Abstract
The possibility was investigated that group Ia muscle spindle afferents and group Ib tendon organ afferents influence spinal motoneurones via shared neuronal pathways. Mutual facilitation of actions of these afferents at a premotoneuronal level has been taken as evidence that they use the same interneurones to evoke post-synaptic potentials (p.s.p.s) in motoneurones. Inhibitory p.s.p.s (i.p.s.p.s) or excitatory p.s.p.s (e.p.s.p.s) were evoked in motoneurones by selective activation of group Ia afferents or group Ib afferents. P.s.p.s following stimulation of both Ia and Ib afferents were then compared with the arithmetic sum of p.s.p.s evoked by each of them separately. When the former were larger the difference was used as a measure of synaptic actions mediated by interneurones co-excited by Ia and Ib afferents. Both excitatory and inhibitory pathways to motoneurones have been found to be shared by Ia and Ib afferents, although the proportion of interneurones actually used in common by these afferents could not be established. The latencies of post-synaptic actions mediated by such interneurones indicated that they were evoked disynaptically or trisynaptically. The study leads to two main conclusions: that group Ia muscle spindle afferents, and in consequence also fusimotor systems, may modulate the reflex action of tendon organs, and that the two groups of afferents are a source of information in a common feed-back system.
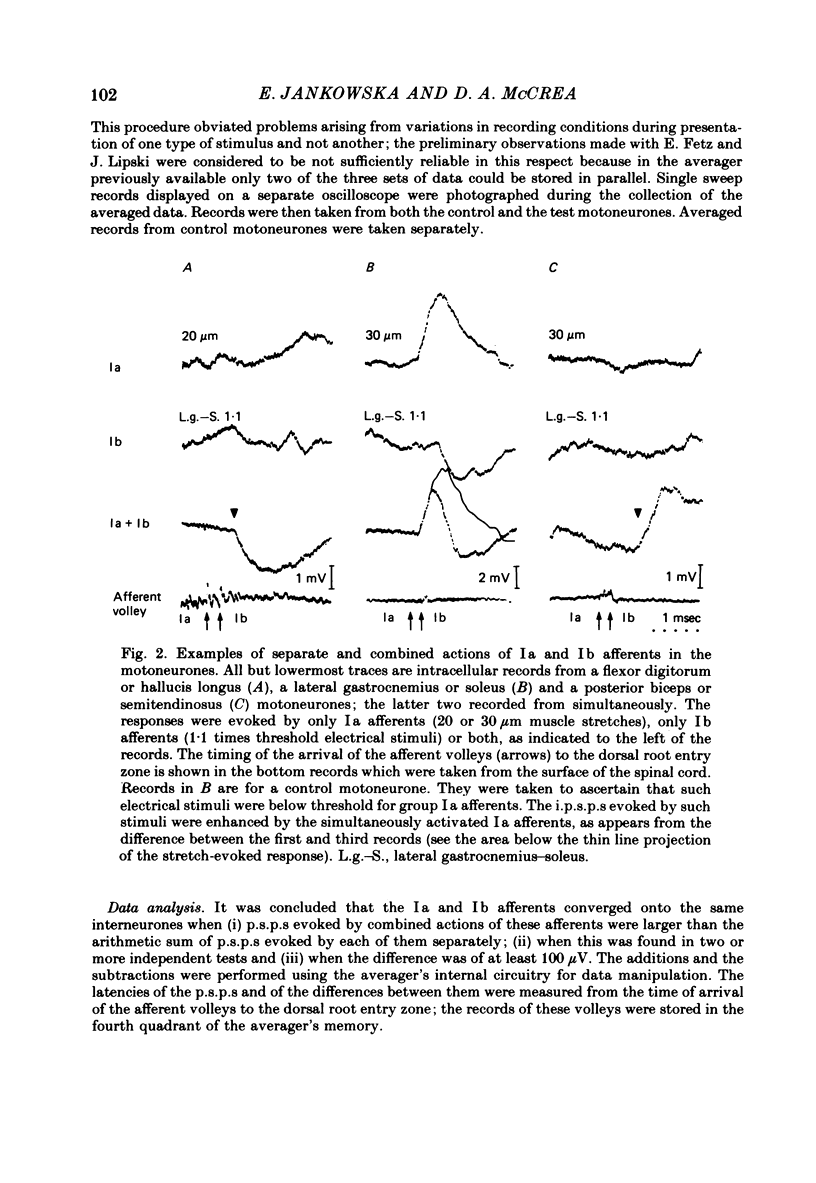
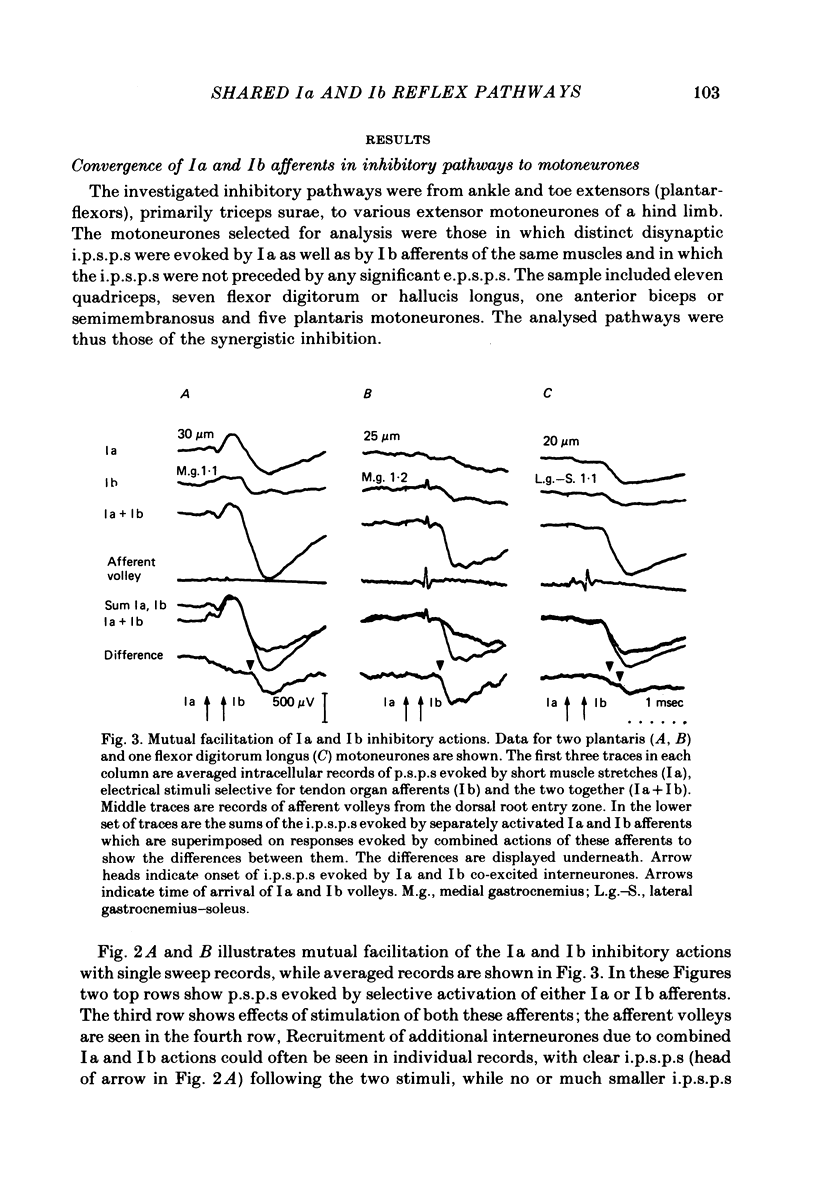
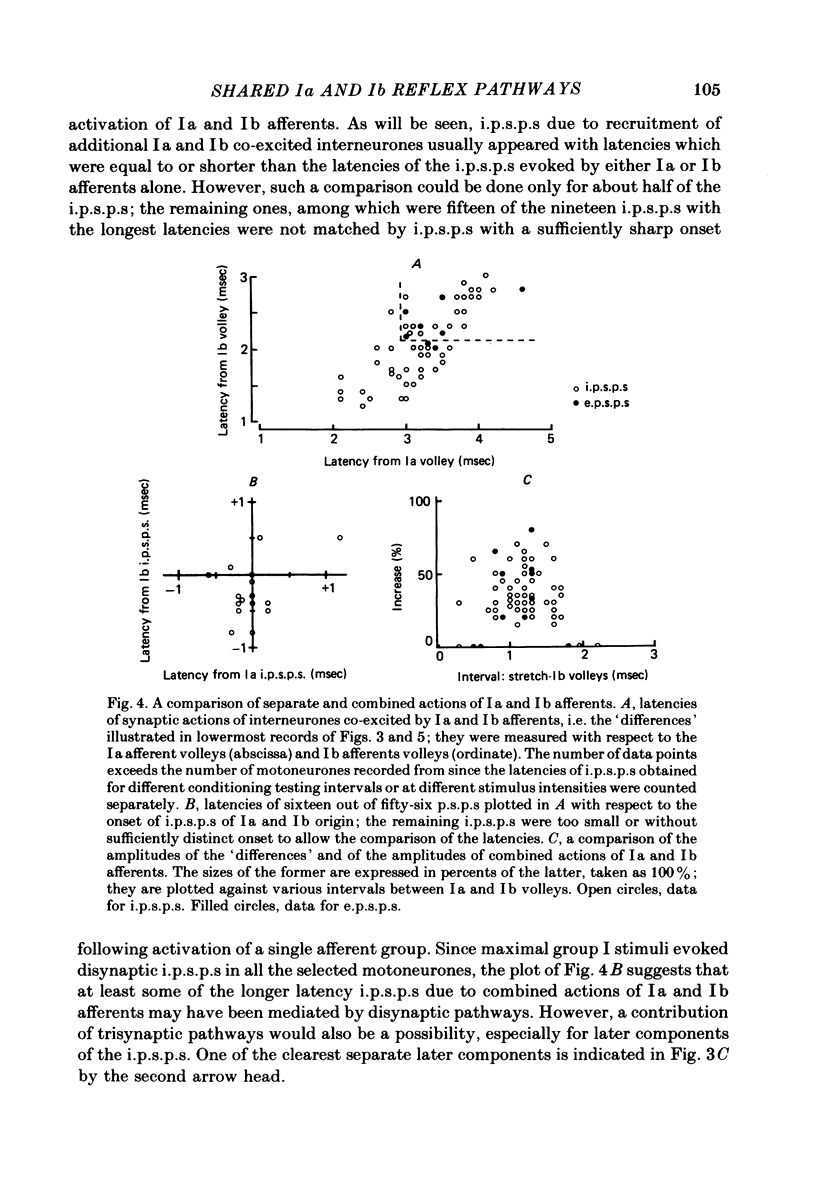
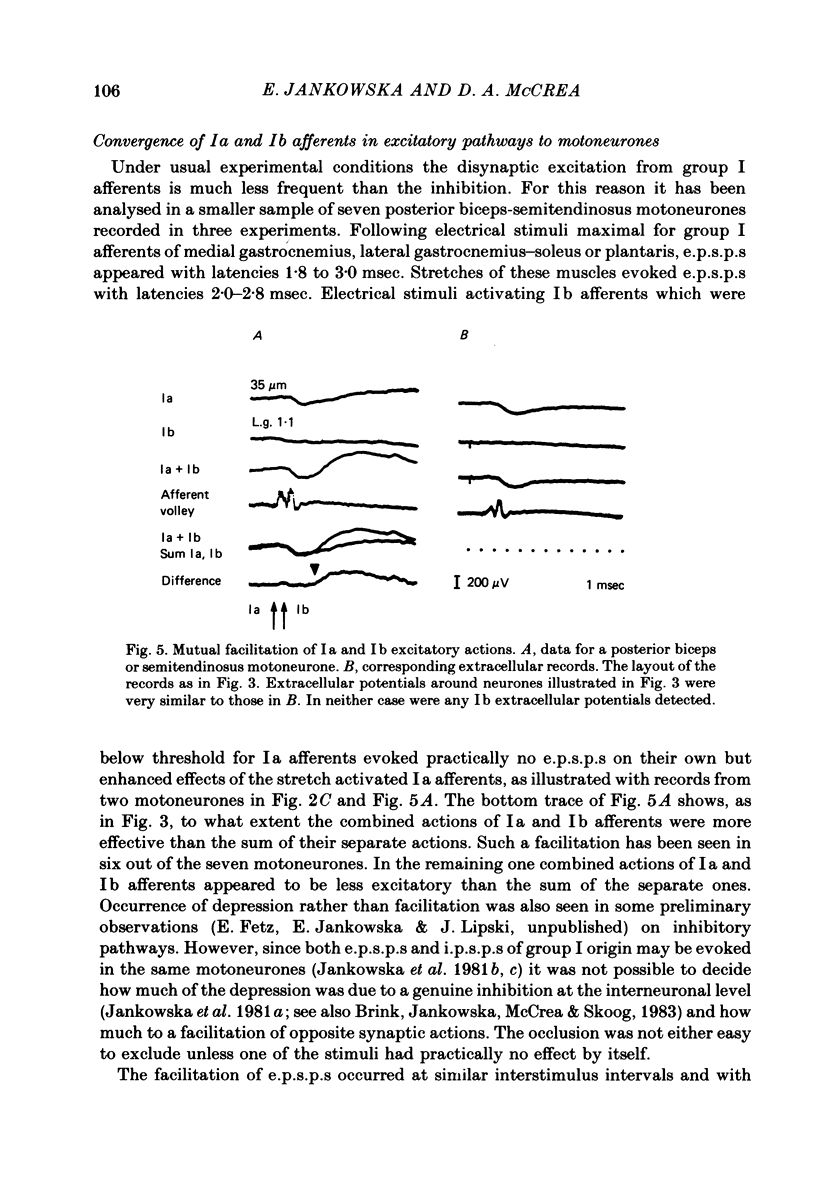
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke D., Hagbarth K. E., Löfstedt L. Muscle spindle activity in man during shortening and lengthening contractions. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:131–142. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarkowska J., Jankowska E., Sybirska E. Common interneurones in reflex pathways from group 1a and 1b afferents of knee flexors and extensors in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:367–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones caused by impulses in Golgi tendon organ afferents. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):227–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetz E. E., Jankowska E., Johannisson T., Lipski J. Autogenetic inhibition of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:173–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R. Reflex self-regulation of muscle contraction and autogenetic inhibition. J Neurophysiol. 1950 Sep;13(5):351–372. doi: 10.1152/jn.1950.13.5.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C. The effect of stretch receptors from muscle on the discharge of motorneurons. J Physiol. 1952 Jul;117(3):359–379. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. J., Jankowska E., Johannisson T. Shared reflex pathways of group I afferents of different cat hind-limb muscles. J Physiol. 1983 May;338:113–128. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. Convergence of excitatory and inhibitory action on interneurones in the lumbosacral cord. Exp Brain Res. 1966;1(4):338–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00237706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. The rubrospinal tract. IV. Effects on interneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1972;15(1):54–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00234958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houk J. C. Regulation of stiffness by skeletomotor reflexes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:99–114. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.000531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Johannisson T., Lipski J. Common interneurones in reflex pathways from group 1a and 1b afferents of ankle extensors in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:381–402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., McCrea D., Mackel R. Oligosynaptic excitation of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:411–425. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., McCrea D., Mackel R. Pattern of 'non-reciprocal' inhibition of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:393–409. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., VOORHOEVE P. Effects from the pyramidal tract on spinal reflex arcs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Nov-Dec;56:201–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Cutaneous facilitation of transmission in reflex pathways from Ib afferents to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;265(3):763–780. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Role of joint afferents in motor control exemplified by effects on reflex pathways from Ib afferents. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:327–343. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A. Multisensory control of spinal reflex pathways. Prog Brain Res. 1979;50:11–28. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60803-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchand R., Bridgman C. F., Shumpert E., Eldred E. Association of tendon organs with spindles in muscles of the cat's leg. Anat Rec. 1971 Jan;169(1):23–32. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091690103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell L. M., Henneman E. Terminals of single Ia fibers: location, density, and distribution within a pool of 300 homonymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):171–187. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Bergego C., Katz R., Morin C. Cutaneous depression of Ib reflex pathways to motoneurones in man. Exp Brain Res. 1981;42(3-4):351–361. doi: 10.1007/BF00237500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Bergego C., Katz R. Reversal in cutaneous of Ib pathways during human voluntary contraction. Brain Res. 1982 Feb 11;233(2):400–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochazka A. Muscle spindle function during normal movement. Int Rev Physiol. 1981;25:47–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochazka A., Stephens J. A., Wand P. Muscle spindle discharge in normal and obstructed movements. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:57–66. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond F. J., Abrahams V. C. Morphology and distribution of muscle spindles in dorsal muscles of the cat neck. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Nov;38(6):1322–1339. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.6.1322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. G., Mendell L. M. Individual EPSPs produced by single triceps surae Ia afferent fibers in homonymous and heteronymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Jul;39(4):679–692. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.4.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrington C. S. On the Anatomical Constitution of Nerves of Skeletal Muscles; with Remarks on Recurrent Fibres in the Ventral Spinal Nerve-root. J Physiol. 1894 Oct 15;17(3-4):210.2–21258. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1894.sp000528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


