Abstract
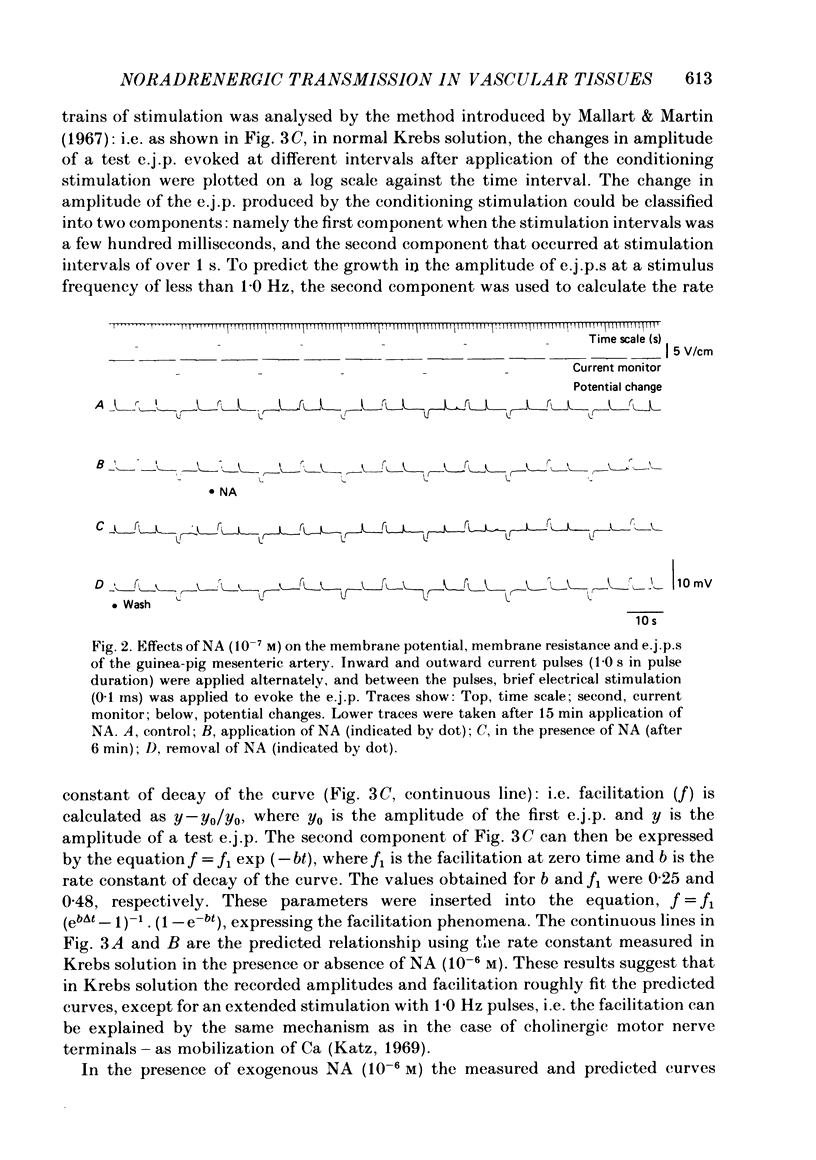
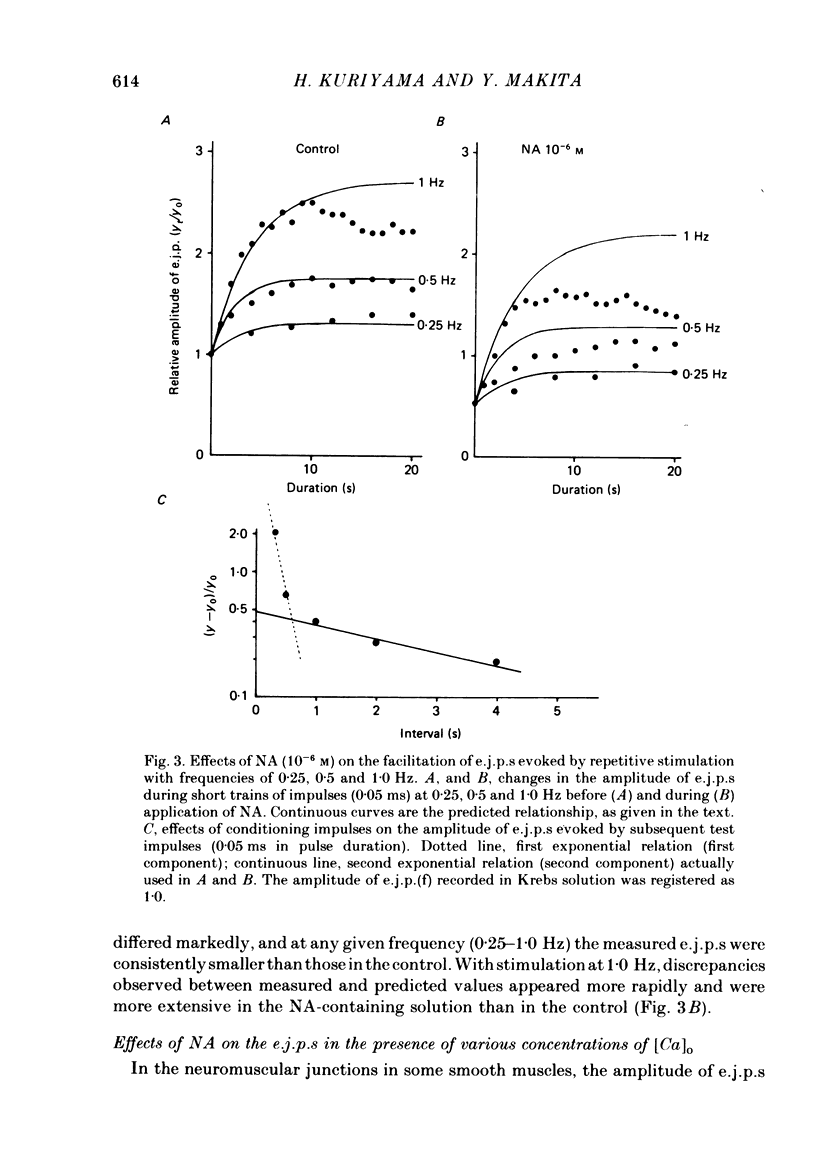
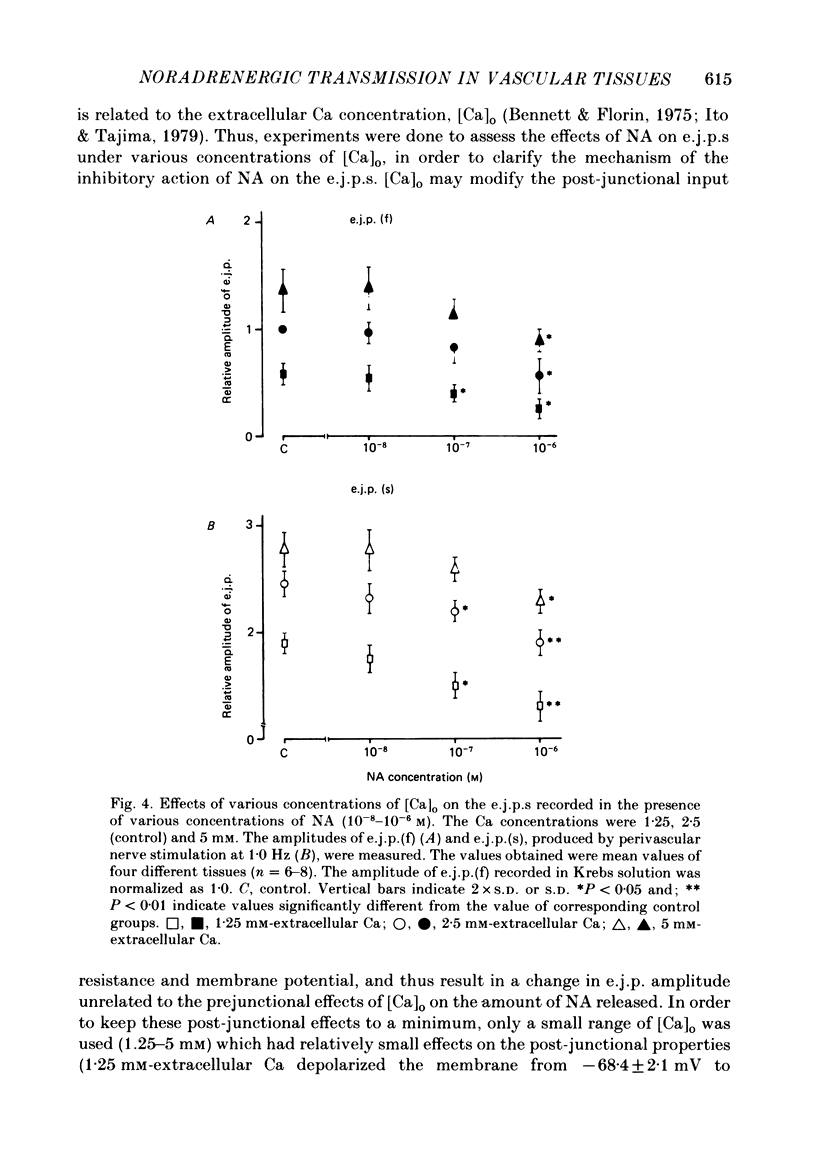
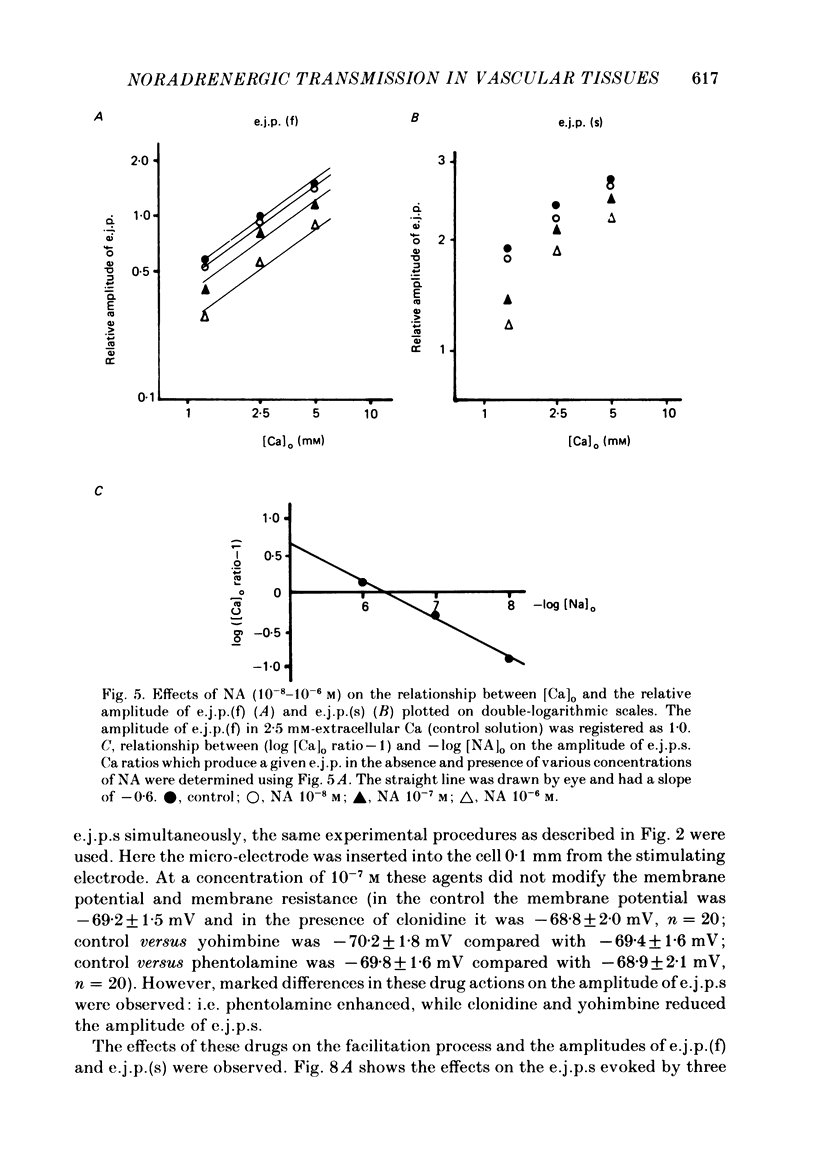
We carried out electrophysiological experiments on guinea-pig mesenteric arteries in an attempt to clarify the modification of noradrenaline (NA) release from noradrenergic nerve terminals by the action of prejunctional adrenoceptors. NA (10(-7)-10(-5) M) suppressed the amplitude of the first excitatory junction potential (e.j.p.(f], the facilitation process, and the e.j.p. after facilitation was completed (e.j.p.(s]with no change in the post-junctional membrane properties of smooth muscles. These actions of NA on e.j.p.s were antagonized by high concentrations of extracellular Ca, [Ca]o, but not in a simple competitive manner. NA (10(-7) M) suppressed the appearance but not the amplitude of the miniature e.j.p.s. These effects of NA on transmission indicate that NA acts on prejunctional nerve terminals and suppresses the release of NA from nerve terminals rather than producing a desensitization of post-junctional adrenoceptors. Prazosin and phentolamine (10(-6) M) did suppress the NA-induced contraction (greater than 10(-6) M) but did not suppress the contraction evoked by perivascular nerve stimulation, below a frequency of 1.0 Hz. At a dose of 10(-7) M, yohimbine, clonidine, prazosin and phentolamine had no effect on the muscle membrane potential and resistance. Yet on the e.j.p.(f), yohimbine and clonidine caused suppression, phentolamine enhancement and prazosin had no effect. On the e.j.p.(s), yohimbine and phentolamine caused enhancement, clonidine suppression and prazosin had no effect. These results indicate that at least three different adrenoceptors are distributed on the neuromuscular junction in this tissue, i.e. alpha 1-extrajunctional, alpha 2-prejunctional, and an unknown subtype of intrajunctional adrenoceptors. Furthermore, the feedback mechanism on NA release is mediated by suppression of the influx of Ca. Nonselective and non-specific actions of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists were also elucidated.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts P., Bartfai T., Stjärne L. Site(s) and ionic basis of alpha-autoinhibition and facilitation of "3H'noradrenaline secretion in guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:297–334. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angus J. A., Korner P. I. Evidence against presynaptic alpha-adrenoreceptor modulation of cardiac sympathetic transmission. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):288–291. doi: 10.1038/286288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Florin T. An electrophysiological analysis of the effect of Ca ions on neuromuscular transmission in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Sep;55(1):97–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07616.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeley A. G., Cunnane T. C., Petersen S. A. Local regulation of transmitter release from rodent sympathetic nerve terminals? J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:93–109. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. C., Kalsner S. An examination of the negative feedback function of presynaptic adrenoceptors in a vascular tissue. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;67(3):401–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Wiley K. S., Slater I. H. In vitro relaxation of arteries and veins by prazosin: alpha-adrenergic blockade with no direct vasodilation. Blood Vessels. 1979;16(3):144–154. doi: 10.1159/000158201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. Evidence for two populations of excitatory receptors for noradrenaline on arteriolar smooth muscle. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):767–768. doi: 10.1038/283767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. Localization of specialized noradrenaline receptors at neuromuscular junctions on arterioles of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1981;313:343–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman M. E., Surprenant A. M. Some properties of the excitatory junction potentials recorded from saphenous arteries of rabbits. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:337–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman M. E., Surprenant A. An electrophysiological analysis of the effects of noradrenaline and alpha-receptor antagonists on neuromuscular transmission in mammalian muscular arteries. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(2):651–661. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Tajima K. An electrophysiological analysis of the actions of prostaglandin on neuromuscular transmission in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):521–537. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajiwara M., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Neuromuscular transmission and smooth muscle membrane properties in the guinea-pig ear artery. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:283–302. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Misu Y. Release of noradrenaline by splenic nerve stimulation and its dependence on calcium. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(2):219–234. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Makita Y. Modulation on neuromuscular transmission by endogenous and exogenous prostaglandins in the guinea-pig mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:431–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. Adrenergic transmissions in the guinea-pig mesenteric artery and their cholinergic modulations. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:383–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Sixth gaddum memorial lecture, National Institute for Medical Research, Mill Hill, January 1977. Presynaptic receptors and their role in the regulation of transmitter release. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;60(4):481–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallart A., Martin A. R. An analysis of facilitation of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):679–694. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Endo T. Presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors. Gen Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;7(5):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(76)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story D. F., McCulloch M. W., Rand M. J., Standford-Starr C. A. Conditions required for the inhibitory feedback loop in noradrenergic transmission. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):62–65. doi: 10.1038/293062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H. Effects of endogenous and exogenous noradrenaline on the smooth muscle of guinea-pig mesenteric vein. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:495–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Kuriyama H. Observation of quantal release of noradrenaline from vascular smooth muscles in potassium-free solution. Jpn J Physiol. 1980;30(4):665–670. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.30.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro N., Gallagher J. P., Nishi S. Facilitation and depression of synaptic transmission in amphibian sympathetic ganglia. Brain Res. 1976 Dec 10;118(1):45–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90840-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhoutte P. M., Verbeuren T. J., Webb R. C. Local modulation of adrenergic neuroeffector interaction in the blood vessel well. Physiol Rev. 1981 Jan;61(1):151–247. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westfall T. C. Local regulation of adrenergic neurotransmission. Physiol Rev. 1977 Oct;57(4):659–728. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.4.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


