Abstract
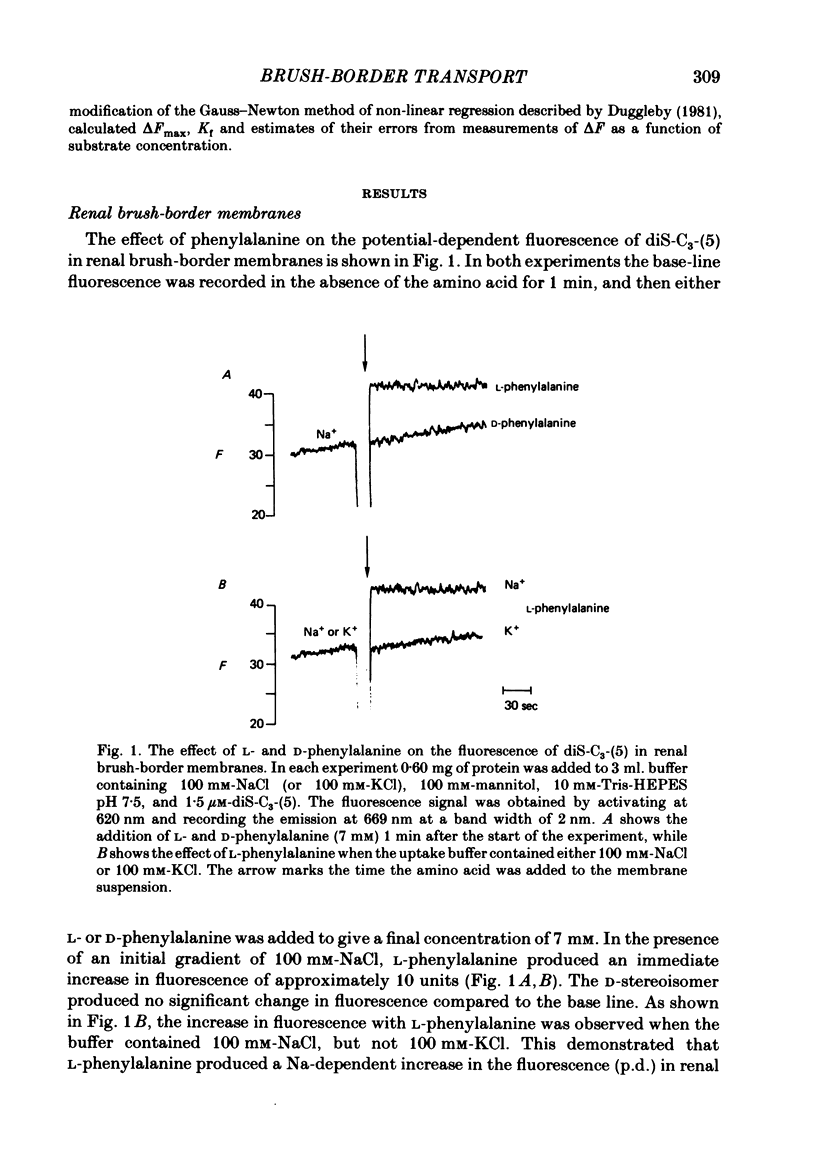
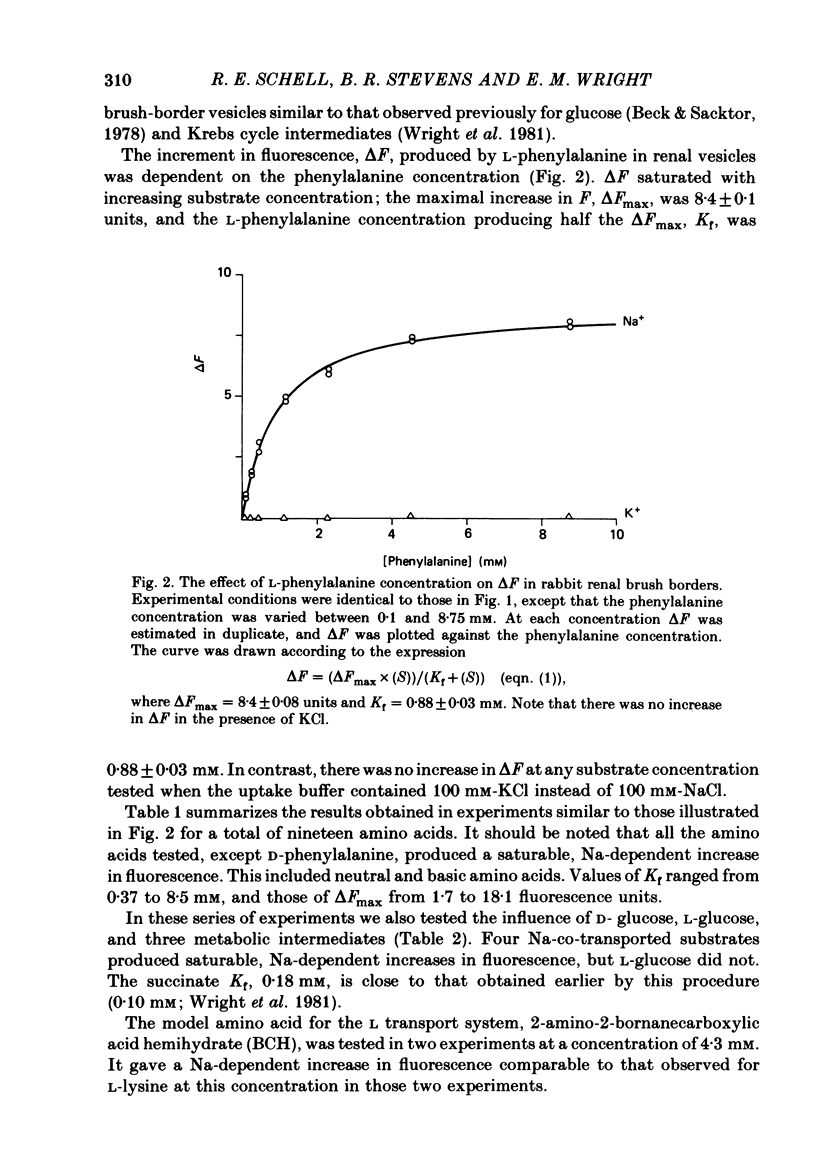
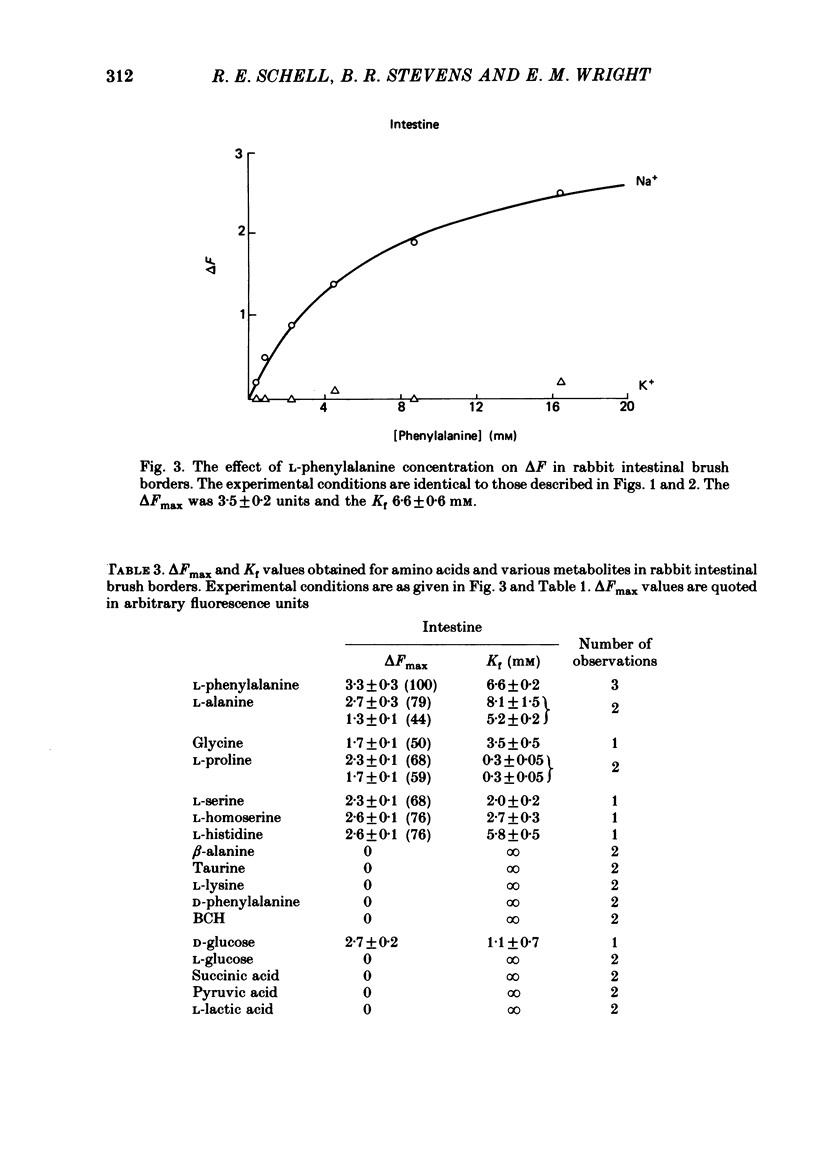
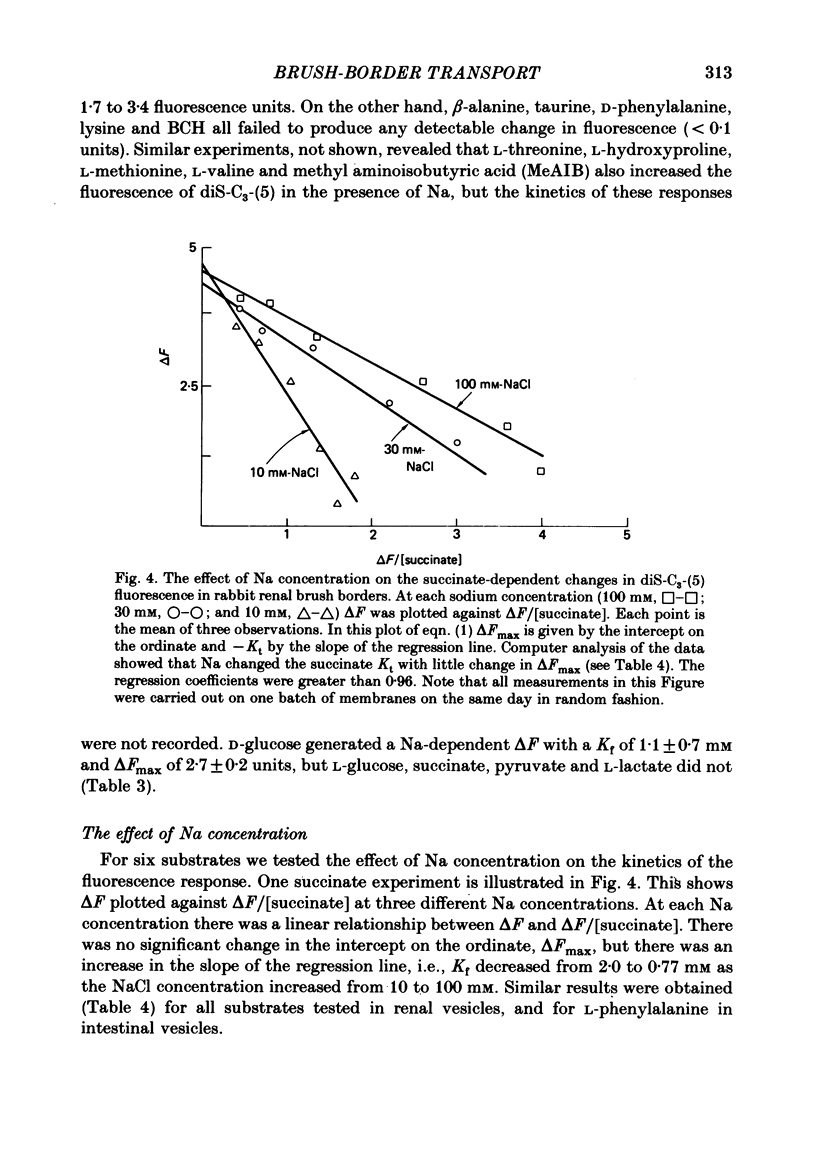
The kinetics of Na-coupled solute transport by renal and jejunal brush-border vesicles in the rabbit were examined using the potential-sensitive fluorescent dye diS-C3-(5). All organic solutes known to be transported across these membranes by Na-coupled mechanisms increase the fluorescence of the dye in the presence of Na, but not K. An increase in fluorescence (delta F) corresponds to a depolarization of the electrical potential difference (5-60 mV) across the brush-border membrane in the intact cell. delta F was independent of the valency of the transported solute. The fluorescence response was saturable, and for twelve solutes the Kf, i.e. the concentration of the substrate generating 50% of the maximal response, agreed quite closely with the Kt values reported from tracer studies. For six solutes increasing the Na concentration decreased Kf, and this agrees with the effect of Na on the kinetics of succinate transport in renal vesicles. We conclude that D-glucose, neutral amino acids and imino acids are co-transported with Na across both renal and jejunal brush-border membranes, and that carboxylic acids, beta-amino acids, and dibasic amino acids are co-transported with Na across the renal, but not jejunal, membranes.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARRY R. J., DIKSTEIN S., MATTHEWS J., SMYTH D. H., WRIGHT E. M. ELECTRICAL POTENTIALS ASSOCIATED WITH INTESTINAL SUGAR TRANSFER. J Physiol. 1964 Jun;171:316–338. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J. C., Sacktor B. Membrane potential-sensitive fluorescence changes during Na+-dependent D-glucose transport in renal brush border membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7158–7162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. B., Salzberg B. M. Optical measurement of membrane potential. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;83:35–88. doi: 10.1007/3-540-08907-1_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggleby R. G. A nonlinear regression program for small computers. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaunitz J. D., Gunther R., Wright E. M. Involvement of multiple sodium ions in intestinal d-glucose transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2315–2318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn P. G., Smyth D. H., Wright E. M. Effects of amino acids, dipeptides and disaccharides on the electric potential across rat small intestine. J Physiol. 1968 Jun;196(3):723–746. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama T., Hoshi T. The effect of D-glucose on the electrical potential profile across the proximal tubule of newt kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 1;282(1):214–225. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90327-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mircheff A. K., Kippen I., Hirayama B., Wright E. M. Delineation of sodium-stimulated amino acid transport pathways in rabbit kidney brush border vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1982;64(1-2):113–122. doi: 10.1007/BF01870773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose R. C., Schultz S. G. Studies on the electrical potential profile across rabbit ileum. Effects of sugars and amino acids on transmural and transmucosal electrical potential differences. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jun;57(6):639–663. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.6.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., ZALUSKY R. INTERACTIONS BETWEEN ACTIVE SODIUM TRANSPORT AND ACTIVE AMINO-ACID TRANSPORT IN ISOLATED RABBIT ILEUM. Nature. 1965 Jan 16;205:292–294. doi: 10.1038/205292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., ZALUSKY R. The interaction between active sodium transport and active sugar transport in the isolated rabbit ileum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 14;71:503–505. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91121-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarzija I., Frömter E. Electrophysiological analysis of rat renal sugar and amino acid transport. III. Neutral amino acids. Pflugers Arch. 1982 May;393(3):119–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarzija I., Hinton B. T., Frömter E. Electrophysiological analysis of rat renal sugar and amino acid transport. II. Dependence on various transport parameters and inhibitors. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Apr;393(2):190–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00582943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Curran P. F. Coupled transport of sodium and organic solutes. Physiol Rev. 1970 Oct;50(4):637–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens B. R., Ross H. J., Wright E. M. Multiple transport pathways for neutral amino acids in rabbit jejunal brush border vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1982;66(3):213–225. doi: 10.1007/BF01868496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens B. R., Wright S. H., Hirayama B. S., Gunther R. D., Ross H. J., Harms V., Nord E., Kippen I., Wright E. M. Organic and inorganic solute transport in renal and intestinal membrane vesicles preserved in liquid nitrogen. Membr Biochem. 1982;4(4):271–282. doi: 10.3109/09687688209065436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. F., Armstrong W. M. Effect of transported solutes on membrane potentials in bullfrog small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jul;221(1):194–201. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.1.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. H., Kippen I., Klinenberg J. R., Wright E. M. Specificity of the transport system for tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates in renal brush borders. J Membr Biol. 1980 Nov 15;57(1):73–82. doi: 10.1007/BF01868987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. H., Kippen I., Wright E. M. Stoichiometry of Na+-succinate cotransport in renal brush-border membranes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1773–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. H., Krasne S., Kippen I., Wright E. M. Na+-dependent transport of tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates by renal brush border membranes. Effects on fluorescence of a potential-sensitive cyanine dye. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 6;640(3):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


