Abstract
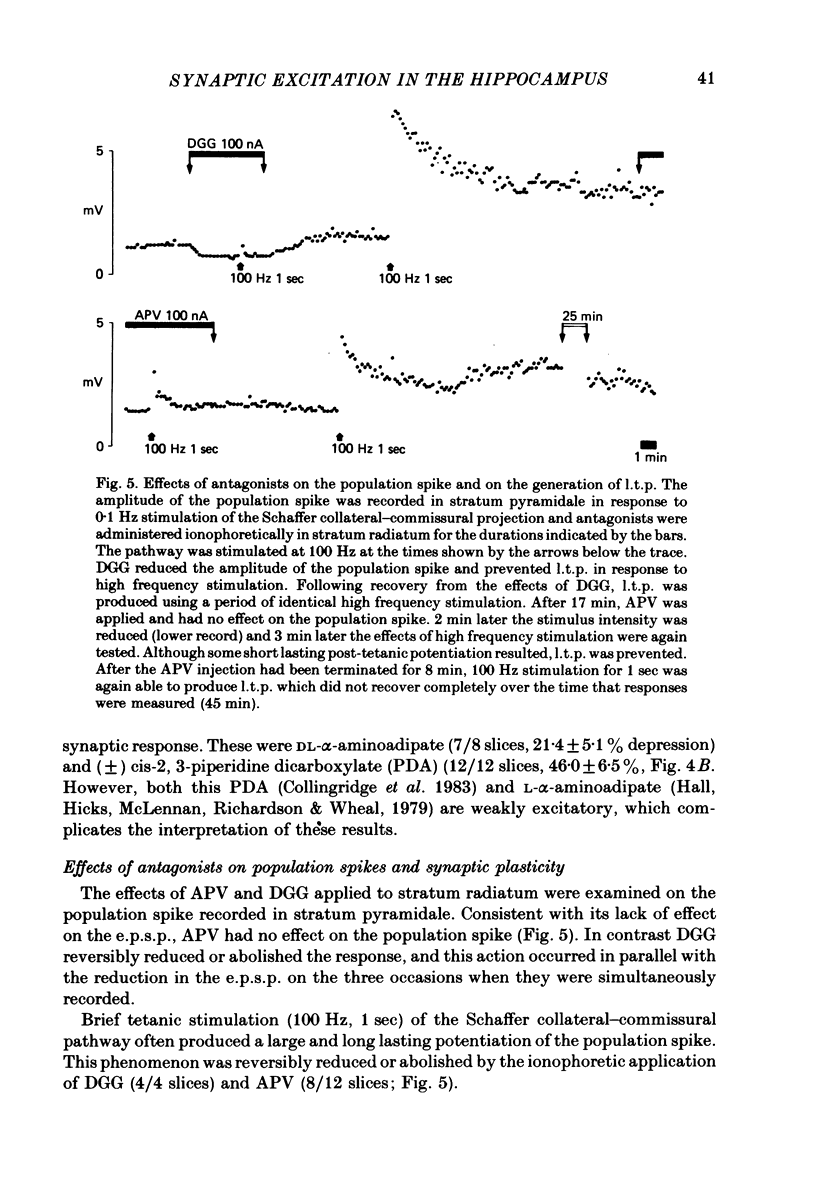
1. The effects of excitatory amino acids and some antagonists applied by ionophoresis to stratum radiatum in the CA1 region of rat hippocampal slices were examined on the locally recorded field e.p.s.p. evoked by stimulation of the Schaffer collateral-commissural projection. 2. L-glutamate, L-aspartate and the more potent and selective excitatory amino acids quisqualate, kainate and N-methyl-DL-aspartate (NMA) depressed the e.p.s.p., presumably through depolarization and/or a change in membrane conductance. 3. The depression induced by kainate considerably outlasted the period of ejection whereas NMA depressions were rapidly reversible and were often followed by a potentiation of the e.p.s.p. In higher doses NMA also depressed the presynaptic fibre volley. The possible involvement of these effects in neurotoxicity and synaptic plasticity is raised. 4. The selective NMA antagonist, DL-2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate (APV) applied in doses which abolished responses to NMA, had no effect on the e.p.s.p. but prevented long term potentiation (l.t.p.) of synaptic transmission evoked by high frequency stimulation of the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway. Other antagonists which had little or no effect on normal synaptic transmission included D-alpha-aminoadipate (DAA), the optical isomers of 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate (APB) and L-glutamate diethylester (GDEE). 5. In contrast, gamma-D-glutamylglycine (DGG), applied in amounts which affected quisqualate and kainate actions as well as those of NMA, was an effective synaptic antagonist whilst having no effect on the presynaptic fibre volley. 6. These results indicate that the synaptic receptor in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway may be of the kainate or quisqualate type. Although NMA receptors do not appear to be involved in normal synaptic transmission in this pathway they may play a role in synaptic plasticity. The interaction of L-glutamate and L-aspartate with these receptors is discussed.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN P. Interhippocampal impulses. II. Apical dendritic activation of CAI neurons. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 Mar 18;48:178–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb01858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alger B. E., Teyler T. J. Long-term and short-term plasticity in the CA1, CA3, and dentate regions of the rat hippocampal slice. Brain Res. 1976 Jul 16;110(3):463–480. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90858-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Bliss T. V., Skrede K. K. Unit analysis of hippocampal polulation spikes. Exp Brain Res. 1971;13(2):208–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00234086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Silfvenius H., Sundberg S. H., Sveen O. A comparison of distal and proximal dendritic synapses on CAi pyramids in guinea-pig hippocampal slices in vitro. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:273–299. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Silfvenius H., Sundberg S. H., Sveen O., Wigström H. Functional characteristics of unmyelinated fibres in the hippocampal cortex. Brain Res. 1978 Apr 7;144(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90431-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Sundberg S. H., Sveen O., Swann J. W., Wigström H. Possible mechanisms for long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in hippocampal slices from guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1980 May;302:463–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry M., Lynch G. Hippocampal glutamate receptors. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Aug 11;38(Spec No)(Pt 1):5–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00235685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzsáki G. Long-term potentiation of the commissural path-CA1 pyramidal cell synapse in the hippocampus of the freely moving rat. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Oct 2;19(3):293–296. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Kehl S. J., McLennan H. The antagonism of amino acid-induced excitations of rat hippocampal CA1 neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:19–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., McLennan H. The effect of kainic acid on excitatory synaptic activity in the rat hippocampal slice preparation. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Nov 18;27(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90201-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotman C. W., Foster A., Lanthorn T. An overview of glutamate as a neurotransmitter. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1981;27:1–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Donnellan J. F., James R. W., Lunt G. G. 2-Amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid as a glutamate antagonist on locust muscle. Nature. 1976 Jul 29;262(5567):408–409. doi: 10.1038/262408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Watkins J. C. Selective antagonism of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation in the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):621–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunwiddie T., Lynch G. Long-term potentiation and depression of synaptic responses in the rat hippocampus: localization and frequency dependency. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:353–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunwiddie T., Madison D., Lynch G. Synaptic transmission is required for initiation of long-term potentiation. Brain Res. 1978 Jul 14;150(2):413–417. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90293-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldowitz D., Scheff S. W., Cotman C. W. The specificity of reactive synaptogenesis: a comparative study in the adult rat hippocampal formation. Brain Res. 1979 Jul 20;170(3):427–441. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90962-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hablitz J. J., Langmoen I. A. Excitation of hippocampal pyramidal cells by glutamate in the guinea-pig and rat. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:317–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Hicks T. P., McLennan H., Richardson T. L., Wheal H. V. The excitation of mammalian central neurones by amino acids. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:29–39. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjorth-Simonsen A. Some intrinsic connections of the hippocampus in the rat: an experimental analysis. J Comp Neurol. 1973 Jan 15;147(2):145–161. doi: 10.1002/cne.901470202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J. D., Flatman J. A., Engberg I. Actions of excitatory amino acids on membrane conductance and potential in motoneurones. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1981;27:205–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J. D., Flatman J. A., Jahnsen H. Extracellular recordings of amino acid induced potential changes in hippocampal slices. J Neurosci Methods. 1981 Feb;3(3):311–315. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(81)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurberg S. Commissural and intrinsic connections of the rat hippocampus. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Apr 15;184(4):685–708. doi: 10.1002/cne.901840405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurberg S., Sørensen K. E. Associational and commissural collaterals of neurons in the hippocampal formation (hilus fasciae dentatae and subfield CA3). Brain Res. 1981 May 18;212(2):287–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90463-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malthe-Sørenssen D., Skrede K. K., Fonnum F. Calcium-dependent release of D-[3H]aspartate evoked by selective electrical stimulation of excitatory afferent fibres to hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. Neuroscience. 1979;4(9):1255–1263. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H., Liu J. The action of six antagonists of the excitatory amino acids on neurones of the rat spinal cord. Exp Brain Res. 1982;45(1-2):151–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00235774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H., Lodge D. The antagonism of amino acid-induced excitation of spinal neurones in the cat. Brain Res. 1979 Jun 15;169(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90375-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler J. V., Vaca K. W., White W. F., Lynch G. S., Cotman C. W. Aspartate and glutamate as possible transmitters of excitatory hippocampal afferents. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):538–540. doi: 10.1038/260538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitsch C. Glutamate as a transmitter of the hippocampal commissural system. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1981;29:97–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padjen A. L., Smith P. A. Possible role of divalent cations in amino acid responses of frog spinal cord. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1981;29:271–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. H., Deadwyler S. A. Kainic acid produces depolarization of CA3 pyramidal cells in the vitro hippocampal slice. Brain Res. 1981 Sep 21;221(1):117–127. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Wester K. Long-lasting facilitation of a synaptic potential following tetanization in the in vitro hippocampal slice. Brain Res. 1975 May 16;89(1):107–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90138-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. Glutamate antagonists in rat hippocampus. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;58(3):341–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07710.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. The actions of glutamic acid on neurons in the rat hippocampal slice. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1981;27:217–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer H. J., Tominez G., Halpern B. Mass spectographic analysis of stimulated release of endogenous amino acids from rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1981 May 11;212(1):194–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Perkins M. N. Quinolinic acid: a potent endogenous excitant at amino acid receptors in CNS. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 10;72(4):411–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm-Mathisen J. Glutamate in hippocampal pathways. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1981;27:43–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Sawchenko P. E., Cowan W. M. Evidence that the commissural, associational and septal projections of the regio inferior of the hippocampus arise from the same neurons. Brain Res. 1980 Sep 15;197(1):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90446-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Wyss J. M., Cowan W. M. An autoradiographic study of the organization of intrahippocampal association pathways in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Oct 15;181(4):681–715. doi: 10.1002/cne.901810402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucek S. The synthesis of acetylcholine in skeletal muscles of the rat. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:53–69. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voneida T. J., Vardaris R. M., Fish S. E., Reiheld C. T. The origin of the hippocampal commissure in the rat. Anat Rec. 1981 Sep;201(1):91–103. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092010112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White W. F., Nadler J. V., Cotman C. W. The effect of acidic amino acid antagonists on synaptic transmission in the hippocampal formation in vitro. Brain Res. 1979 Mar 23;164:177–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieraszko A., Lynch G. Stimulation-dependent release of possible transmitter substances from hippocampal slices studied with localized perfusion. Brain Res. 1979 Jan 12;160(2):372–376. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90435-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieraszko A. Stimulation-dependent uptake of glutamic acid by hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1981 Feb 23;207(1):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90695-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


