Abstract
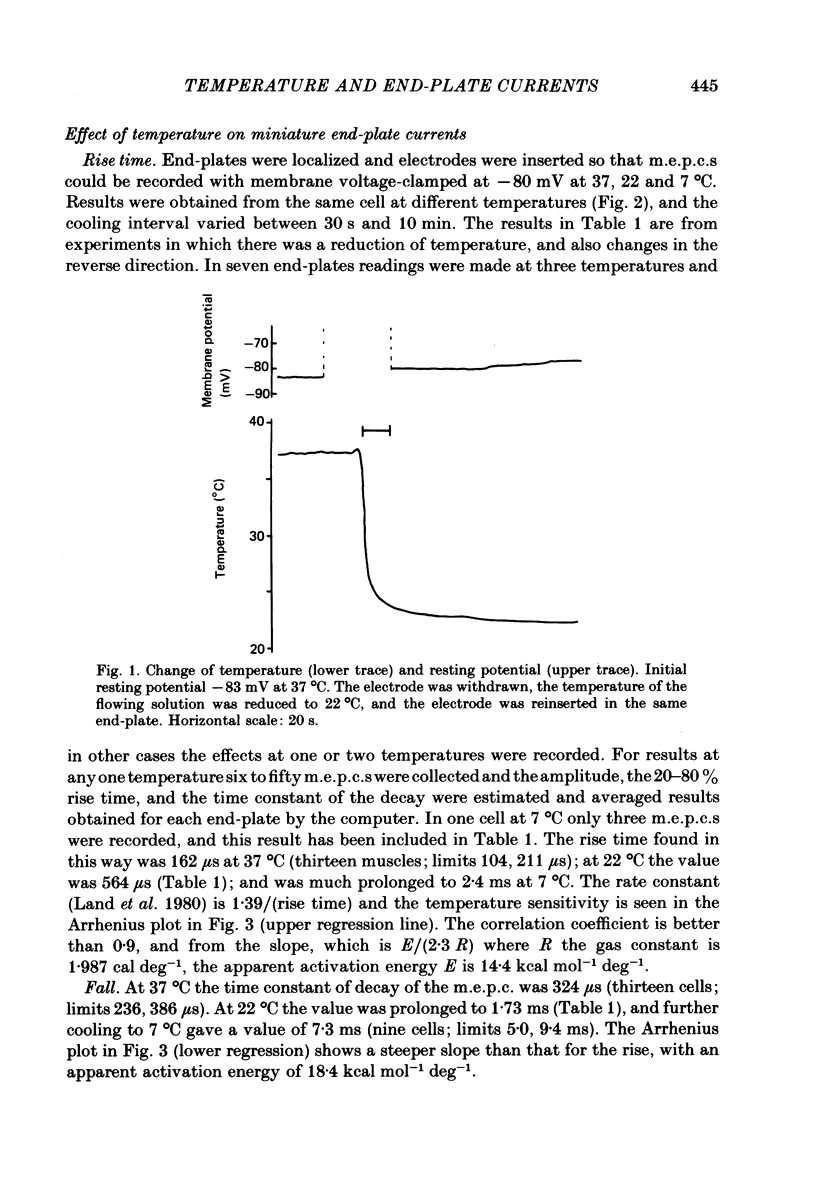
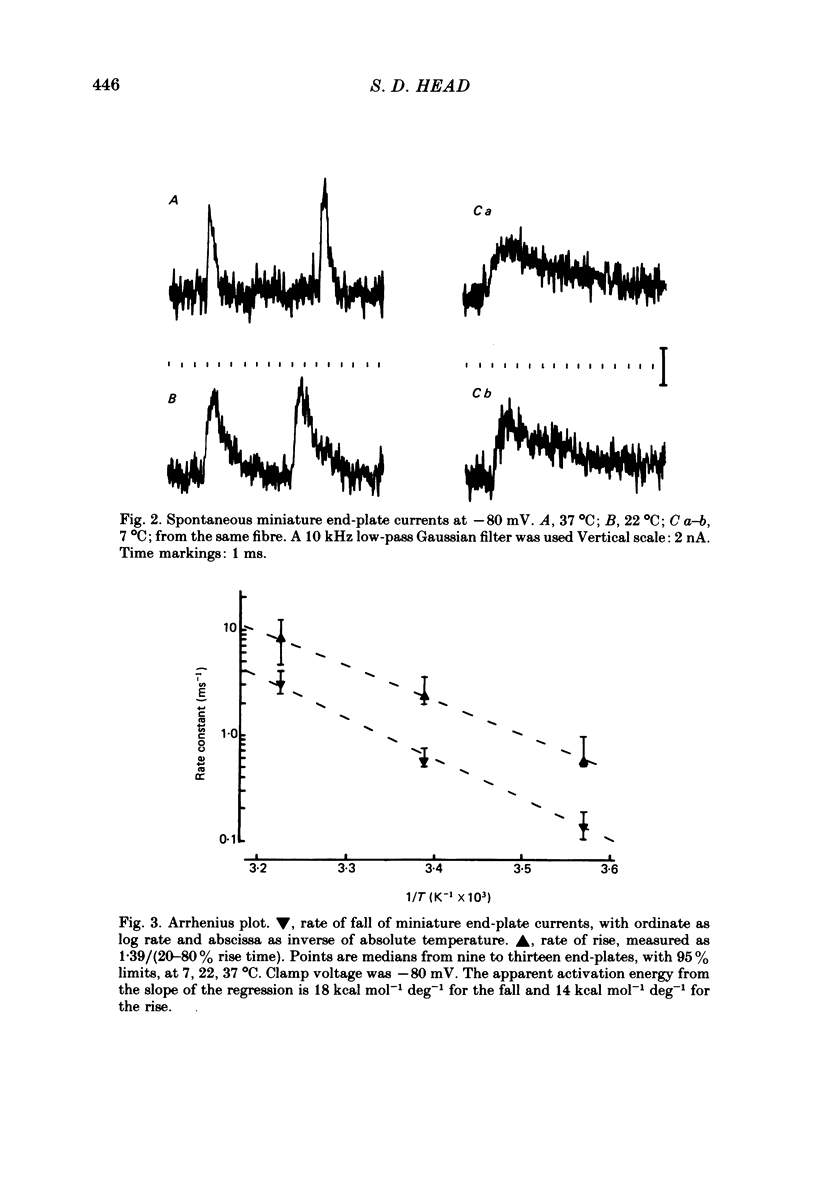
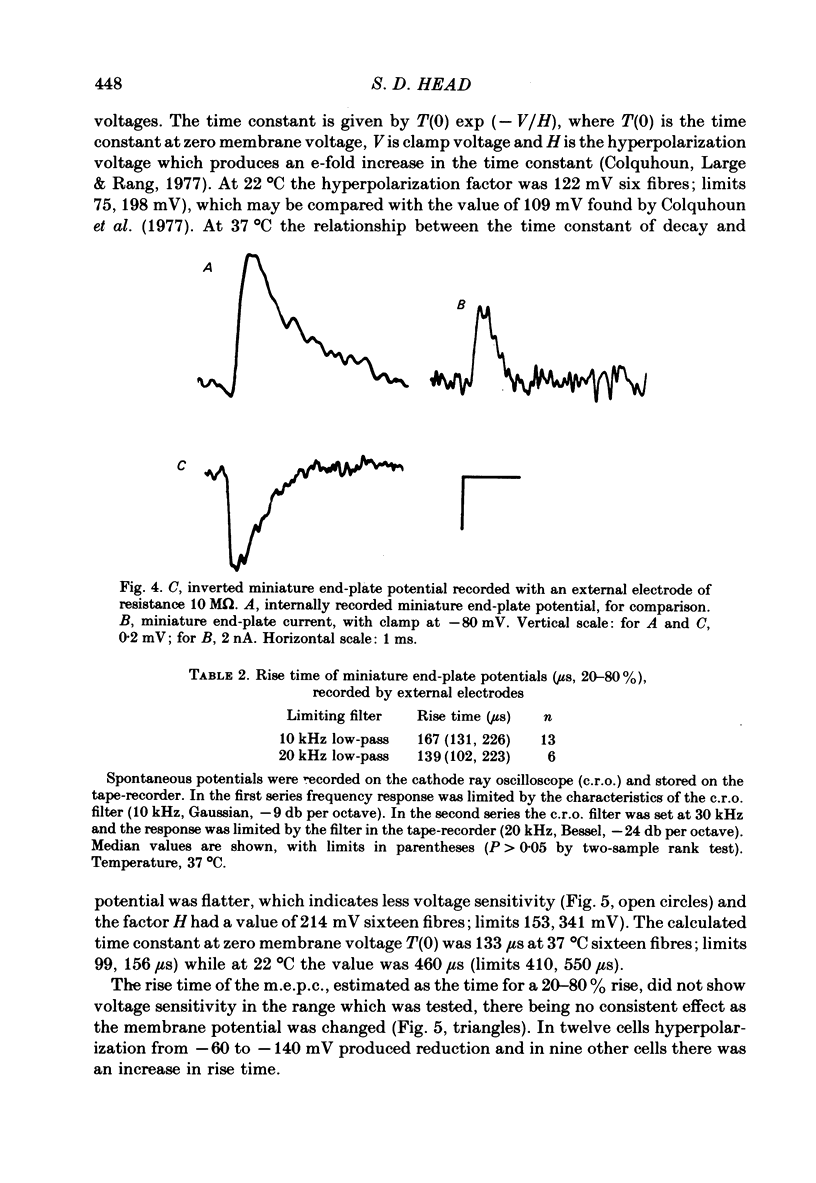
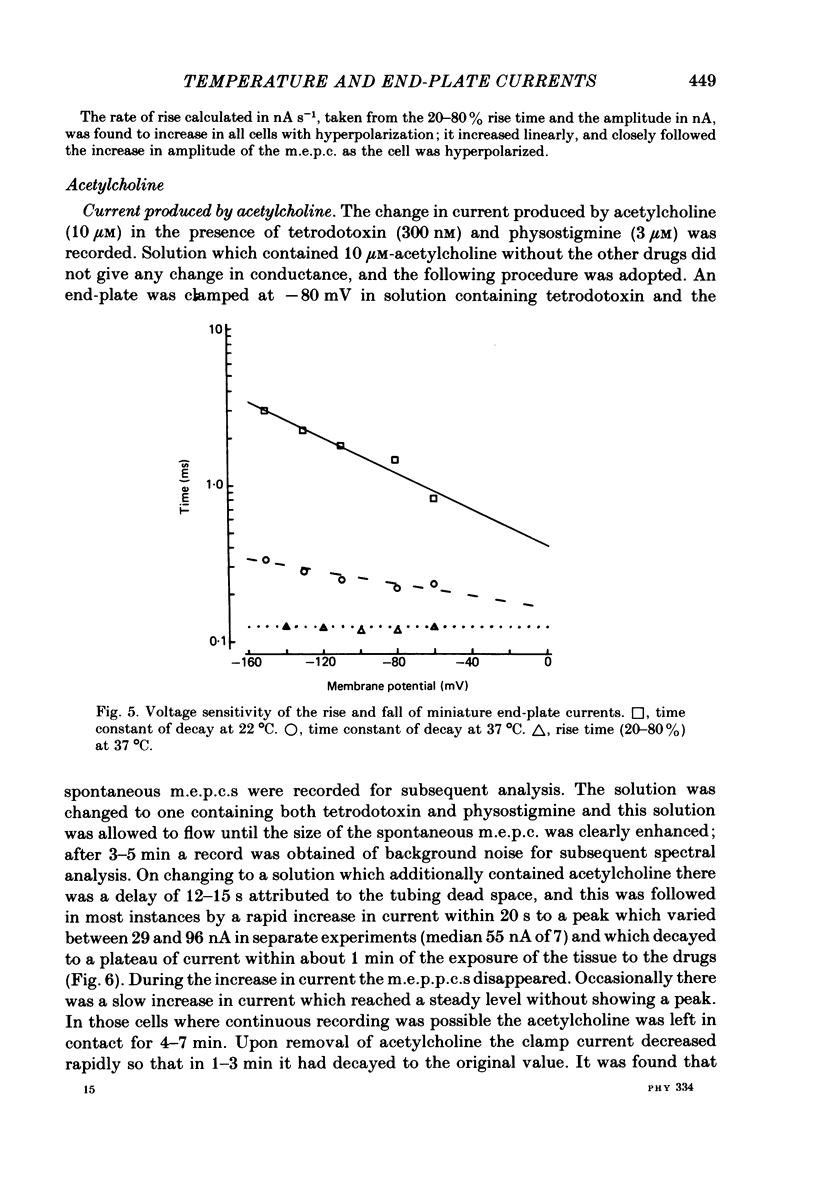
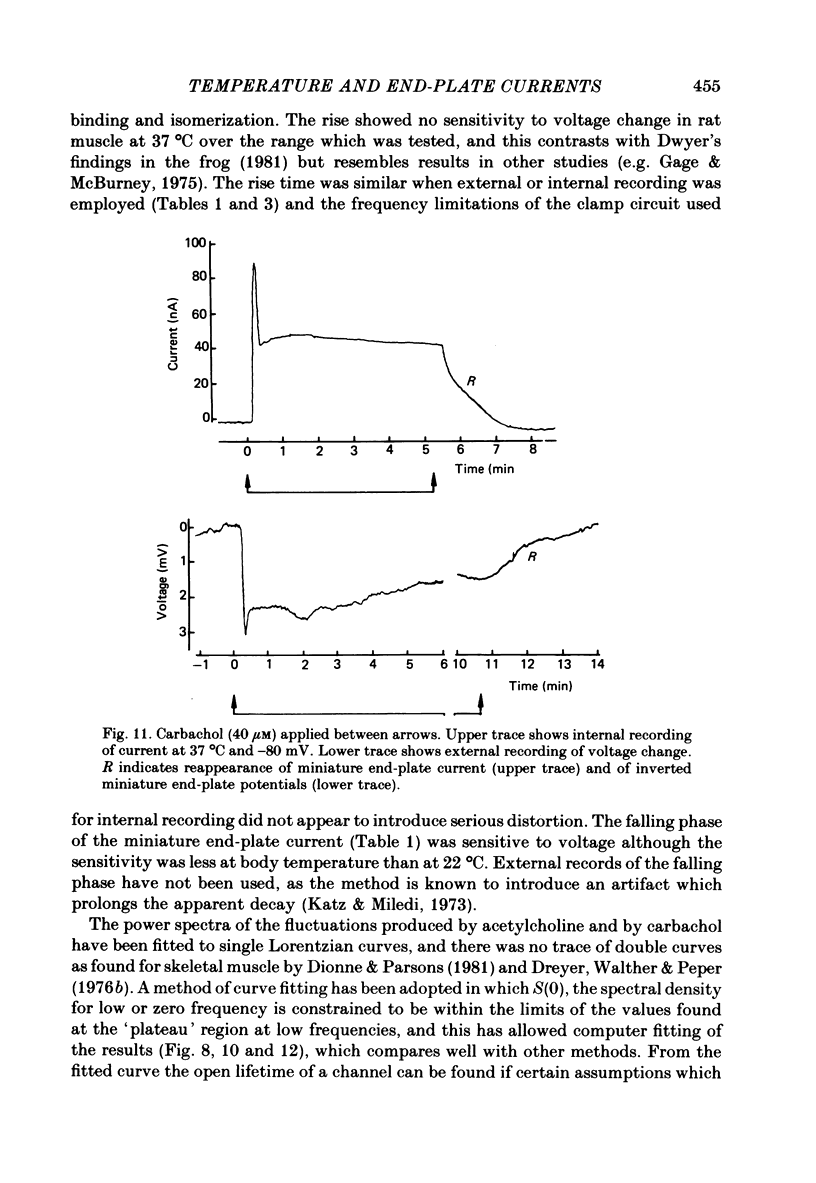
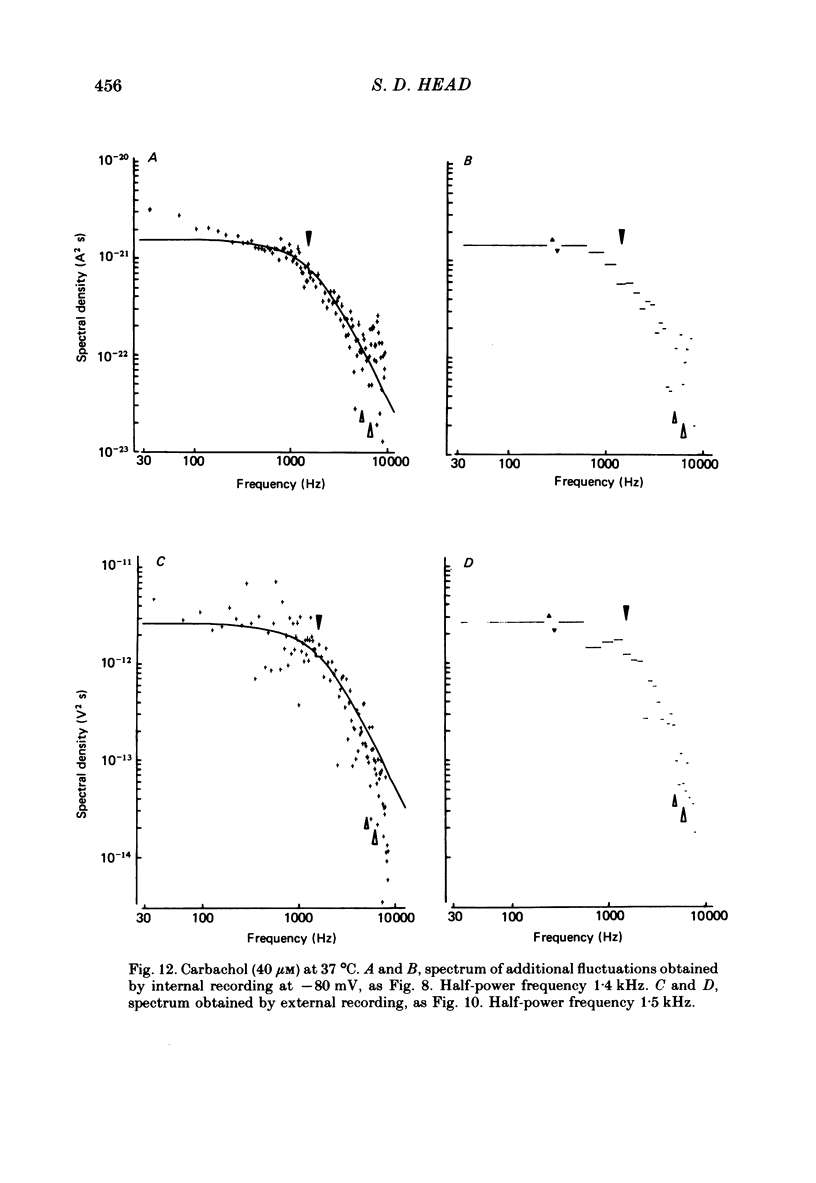
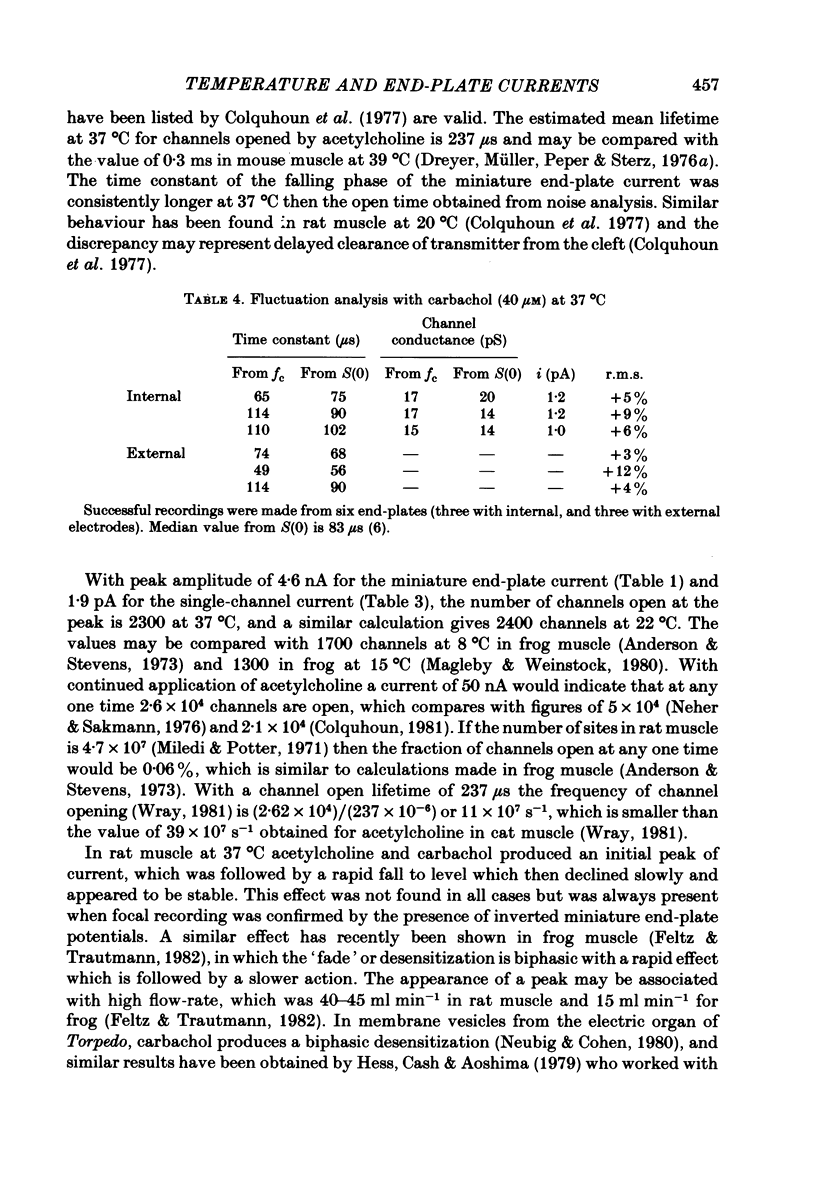
1. Spontaneous miniature end-plate currents (m.e.p.c.s.) were recorded in rat diaphragm at 7, 22 and 37 degrees C at -80 mV. The onset rate, measured as 20-80% rise time, was sensitive to temperature with activation energy 14 kcal mol-1 deg-1, and was not sensitive to membrane voltage between -60 and -130 mV. 2. The rise time recorded by external electrodes was 144 microseconds at 37 degrees C (6) and was similar to that found by internal electrodes. 3. The fall time was temperature-sensitive with activation 18 kcal, and was prolonged when the end-plate was hyperpolarized. 4. With acetylcholine (10 microM) the current increased to a peak and then fell within 30 s to a value which declined slowly. From fluctuation analysis the channel open time of 237 microseconds (7) at 37 degrees C was estimated. External recording gave comparable values (4). Comparison of the initial estimates with those obtained after 3-6 min of continued application showed no consistent change. The channel conductance was 26 pS at 37 degrees C. 5. The time constant of m.e.p.c. decay was consistently longer than the channel open time obtained from noise analysis. 6. With carbachol (40 microM) the current increased to a peak and then declined to a steady value. Fluctuation analysis by internal and external recording gave an increase of 5% in root mean square current with channel open time of 83 microseconds (6) at 37 degrees C, and channel conductance 17 pS.
Full text
PDF




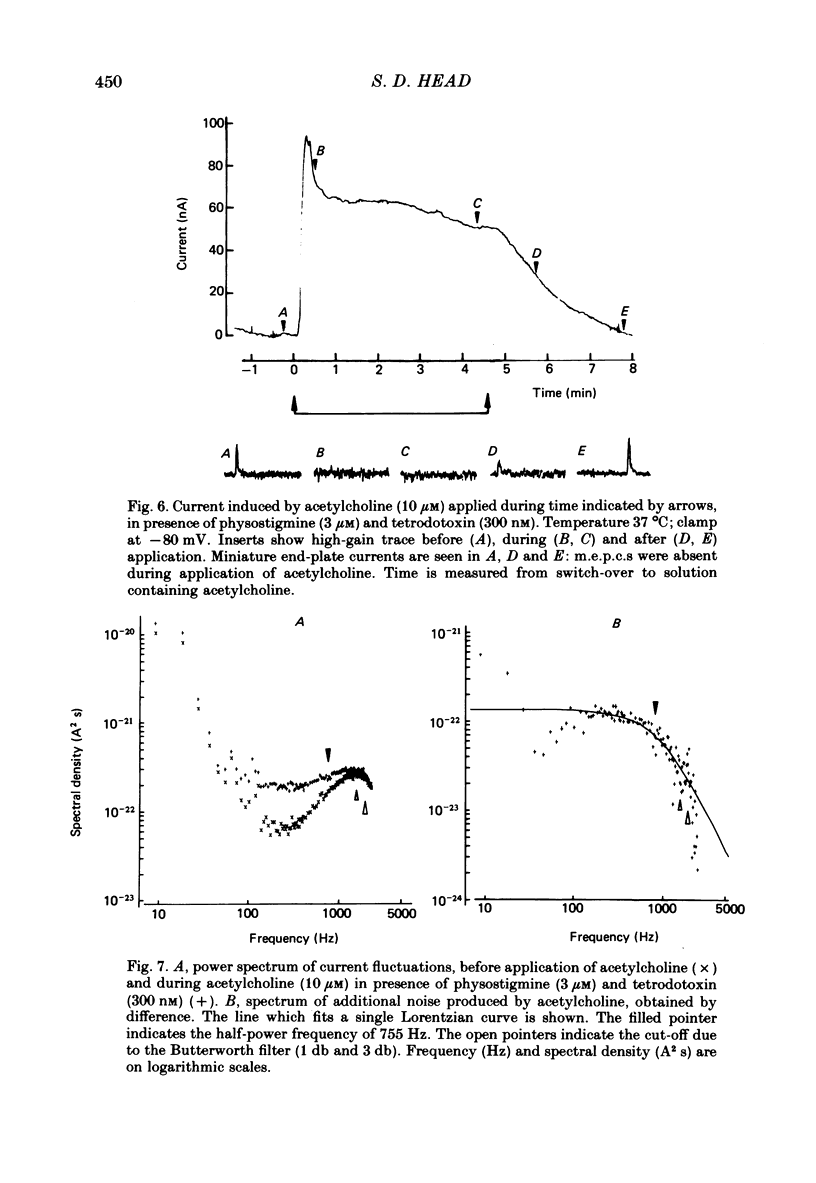
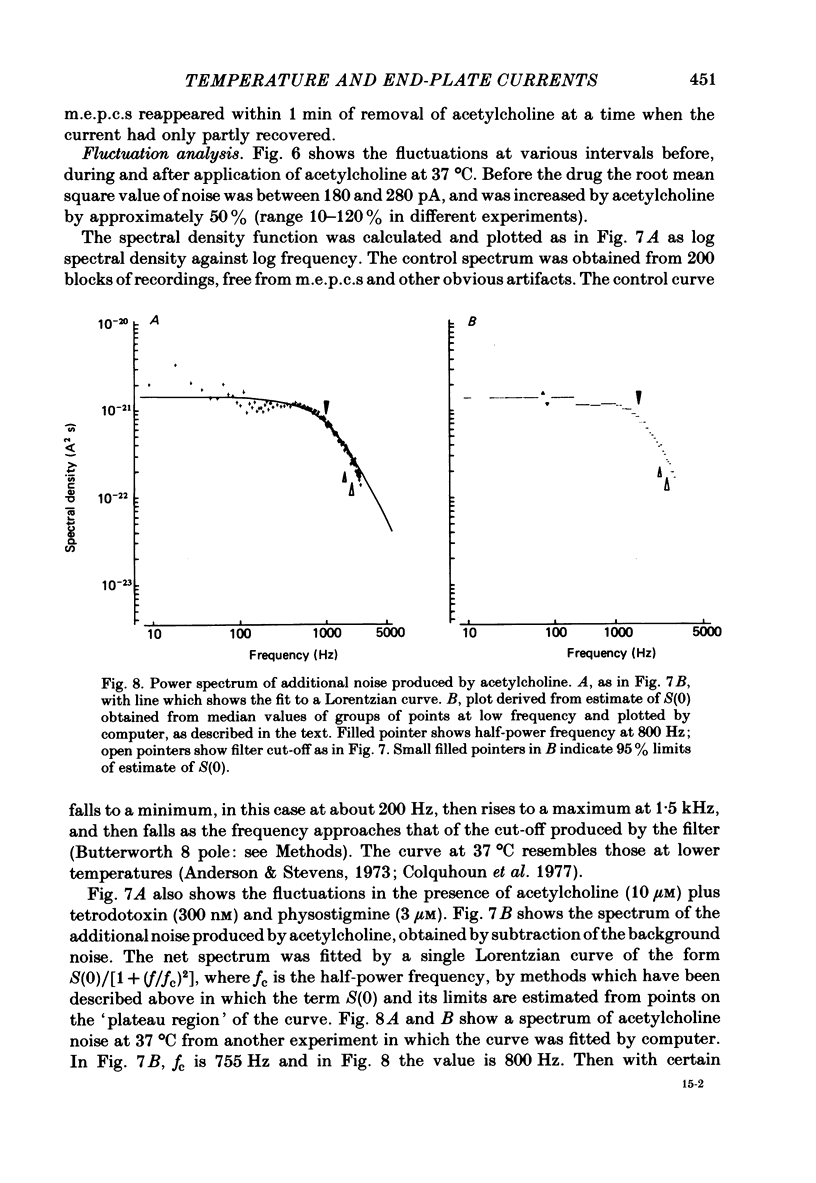
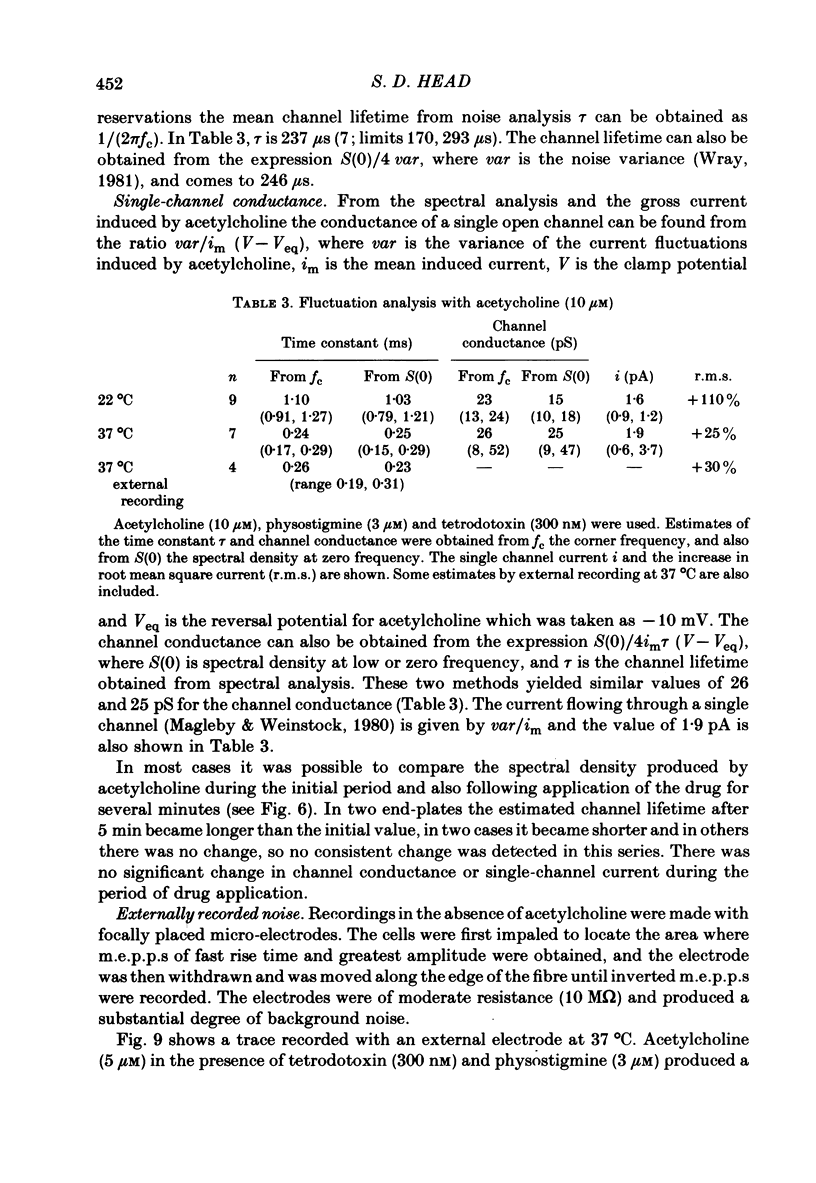
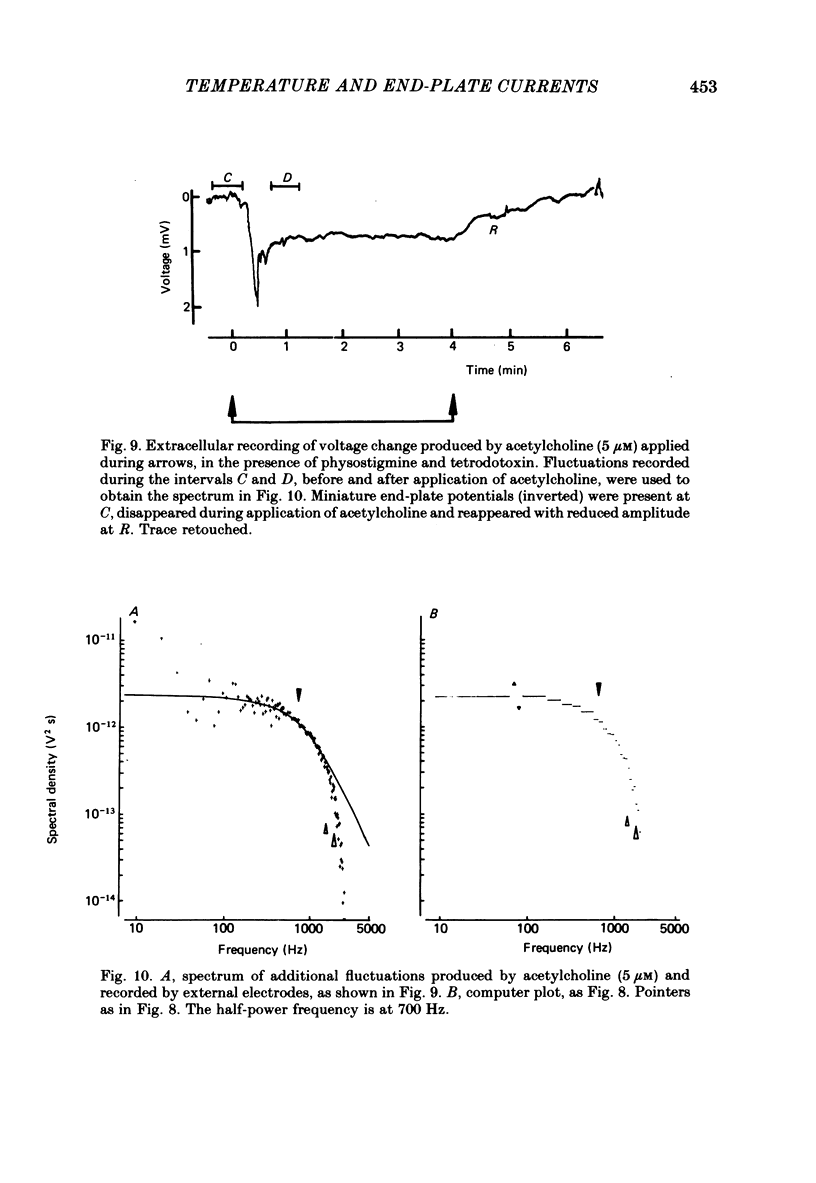



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE W. V. Structural variations of nerve endings in the striated muscles of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1957 Dec;108(3):445–463. doi: 10.1002/cne.901080306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Large W. A., Rang H. P. An analysis of the action of a false transmitter at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(2):361–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fluctuations in the microsecond time range of the current through single acetylcholine receptor ion channels. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):464–466. doi: 10.1038/294464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datyner N. B., Gage P. W. Phasic secretion of acetylcholine at a mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:299–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Parsons R. L. Characteristics of the acetylcholine-operated channel at twitch and slow fibre neuromuscular junctions of the garter snake. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:145–158. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer F., Müller K. D., Peper K., Sterz R. The M. omohyoideus of the mouse as a convenient mammalian muscle preparation. A study of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors by noise analysis and cooperativity. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Dec 28;367(2):115–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00585146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer F., Walther C., Peper K. Junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors in normal and denervated frog muscle fibres. Noise analysis experiments with different agonists. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Oct 15;366(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF02486555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer T. M. The rising phase of the miniature endplate current at the frog neuromuscular junction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 6;646(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90271-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltz A., Trautmann A. Desensitization at the frog neuromuscular junction: a biphasic process. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:257–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N. Effects of membrane potential, temperature and neostigmine on the conductance change caused by a quantum or acetylcholine at the toad neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):385–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N. Miniature end-plate currents and potentials generated by quanta of acetylcholine in glycerol-treated toad sartorius fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(1):79–94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess G. P., Cash D. J., Aoshima H. Acetylcholine receptor-controlled ion fluxes in membrane vesicles investigated by fast reaction techniques. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):329–331. doi: 10.1038/282329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The binding of acetylcholine to receptors and its removal from the synaptic cleft. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):549–574. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. An investigation of spontaneous activity at the neuromuscular junction of the rat. J Physiol. 1956 Jun 28;132(3):650–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land B. R., Salpeter E. E., Salpeter M. M. Acetylcholine receptor site density affects the rising phase of miniature endplate currents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3736–3740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Weinstock M. M. Nickel and calcium ions modify the characteristics of the acetylcholine receptor-channel complex at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:203–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews-Bellinger J., Salpeter M. M. Distribution of acetylcholine receptors at frog neuromuscular junctions with a discussion of some physiological implications. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:197–213. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Potter L. T. Acetylcholine receptors in muscle fibres. Nature. 1971 Oct 29;233(5322):599–603. doi: 10.1038/233599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negrette J., Del Castillo J., Escobar I., Yankelevich G. Spreading activation of end-plate receptors by single transmitter quanta. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 2;235(57):158–159. doi: 10.1038/newbio235158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Single-channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):799–802. doi: 10.1038/260799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubig R. R., Cohen J. B. Permeability control by cholinergic receptors in Torpedo postsynaptic membranes: agonist dose-response relations measured at second and millisecond times. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2770–2779. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade P. T., Barchi R. L. Characteristics of the chloride conductance in muscle fibers of the rat diaphragm. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Mar;69(3):325–342. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray D. Prolonged exposure to acetylcholine: noise analysis and channel inactivation in cat tenuissimus muscle. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:37–56. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


