Abstract
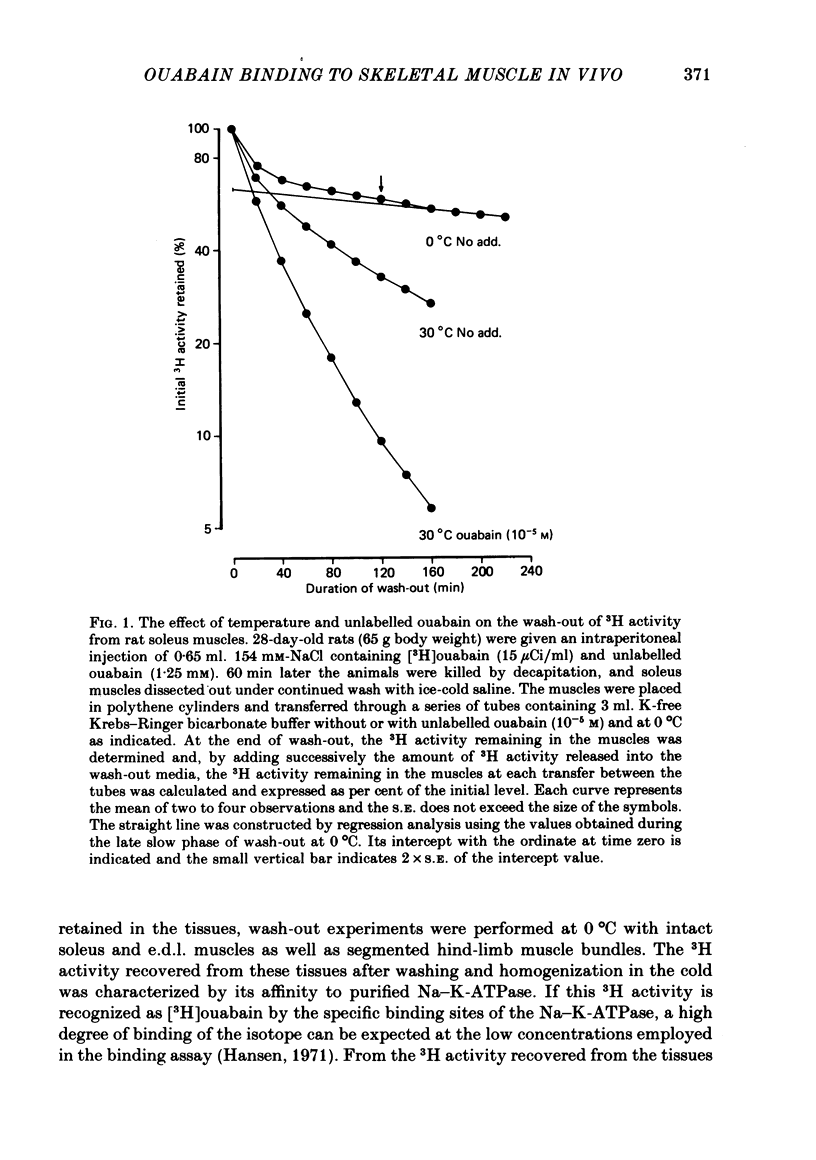
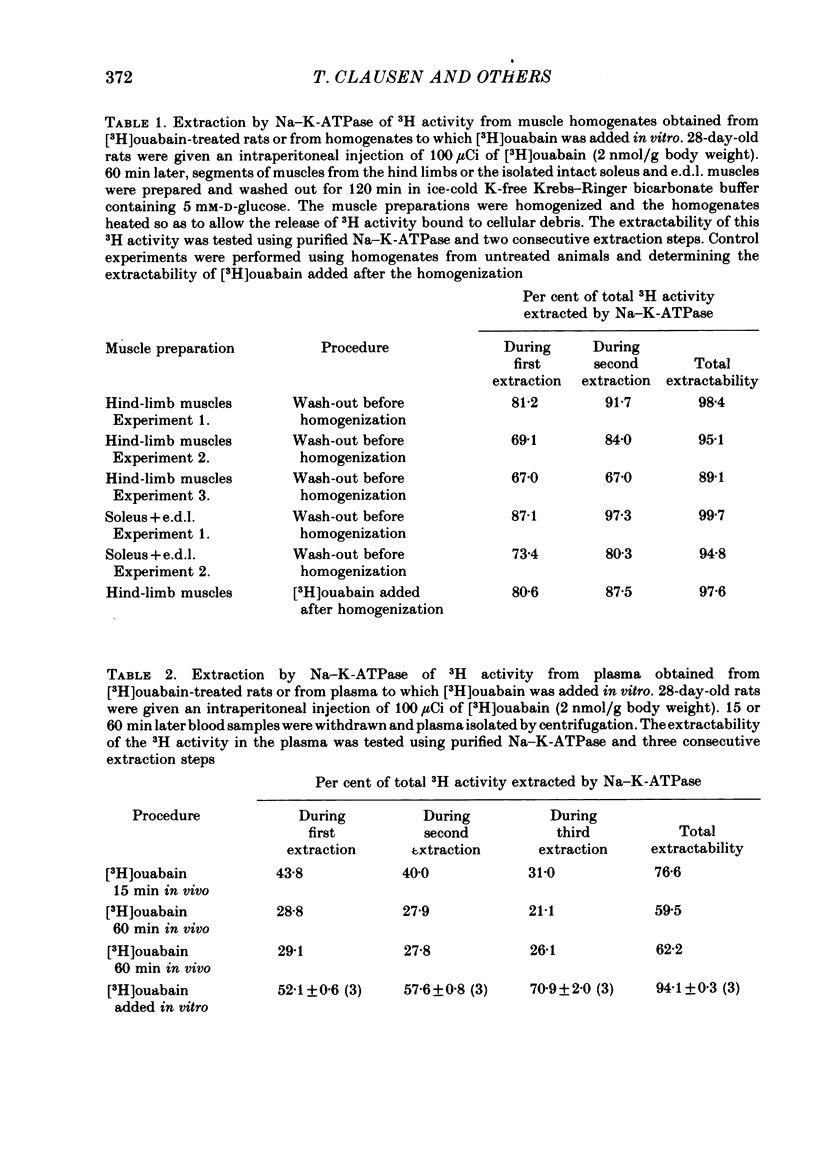
1. Following intraperitoneal injection of [3H]ouabain in rats, the isotope is rapidly distributed in blood plasma available for binding to the Na-K-ATPase in the plasma membranes of most tissues. In skeletal muscle tissue excised and washed 4 × 30 min in ice-cold buffer, 95% of the 3H activity retained was shown to be [3H]ouabain using a specific binding assay.
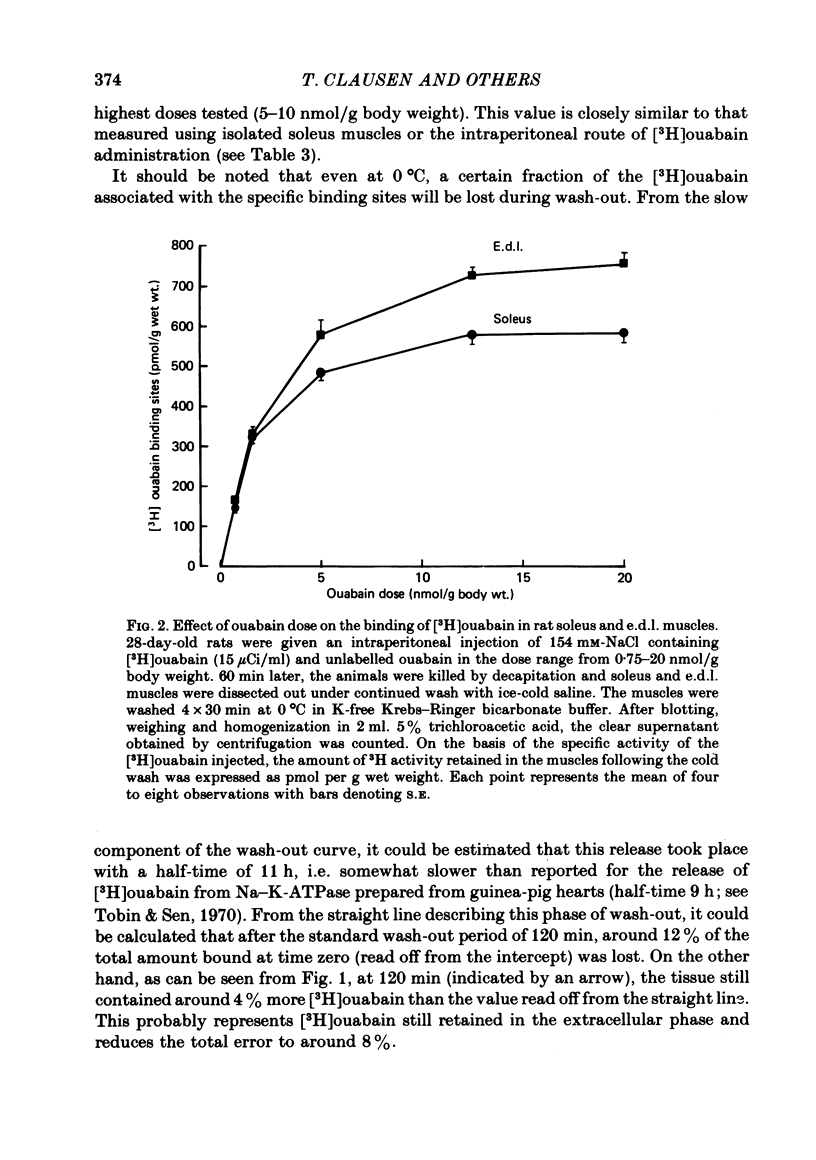
2. The [3H]ouabain bound to soleus and extensor digitorum longus (e.d.l.) muscles in vivo and retained following wash-out in the cold showed the same saturation characteristics as those determined when binding took place in vitro.
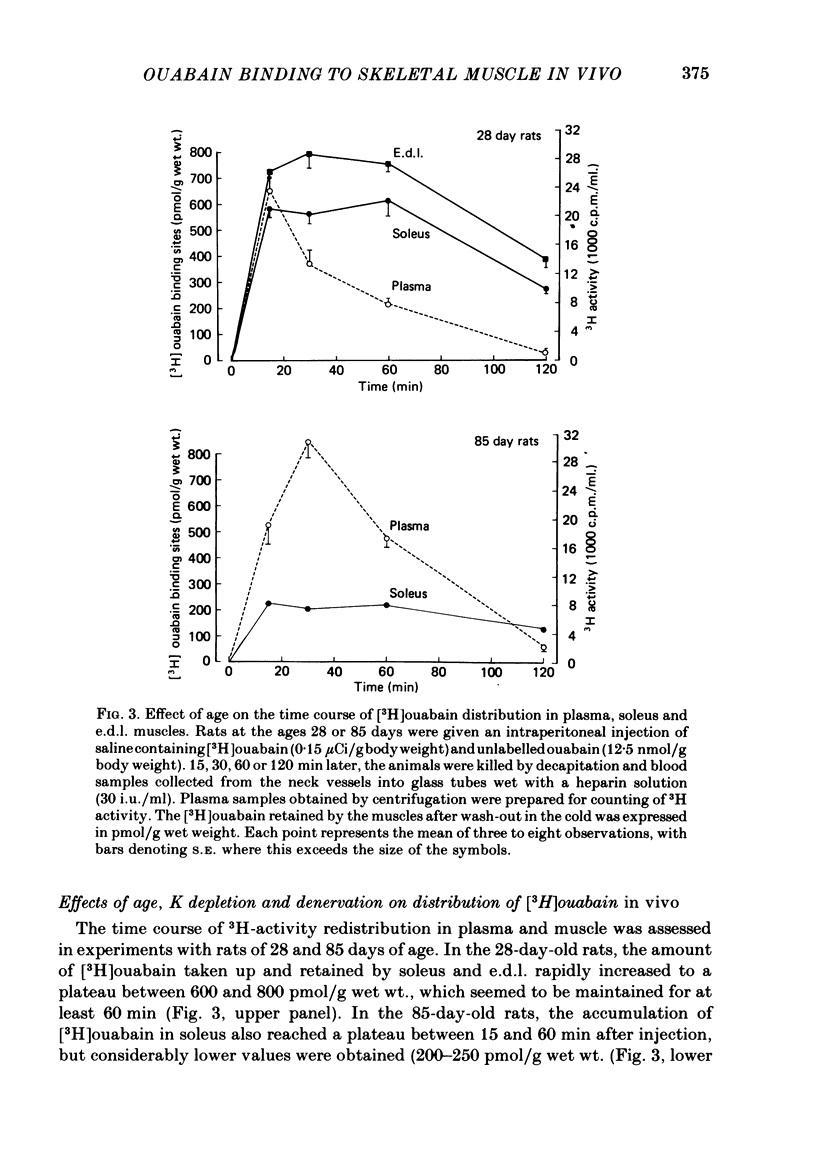
3. In soleus and e.d.l. muscles obtained from 28-day-old rats, the number of [3H]ouabain binding sites measured in vivo was 583±19 and 720±22 pmol/g wet wt., respectively, i.e. in good agreement with previous and present results obtained in vitro.
4. In vivo measurements showed that 7 days after denervation, the number of [3H]ouabain binding sites in soleus and e.d.l. muscles was reduced by 22 and 13%, respectively.
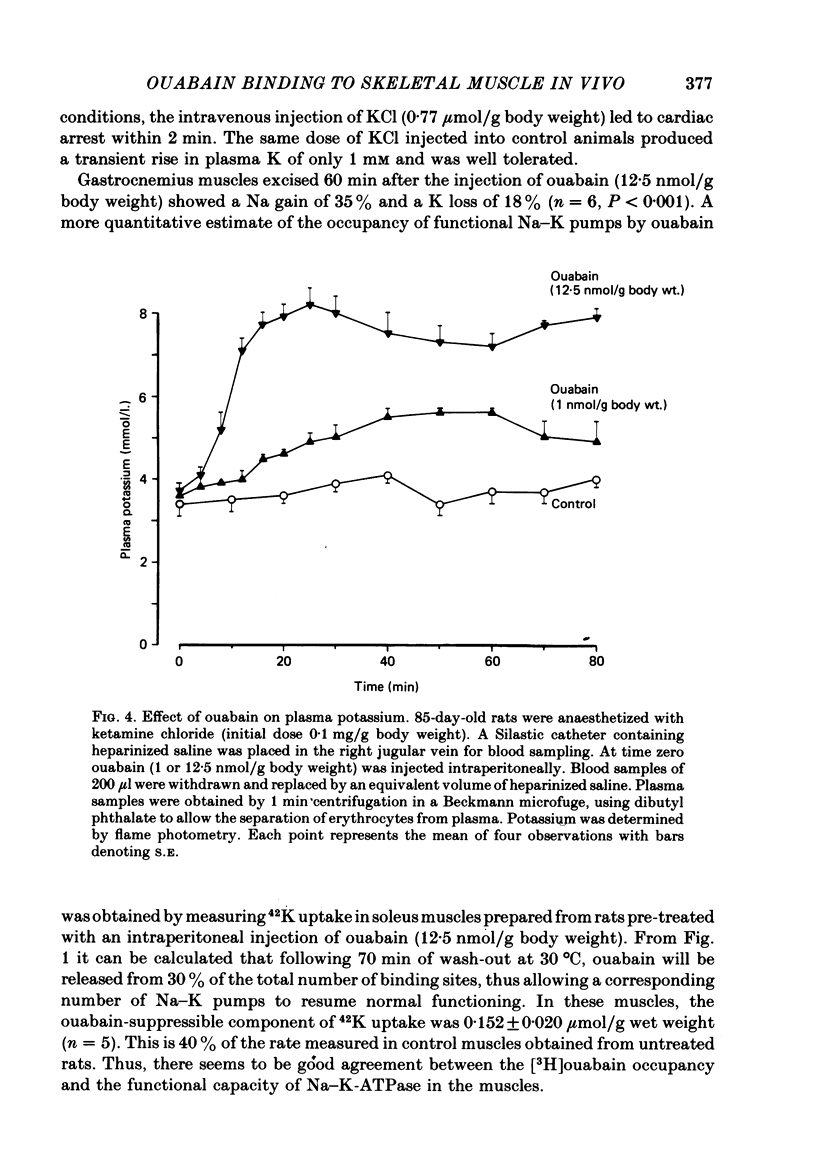
5. In the age interval from 28 to 85 days, the number of [3H]ouabain binding sites in soleus was found to decrease by 58%. Following I.P. injection of [3H]ouabain, the 85-day-old rats showed a more pronounced and sustained rise in plasma 3H activity, which in part can be due to the reduced capacity for [3H]ouabain binding in skeletal muscle.
6. K depletion induced by the administration of K-deficient diet for 3 weeks reduced [3H]ouabain binding by 63% in soleus muscles. In the K-depleted animals, the plasma 3H activity measured 15 min after I.P. injection of [3H]ouabain was 77% higher than in controls receiving the same dose per kg body weight.
7. The present in vivo results provide further support for the idea that increased digitalis toxicity due to increasing age or K depletion is related to reduced binding capacity for digitalis glycosides in skeletal muscle.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Willis J. S. Binding of the cardiac glycoside ouabain to intact cells. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):441–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX E., ROXBURGH G., WRIGHT S. E. The metabolism of ouabain in the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1959 Sep;11:535–539. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1959.tb12592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinet A., Clausen T., Girardier L. Microcalorimetric determination of energy expenditure due to active sodium-potassium transport in the soleus muscle and brown adipose tissue of the rat. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(1):43–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Hansen O. Active Na-K transport and the rate of ouabain binding. The effect of insulin and other stimuli on skeletal muscle and adipocytes. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(2):415–430. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Hansen O., Larsson L. I. Sympathetic nerve terminal destruction has no effect on specific [3H]ouabain binding to intact mouse and rat skeletal muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 10;72(4):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90571-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Hansen O. The Na+-K+-pump, energy metabolism, and obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 29;104(2):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90644-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Kohn P. G. The effect of insulin on the transport of sodium and potassium in rat soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(1):19–42. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Sellin L. C., Thesleff S. Quantitative changes in ouabain binding after denervation and during reinnervation of mouse skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Mar;111(3):373–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Wang P., Orskov H., Kristensen O. Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Relationships between changes in plasma water, electrolytes, insulin and catecholamines during attacks. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1980 May;40(3):211–220. doi: 10.3109/00365518009095569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crettaz M., Prentki M., Zaninetti D., Jeanrenaud B. Insulin resistance in soleus muscle from obese Zucker rats. Involvement of several defective sites. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):525–534. doi: 10.1042/bj1860525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desnuelle C., Lombet A., Serratrice G., Lazdunski M. Sodium channel and sodium pump in normal and pathological muscles from patients with myotonic muscular dystrophy and lower motor neuron impairment. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):358–367. doi: 10.1172/JCI110459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann E., Philipp G., Tanner Ouabain-receptor interactions in (Na+ + K+)-ATPase preparations. A contribution to the problem of nonlinear Scatchard plots. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 2;455(2):287–296. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90305-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen O., Jensen J., Nøorby J. G., Ottolenghi P. A new proposal regarding the subunit composition of (Na+ + K+)ATPase. Nature. 1979 Aug 2;280(5721):410–412. doi: 10.1038/280410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen O., Skou J. C. A study on the influence of the concentration of Mg 2+ , P i , K + , Na + , and Tris on (Mg 2+ + P i )-supported g-strophanthin binding to (Na + = K + )activated ATPase from ox brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 7;311(1):51–66. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen O. The relationship between G-strophanthin-binding capacity and ATPase activity in plasma-membrane fragments from ox brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):122–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90364-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+ plus K+ )-ATPase. 3. Purification from the outer medulla of mammalian kidney after selective removal of membrane components by sodium dodecylsulphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):36–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L., Skou J. C. Purification and characterization of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. I. The influence of detergents on the activity of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in preparations from the outer medulla of rabbit kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):366–380. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen K., Nørgaard A., Clausen T. Age-dependent changes in the number of [3H]ouabain-binding sites in rat soleus muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 7;686(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiger R. E., Seta K., Vitale J. J., Lown B. Effects of chronic depletion of potassium and magnesium upon the action of acetylstrophanthidin on the heart. Am J Cardiol. 1966 Apr;17(4):520–527. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(66)90243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn P. G., Clausen T. The relationship between the transport of glucose and cations across cell membranes in isolated tissues. VI. The effect of insulin, ouabain, and metabolic inhibitors on the transport of 3-O-methylglucose and glucose in rat soleus muscles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 2;225(2):277–290. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. H., Romsos D. R., Akera T., Leveille G. A. Na+,K+-ATPase enzyme units in skeletal muscle from lean and obese mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jan 30;80(2):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90690-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh A. J., Lloyd B. L., Taylor R. R. Age dependence of myocardial Na+-K+-ATPase activity and digitalis intoxication in the dog and guinea pig. Circ Res. 1981 Mar;48(3):329–333. doi: 10.1161/01.res.48.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nørgaard A., Kjeldsen K., Clausen T. Potassium depletion decreases the number of 3H-ouabain binding sites and the active Na-K transport in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1981 Oct 29;293(5835):739–741. doi: 10.1038/293739a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma V. K., Banerjee S. P. The effect of 6-hydroxydopamine on specific [3H]ouabain binding to some sympathetically innervated organs of the cat. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;13(5):796–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin T., Sen A. K. Stability and ligand sensitivity of (3H)ouabain binding to (Na+ + K+)ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 14;198(1):120–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venosa R. A., Horowicz P. Density and apparent location of the sodium pump in frog sartorius muscle. J Membr Biol. 1981 Apr 30;59(3):225–232. doi: 10.1007/BF01875427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettrell G., Andersson K. E. Clinical pharmacokinetics of digoxin in infants. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1977 Jan-Feb;2(1):17–31. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197702010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZEEMAN S., HIRSCH S., BELLET S. The effect of potassium depletion induced by desoxycorticosterone acetate on the lethal dose of lanatoside C in dogs: relationship of plasma levels, skeletal and cardiac muscle potassium content to the lethal dose. Am J Med Sci. 1954 Jan;227(1):65–73. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195401000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


