In the title compound, the dihedral angle between the 2H-chromen-2-one ring system and the tert-butylacetate moiety is 72.72 (9)°. In the crystal, the molecules are connected through C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, generating C(6) chains and R22(20) loops that are reinforced by weak aromatic π–π stacking interactions.
Keywords: crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface, coumarin, hydrogen bond
Abstract
In the title compound, C15H16O4, the dihedral angle between the 2H-chromen-2-one ring system and the tert-butylacetate moiety is 72.72 (9)°. In the crystal, the molecules are connected through C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, generating C(6) chains and R22(20) loops that are reinforced by weak aromatic π–π stacking interactions. The H⋯H, H⋯O/O⋯H, H⋯C/C⋯H and C⋯C contacts contribute 50.6, 29.1, 8.5 and 6.8%, respectively, to the Hirshfeld surface.
Structure description
The title coumarin derivative, C15H16O4 (I), was synthesized by a research team led by Professor Djandé (LC2M, Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso) as part of the AFRAMED project (Kenfack Tsobnang et al., 2024 ▸). Coumarin-derived compounds exhibit various biological activities, such as anticancer (Yadav et al., 2024 ▸; Rawat et al., 2022 ▸), anticoagulant (Singh et al., 2019), anti-inflammatory (Todeschini et al., 1998 ▸) and anti-glaucoma (Ziki et al., 2023 ▸) properties.
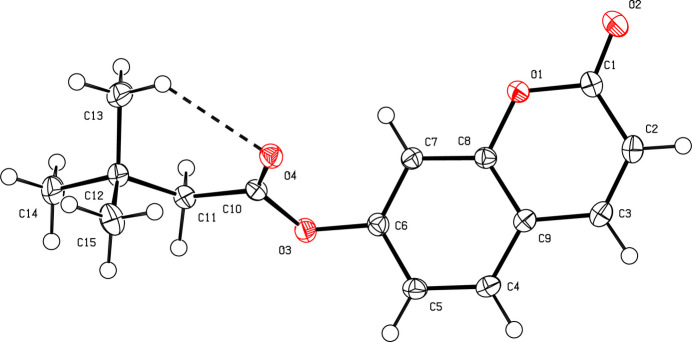
As shown in Fig. 1 ▸, the 2H-chromen-2-one moiety formed by atoms C1–C9/O1/O2 in (I) is almost planar with an r.m.s deviation of 0.027 Å and the dihedral angle between this ring system and the plane formed by atoms C10–C12/C14 in the tert-butylacetate moiety is 72.72 (9)°. An S(6) ring motif resulting from an intramolecular C13—H13B⋯O4 hydrogen bond is observed (Table 1 ▸). The plane passing through atoms C10–C12/C14 of the tert-butylacetate moiety contains the ester function atoms (r.m.s = 0.228 Å), but methyl atoms C13 and C15 atoms are on either side of this plane with deviations of 1.275 (1) and −1.244 (1) Å, respectively.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of (I) with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C5—H5⋯O4i | 0.95 | 2.50 | 3.4144 (13) | 161 |
| C11—H11B⋯O2ii | 0.99 | 2.52 | 3.2523 (13) | 131 |
| C13—H13B⋯O4 | 0.98 | 2.43 | 3.0924 (14) | 124 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
In the crystal of (I), molecules are linked by weak hydrogen bonds of the C—H⋯O type. A pair of C11—H11B⋯O2(−x + 2, −y, −z + 1) hydrogen bonds generates a centrosymmetric  (20) loop, as shown in Fig. 3. The C5—H5⋯O4(x − 1, y, z) hydrogen bonds form C(6) chains propagating in the [100] direction (Fig. 2 ▸). Aromatic π–π stacking interactions between the pyrone ring (centroid Cg1) and benzene ring (centroid Cg2) of a symmetry-related (1 − x, −y, 1 − z) molecule reinforce the cohesion of molecules [Cg1⋯Cg2 = 3.5485 (8) with a slippage of 1.042 Å],
(20) loop, as shown in Fig. 3. The C5—H5⋯O4(x − 1, y, z) hydrogen bonds form C(6) chains propagating in the [100] direction (Fig. 2 ▸). Aromatic π–π stacking interactions between the pyrone ring (centroid Cg1) and benzene ring (centroid Cg2) of a symmetry-related (1 − x, −y, 1 − z) molecule reinforce the cohesion of molecules [Cg1⋯Cg2 = 3.5485 (8) with a slippage of 1.042 Å],
Figure 2.
Part of the crystal of (I) showing the formation of an undulating network along the b axis [C(6) and  (20) motifs]. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
(20) motifs]. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
The Hirshfeld surface and two-dimensional fingerprint (FP) plot of (1) (Fig. 3 ▸) generated by CrystalExplorer21.5 (Spackman et al., 2021 ▸) confirmed the above interactions. The fingerprint plots show the different contributions of the atoms in the crystal-to-surface contacts. The most important contributions are H⋯H and H⋯O/O⋯H contacts with 50.6 and 29.1%, respectively (Fig. 3 ▸d and 3f). The H⋯C/C⋯H and C⋯C contacts contribute 8.5 and 6.8%, respectively. These values are close to those of 2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl 4- tert-butylbenzoate (Kenfack Tsobnang et al., 2024 ▸).
Figure 3.
(a), (b) Hirshfeld surface of (I) mapped over dnorm, (c) overall two-dimensional fingerprint plot of and those delineated into contributions from different contacts: (d) H⋯H, (d) H⋯C/C⋯H and (e) H⋯O/O⋯H.
Synthesis and crystallization
To a solution of tert-butylacetyl chloride (6.2 mmol, 0.9 ml) in dried diethyl ether (16 ml) was added dried pyridine (4.7 molar equivalents; 2.31 ml) and 7-hydroxycoumarin (6.17 mmol, 1.00 g) in small portions over 30 min. The mixture was left under agitation at room temperature for 3 h and then poured into 40 ml of chloroform. The solution was acidified with dilute hydrochloric acid (5%) until the pH was 2–3. The organic layer was extracted, washed four times with 25 ml of water to neutrality, dried over MgSO4 and the solvent removed. The resulting crude product was filtered off with suction, washed with petroleum ether and recrystallized from acetone solution as colorless crystals of the title compound. Yield = 79%, m.p. = 368–371 K.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C15H16O4 |
| M r | 260.28 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P
|
| Temperature (K) | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 6.1599 (9), 7.2029 (11), 15.202 (2) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 98.765 (5), 99.335 (5), 91.228 (5) |
| V (Å3) | 657.05 (17) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.10 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.20 × 0.12 × 0.07 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker D8 Venture |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 53961, 4064, 3720 |
| R int | 0.050 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.719 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)], wR(F2), S | 0.043, 0.137, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 4064 |
| No. of parameters | 172 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.37, −0.28 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314625001890/hb4507sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314625001890/hb4507Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314625001890/hb4507Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2427772
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the PMD2X X-ray diffraction facility (https://crm2.univ-lorraine.fr/lab/fr/services/pmd2x) of the Université de Lorraine for the X-ray diffraction measurements and the AFRAMED project. CCDC is also thanked for providing access to the Cambridge Structural Database through the FAIRE program. The authors are very grateful to UNESCO, CNRS and the IUCr for their support of the AFRAMED project.
full crystallographic data
2-Oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl tert-butylacetate . Crystal data
| C15H16O4 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 260.28 | F(000) = 276 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.316 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Melting point: 368 K |
| a = 6.1599 (9) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 7.2029 (11) Å | Cell parameters from 4066 reflections |
| c = 15.202 (2) Å | θ = 2.9–30.8° |
| α = 98.765 (5)° | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 99.335 (5)° | T = 100 K |
| γ = 91.228 (5)° | Prism, yellow |
| V = 657.05 (17) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.12 × 0.07 mm |
2-Oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl tert-butylacetate . Data collection
| Bruker D8 Venture diffractometer | 3720 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.050 |
| Mirror monochromator | θmax = 30.8°, θmin = 2.9° |
| φ and ω scan | h = −8→8 |
| 53961 measured reflections | k = −10→10 |
| 4064 independent reflections | l = −21→21 |
2-Oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl tert-butylacetate . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.137 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0778P)2 + 0.2223P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4064 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 172 parameters | Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3 |
2-Oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl tert-butylacetate . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
2-Oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl tert-butylacetate . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O3 | 0.53573 (12) | 0.19418 (10) | 0.29426 (5) | 0.02062 (16) | |
| O1 | 0.88247 (11) | 0.15470 (10) | 0.59464 (5) | 0.01913 (16) | |
| O4 | 0.84148 (12) | 0.38219 (10) | 0.30532 (5) | 0.02129 (16) | |
| O2 | 1.04542 (14) | 0.10787 (12) | 0.72944 (5) | 0.02755 (18) | |
| C9 | 0.51037 (15) | 0.26016 (12) | 0.56924 (6) | 0.01750 (18) | |
| C6 | 0.53813 (16) | 0.22422 (13) | 0.38729 (6) | 0.01796 (18) | |
| C5 | 0.34391 (15) | 0.28555 (13) | 0.41609 (7) | 0.01937 (18) | |
| H5 | 0.222778 | 0.314675 | 0.374030 | 0.023* | |
| C4 | 0.33122 (15) | 0.30309 (13) | 0.50706 (7) | 0.01946 (19) | |
| H4 | 0.200134 | 0.344549 | 0.527611 | 0.023* | |
| C8 | 0.70128 (15) | 0.20004 (13) | 0.53717 (6) | 0.01673 (17) | |
| C7 | 0.71880 (15) | 0.18000 (13) | 0.44623 (6) | 0.01781 (18) | |
| H7 | 0.849197 | 0.137745 | 0.425327 | 0.021* | |
| C10 | 0.70385 (15) | 0.27069 (13) | 0.26024 (6) | 0.01775 (18) | |
| C1 | 0.88143 (17) | 0.15948 (14) | 0.68557 (6) | 0.02053 (19) | |
| C3 | 0.50766 (17) | 0.27137 (14) | 0.66442 (7) | 0.02070 (19) | |
| H3 | 0.380241 | 0.311803 | 0.688282 | 0.025* | |
| C2 | 0.68492 (18) | 0.22481 (14) | 0.71993 (7) | 0.0225 (2) | |
| H2 | 0.681287 | 0.234916 | 0.782707 | 0.027* | |
| C11 | 0.68111 (16) | 0.19153 (14) | 0.16148 (6) | 0.01956 (18) | |
| H11A | 0.522872 | 0.186209 | 0.134991 | 0.023* | |
| H11B | 0.728920 | 0.060533 | 0.156411 | 0.023* | |
| C12 | 0.80830 (16) | 0.29648 (14) | 0.10383 (6) | 0.02054 (19) | |
| C13 | 1.05795 (18) | 0.29276 (19) | 0.13479 (8) | 0.0305 (2) | |
| H13A | 1.135176 | 0.360602 | 0.096951 | 0.046* | |
| H13B | 1.096000 | 0.353175 | 0.197906 | 0.046* | |
| H13C | 1.102008 | 0.162119 | 0.129266 | 0.046* | |
| C15 | 0.7374 (2) | 0.50003 (16) | 0.10722 (7) | 0.0284 (2) | |
| H15A | 0.820076 | 0.565015 | 0.070105 | 0.043* | |
| H15B | 0.579442 | 0.500204 | 0.083962 | 0.043* | |
| H15C | 0.767411 | 0.564855 | 0.169777 | 0.043* | |
| C14 | 0.74935 (19) | 0.19270 (17) | 0.00628 (7) | 0.0277 (2) | |
| H14A | 0.827400 | 0.255304 | −0.033149 | 0.041* | |
| H14B | 0.792917 | 0.062204 | 0.003871 | 0.041* | |
| H14C | 0.590176 | 0.194470 | −0.014024 | 0.041* |
2-Oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl tert-butylacetate . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O3 | 0.0191 (3) | 0.0257 (3) | 0.0169 (3) | −0.0023 (3) | 0.0020 (2) | 0.0045 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0186 (3) | 0.0219 (3) | 0.0171 (3) | 0.0041 (2) | 0.0023 (2) | 0.0040 (2) |
| O4 | 0.0204 (3) | 0.0241 (3) | 0.0187 (3) | −0.0014 (3) | 0.0019 (2) | 0.0032 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0274 (4) | 0.0334 (4) | 0.0216 (4) | 0.0057 (3) | −0.0004 (3) | 0.0074 (3) |
| C9 | 0.0181 (4) | 0.0150 (4) | 0.0201 (4) | 0.0005 (3) | 0.0050 (3) | 0.0028 (3) |
| C6 | 0.0184 (4) | 0.0182 (4) | 0.0177 (4) | −0.0005 (3) | 0.0030 (3) | 0.0041 (3) |
| C5 | 0.0156 (4) | 0.0199 (4) | 0.0229 (4) | 0.0003 (3) | 0.0018 (3) | 0.0058 (3) |
| C4 | 0.0163 (4) | 0.0188 (4) | 0.0244 (4) | 0.0015 (3) | 0.0057 (3) | 0.0042 (3) |
| C8 | 0.0167 (4) | 0.0155 (4) | 0.0181 (4) | 0.0014 (3) | 0.0026 (3) | 0.0034 (3) |
| C7 | 0.0175 (4) | 0.0186 (4) | 0.0180 (4) | 0.0023 (3) | 0.0041 (3) | 0.0035 (3) |
| C10 | 0.0176 (4) | 0.0189 (4) | 0.0176 (4) | 0.0031 (3) | 0.0024 (3) | 0.0054 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0244 (5) | 0.0197 (4) | 0.0173 (4) | 0.0006 (3) | 0.0024 (3) | 0.0037 (3) |
| C3 | 0.0222 (4) | 0.0195 (4) | 0.0214 (4) | 0.0010 (3) | 0.0078 (3) | 0.0019 (3) |
| C2 | 0.0274 (5) | 0.0232 (4) | 0.0174 (4) | 0.0008 (4) | 0.0060 (3) | 0.0021 (3) |
| C11 | 0.0197 (4) | 0.0213 (4) | 0.0171 (4) | 0.0010 (3) | 0.0020 (3) | 0.0029 (3) |
| C12 | 0.0202 (4) | 0.0258 (4) | 0.0156 (4) | 0.0012 (3) | 0.0030 (3) | 0.0032 (3) |
| C13 | 0.0198 (5) | 0.0468 (7) | 0.0245 (5) | −0.0003 (4) | 0.0048 (4) | 0.0032 (4) |
| C15 | 0.0382 (6) | 0.0250 (5) | 0.0223 (5) | 0.0003 (4) | 0.0024 (4) | 0.0075 (4) |
| C14 | 0.0294 (5) | 0.0354 (6) | 0.0172 (4) | 0.0008 (4) | 0.0040 (4) | 0.0011 (4) |
2-Oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl tert-butylacetate . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O3—C10 | 1.3710 (11) | C3—C2 | 1.3490 (14) |
| O3—C6 | 1.3953 (11) | C3—H3 | 0.9500 |
| O1—C1 | 1.3785 (11) | C2—H2 | 0.9500 |
| O1—C8 | 1.3791 (11) | C11—C12 | 1.5339 (14) |
| O4—C10 | 1.2033 (12) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| O2—C1 | 1.2151 (12) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C9—C8 | 1.3970 (13) | C12—C15 | 1.5344 (15) |
| C9—C4 | 1.4044 (13) | C12—C13 | 1.5355 (15) |
| C9—C3 | 1.4396 (13) | C12—C14 | 1.5380 (14) |
| C6—C7 | 1.3862 (13) | C13—H13A | 0.9800 |
| C6—C5 | 1.3971 (13) | C13—H13B | 0.9800 |
| C5—C4 | 1.3845 (13) | C13—H13C | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C15—H15A | 0.9800 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C15—H15B | 0.9800 |
| C8—C7 | 1.3900 (13) | C15—H15C | 0.9800 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C14—H14A | 0.9800 |
| C10—C11 | 1.5054 (13) | C14—H14B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.4540 (14) | C14—H14C | 0.9800 |
| C10—O3—C6 | 119.43 (7) | C1—C2—H2 | 119.3 |
| C1—O1—C8 | 121.85 (8) | C10—C11—C12 | 117.18 (8) |
| C8—C9—C4 | 118.47 (9) | C10—C11—H11A | 108.0 |
| C8—C9—C3 | 117.80 (9) | C12—C11—H11A | 108.0 |
| C4—C9—C3 | 123.72 (9) | C10—C11—H11B | 108.0 |
| C7—C6—O3 | 120.83 (8) | C12—C11—H11B | 108.0 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 122.58 (9) | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.2 |
| O3—C6—C5 | 116.39 (8) | C11—C12—C15 | 110.51 (8) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 118.78 (9) | C11—C12—C13 | 111.12 (8) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.6 | C15—C12—C13 | 110.36 (9) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.6 | C11—C12—C14 | 106.66 (8) |
| C5—C4—C9 | 120.60 (9) | C15—C12—C14 | 109.16 (8) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C13—C12—C14 | 108.94 (8) |
| C9—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C12—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| O1—C8—C7 | 116.34 (8) | C12—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| O1—C8—C9 | 121.32 (8) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 122.33 (9) | C12—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 117.24 (8) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 121.4 | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 121.4 | C12—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| O4—C10—O3 | 123.07 (9) | C12—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| O4—C10—C11 | 128.49 (9) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| O3—C10—C11 | 108.45 (8) | C12—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| O2—C1—O1 | 116.63 (9) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 126.14 (9) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 117.23 (9) | C12—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C9 | 120.42 (9) | C12—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.8 | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C9—C3—H3 | 119.8 | C12—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.30 (9) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.3 | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
2-Oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl tert-butylacetate . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C5—H5···O4i | 0.95 | 2.50 | 3.4144 (13) | 161 |
| C11—H11B···O2ii | 0.99 | 2.52 | 3.2523 (13) | 131 |
| C13—H13B···O4 | 0.98 | 2.43 | 3.0924 (14) | 124 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y, z; (ii) −x+2, −y, −z+1.
References
- Bruker (2019). APEX4 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Kenfack Tsobnang, P., Ziki, E., Siaka, S., Yoda, J., Kamal, S., Bouraima, A., Djifa Hounsi, A., Wenger, E., Bendeif, E.-E. & Lecomte, C. (2024). Acta Cryst. E80, 106–109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rawat, A. A. & Reddy, V. B. (2022). Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 5, 100038.
- Spackman, P. R., Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2021). J. Appl. Cryst.54, 1006–1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2020). Acta Cryst. E76, 1–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Todeschini, A. R., de Miranda, A. L. P., da Silva, K. C. M., Parrini, S. C. & Barreiro, E. J. (1998). Eur. J. Med. Chem.33, 189–199.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst.43, 920–925.
- Yadav, A. K., Shrestha, R. M. & Yadav, P. N. (2024). Eur. J. Med. Chem. p. 267.
- Ziki, E., Akonan, L., Kouman, K. C., Dali, D., Megnassan, E., Kakou-Yao, R., Tenon, A. J., Frecer, V. & Miertus, S. J. (2023). J. Pharm. Res. Int.35, 10–33.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314625001890/hb4507sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314625001890/hb4507Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314625001890/hb4507Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2427772
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report