Full text
PDF
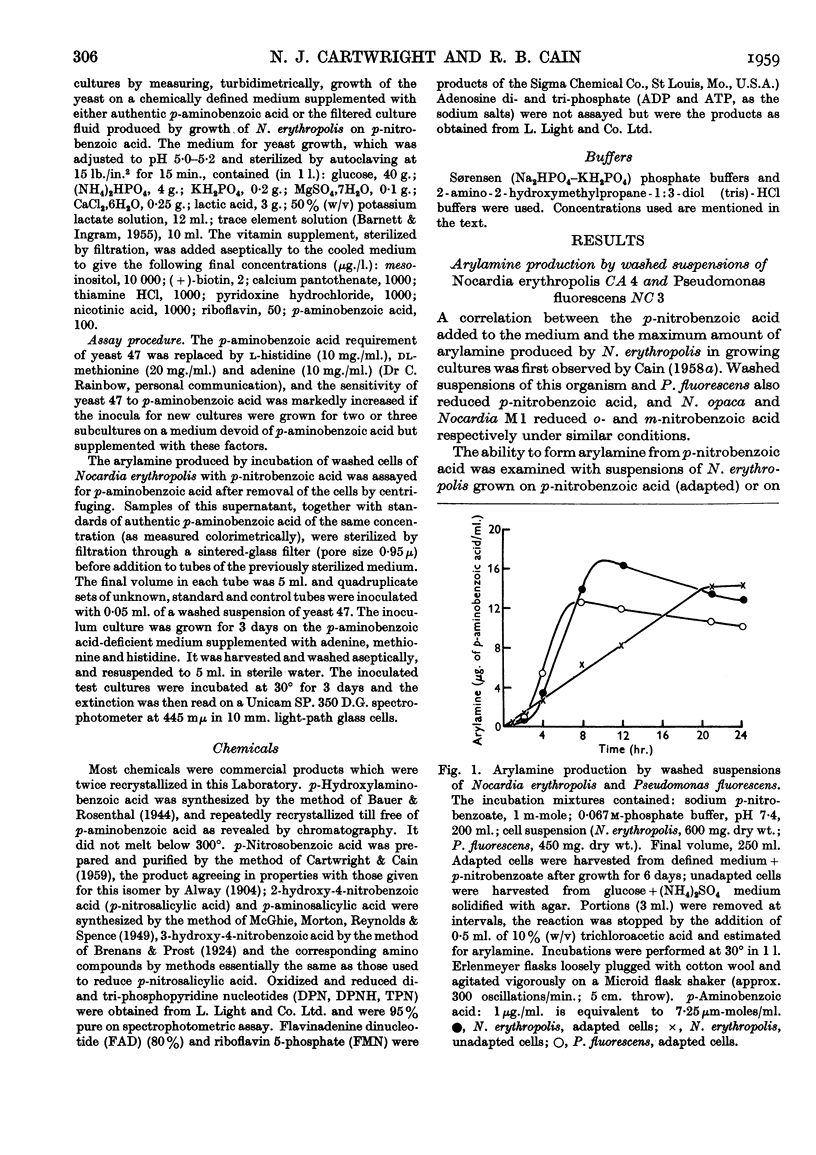

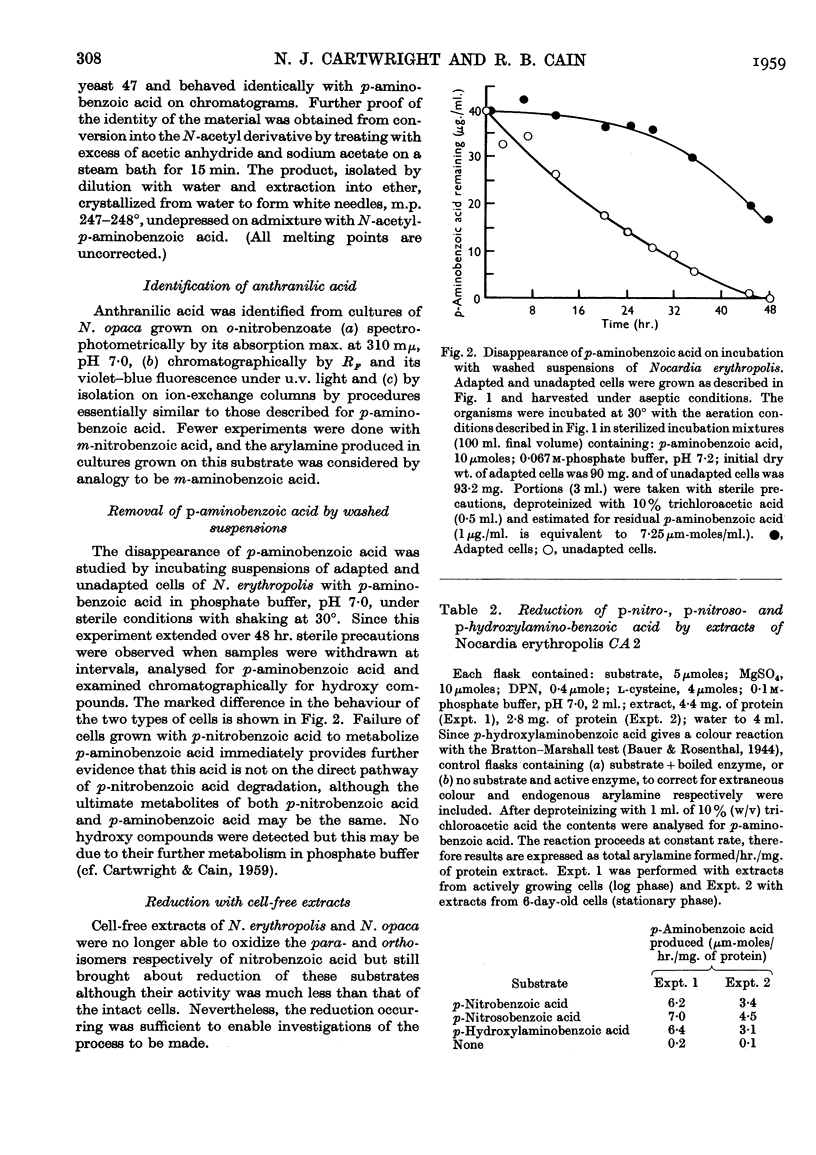


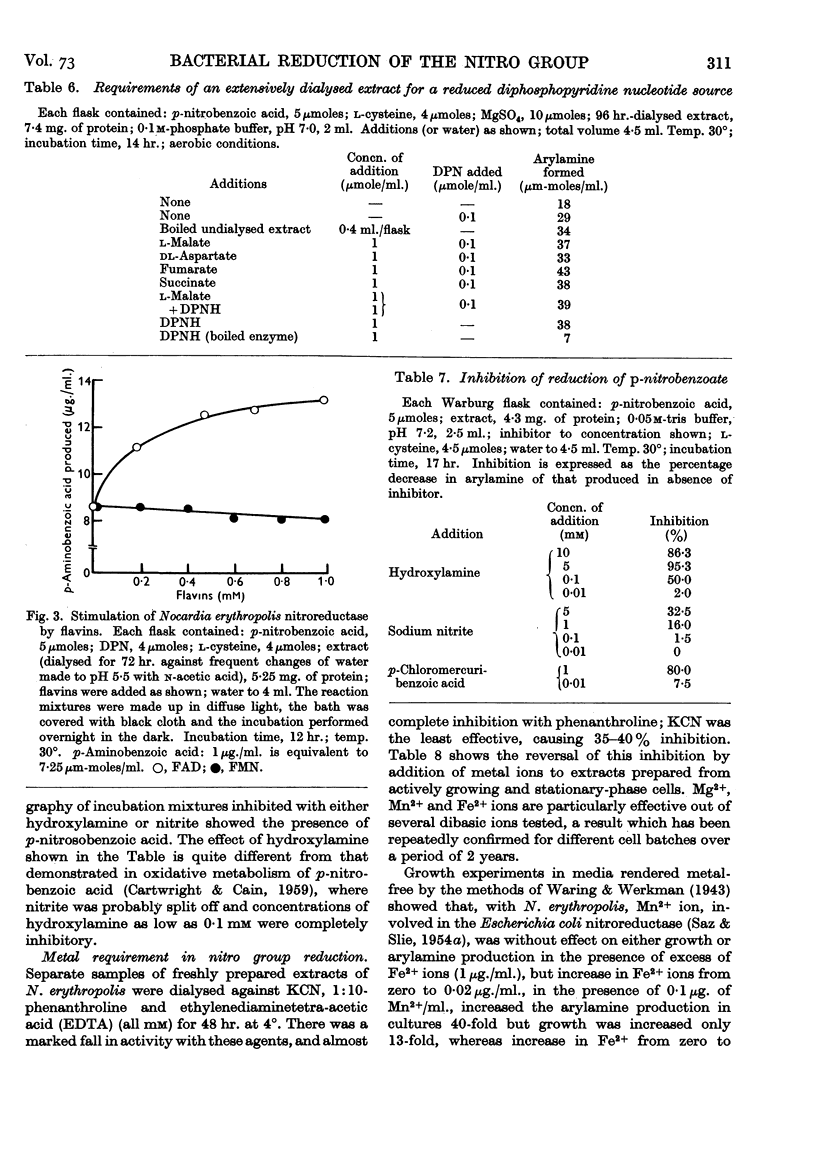
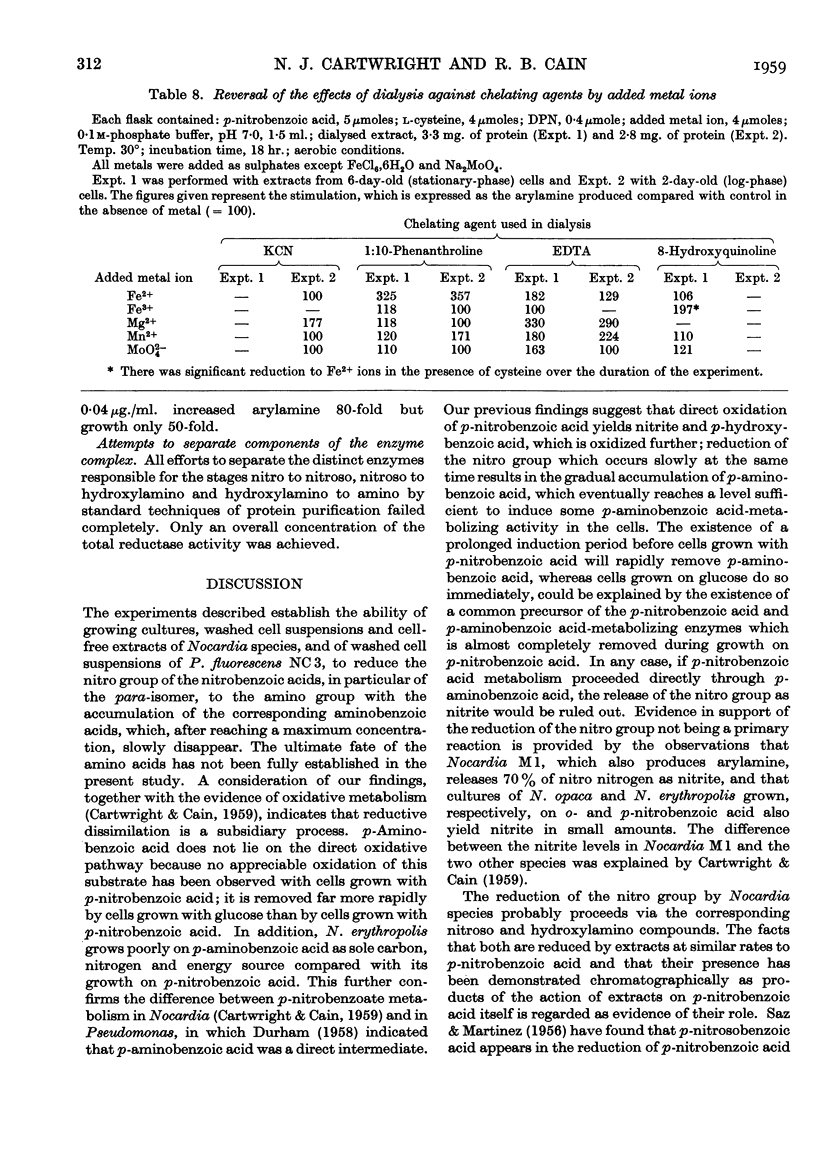


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRODIE A. F., GOTS J. S. Nitrofurans as electron acceptors for certain respiratory enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Jul;39(1):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90270-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSH M. T., TOUSTER O., BROCKMAN J. E. The production of beta-nitropropionic acid by a strain of Aspergillus flavus. J Biol Chem. 1951 Feb;188(2):685–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAIN R. B. The microbial metabolism of nitro-aromatic compounds. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Aug;19(1):1–14. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTWRIGHT N. J., CAIN R. B. Bacterial degradation of the nitrobenzoic acids. Biochem J. 1959 Feb;71(2):248–261. doi: 10.1042/bj0710248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUTTS N. S., RAINBOW C. Studies of a yeast exacting towards p-aminobenzoic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1950 May;4(2):150–155. doi: 10.1099/00221287-4-2-150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE LA HABA G. Studies on the mechanism of nitrate assimilation in neurospora. Science. 1950 Aug 18;112(2903):203–204. doi: 10.1126/science.112.2903.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURHAM N. N. Studies on the metabolism of p-nitrobenzoic acid. Can J Microbiol. 1958 Apr;4(2):141–148. doi: 10.1139/m58-015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGAMI F., EBATA M., SATO R. Reduction of chloromycetin by a cell-free bacterial extract and its relation to nitrite reduction. Nature. 1951 Jan 20;167(4238):118–119. doi: 10.1038/167118a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greville G. D., Stern K. G. The reduction of dinitrophenols by redox indicators and enzymes. Biochem J. 1935 Feb;29(2):487–499. doi: 10.1042/bj0290487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOTAKE Y., SHIRAI Y. Uber die Entstehung der 5-Oxy-anthranilsäure aus Anthranilsäure im tierischen Organismus. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1953;295:160–163. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1953.295.1.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLE H. N. The oxidation of 2-nitropropane by extracts of pea plants. J Biol Chem. 1957 Nov;229(1):231–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTINEZ L. M., SAZ A. K. Enzymatic basis of resistance to aureomycin. I. Differences between flavoprotein nitro reductases of sensitive and resistant Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1956 Nov;223(1):285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLAS D. J., NASON A. Diphosphopyridine nucleotide-nitrate reductase from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1955 May;69(5):580–583. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.5.580-583.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLAS D. J., NASON A. Mechanism of action of nitrate reductase from Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1954 Nov;211(1):183–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER V. H. Enzymic reduction of 2:4-dinitrophenol by rat-tissue homogenates. Biochem J. 1952 Jun;51(3):363–370. doi: 10.1042/bj0510363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARTRIDGE C. W. H., BONNER D. M., YANOFSKY C. A quantitative study of the relationship between tryptophan and niacin in Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1952 Jan;194(1):269–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAISTRICK H., STOSSL A. Studies in the biochemistry of micro-organisms. 104. Metabolites of Penicillium atrovenetum G. Smith: beta-nitropropionic acid, a major metabolite. Biochem J. 1958 Apr;68(4):647–653. doi: 10.1042/bj0680647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAZ A. K., SLIE R. B. Reversal of aureomycin inhibition of bacterial cell-free nitro reductase by manganese. J Biol Chem. 1954 Sep;210(1):407–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAZ A. K., SLIE R. B. The inhibition of organiz nitro reductase by aureomycin in cell-free extracts. II. Cofactor requirements for the nitro reductase enzyme complex. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Jul;51(1):5–16. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90447-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH G. N., WORREL C. S. The decomposition of chloromycetin (chloramphenicol) by microorganisms. Arch Biochem. 1950 Sep;28(2):232–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZUCKER M., NASON A. A pyridine nucleotide-hydroxylamine reductase from Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1955 Mar;213(1):463–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


