Abstract
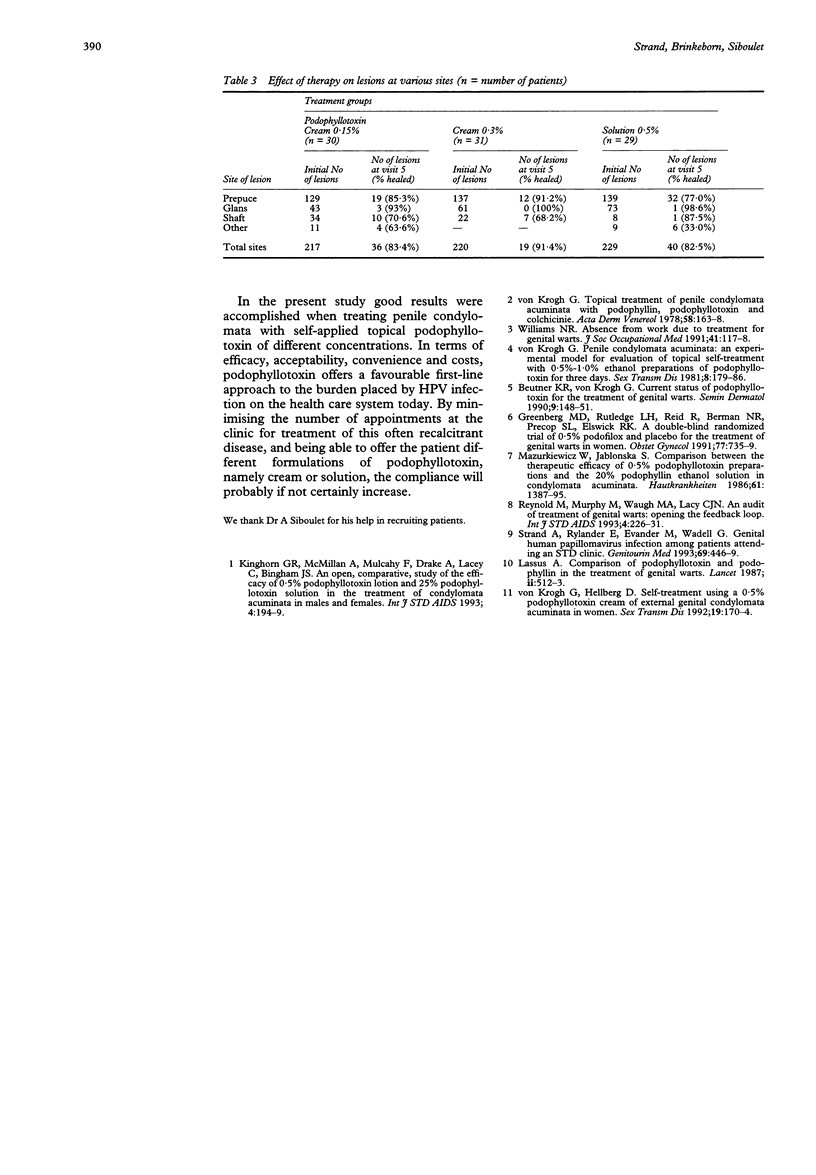
OBJECTIVE--To evaluate the clinical efficacy of a 0.15% and a 0.3% cream formulation of podophyllotoxin in comparison with the 0.5% solution in the treatment of condylomata acuminata and to compare the treatment modalities regarding side effects. DESIGN--The study was designed as an open randomised trial. Ninety male patients with signs of penile HPV infection, with either acuminate or papular lesions, were randomised into three parallel treatment groups. The study medication comprised 0.15% and 0.3% cream and 0.5% solution of podophyllotoxin. The patients treated themselves twice daily for three consecutive days and if total regression of the warts was not achieved after this first treatment cycle, further treatment cycles at 7-day intervals were to be repeated up to a maximum of four treatments. SETTING--The study was carried out in three outpatient clinics: two STD clinics, Department of Dermatology and Venereology, University Hospital (45 patients) and Institut Antoine Fournier, Paris (30 patients), and one military hospital, S1/FO 47/48, Sjukhusenheten, Enköping (15 patients). RESULTS--Statistical evaluation of the treatment effect was based on a "Response rate" calculation at each visit. The number of completely responding patients after the first, second, third and fourth cycle were 40 (44%), 61 (68%), 67 (74%) and 70 (78%), respectively. There was no statistically significant difference between the three treatments after four treatment cycles. However, the 0.15% cream had a significantly slower onset of efficacy as compared with the 0.3% cream and 0.5% solution. Adverse effects were less severe and less frequent with the 0.15% cream than with the other treatment modalities. Severe adverse effects were reported by 12 patients, of whom two were treated with 0.15% cream, five with 0.3% cream and five with 0.5% solution. Thirty-one patients were completely free from adverse effects. CONCLUSION--In this open randomised study with three parallel treatment groups, two cream formulations of 0.15% and 0.3% podophyllotoxin and a 0.5% solution of the same drug all showed an equally good response rate after four treatment cycles. Reported adverse effects were few and mild. The convenience of having different formulations to offer when prescribing treatment for condylomata must be considered.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutner K. R., von Krogh G. Current status of podophyllotoxin for the treatment of genital warts. Semin Dermatol. 1990 Jun;9(2):148–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. D., Rutledge L. H., Reid R., Berman N. R., Precop S. L., Elswick R. K., Jr A double-blind, randomized trial of 0.5% podofilox and placebo for the treatment of genital warts in women. Obstet Gynecol. 1991 May;77(5):735–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinghorn G. R., McMillan A., Mulcahy F., Drake S., Lacey C., Bingham J. S. An open, comparative, study of the efficacy of 0.5% podophyllotoxin lotion and 25% podophyllotoxin solution in the treatment of condylomata acuminata in males and females. Int J STD AIDS. 1993 Jul-Aug;4(4):194–199. doi: 10.1177/095646249300400403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassus A. Comparison of podophyllotoxin and podophyllin in treatment of genital warts. Lancet. 1987 Aug 29;2(8557):512–513. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91823-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurkiewicz W., Jablonska S. Vergleichende Untersuchungen zwischen 0.5% Podophyllotoxin-Präparaten (Condyline) und 20% Podophyllin, gelöst in Alkohol, bei der Therapie von spitzen Kondylomen. Z Hautkr. 1986 Oct 1;61(19):1387–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds M., Murphy M., Waugh M. A., Lacey C. J. An audit of treatment of genital warts: opening the feedback loop. Int J STD AIDS. 1993 Jul-Aug;4(4):226–231. doi: 10.1177/095646249300400410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand A., Rylander E., Evander M., Wadell G. Genital human papillomavirus infection among patients attending an STD clinic. Genitourin Med. 1993 Dec;69(6):446–449. doi: 10.1136/sti.69.6.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Krogh G., Hellberg D. Self-treatment using a 0.5% podophyllotoxin cream of external genital condylomata acuminata in women. A placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Sex Transm Dis. 1992 May-Jun;19(3):170–174. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199205000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Krogh G. Penile condylomata acuminata: an experimental model for evaluation of topical self-treatment with 0.5--1.0% ethanolic preparations of podophyllotoxin for three days. Sex Transm Dis. 1981 Jul-Sep;8(3):179–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Krogh G. Topical treatment of penile condylomata acuminata with podophyllin, podophyllotoxin and colchicine. A comparative study. Acta Derm Venereol. 1978;58(2):163–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


