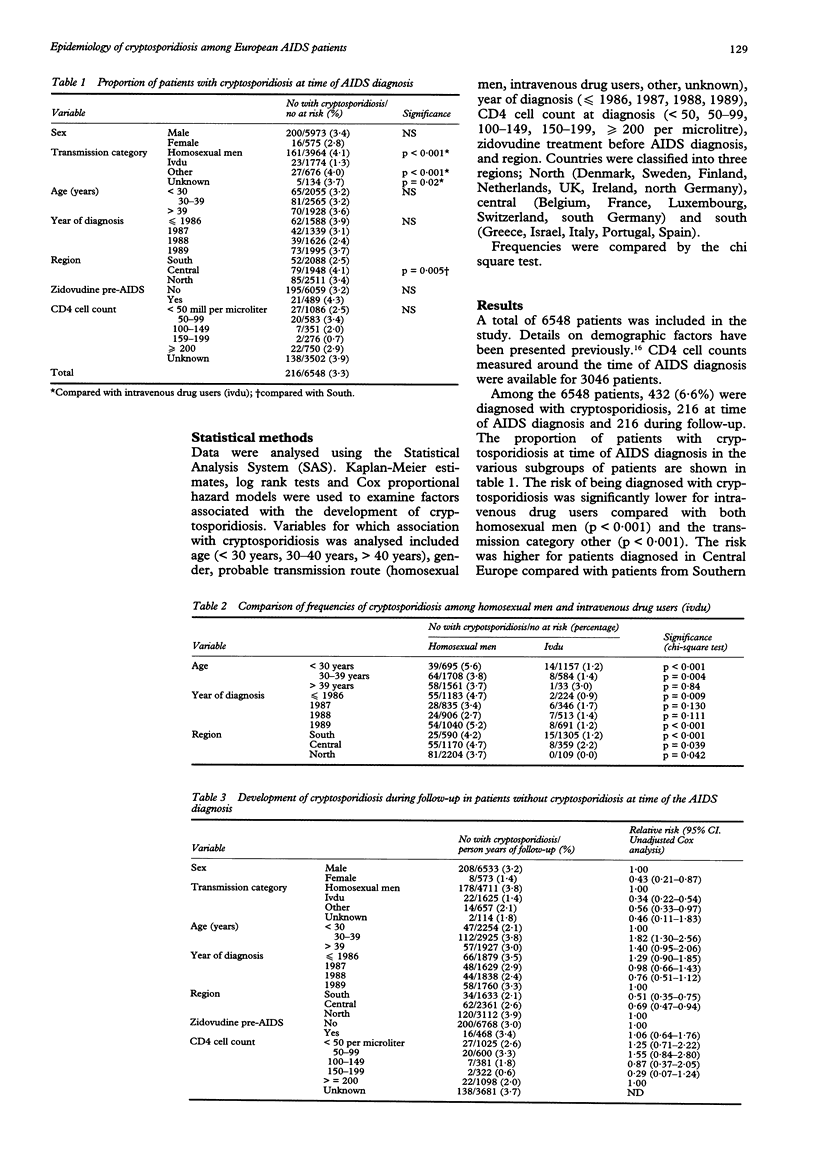
OBJECTIVE: To study epidemiology and possible risk factors associated with the development of cryptosporidiosis among European patients with AIDS. METHODS: An inception cohort of 6548 patients with AIDS, consecutively diagnosed from 1979 to 1989, from 52 centres in 17 European countries was studied. Data on all AIDS defining events were collected retrospectively from patients' clinical records. Kaplan-Meier estimates, log rank tests and Cox proportional hazard models were used to examine for possible risk factors associated with cryptosporidiosis. RESULTS: Cryptosporidiosis was diagnosed in 432 (6.6%) patients, 216 at time of the AIDS diagnosis and 216 during follow-up. The probability of being diagnosed with cryptosporidiosis at AIDS diagnosis was significantly lower for intravenous drug users (1.3%) than for homosexual men (4.1%) and for patients belonging to other transmission categories (4.0%) (p < 0.001). The probability was also higher for patients from Central Europe compared with patients from South Europe (4.1% versus 2.5%, p = 0.005). The rate of developing cryptosporidiosis after the diagnosis of AIDS was 3 per 100 patient years of follow-up. The rate was significantly lower for intravenous drug users than for homosexual men (relative risk 0.34, 95% confidence limits 0.22-0.54) and for women compared with men (RR 0.43 (0.21-0.87)). The risk was higher in North Europe than in South and Central Europe. In a multivariate analysis only transmission category remained a significant predictor for the development of cryptosporidiosis. CONCLUSION: The development of cryptosporidiosis in AIDS patients may be associated with sexual risk behaviour.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antony M. A., Brandt L. J., Klein R. S., Bernstein L. H. Infectious diarrhea in patients with AIDS. Dig Dis Sci. 1988 Sep;33(9):1141–1146. doi: 10.1007/BF01535791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanshard C., Jackson A. M., Shanson D. C., Francis N., Gazzard B. G. Cryptosporidiosis in HIV-seropositive patients. Q J Med. 1992 Nov-Dec;85(307-308):813–823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifford C. P., Crook D. W., Conlon C. P., Fraise A. P., Day D. G., Peto T. E. Impact of waterborne outbreak of cryptosporidiosis on AIDS and renal transplant patients. Lancet. 1990 Jun 16;335(8703):1455–1456. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91478-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colebunders R., Lusakumuni K., Nelson A. M., Gigase P., Lebughe I., van Marck E., Kapita B., Francis H., Salaun J. J., Quinn T. C. Persistent diarrhoea in Zairian AIDS patients: an endoscopic and histological study. Gut. 1988 Dec;29(12):1687–1691. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.12.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly G. M., Dryden M. S., Shanson D. C., Gazzard B. G. Cryptosporidial diarrhoea in AIDS and its treatment. Gut. 1988 May;29(5):593–597. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.5.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Antonio R. G., Winn R. E., Taylor J. P., Gustafson T. L., Current W. L., Rhodes M. M., Gary G. W., Jr, Zajac R. A. A waterborne outbreak of cryptosporidiosis in normal hosts. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Dec;103(6 ):886–888. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-6-886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. E., Thomas P. A., Landesman S. H., Mildvan D., Seidlin M., Friedland G. H., Holzman R., Starrett B., Braun J., Bryan E. L. The spectrum of HIV-1-related disease among outpatients in New York City. AIDS. 1992 Aug;6(8):849–859. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199208000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon B. E., Druckman D. A., Vernon A., Quinn T. C., Polk B. F., Modlin J. F., Yolken R. H., Bartlett J. G. Prevalence of enteric pathogens in homosexual men with and without acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1988 Apr;94(4):984–993. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90557-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren J. D., Pedersen C., Clumeck N., Gatell J. M., Johnson A. M., Ledergerber B., Vella S., Phillips A., Nielsen J. O. Survival differences in European patients with AIDS, 1979-89. The AIDS in Europe Study Group. BMJ. 1994 Apr 23;308(6936):1068–1073. doi: 10.1136/bmj.308.6936.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malebranche R., Arnoux E., Guérin J. M., Pierre G. D., Laroche A. C., Péan-Guichard C., Elie R., Morisset P. H., Spira T., Mandeville R. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome with severe gastrointestinal manifestations in Haiti. Lancet. 1983 Oct 15;2(8355):873–878. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90868-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martino P., Gentile G., Caprioli A., Baldassarri L., Donelli G., Arcese W., Fenu S., Micozzi A., Venditti M., Mandelli F. Hospital-acquired cryptosporidiosis in a bone marrow transplantation unit. J Infect Dis. 1988 Sep;158(3):647–648. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.3.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navin T. R., Juranek D. D. Cryptosporidiosis: clinical, epidemiologic, and parasitologic review. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 May-Jun;6(3):313–327. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen C., Gerstoft J., Tauris P., Lundgren J. D., Gøtzsche P. C., Buhl M., Salim Y., Schmidt K. Opportunistic infections and malignancies in 231 Danish AIDS patients. AIDS. 1990 Mar;4(3):233–238. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199003000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravn P., Lundgren J. D., Kjaeldgaard P., Holten-Anderson W., Højlyng N., Nielsen J. O., Gaub J. Nosocomial outbreak of cryptosporidiosis in AIDS patients. BMJ. 1991 Feb 2;302(6771):277–280. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6771.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- René E., Marche C., Regnier B., Saimot A. G., Vilde J. L., Perrone C., Michon C., Wolf M., Chevalier T., Vallot T. Intestinal infections in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. A prospective study in 132 patients. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 May;34(5):773–780. doi: 10.1007/BF01540353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson A. J., Frankenberg R. A., Buck A. C., Selkon J. B., Colbourne J. S., Parsons J. W., Mayon-White R. T. An outbreak of waterborne cryptosporidiosis in Swindon and Oxfordshire. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Dec;107(3):485–495. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800049189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selik R. M., Starcher E. T., Curran J. W. Opportunistic diseases reported in AIDS patients: frequencies, associations, and trends. AIDS. 1987 Sep;1(3):175–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewankambo N., Mugerwa R. D., Goodgame R., Carswell J. W., Moody A., Lloyd G., Lucas S. B. Enteropathic AIDS in Uganda. An endoscopic, histological and microbiological study. AIDS. 1987 May;1(1):9–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Lane H. C., Gill V. J., Manischewitz J. F., Quinnan G. V., Fauci A. S., Masur H. Intestinal infections in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Etiology and response to therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Mar;108(3):328–333. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-3-328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soave R., Armstrong D. Cryptosporidium and cryptosporidiosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):1012–1023. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.6.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. J., Markson L. E., McKee L., Houchens R., Fanning T. The AIDS-defining diagnosis and subsequent complications: a survival-based severity index. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(10):1059–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Arminio Monforte A., Vago L., Lazzarin A., Boldorini R., Bini T., Guzzetti S., Antinori S., Moroni M., Costanzi G. AIDS-defining diseases in 250 HIV-infected patients; a comparative study of clinical and autopsy diagnoses. AIDS. 1992 Oct;6(10):1159–1164. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199210000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


