Abstract
1. Catecholamine synthesis in rabbit carotid body was studied in vitro using [3H]DOPA and [3H]tyrosine as precursors. The effects of sympathectomy and transection of the carotid sinus nerve on [3H]dopamine ([3H]DA) and [3H]noradrenaline ([3H]NA) synthesis were investigated in chronically denervated carotid bodies.
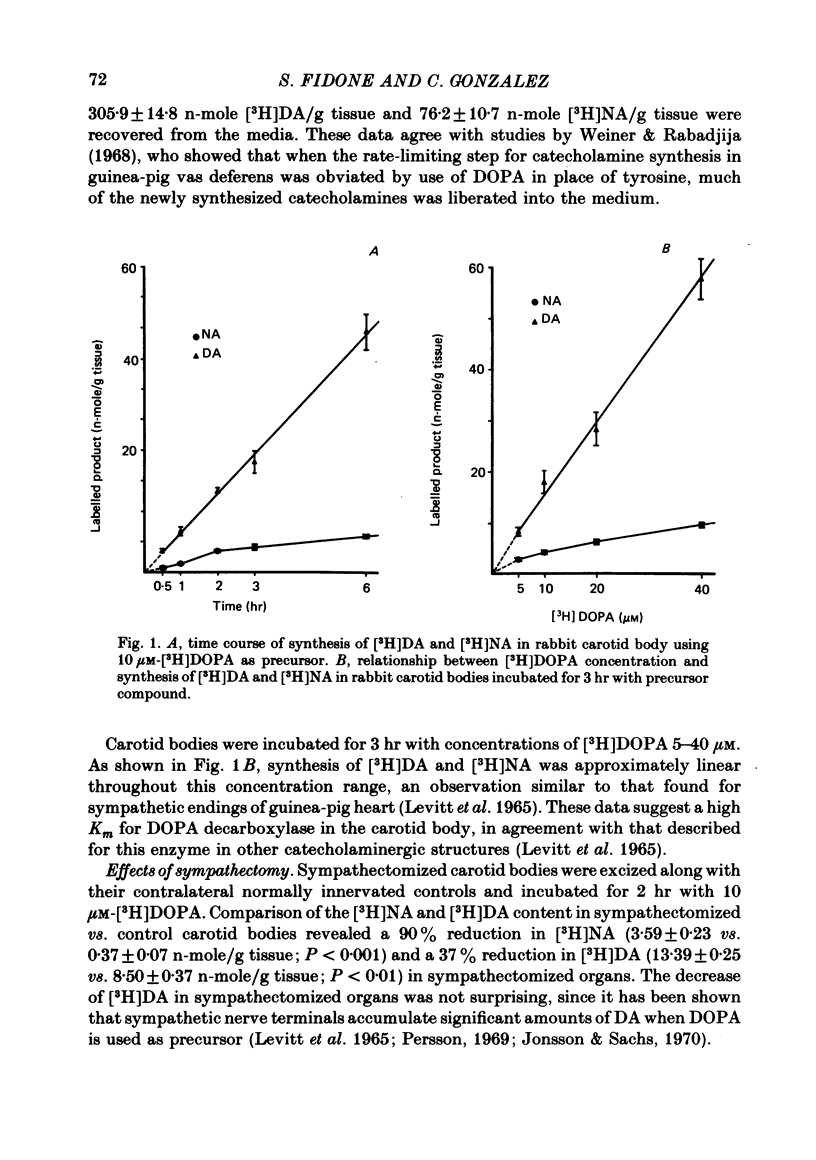
2. When [3H]DOPA was used as precursor, the synthesis of [3H]DA was linear for more than 6 hr. The carotid body synthesized larger amounts of [3H]catecholamines than when [3H]tyrosine was used as precursor, but most of this excess was liberated into the incubation media. Using 10 μM-[3H]DOPA as precursor, the synthesis rates were 6·76 and 1·51 n-mole/g per hr for [3H]DA and [3H]NA, respectively; with 40 μM-[3H]DOPA, these values increased to 19·22 and 3·23 n-mole/g per hr, respectively.
3. The relationship between [3H]DOPA concentration and [3H]DA synthesis was linear throughout the range 5-40 μM-[3H]DOPA.
4. Sympathectomy reduced the synthesis of [3H]NA by 90% and [3H]DA by 37% when [3H]DOPA was used as precursor.
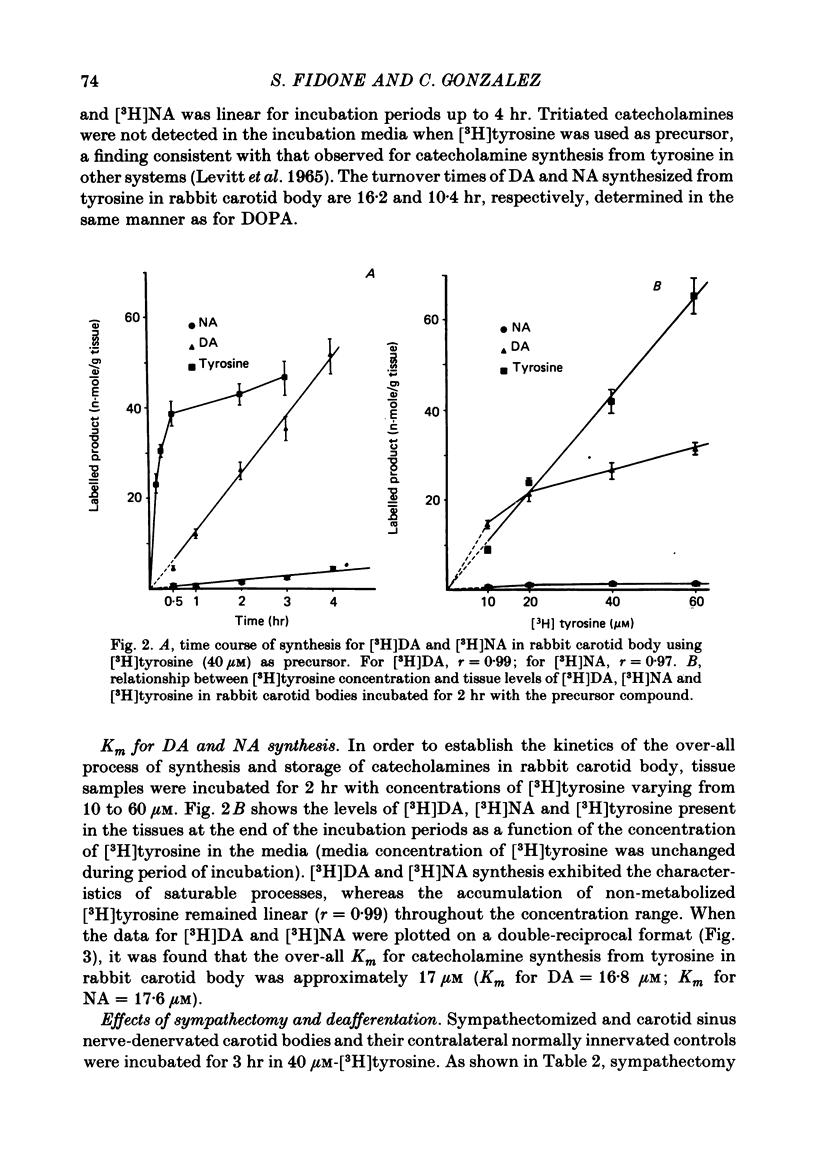
5. When [3H]tyrosine (40 μM) was used as precursor, synthesis of [3H]catecholamines was linear for at least 4 hr, with rates of 12·10 and 0·85 n-mole/g per hr for [3H]DA and [3H]NA, respectively.
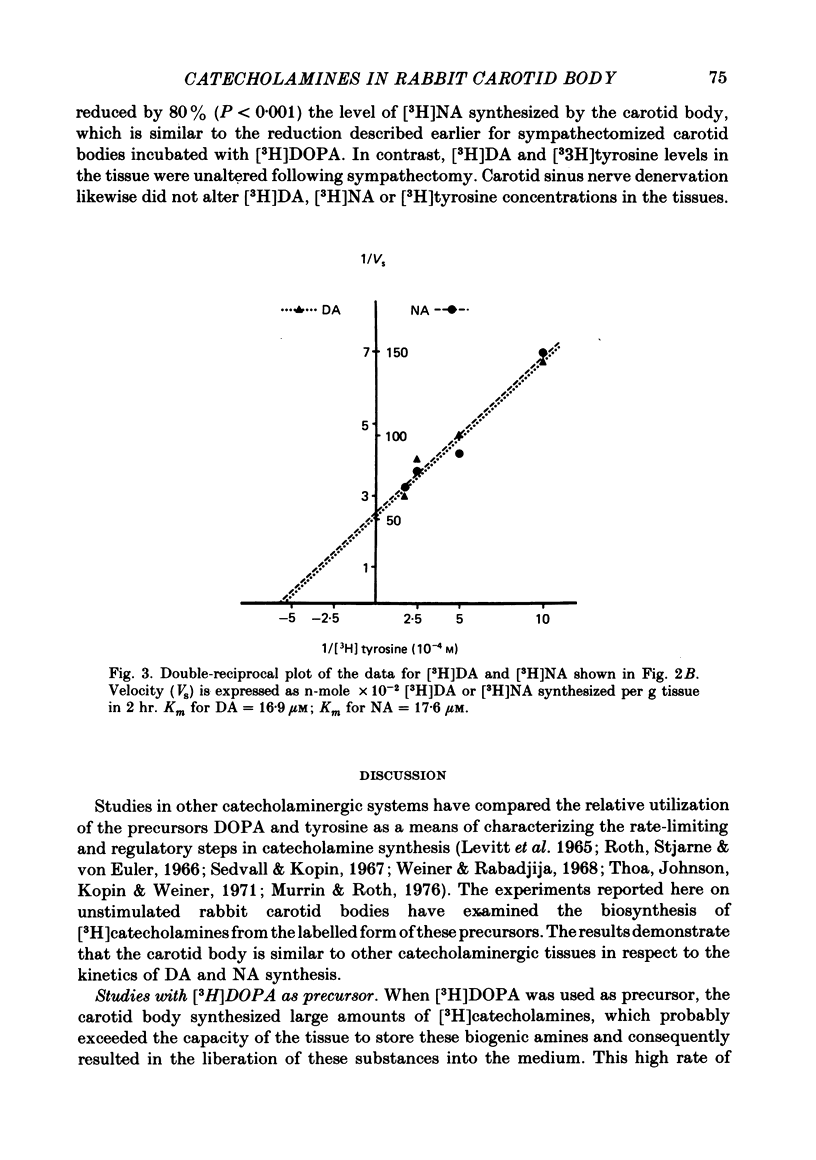
6. [3H]DA and [3H]NA synthesis from [3H]tyrosine exhibited the characteristics of saturable processes, with Km values of 16·8 and 17·6 μM, respectively.
7. 6-methyltetrahydropterine (6-MPH4, 100 μM), a synthetic analogue of the natural co-factor for tyrosine hydroxylase, increased [3H]DA and [3H]NA synthesis from [3 H]tyrosine in both the carotid body and superior cervical ganglion, with the greatest effect seen in the carotid body.
8. When [3H]tyrosine was used as precursor, sympathectomy of the carotid body reduced [3H]NA synthesis by 80%, but did not alter [3H]DA or [3H]tyrosine levels in the tissue. Transection of the carotid sinus nerve had no effect on [3H]catecholamine synthesis in the carotid body.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacopoulos N. G., Bhatnagar R. K. Correlation between tyrosine hydroxylase activity and catecholamine concentration or turnover in brain regions. J Neurochem. 1977 Oct;29(4):639–643. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb07780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besson M. J., Cheramy A., Feltz P., Glowinski J. Release of newly synthesized dopamine from dopamine-containing terminals in the striatum of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):741–748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black A. M., Comroe J. H., Jr, Jacobs L. Species difference in carotid body response of cat and dog to dopamine and serotonin. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1097–1102. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiocchio S. R., Biscardi A. M., Tramezzani J. H. Catecholamines in the carotid body of the cat. Nature. 1966 Nov 19;212(5064):834–835. doi: 10.1038/212834a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiocchio S. R., King M. P., Angelakos E. T. Carotid body catecholamines. Histochemical studies on the effects of drug treatments. Histochemie. 1971;25(1):52–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00303945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dearnaley D. P., Fillenz M., Woods R. I. The identification of dopamine in the rabbit's carotid body. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Jun 11;170(1019):195–203. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C., Kwok Y., Gibb J., Fidone S. Effects of hypoxia on tyrosine hydroxylase activity in rat carotid body. J Neurochem. 1979 Sep;33(3):713–719. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C., Kwok Y., Gibb J., Fidone S. Physiological and pharmacologic effects on TH activity in rabbit and cat carotid body. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jan;240(1):R38–R43. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1981.240.1.R38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C., Obeso A., Fidone S. Tris buffer: effects on catecholamine synthesis. J Neurochem. 1979 Mar;32(3):1143–1145. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanbauer I., Hellstrom S. The regulation of dopamine and noradrenaline in the rat carotid body and its modification by denervation and by hypoxia. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:21–34. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanbauer I., Lovenberg W., Costa E. Induction of tyrosine 3-monooxygenase in carotid body of rats exposed to hypoxic conditions. Neuropharmacology. 1977 Apr;16(4):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(77)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström S., Hanbauer I., Costa E. Selective decrease of dopamine content in rat carotid body during exposure to hypoxic conditions. Brain Res. 1976 Dec 17;118(2):352–355. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90725-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström S., Koslow S. H. Biogenic amines in carotid body of adult and infant rats--a gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric assay. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Apr;93(4):540–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb05846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helpap B., Hempel K. Autoradiographische Untersuchungen mit 3H-DOPA zum Catecholamin-Stoffwechsel des Karotiskörperchens. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 1968;52:464–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand J. G., Barker D. L., Herbert E., Kravitz E. A. Screening for neurotransmitters: a rapid radiochemical procedure. J Neurobiol. 1971;2(3):231–246. doi: 10.1002/neu.480020305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson G., Sachs C. Synthesis of noradrenaline from 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) and dopamine in adrenergic nerves of mouse atrium--effect of reserpine, monoamine oxidase and tyrosine hydroxylase inhibition. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Nov;80(3):307–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04795.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettler R., Bartholini G., Pletscher A. In vivo enhancement of tyrosine hydroxylation in rat striatum by tetrahydrobiopterin. Nature. 1974 May 31;249(456):476–478. doi: 10.1038/249476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVER J. D., BOYD J. D. Osmiophile granules in the glomus cells of the rabbit carotid body. Nature. 1957 May 25;179(4569):1082–1083. doi: 10.1038/1791082b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVITT M., SPECTOR S., SJOERDSMA A., UDENFRIEND S. ELUCIDATION OF THE RATE-LIMITING STEP IN NOREPINEPHRINE BIOSYNTHESIS IN THE PERFUSED GUINEA-PIG HEART. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Apr;148:1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVENBERG W., WEISSBACH H., UDENFRIEND S. Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:89–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llados F., Zapata P. Effects of adrenoceptor stimulating and blocking agents on carotid body chemosensory inhibition. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:501–509. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llados F., Zapata P. Effects of dopamine analogues and antagonists on carotid body chemosensors in situ. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:487–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinoff P. B., Axelrod J. Biochemistry of catecholamines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:465–500. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murrin L. C., Roth R. H. Dopaminergic neurons: effects of electrical stimulation on dopamine biosynthesis. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 May;12(3):463–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGATSU T., LEVITT M., UDENFRIEND S. TYROSINE HYDROXYLASE. THE INITIAL STEP IN NOREPINEPHRINE BIOSYNTHESIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2910–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick R. L., Barchas J. D. Dopamine synthesis in rat brain striatal synaptosomes. II. Dibutyryl cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphoric acid and 6-methyltetrahydropterine-induced synthesis increases without an increase in endogenous dopamine release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Apr;197(1):97–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson T. Central and peripheral catecholamine turnover studied by means of 3H-DOPA and 3H-tyrosine. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1969;27(6):397–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1969.tb00486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. H., Stjärne L., von Euler U. S. Acceleration of noradrenaline biosynthesis by nerve stimulation. Life Sci. 1966 Jun;5(12):1071–1075. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(66)90089-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson S. R., Aminoff M. J., Jaffe R. A., Vidruk E. H. Analysis of inhibitory effect of dopamine on carotid body chemoreceptors in cats. Am J Physiol. 1976 Jun;230(6):1494–1498. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.6.1494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedvall G. C., Kopin I. J. Acceleration of norepinephrine synthesis in the rat submaxillary gland in vivo during sympathetic nerve stimulation. Life Sci. 1967 Jan 1;6(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90360-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiman R., Akino M., Kaufman S. Solubilization and partial purification of tyrosine hydroxylase from bovine adrenal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1330–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoa N. B., Johnson D. G., Kopin I. J., Weiner N. Acceleration of catecholamine formation in the guinea-pig vas deferens after hypogastric nerve stimulation: roles of tyrosine hydroxylase and new protein synthesis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Sep;178(3):442–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Zaltzman-Nirenberg P., Gordon R., Spector S. Evaluation of the biochemical effects produced in vivo by inhibitors of the three enzymes involved in norepinephrine biosynthesis. Mol Pharmacol. 1966 Mar;2(2):95–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Zaltzman-Nirenberg P., Nagatsu T. Inhibitors of purified beef adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1965 May;14(5):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(65)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner N., Rabadjija M. The effect of nerve stimulation on the synthesis and metabolism of norepinephrine in the isolated guinea-pig hypogastric nerve-vas deferens preparation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Mar;160(1):61–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapata P. Effects of dopamine on carotid chemo- and baroreceptors in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(1):235–251. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapata P., Hess A., Bliss E. L., Eyzaguirre C. Chemical, electron microscopic and physiological observations on the role of catecholamines in the carotid body. Brain Res. 1969 Jul;14(2):473–496. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


