Abstract
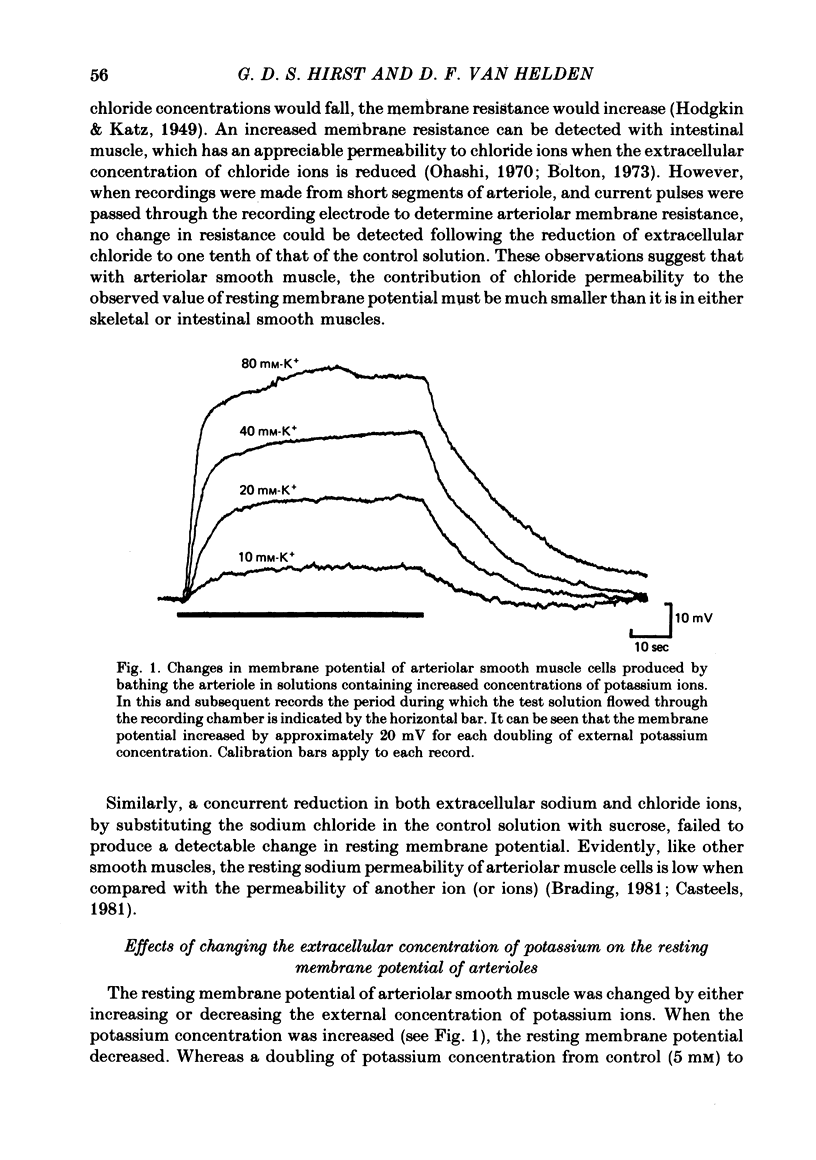
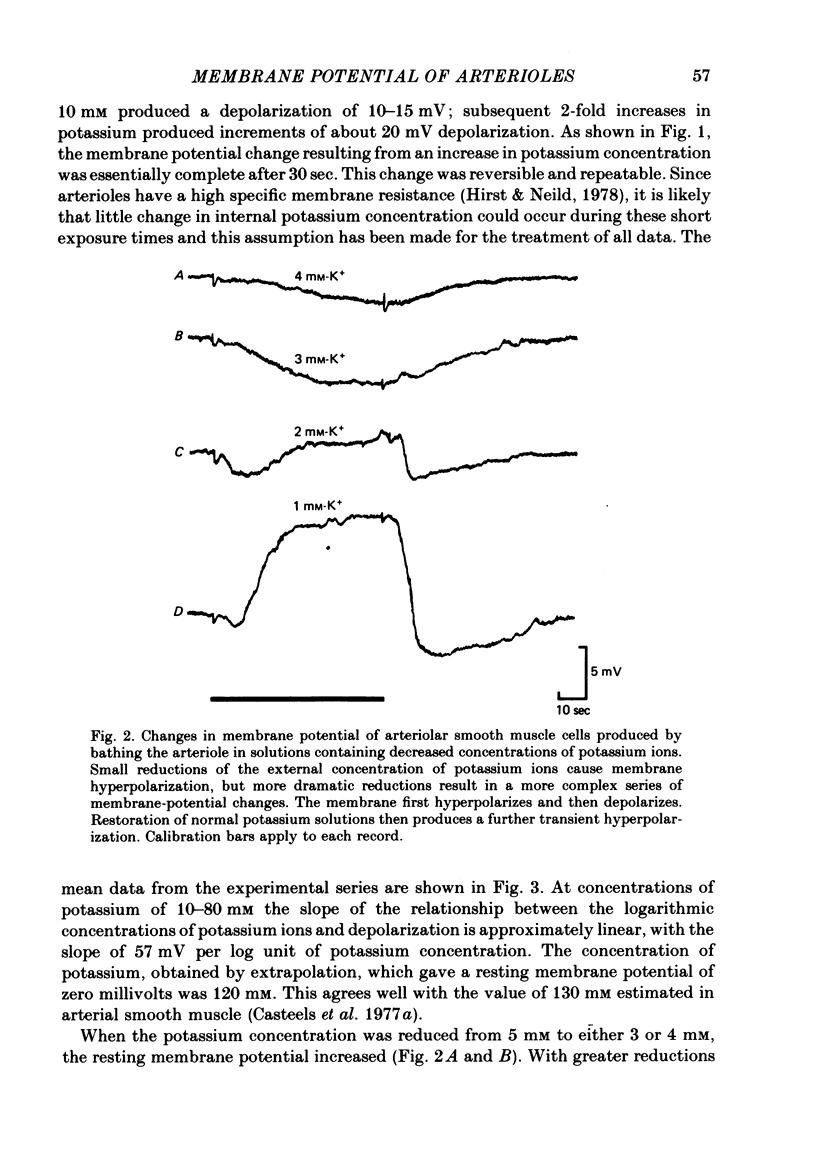
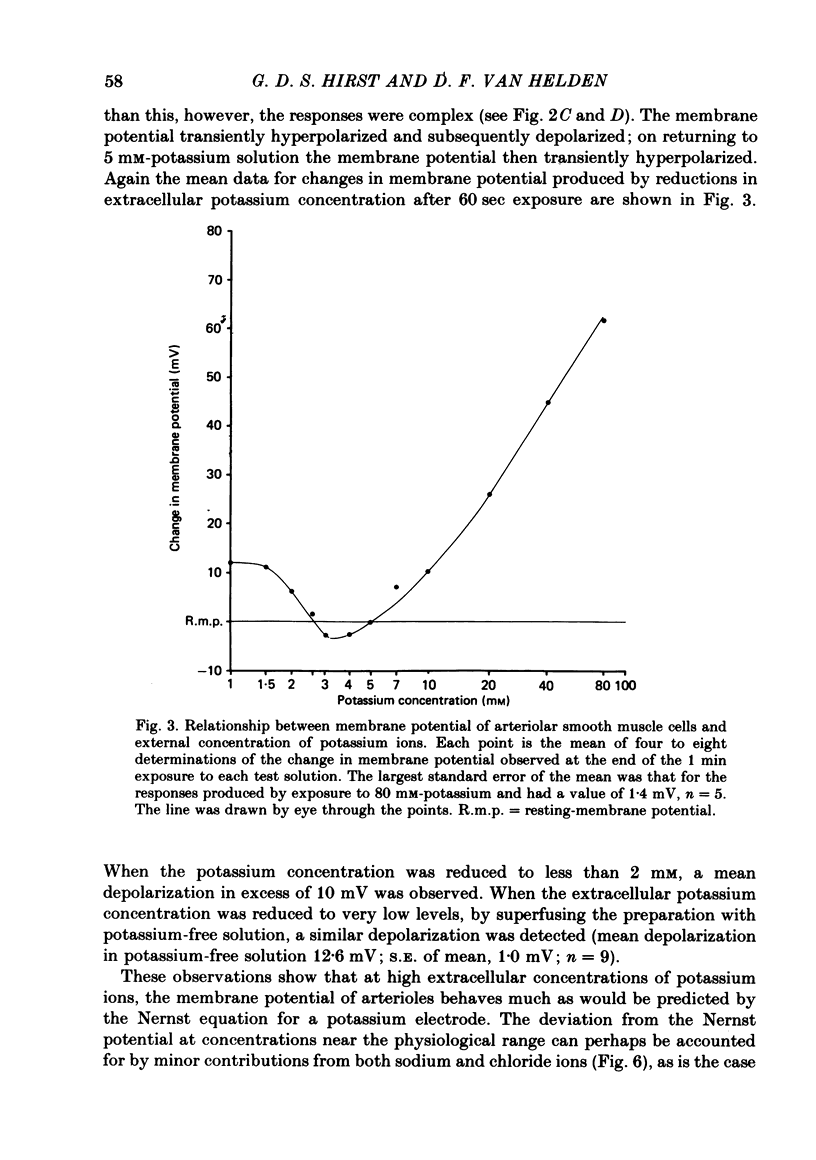
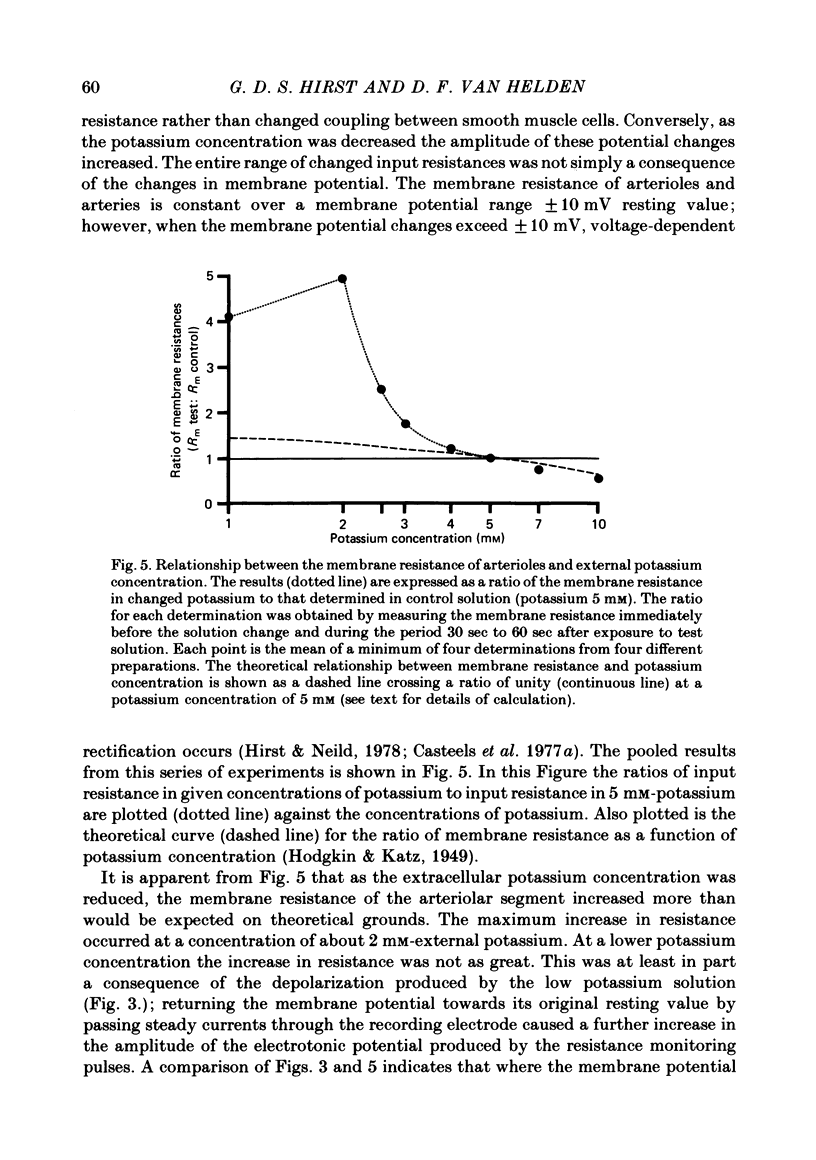
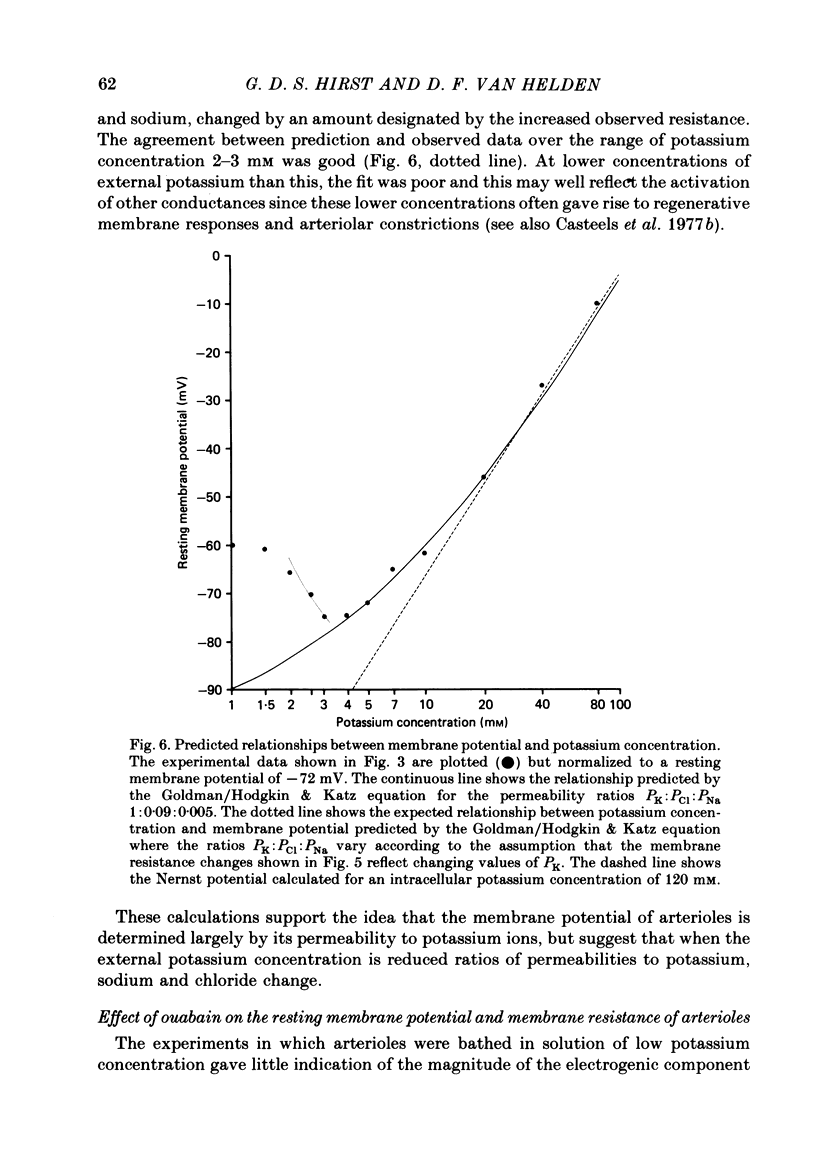
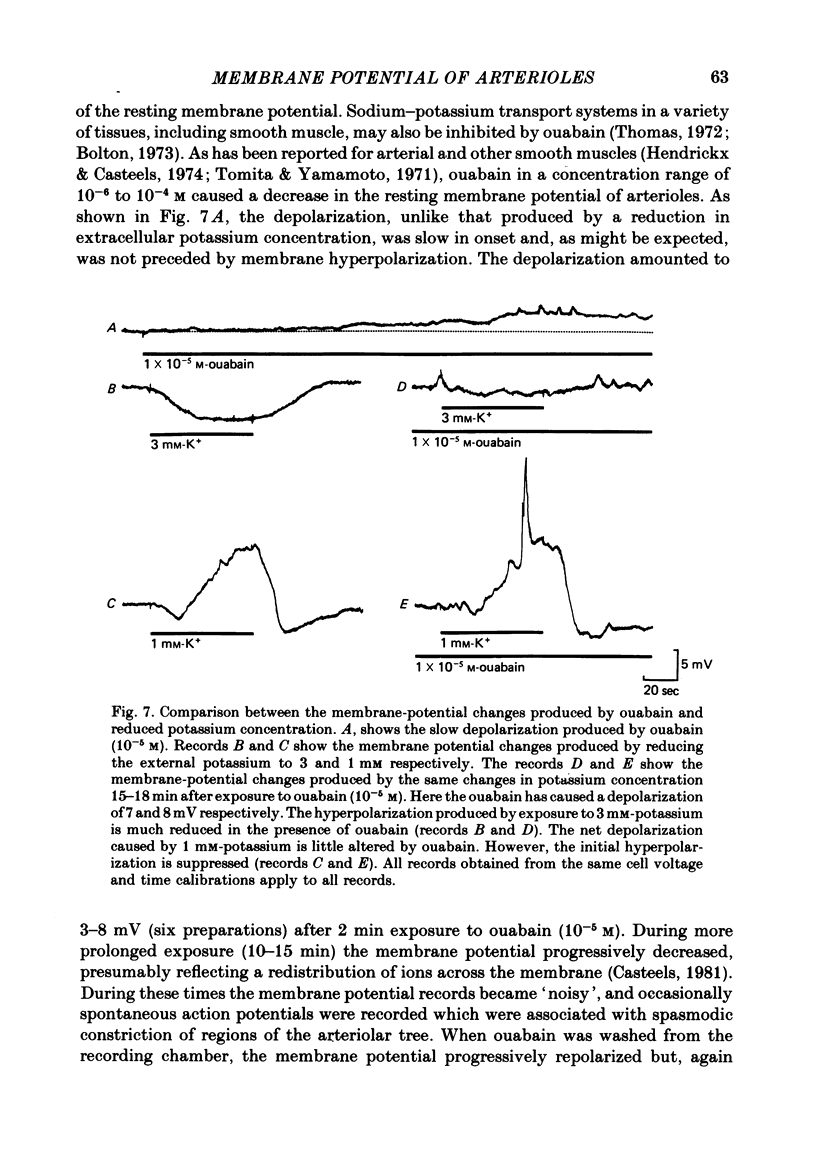
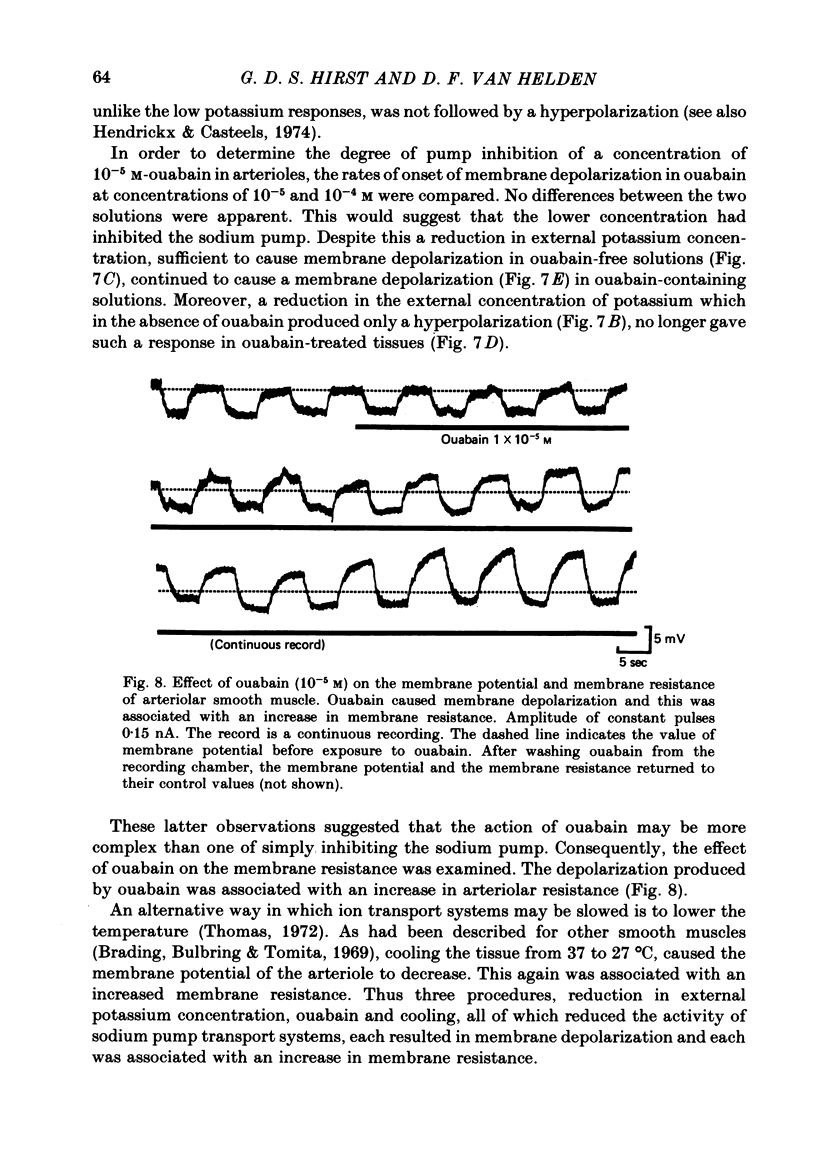
1. The changes in the resting membrane potential of arterioles produced by rapid and brief changes in external ionic concentrations were measured. 2. The resting membrane potential was insensitive to changes in the external concentrations of both sodium and chloride ions but sensitive to changes in the external concentration of potassium ions. 3. Increasing the external concentrations of potassium ions produced depolarizations that were well described by the Nernst equation. 4. Decreased external concentrations of potassium ions produced membrane depolarizations which appeared to result not from inhibition of an electrogenic sodium pump but rather from a change in the resting conductance of the arteriolar membrane to potassium ions. 5. Ouabain caused both membrane depolarization and an increase in membrane resistance. 6. It is suggested that at rest, arteriolar smooth muscle is permeant predominantly to potassium ions, with only small contributions from chloride and sodium ions. No evidence was obtained which would support the idea that an appreciable proportion of the resting membrane potential depended upon current flow from an electrogenic sodium pump.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett M. R. Model of the membrane of smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig taenia coli muscle during transmission from inhibitory and excitatory nerves. Nature. 1966 Sep 10;211(5054):1149–1152. doi: 10.1038/2111149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. Effects of electrogenic sodium pumping on the membrane potential of longitudinal smooth muscle from terminal ileum of guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1973 Feb;228(3):693–712. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brading A. F. Analysis of the effluxes of sodium, potassium and chloride ions from smooth muscle in normal and hypertonic solutions. J Physiol. 1971 May;214(3):393–416. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brading A. F. Maintenance of ionic composition. Br Med Bull. 1979 Sep;35(3):227–234. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brading A., Bülbring E., Tomita T. The effect of temperature on the membrane conductance of the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(3):621–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R., Droogmans G., Hendrickx H. Electrogenic sodium pump in smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig's taenia coli. J Physiol. 1971 Sep;217(2):297–313. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R., Droogmans G., Hendrickx H. Membrane potential of smooth muscle cells in K-free solution. J Physiol. 1971 Sep;217(2):281–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. Excitation-contraction coupling in the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit main pulmonary artery. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):63–79. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. The membrane properties of the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit main pulmonary artery. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):41–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMAN M. E. Membrane potentials recorded with high-resistance micro-electrodes; and the effects of changes in ionic environment on the electrical and mechanical activity of the smooth muscle of the taenia coli of the guineapig. J Physiol. 1958 May 28;141(3):464–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder D. R., Sperelakis N. Membrane electrical properties of vascular smooth muscle from the guinea pig superior mesenteric artery. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Dec 28;378(2):111–119. doi: 10.1007/BF00584443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickx H., Casteels R. Electrogenic sodium pump in arterial smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1974;346(4):299–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00596185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermsmeyer K. Electrogenesis of increased norepinephrine sensitivity of arterial vascular muscle in hypertension. Circ Res. 1976 May;38(5):362–367. doi: 10.1161/01.res.38.5.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. An analysis of excitatory junctional potentials recorded from arterioles. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:87–104. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. Some properties of spontaneous excitatory junction potentials recorded from arterioles of guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:43–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D. Neuromuscular transmission in arterioles of guinea-pig submucosa. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):263–275. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., LEWIS P. R. The resting exchange of radioactive potassium in crab nerve. J Physiol. 1951 Mar;113(1):73–98. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURIYAMA H. The influence of potassium, sodium and chloride on the membrane potential of the smooth muscle of taenia coli. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:15–28. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajiwara M., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Neuromuscular transmission and smooth muscle membrane properties in the guinea-pig ear artery. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:283–302. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. Adrenergic transmissions in the guinea-pig mesenteric artery and their cholinergic modulations. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:383–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R., PILAR G. DUAL MODE OF SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION IN THE AVIAN CILIARY GANGLION. J Physiol. 1963 Sep;168:443–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oashi H. An estimate of the proportion of the resting membrane conductance of the smooth muscle of guinea-pog taenia coli attributable to chloride. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):405–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Electrogenic sodium pump in nerve and muscle cells. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jul;52(3):563–594. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.3.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T., Yamamoto T. Effects of removing the external potassium on the smooth muscle of guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;212(3):851–868. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



