Abstract
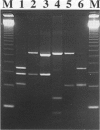
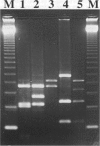
OBJECTIVES--To employ polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis for the rapid differentiation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae protein IB (PIB) isolates and to compare its usefulness with the widely accepted auxotype/serovar classification scheme. METHODS--The outer membrane protein IB genes of 47 gonococcal isolates belonging to 10 different serovars were amplified by PCR. The approximately 1 kb DNA products were then digested separately with restriction enzymes CfoI and MspA1I, and electrophoresed on agarose gels. RESULTS--Cleavage of PIB genes by MspA1I and CfoI differentiated all the N gonorrhoeae strains into five and six PCR-RFLP profiles, respectively. PCR-RFLP was more discriminatory than auxotyping, which classifies the strains into only two auxotypes. Some strains belonging to common serovars could be further differentiated. A combination of PCR-RFLP analysis, auxotyping and serotyping further increased the discrimination of the strains into 34 subtypes. The PCR-RFLP method was easy to perform, reliable, reproducible, and consistent with published nucleotide sequence data. CONCLUSION--The PCR-RFLP method can augment auxotyping and serotyping or be used as a preliminary screening tool to differentiate N gonorrhoeae strains in areas where serotyping reagents are not easily available.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akopyanz N., Bukanov N. O., Westblom T. U., Kresovich S., Berg D. E. DNA diversity among clinical isolates of Helicobacter pylori detected by PCR-based RAPD fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):5137–5142. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.5137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbut F., Mario N., Delmée M., Gozian J., Petit J. C. Genomic fingerprinting of Clostridium difficile isolates by using a random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) assay. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Dec 1;114(2):161–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt N. J., Lambden P. R., Heckels J. E. The nucleotide sequence of the por gene from Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain P9 encoding outer membrane protein PIB. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4258–4258. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt N. J., Virji M., Vayreda F., Lambden P. R., Heckels J. E. Gonococcal outer-membrane protein PIB: comparative sequence analysis and localization of epitopes which are recognized by type-specific and cross-reacting monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Nov;136(11):2165–2172. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-11-2165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonetti N. H., Simnad V. I., Seifert H. S., So M., Sparling P. F. Genetics of protein I of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: construction of hybrid porins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6841–6845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill M. J., Jayamohan J., Lessing M. P., Ison C. A. Naturally occurring PIA/PIB hybrids of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1994 Jun 1;119(1-2):161–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1994.tb06883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill M. J. Serotyping Neisseria gonorrhoeae: a report of the Fourth International Workshop. Genitourin Med. 1991 Feb;67(1):53–57. doi: 10.1136/sti.67.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Seiff M. E., Blake M. S., Koomey M. Porin protein of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: cloning and gene structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8135–8139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamboy W. F. Computing genetic similarity coefficients from RAPD data: correcting for the effects of PCR artifacts caused by variation in experimental conditions. PCR Methods Appl. 1994 Aug;4(1):38–43. doi: 10.1101/gr.4.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Q. C., Chow V. T., Poh C. L. Polymerase chain reaction and direct sequencing of Neisseria gonorrhoeae protein IB gene: partial nucleotide and amino acid sequence analysis of strains S4, S11, S48 (serovar IB4) and S34 (serovar IB5). Med Microbiol Immunol. 1993 Jul;182(3):137–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00190266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier S. I., Wernars K. Typing of Listeria strains by random amplification of polymorphic DNA. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jun;143(5):499–505. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poh C. L., Khng H. P., Lim C. K., Loh G. K. Molecular typing of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Genitourin Med. 1992 Apr;68(2):106–110. doi: 10.1136/sti.68.2.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poh C. L., Lau Q. C. Subtyping of Neisseria gonorrhoeae auxotype-serovar groups by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Med Microbiol. 1993 May;38(5):366–370. doi: 10.1099/00222615-38-5-366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poh C. L., Ocampo J. C., Loh G. K. Genetic relationships among Neisseria gonorrhoeae serovars analysed by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. Epidemiol Infect. 1992 Feb;108(1):31–38. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800049475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poh C. L., Ocampo J. C., Sng E. H., Bygdeman S. M. Characterisation of PPNG and non-PPNG Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates from Singapore. Genitourin Med. 1991 Oct;67(5):389–393. doi: 10.1136/sti.67.5.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarafian S. K., Knapp J. S. Molecular epidemiology of gonorrhea. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2 (Suppl):S49–S55. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.suppl.s49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H., Moyes A., Tait I. B., McCartney A. C., Gallacher G. Non-typable quinolone-resistant gonococci. Lancet. 1990 Mar 10;335(8689):604–604. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90385-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]