Abstract
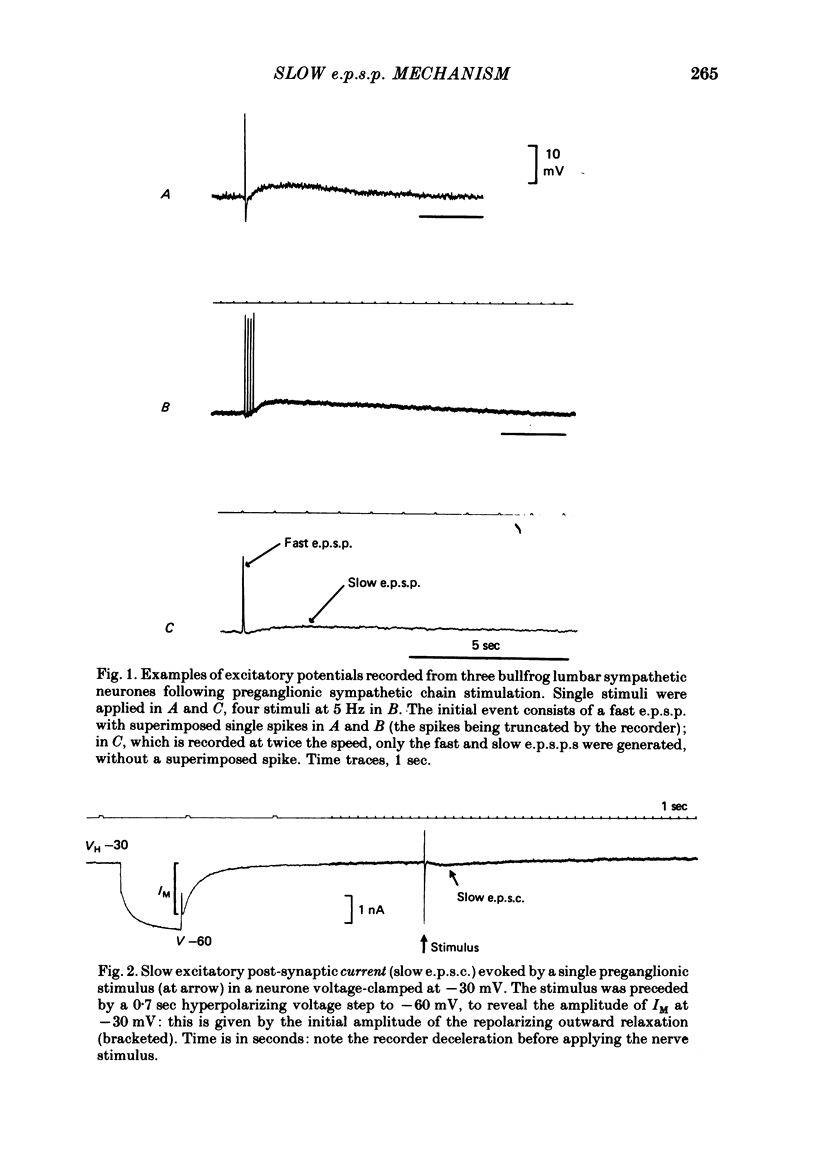
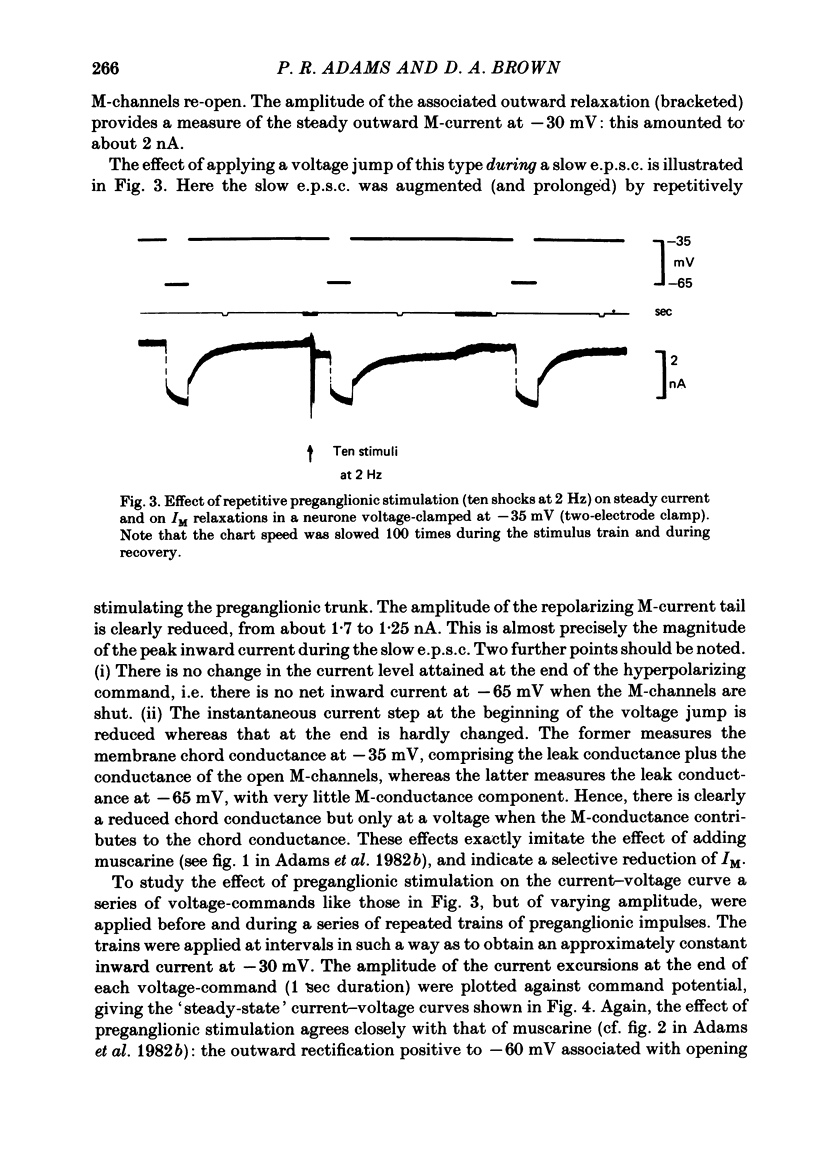
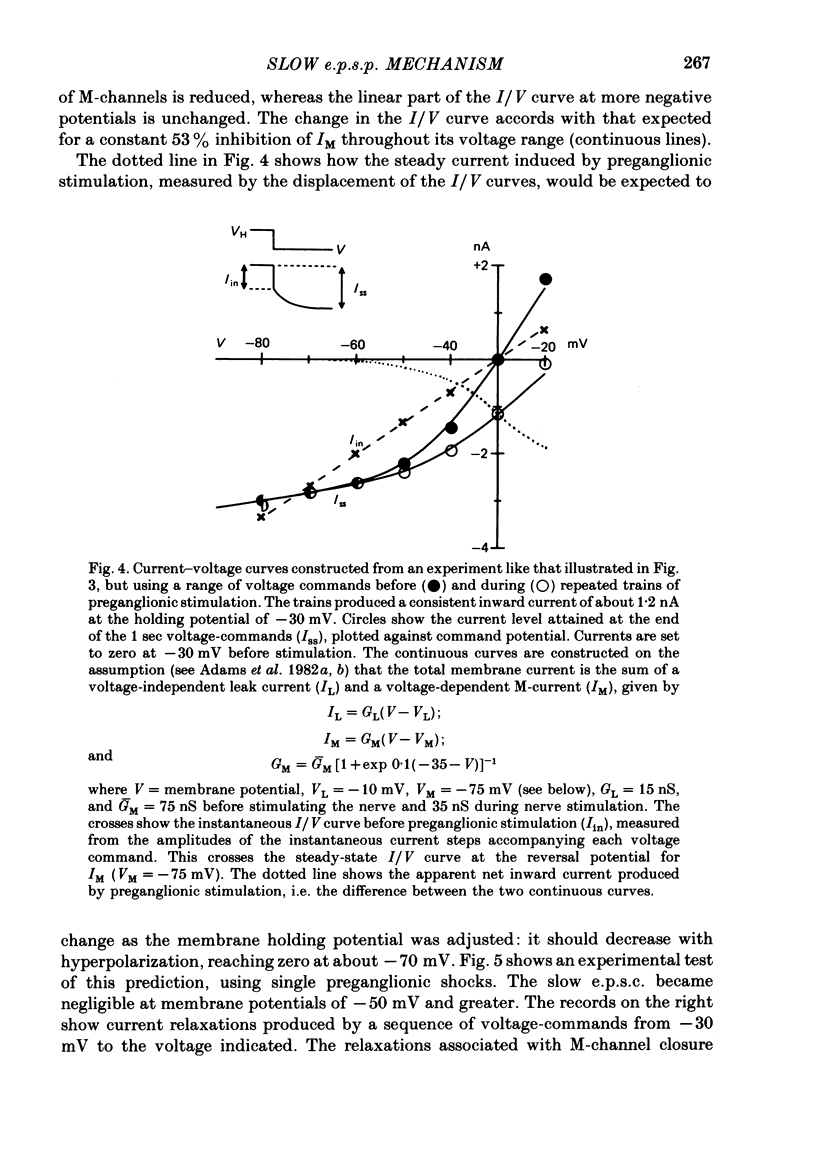
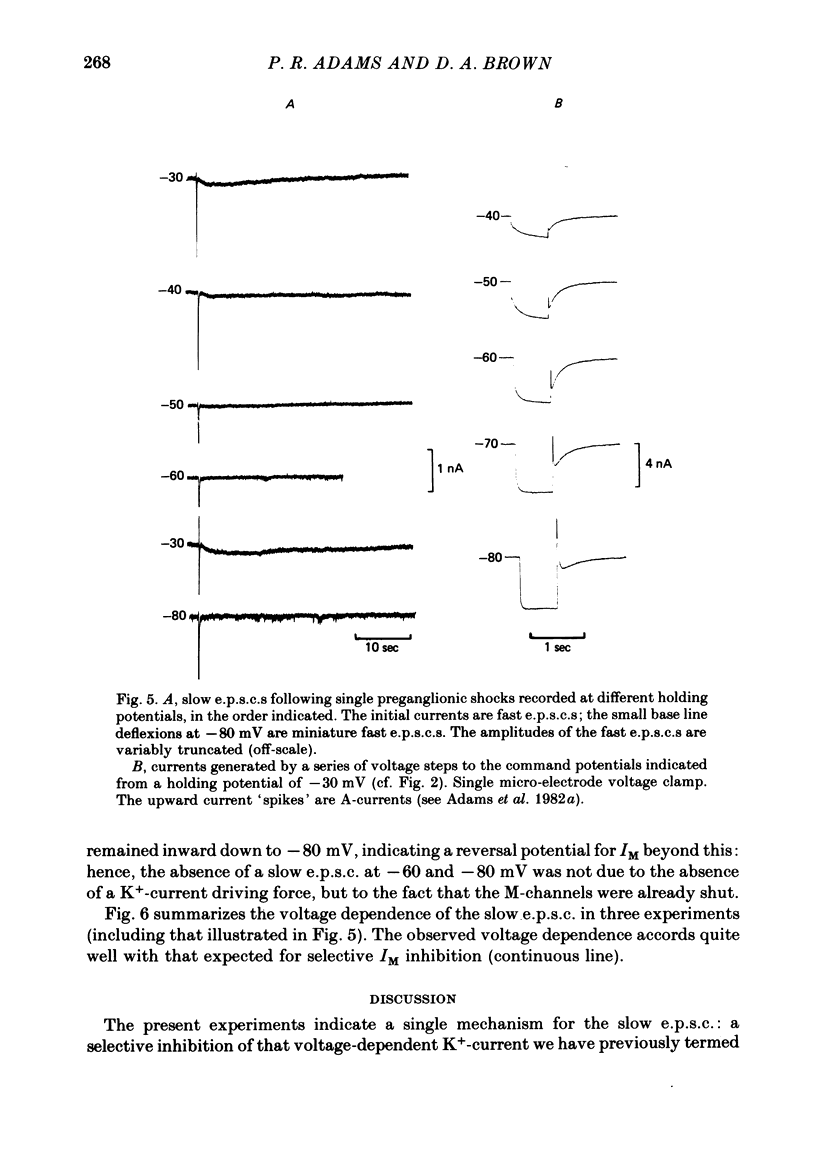
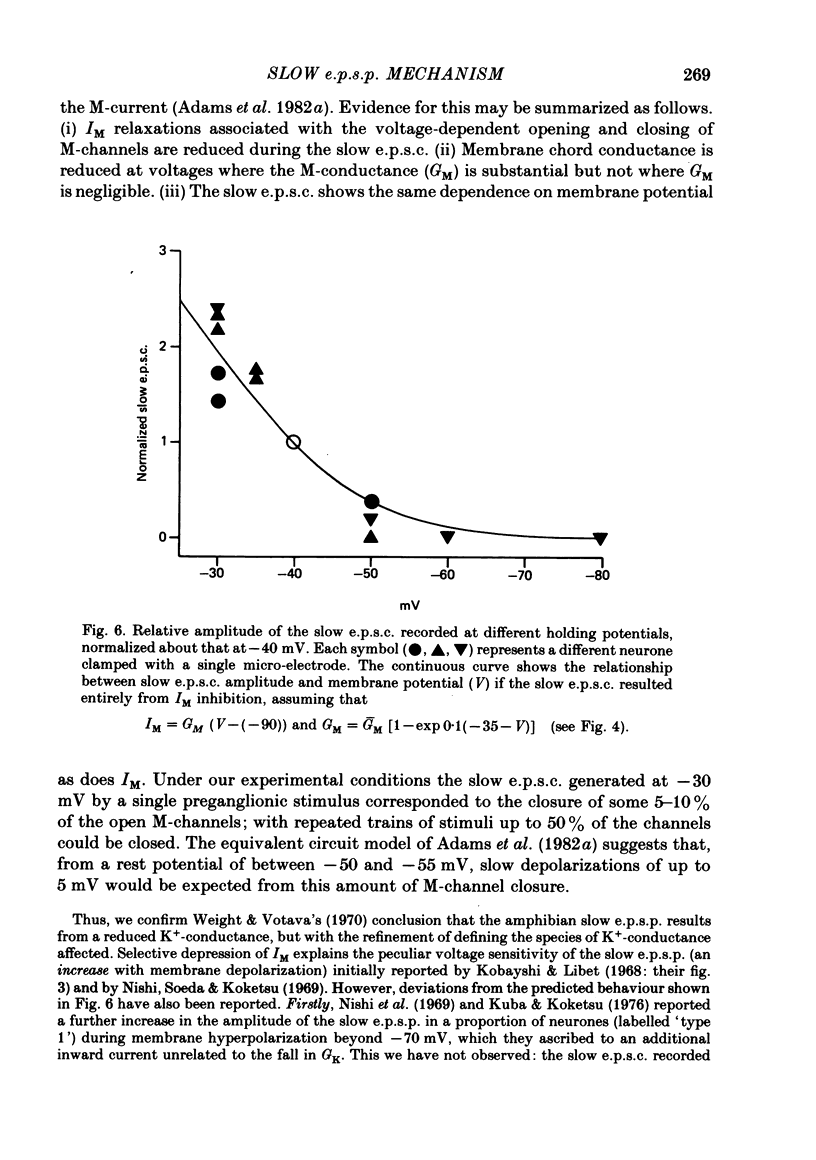
1. Slow muscarinic excitatory post-synaptic currents (slow e.p.s.c.s) generated by preganglionic nerve stimuli were recorded in voltage-clamped bullfrog sympathetic neurones. 2. IM--an outward, voltage-dependent, K+-current--was inhibited during the slow e.p.s.c., and membrane conductance was reduced in a voltage-dependent manner. 3. The slow e.p.s.c. was associated with reduced outward rectification in the steady-state current--voltage (I/V) curve at membrane potentials more positive than--60 m V, with no change in the shape of the non-rectifying part of the I/V curve at more negative potential. 4. The amplitude of the slow e.p.s.c. was reduced by membrane hyperpolarization, to zero at membrane potentials equal to, or more negative than, -60 m V. The voltage sensitivity of the slow e.p.s.c. accorded with that of IM. 5. It is concluded that the slow e.p.s.c. results from a selective inhibition of IM.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. M-currents and other potassium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:537–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. Pharmacological inhibition of the M-current. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:223–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A. Luteinizing hormone-releasing factor and muscarinic agonists act on the same voltage-sensitive K+-current in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;68(3):353–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb14547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACKMAN J. G., GINSBORG B. L., RAY C. Synaptic transmission in the sympathetic ganglion of the frog. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167:355–373. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimble M. J., Wallis D. I. The role of muscarinic receptors in synaptic transmission and its modulation in the rabbit superior cervical ganglion. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Nov;29(1):117–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Brown D. A. M-Currents in voltage-clamped mammalian sympathetic neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Jul 17;24(3):289–294. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles W., Shibata E. Autonomic transmitter actions on cardiac pacemaker tissue: a brief review. Fed Proc. 1981 Sep;40(11):2618–2624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y., Kuffler S. W. A peptide as a possible transmitter in sympathetic ganglia of the frog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1501–1505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Kandel E. R. Mechanism of calcium current modulation underlying presynaptic facilitation and behavioral sensitization in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6912–6916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Libet B. Generation of slow postsynaptic potentials without increases in ionic conductance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1304–1311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Libet B. Is inactivation of potassium conductance involved in slow postsynaptic excitation of sympathetic ganglion cells? Effects of nicotine. Life Sci. 1974 May 16;14(10):1871–1883. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90404-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koketsu K. Cholinergic synaptic potentials and the underlying ionic mechasims. Fed Proc. 1969 Jan-Feb;28(1):101–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Koketsu K. Analysis of the slow excitatory postsynaptic potential in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Jpn J Physiol. 1976;26(6):651–669. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.26.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Nishi S. Characteristics of fast excitatory postsynaptic current in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Effects of membrane potential, temperature and Ca ions. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Jan 31;378(3):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00592737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIBET B. SLOW SYNAPTIC RESPONSES AND EXCITATORY CHANGES IN SYMPATHETIC GANGLIA. J Physiol. 1964 Oct;174:1–25. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libet B., Chichibu S., Tosaka T. Slow synaptic responses and excitability in sympathetic ganglia of the bullfrog. J Neurophysiol. 1968 May;31(3):383–395. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.3.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libet B. Generation of slow inhibitory and excitatory postsynaptic potentials. Fed Proc. 1970 Nov-Dec;29(6):1945–1956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Connor E. A., Dionne V. E., Parsons R. L. Voltage clamp study of fast excitatory synaptic currents in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Jan;75(1):39–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISHI S., KOKETSU K. Electrical properties and activities of single sympathetic neurons in frogs. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1960 Feb;55:15–30. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030550104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., Koketsu K. Early and late after discharges of amphibian sympathetic ganglion cells. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Jan;31(1):109–121. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., Soeda H., Koketsu K. Studies on sympathetic B and C neurons and patterns of pregnaglionic innervation. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Aug;66(1):19–32. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030660103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., Soeda H., Koketsu K. Unusual nature of ganglionic slow EPSP studied by a voltage-clamp method. Life Sci. 1969 Jan 1;8(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosaka T., Chichibu S., Libet B. Intracellular analysis of slow inhibitors and excitatory postsynaptic potentials in sympathetic ganglia of the frog. J Neurophysiol. 1968 May;31(3):396–409. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weight F. F., Votava J. Slow synaptic excitation in sympathetic ganglion cells: evidence for synaptic inactivation of potassium conductance. Science. 1970 Nov 13;170(3959):755–758. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3959.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. A., Wachtel H. Prolonged inhibition in burst firing neurons: synaptic inactivation of the slow regenerative inward current. Science. 1978 Nov 17;202(4369):772–775. doi: 10.1126/science.715442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



