Abstract
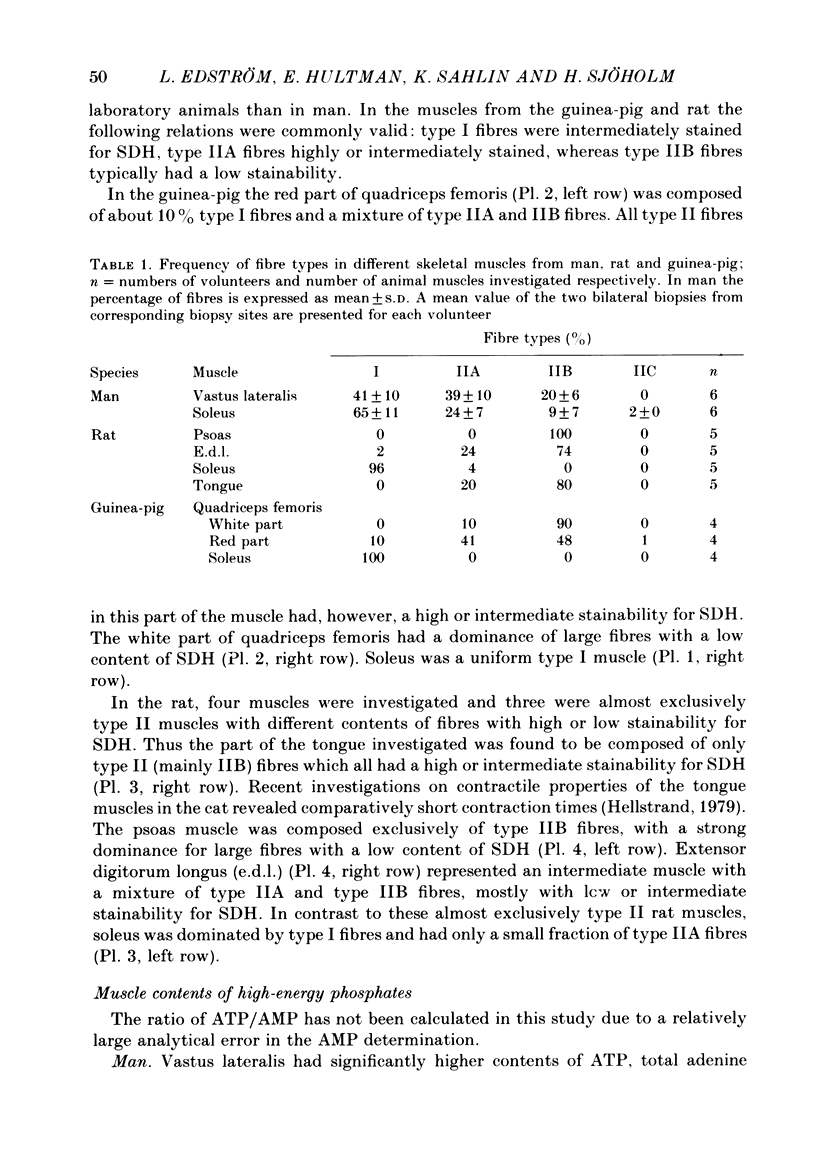
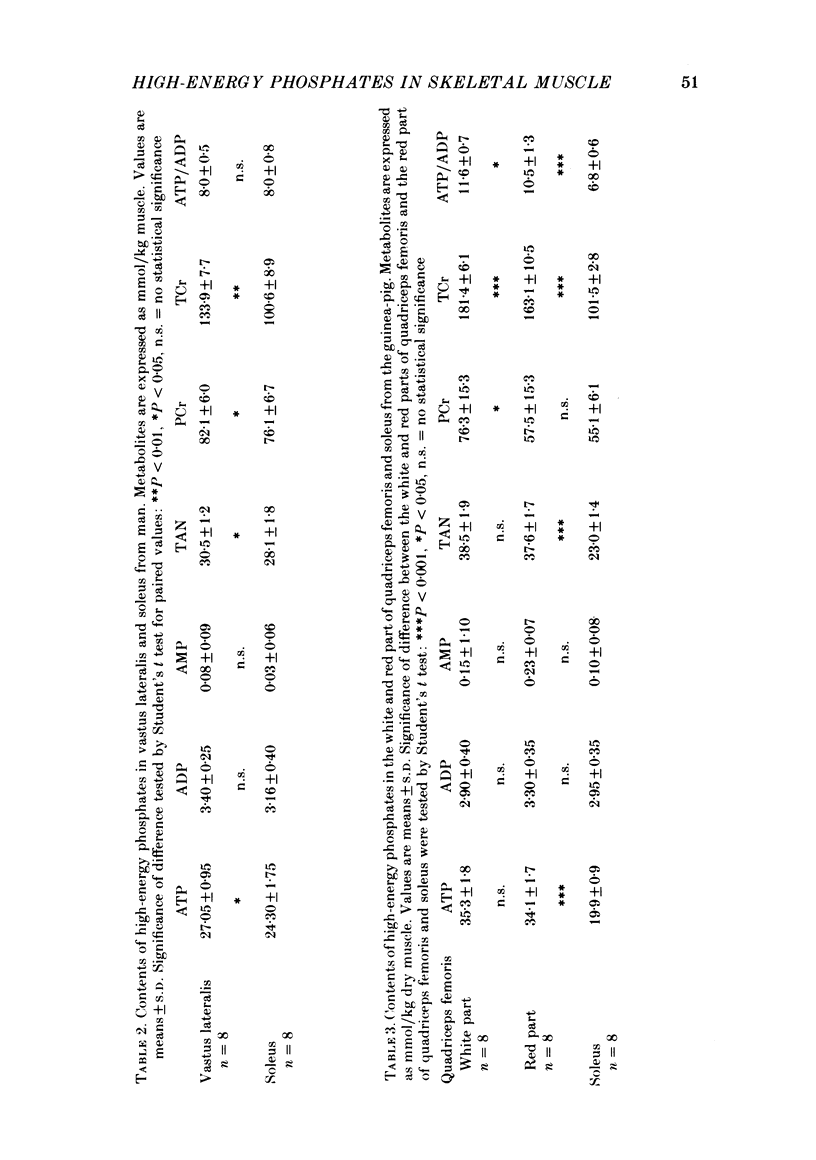
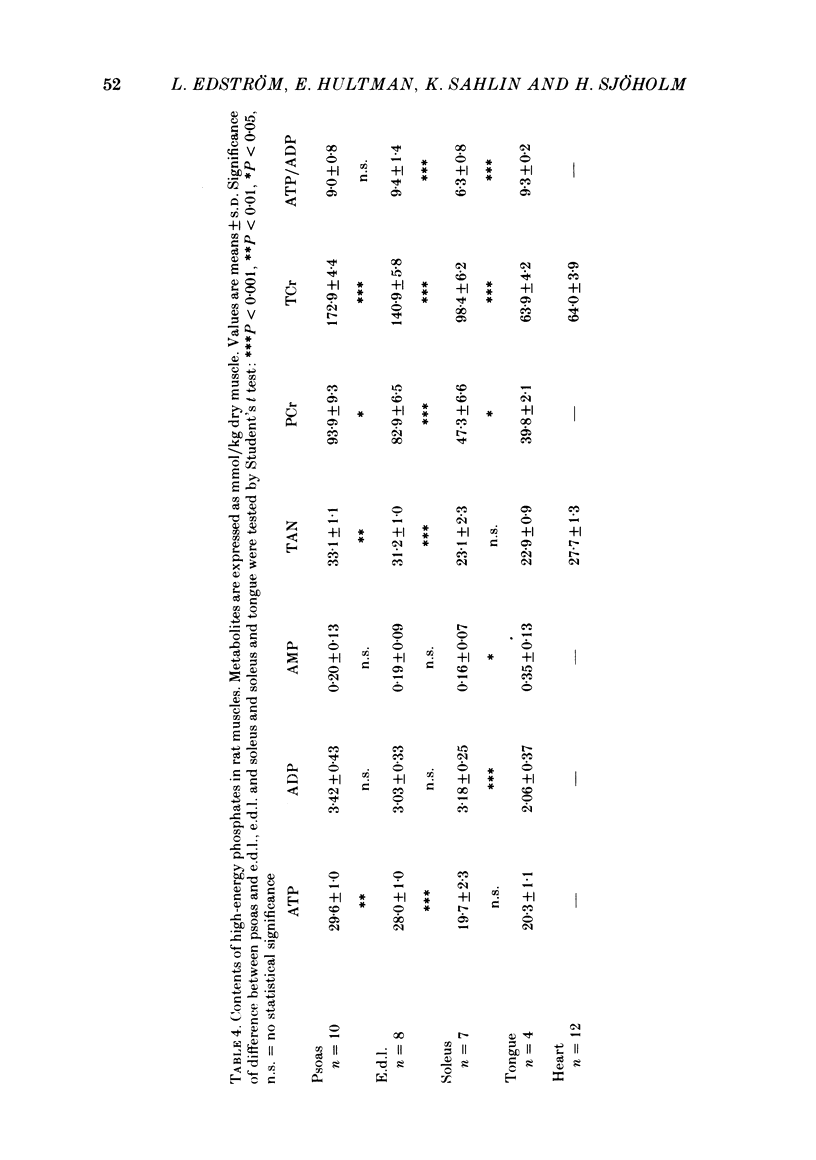
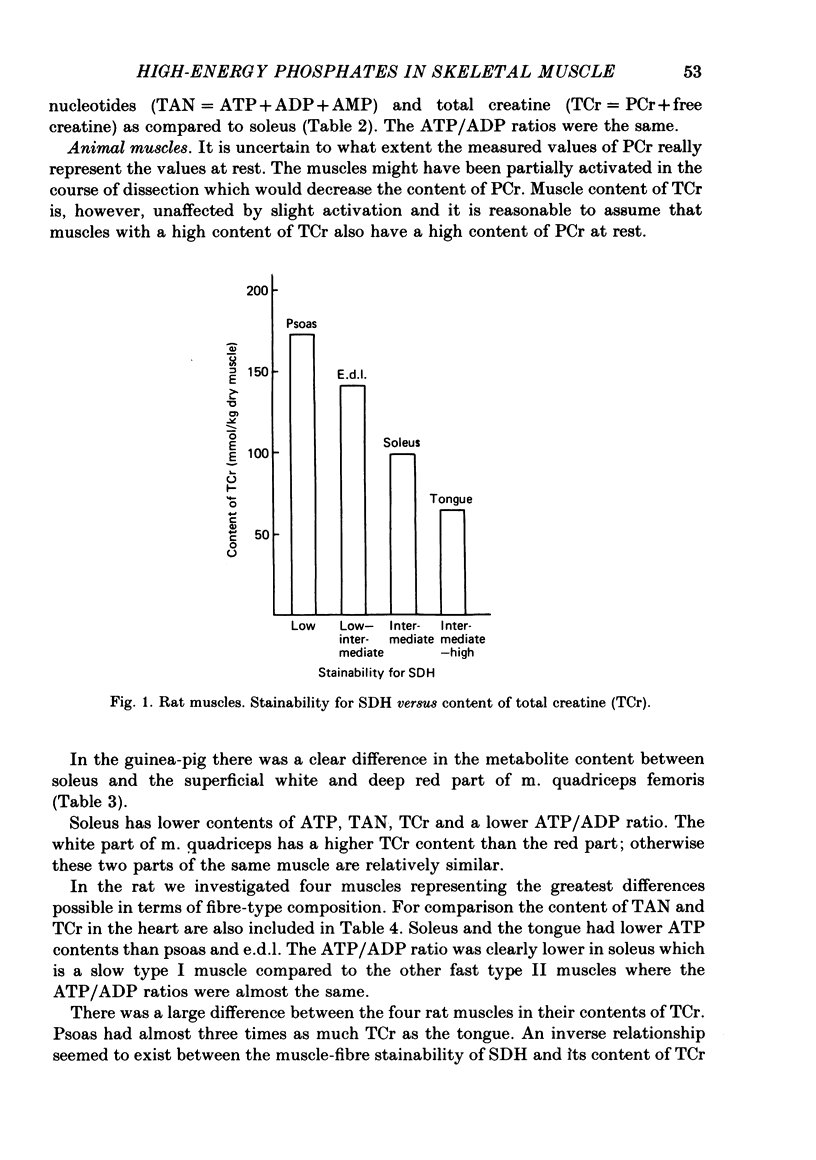
1. The contents of high-energy phosphates at rest have been measured in skeletal muscles with different fibre-type composition from rat, guinea-pig and man. All muscles studied biochemically have been characterized histochemically. 2. Fast-twitch muscles had a higher ATP/ADP ratio than slow-twitch muscles and, with the exception of the tongue in the rat, higher contents of ATP and phosphocreatine. 3. There was an inverse relationship between the content of phosphocreatine and the stainability for succinyl dehydrogenase, which is a marker enzyme for oxidative capacity. 4. The biochemical and histochemical data are discussed in relation to known morphological and functional properties of the different muscle-fibre types. It is concluded that fast-twitch fibres have a high ATP/ADP ratio favouring a fast acceleration of energy production. The content of phosphocreatine seems to be related to the glycolytic capacity but not to the contraction time. In addition to being an immediate energy source, phosphocreatine functions as a buffer against lactic acidosis.
Full text
PDF







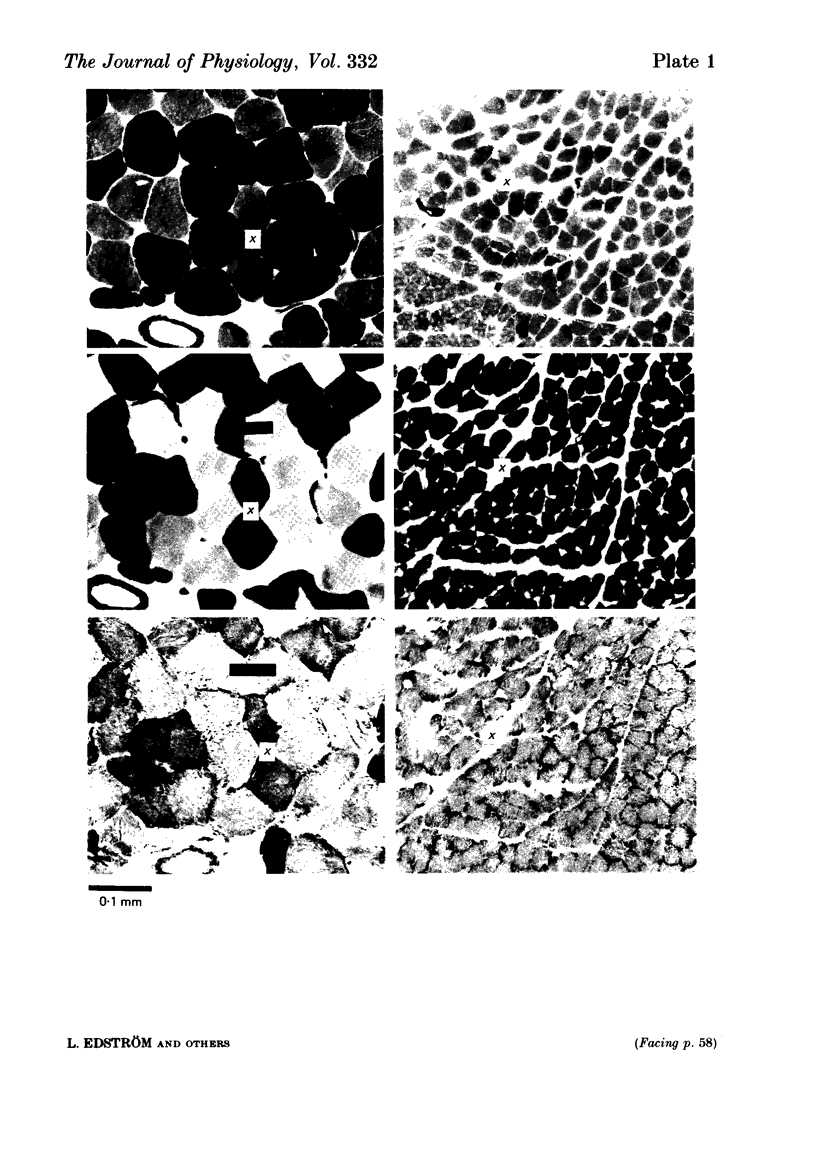
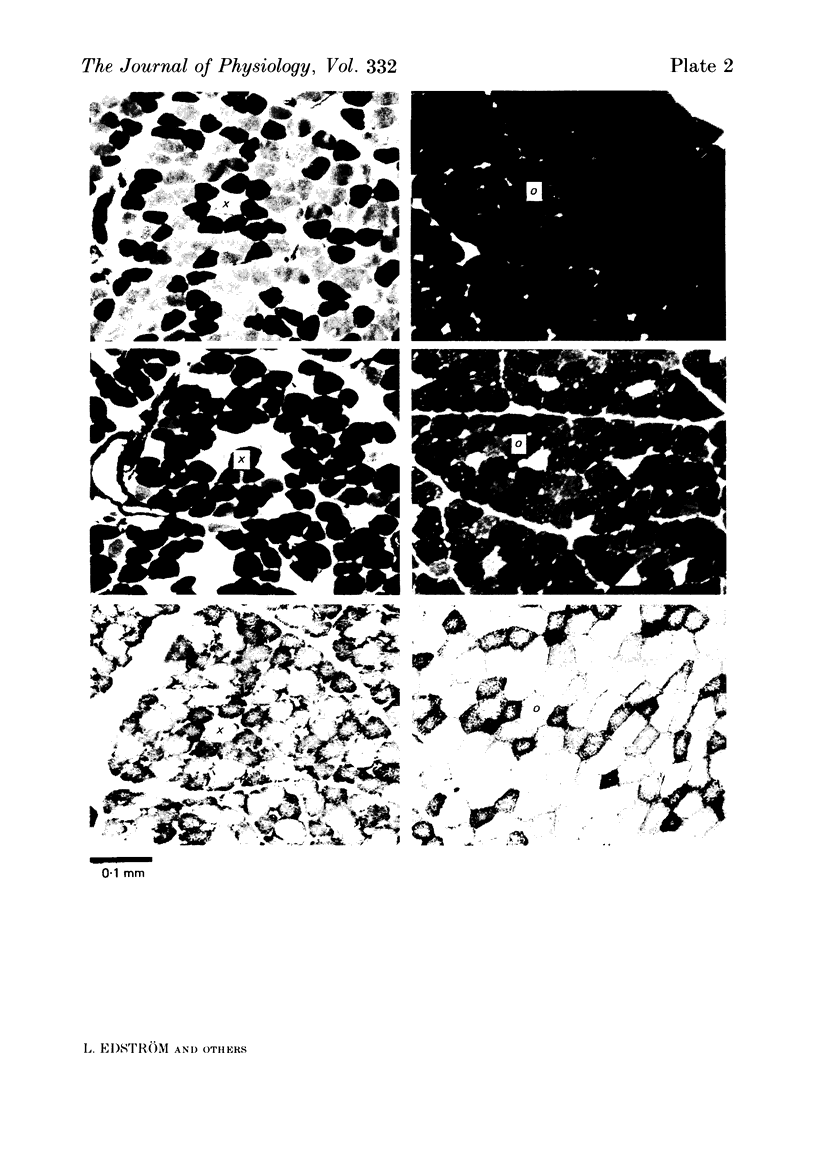
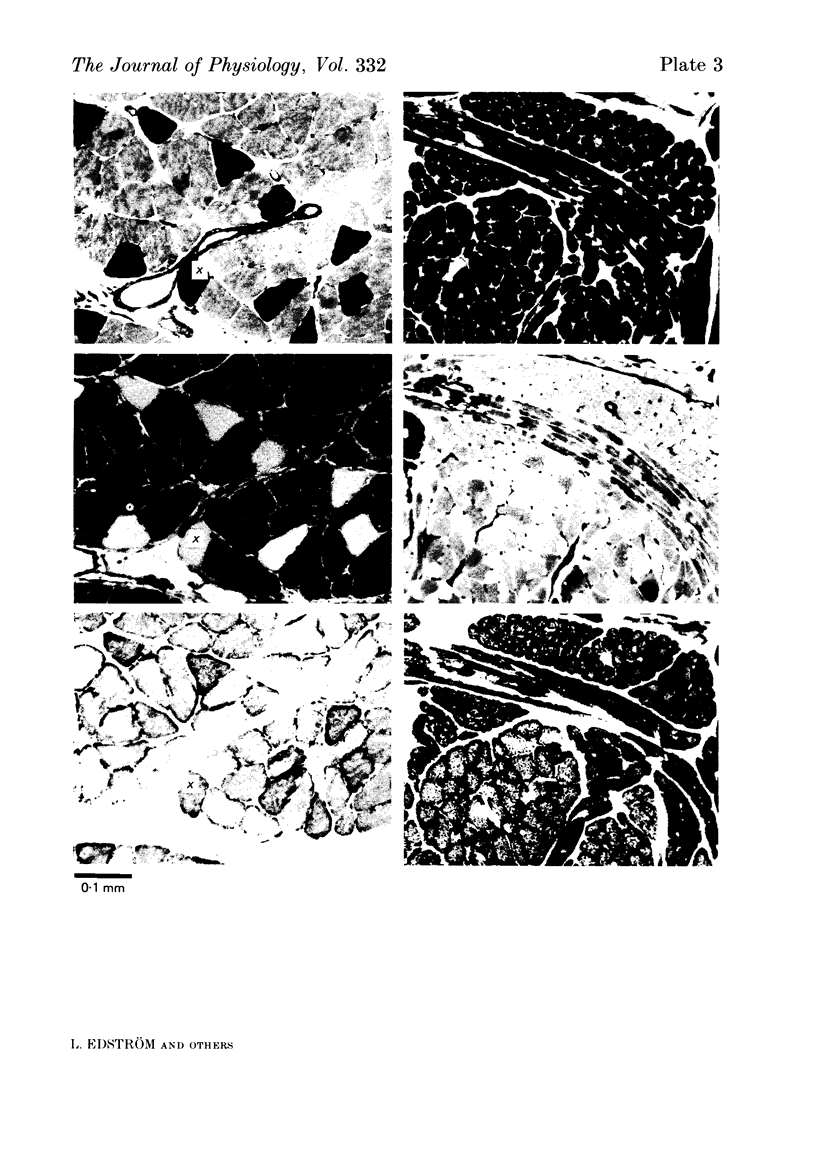
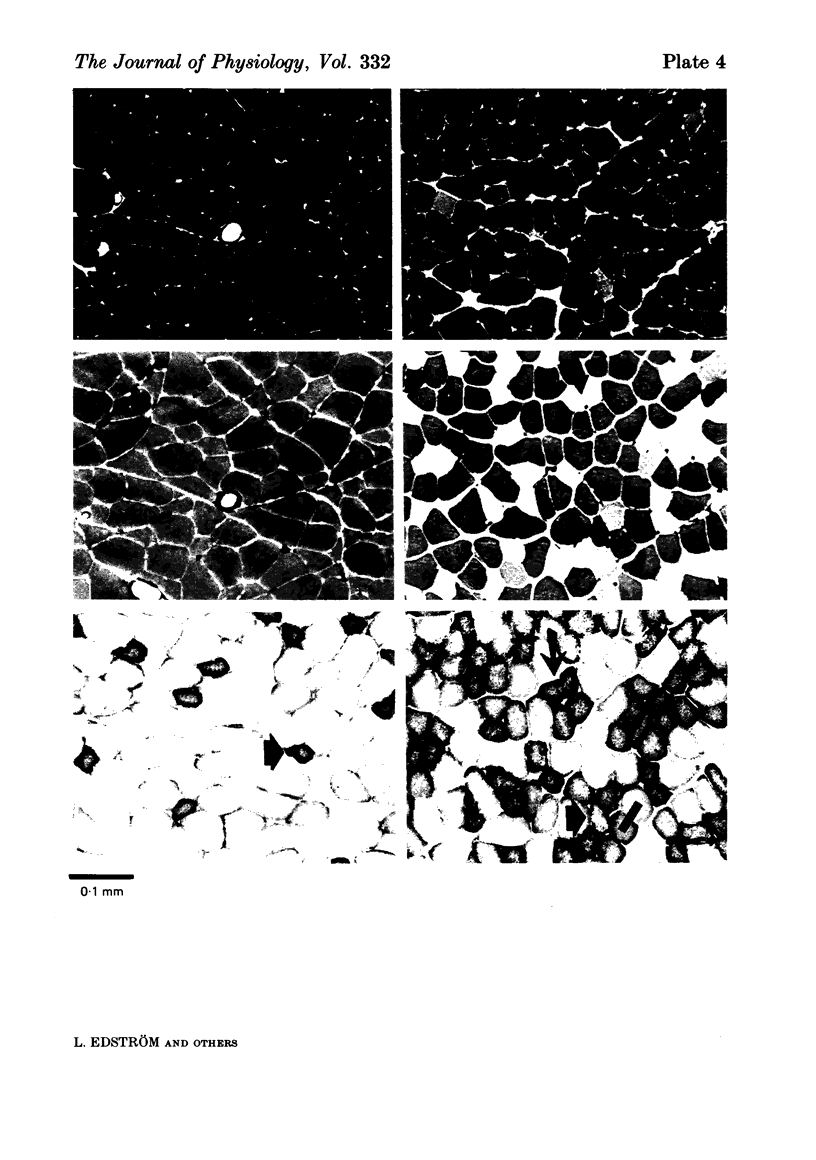
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin K. M., Tipton C. M. Work and metabolic patterns of fast and slow twitch skeletal muscle contracting in situ. Pflugers Arch. 1972;334(4):345–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00592168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beis I., Newsholme E. A. The contents of adenine nucleotides, phosphagens and some glycolytic intermediates in resting muscles from vertebrates and invertebrates. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;152(1):23–32. doi: 10.1042/bj1520023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs F. N., Poland J. L., Solaro R. J. Relative capabilities of sarcoplasmic reticulum in fast and slow mammalian skeletal muscles. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(3):587–594. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Kaiser K. K. Muscle fiber types: how many and what kind? Arch Neurol. 1970 Oct;23(4):369–379. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480280083010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchthal F., Schmalbruch H. Motor unit of mammalian muscle. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jan;60(1):90–142. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Levine D. N., Tsairis P., Zajac F. E., 3rd Physiological types and histochemical profiles in motor units of the cat gastrocnemius. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):723–748. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. Motor unit properties and selective involvement in movement. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1975;3:31–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány M. ATPase activity of myosin correlated with speed of muscle shortening. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6 Suppl):197–218. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLSON F. D., SIGER A. The creatine phosphoryltransfer reaction in iodoacetate-poisoned muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Nov;43:301–313. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.2.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. I. Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jan;52(1):129–197. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström L., Kugelberg E. Histochemical composition, distribution of fibres and fatiguability of single motor units. Anterior tibial muscle of the rat. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;31(5):424–433. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.5.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström L., Nyström B. Histochemical types and sizes of fibres in normal human muscles. A biopsy study. Acta Neurol Scand. 1969;45(3):257–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1969.tb01238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essén B., Jansson E., Henriksson J., Taylor A. W., Saltin B. Metabolic characteristics of fibre types in human skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Oct;95(2):153–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb10038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F. On the relationship of ultrastructural and cytochemical features of color in mammalian skeletal muscle. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969;95(3):462–482. doi: 10.1007/BF00995217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. C., Hultman E., Nordesjö L. O. Glycogen, glycolytic intermediates and high-energy phosphates determined in biopsy samples of musculus quadriceps femoris of man at rest. Methods and variance of values. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1974 Apr;33(2):109–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugelberg E. Histochemical composition, contraction speed and fatiguability of rat soleus motor units. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Oct;20(2):177–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugelberg E., Lindegren B. Transmission and contraction fatigue of rat motor units in relation to succinate dehydrogenase activity of motor unit fibres. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:285–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry O. H., Passonneau J. V. Kinetic evidence for multiple binding sites on phosphofructokinase. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2268–2279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NACHLAS M. M., TSOU K. C., DE SOUZA E., CHENG C. S., SELIGMAN A. M. Cytochemical demonstration of succinic dehydrogenase by the use of a new p-nitrophenyl substituted ditetrazole. J Histochem Cytochem. 1957 Jul;5(4):420–436. doi: 10.1177/5.4.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehunen S., Härkönen M. High-energy phosphate compounds in human slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibres. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1980 Feb;40(1):45–54. doi: 10.3109/00365518009091526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERAYDARIAN K., MOMMAERTS W. F., WALLNER A. The amount and compartmentalization of adenosine diphosphate in muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 17;65:443–460. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90447-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltin B., Henriksson J., Nygaard E., Andersen P., Jansson E. Fiber types and metabolic potentials of skeletal muscles in sedentary man and endurance runners. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977;301:3–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb38182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiaffino S., Hanzlíková V., Pierobon S. Relations between structure and function in rat skeletal muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1970 Oct;47(1):107–119. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhagen C., Hirche H. J., Nestle H. W., Bovenkamp U., Hosselmann I. The interstitial pH of the working gastrocnemius muscle of the dog. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Dec 28;367(2):151–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00585151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLS J. B. COMPARISON OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES BETWEEN SLOW AND FAST MAMMALIAN MUSCLES. J Physiol. 1965 May;178:252–269. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendt I. R., Gibbs C. L. Energy production of rat extensor digitorum longus muscle. Am J Physiol. 1973 May;224(5):1081–1086. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.5.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]