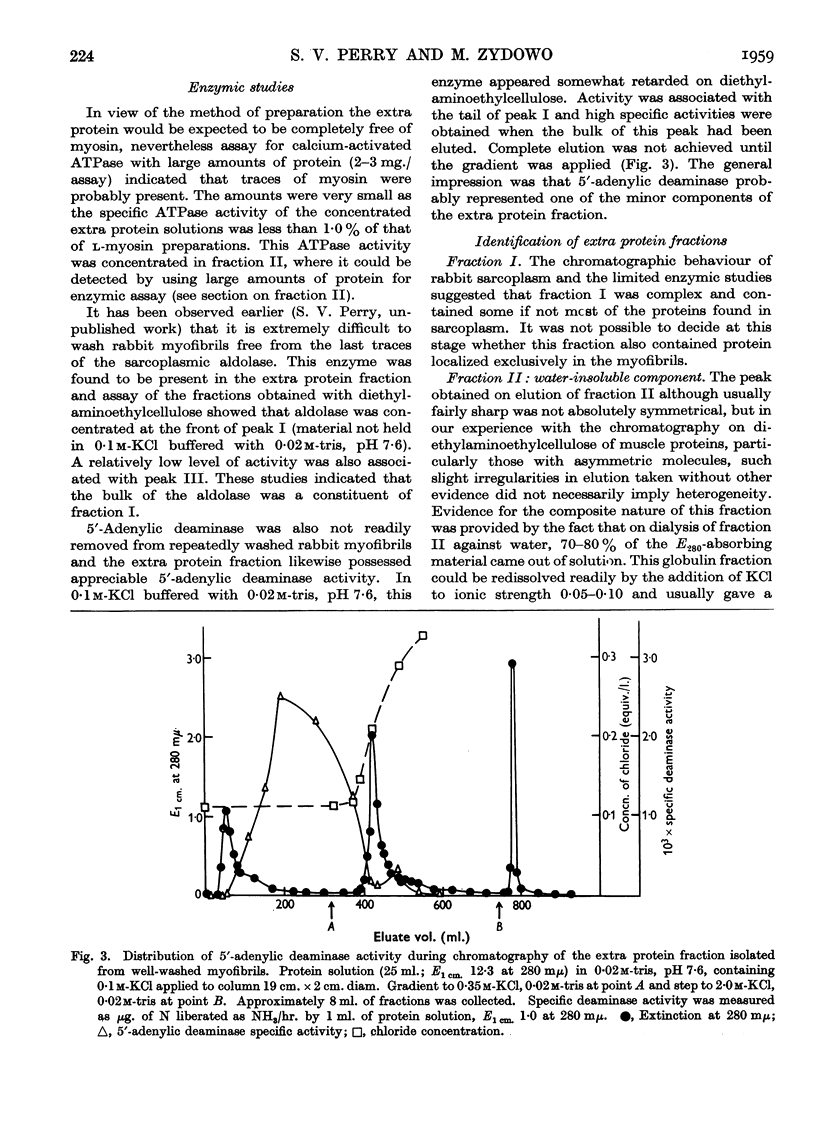
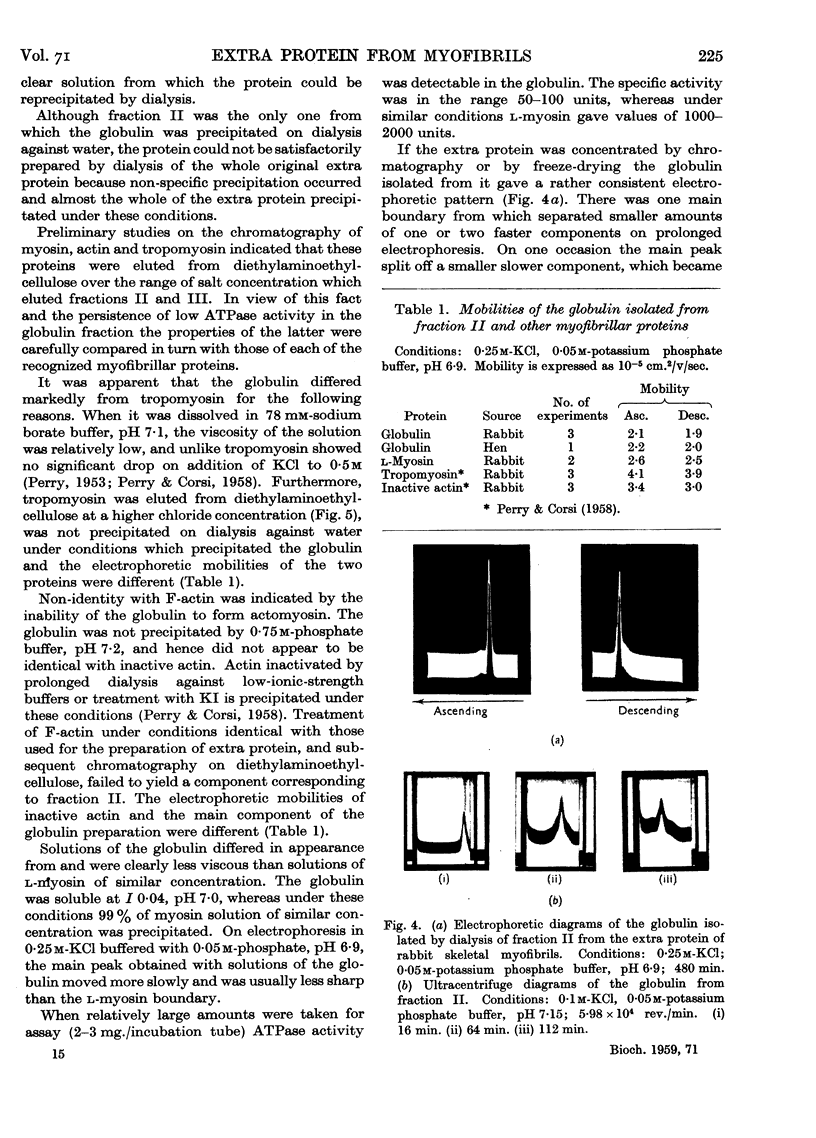
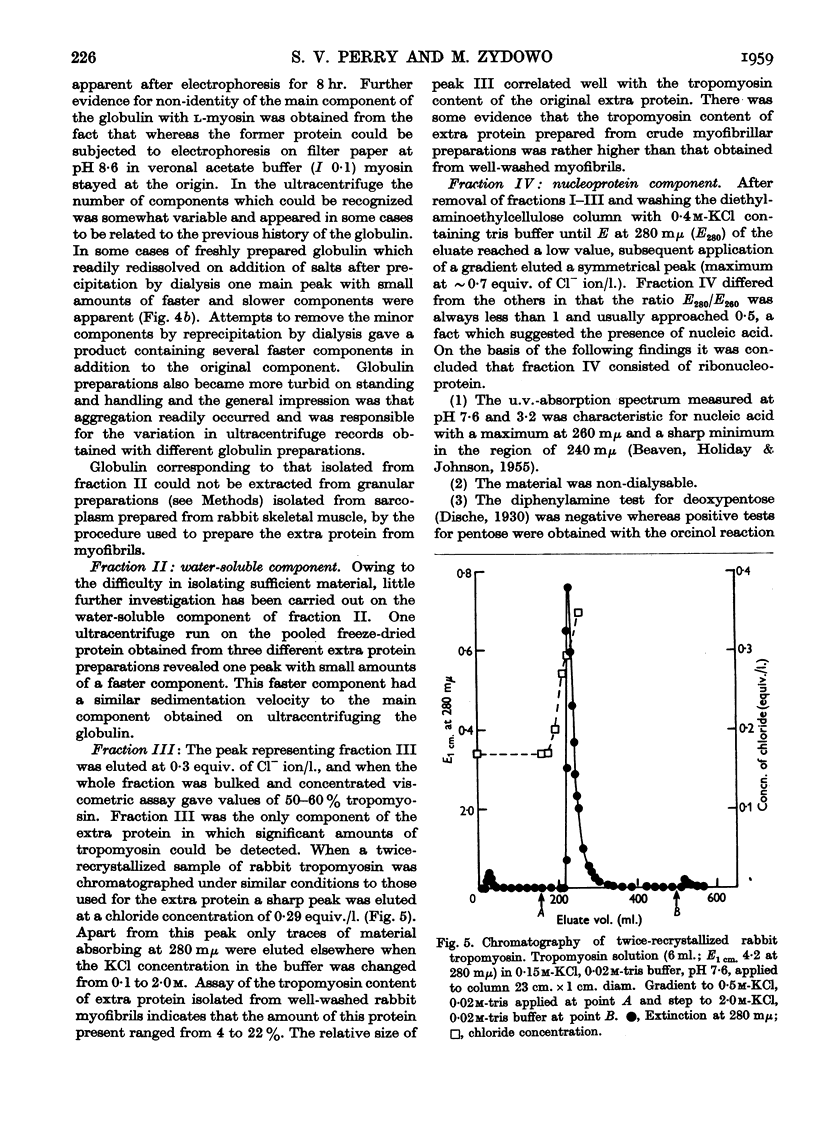
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey K. Myosin and adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochem J. 1942 Feb;36(1-2):121–139. doi: 10.1042/bj0360121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey K. Tropomyosin: a new asymmetric protein component of the muscle fibril. Biochem J. 1948;43(2):271–279. doi: 10.1042/bj0430271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORSI A. Some observations on the extra-protein of cross-striated muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Sep;25(3):640–641. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90538-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE VILLAFRANCA G. W. A study on the nature of the A band of cross-striated muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Apr;61(2):378–383. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. Spectrophotometric method for the determination of free pentose and pentose in nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):379–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREY T. C., PERRY S. V. A study of the effects of substrate concentration and certain relaxing factors on the magnesium-activated myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1956 Sep;64(1):184–192. doi: 10.1042/bj0640184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMOIR G. Fish tropomyosin and fish nucleotropomyosin. Biochem J. 1951 Feb;48(2):146–151. doi: 10.1042/bj0480146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON J., HUXLEY H. E. Quantitative studies on the structure of cross-striated myofibrils. II. Investigations by biochemical techniques. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Feb;23(2):250–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90326-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSELBACH W., SCHNEIDER G. Der L-Myosin- und Aktingehalt des Kaninchenmuskels. Biochem Z. 1951;321(6):462–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOUIS P. Recherches sur la fraction Y des protéines de muscles de lapin. Experientia. 1954 Jun 15;10(6):258–259. doi: 10.1007/BF02157396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIHALYI E., LAKI K., KNOLLER M. I. Nucleic acid and nucleotide content of myosin preparations. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 May;68(1):130–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90333-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY S. V., CORSI A. Extraction of proteins other than myosin from the isolated rabbit myofibril. Biochem J. 1958 Jan;68(1):5–12. doi: 10.1042/bj0680005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY S. V. The protein components of the isolated myofibril. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):114–122. doi: 10.1042/bj0550114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROODYN D. B. The enzymic properties of rat-liver nuclei. 1. Estimation of the extent to which contaminant material contributes to the activity observed in the nuclear fraction. Biochem J. 1956 Oct;64(2):361–368. doi: 10.1042/bj0640361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZENT-GYORGYI A. G., MAZIA D., SZENT-GYORGYI A. On the nature of the cross-striation of body muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Mar;16(3):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90235-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYATT G. R. The purine and pyrimidine composition of deoxypentose nucleic acids. Biochem J. 1951 May;48(5):584–590. doi: 10.1042/bj0480584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




