Abstract
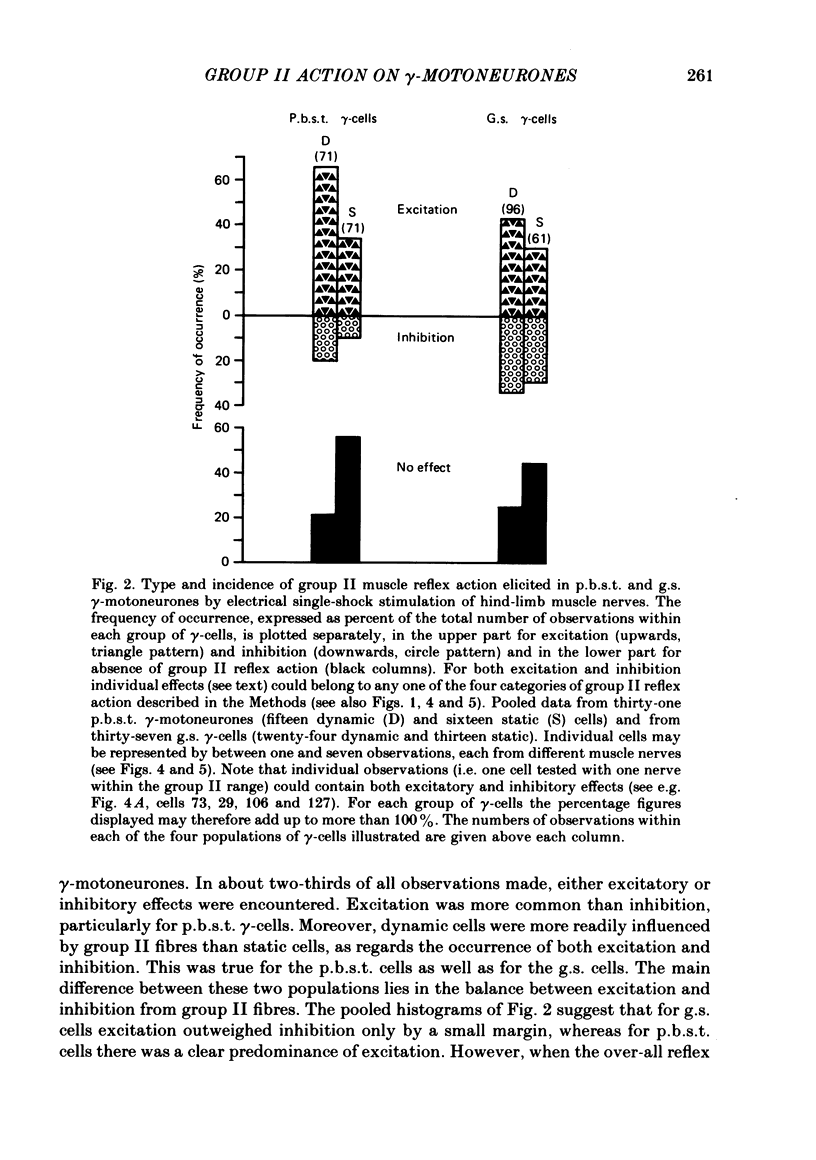
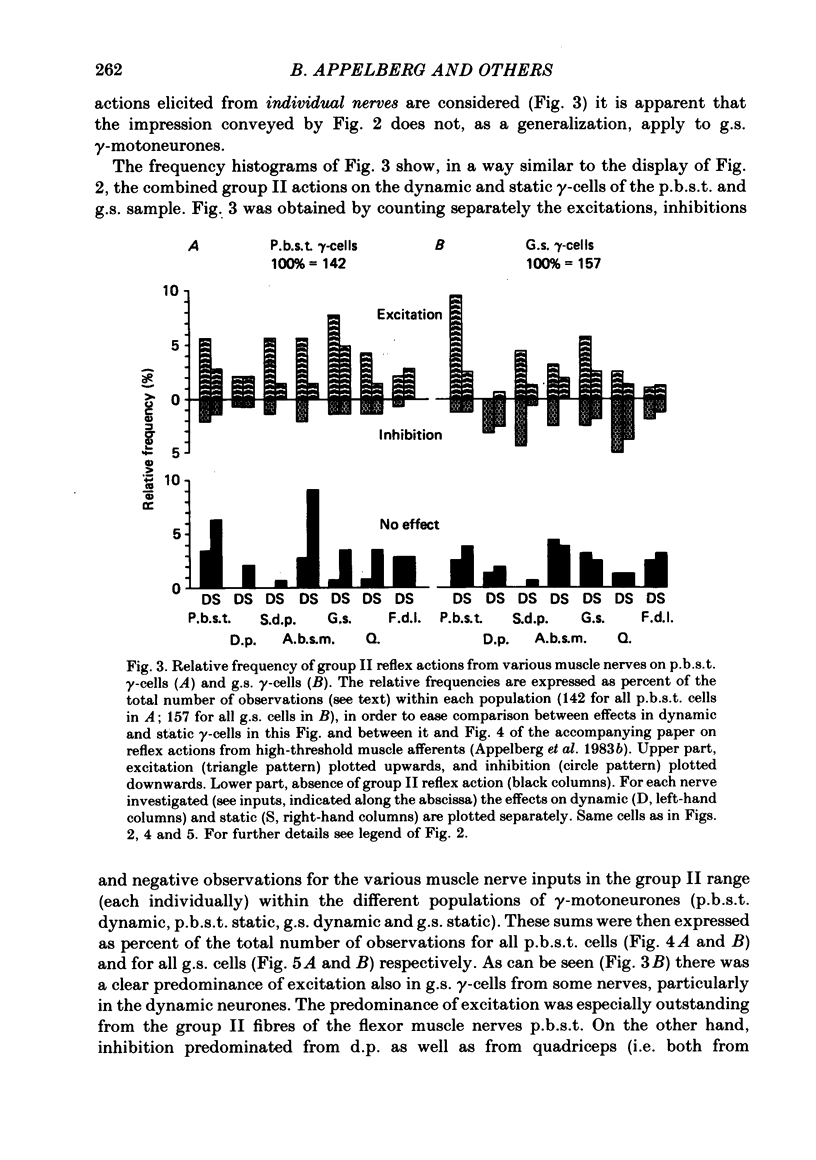
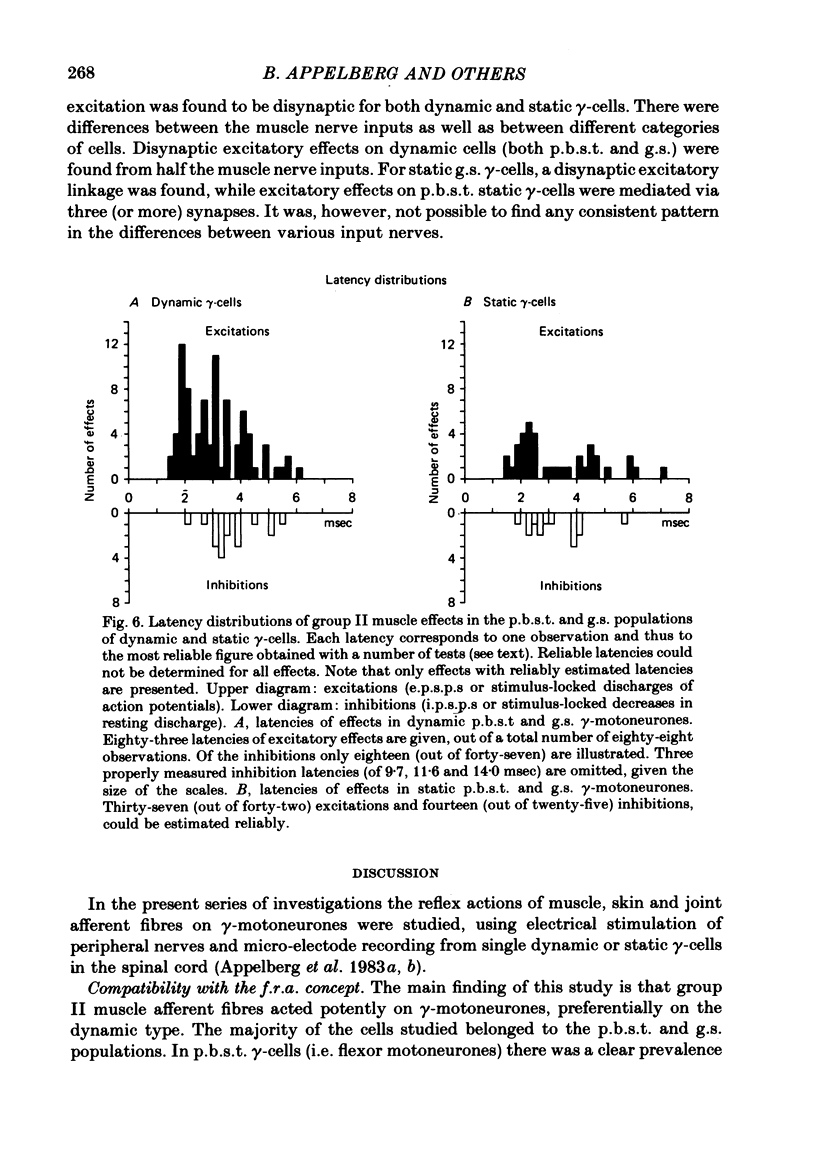
The reflex effects elicited by electrical stimulation of group II muscle afferent fibres were recorded with micro-electrodes in ninety-eight hind-limb gamma-motoneurones of cats anaesthetized with chloralose. Eighty-one of the gamma-cells were classified as either static or dynamic by means of stimulation in the mesencephalic area for dynamic control known to influence dynamic gamma-motoneurones selectively. A high responsiveness to activity in group II muscle fibres was found for the whole sample of gamma-cells. Group II muscle action on dynamic gamma-motoneurones was found to be more frequent than that on static ones. Excitation from group II fibres outweighed inhibition. This was clear cut for flexor gamma-motoneurones. In extensor gamma-cells, excitation prevailed by a small margin only. However, for both static and dynamic extensor gamma-cells, excitation prevailed from both posterior biceps--semitendinosus and the gastrocnemius--soleus nerves, whereas inhibition was more frequent from the deep peroneal and quadriceps nerves. All the reflex effects studied were likely to be mediated via oligosynaptic pathways. The shortest latencies of excitatory effects were compatible with a disynaptic coupling. The fastest inhibitions were presumably trisynaptic. The present findings, supported by a parallel study of reflexes evoked by group III muscle afferents, strongly suggest that the reflexes on gamma-motoneurones are not organized in accordance with the concept of flexion reflex afferents as conceived for alpha-motoneurones. The interpretation of the results suggests a particularly independent position for dynamic gamma-cells in relation to alpha- and static gamma-motoneurones. Hence, the results also furnish an argument against the concept of alpha-gamma linkage.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelberg B., Hulliger M., Johansson H., Sojka P. Actions on gamma-motoneurones elicited by electrical stimulation of group I muscle afferent fibres in the hind limb of the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:237–253. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Hulliger M., Johansson H., Sojka P. Actions on gamma-motoneurones elicited by electrical stimulation of group III muscle afferent fibres in the hind limb of the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:275–292. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Hulliger M., Johansson H., Sojka P. Fusimotor reflexes in triceps surae elicited by natural stimulation of muscle afferents from the cat ipsilateral hind limb. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:211–229. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Hulliger M., Johansson H., Sojka P. Recurrent actions on gamma-motoneurones mediated via large and small ventral root fibres in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:293–305. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Johansson H., Kalistratov G. The influence of group II muscle afferents and low threshold skin afferents on dynamic fusimotor neurones to the triceps surae of the cat. Brain Res. 1977 Aug 19;132(1):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90713-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd I. A., Kalu K. U. Scaling factor relating conduction velocity and diameter for myelinated afferent nerve fibres in the cat hind limb. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:277–297. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppin C. M., Jack J. J. Internodal length and conduction velocity of cat muscle afferent nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(1):92P–93P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu T. C., Schomburg E. D. Electrophysiological investigation of the projection of secondary muscle spindle afferents in the cat spinal cord. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Jul;91(3):314–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05687.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granit R. Interpretation of supraspinal effects on the gamma system. Prog Brain Res. 1979;50:147–154. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60815-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner S., Hongo T., Lund S. Descending monosynaptic and reflex control of gamma-motoneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Apr;75(4):592–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner S. Supraspinal and segmental control of static and dynamic gamma-motoneurones in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1969;327:1–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C. Relation of function to diameter in afferent fibers of muscle nerves. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Sep 20;38(1):117–131. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A. Monosynaptic excitation of motoneurones from muscle spindle secondary endings of intercostal and triceps surae muscles in the cat. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(2):64P–66P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Characteristics of the excitatory pathway from group II muscle afferents to alpha motoneurones. Brain Res. 1975 May 9;88(3):538–542. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90667-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Comments on reflex actions evoked by electrical stimulation of group II muscle afferents. Brain Res. 1977 Feb 25;122(3):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90466-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews P. B. Evidence that the secondary as well as the primary endings of the muscle spindles may be responsible for the tonic stretch reflex of the decerebrate cat. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(2):365–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noth J., Thilmann A. Autogenetic excitation of extensor gamma-motoneurones by group II muscle afferents in the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Apr;17(1-2):23–26. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer E. K., Watt D. G., Taylor A., Reinking R. M., Stuart D. G. Analysis of muscle receptor connections by spike-triggered averaging. 2. Spindle group II afferents. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1393–1402. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


